Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Drug Cards 2
Caricato da
p_dawgTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Drug Cards 2
Caricato da
p_dawgCopyright:
Formati disponibili
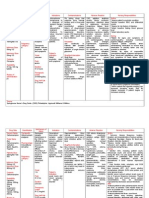
Classification Dopamine agonists Levodopa / carbidopa
Indications PD Dementia.
Contraindications Abrupt discontinuation Asthma or emphysema Cardiac disease, hypotension Active peptic ulcers Diabetes Renal / hepatic disease Glaucoma and psychosis Pregnancy and lactation Nursing Considerations
Mechanism of Action
Adverse Effects
Actively transported into CNS and converted into dopamine. Levodopa crosses BBB, but has many adverse effects when it dopamine in blood stream, so with carbidopa combo it doesnt convert into dopamine till its in brain. That dec. the side effects, but needs to administered in bigger doses this way.
Dyskinesias (involuntary body part movements) Nausea, vomiting, and anorexia Anxiety, agitation, confusion, depression, psychosis Hypotension, dizziness, syncope
Usually given as LevodopaCarbidopa-Entacapone combinations to enhance CNS entry Young patients respond better Long time periods of use lead to tolerance and drug wearing off
Classification acetaminophen Nonopioid analgesic (Pain medication for mild to moderate pain), antipyretic (prevent or reduce fever). PO/RECT 325-650 mg q46hr prn, max 4g/day.
Indications Mild to moderate pain or fever, arthralgia (pain in a joint), dental pain, dysmenorrhea (painful menstruation or abdominal cramps), headache, myalgia (pain in a muscle), osteoarthritis. Adverse Effects drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, GI bleeding, seizure, renal failure, leukopenia, rash, hypersensitivity, cyanosis, jaundice, coma, death, CNS stimulation, delirium followed by vascular collapse.
Contraindications Hypersensitivity, intolerance to tartrazine, alcohol, table sugar, saccharin, depending on product.
Mechanism of Action May block pain impulses peripherally that occur in response to inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis; does not possess anti-inflammatory properties; antipyretic action results from inhibition of prostaglandins in the CNS.
Nursing Considerations Assess health status and alcohol usage before administering. Assess for pain (type and location), use pain scale. Allergic reactions like rash, if it occurs product may have to discontinued. Decreasing output may indicate renal failure.
Classification Calcium Channel Blockers amlodipine (Norvasc) PO/IV
Indications Angina Pectoris Hypertension Atrial Fibrillation Atherosclerosis Tachycardia
Contraindications Allergy Digoxin use (increases serum digoxin levels) -blocker use (additive effects to both medications)
Mechanism of Action Dilates and relaxes arterial muscle, decreases blood pressure and heart rate, thus decreasing cardiac workload
Adverse Effects Hypotension Bradycardia Nausea Headache Dizziness
Nursing Considerations Thorough cardiovascular assessment is required prior to administration immediate release forms have a very short duration and require frequent administration
Classification
Indications
Contraindications
Parathyroid- like drug Rocaltrol (calcitriol)
Hypocalcemia Hypoparathyroidism
Magnesium containing antacids. Hypersenstivity
Mechanism of Action Stimulates calcium absorption from GI tract and promotes movement of calcium from bone to blood.
Adverse Effects Headache N/V/C HTN Arrhythmias Pancreatitis Bone and muscle pain Decreased lidibo
Nursing Considerations Avoid magnesium containing antacids with the drug. Give drug without regard for food,
Classification
Indications
Contraindications
Cholinesterase Inhibitors
Examples: donepezil, rivastigmine, and galantamine
Dementia
Known drug allergies
Mechanism of Action Prevent the breakdown of acetylcholine in the synapse Drugs not curative; only slow disease progression
Adverse Effects
Nursing Considerations
GI upset: nausea, vomiting, Donepezil may be taken with or and anorexia without food Increased urination Drugs may lead to bradycardia and heartblock Drugs can cause significant weight loss Can increase gastric acid secretions
Classification
Indications
Contraindications
NMDA Antagonists
Examples: memantine
Monotherapy or adjunct therapy with cholinesterase inhibitors for AD
Known drug allergies
Mechanism of Action Increases glutamate (amino acid) availability; leads to decreased symptoms
Adverse Effects Acne AV block Cerebral infarction Gallstones Hepatitis Impotence Sedation Hypotension
Nursing Considerations Adjustments in dose based on age is not required However: Monitor kidney and liver function along with BP
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Drug Cards 3Documento3 pagineDrug Cards 3p_dawgNessuna valutazione finora
- Antihypertensive Pharmacologic Agents: Nr33 K Burger, Msed, MSN, RN, CneDocumento28 pagineAntihypertensive Pharmacologic Agents: Nr33 K Burger, Msed, MSN, RN, CneLopez JoeNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug CardsDocumento6 pagineDrug Cardsp_dawgNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationDocumento7 pagineDrugs Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ConsiderationPrincess Jenelly CampomanesNessuna valutazione finora
- Congestive Heart Failure: CardiacDocumento36 pagineCongestive Heart Failure: CardiacHUZAIFA YAMAANNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharm 2 TestDocumento7 paginePharm 2 TestJaime HayesNessuna valutazione finora
- CHF Drugs Guide: Key Medications for Treating Congestive Heart FailureDocumento21 pagineCHF Drugs Guide: Key Medications for Treating Congestive Heart Failuremohsen mirdamadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiotronic MedicationsDocumento13 pagineCardiotronic MedicationsTee WoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug CardsDocumento16 pagineDrug Cardsp_dawg100% (7)
- Antiparkinson Drugs09Documento39 pagineAntiparkinson Drugs09Gurveer ToorNessuna valutazione finora
- Of Angina Pectoris. Decreased Rate of Cardiovascular Mortality and Hospitalization in Patients With Heart FailureDocumento31 pagineOf Angina Pectoris. Decreased Rate of Cardiovascular Mortality and Hospitalization in Patients With Heart Failurenaikram420Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dopamine Hydrochloride GuideDocumento8 pagineDopamine Hydrochloride GuideMaurence John Feliciano LuluquisenNessuna valutazione finora
- Mood Stabilisers: PsychopharmacologyDocumento50 pagineMood Stabilisers: Psychopharmacologymeno321Nessuna valutazione finora
- Piperacillin-Tazobactam AntibioticDocumento9 paginePiperacillin-Tazobactam Antibiotic배기숭Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Med ChartsDocumento6 pagineCardiac Med ChartsNursingSchoolNotes100% (15)
- Drug StudyDocumento12 pagineDrug StudyAngeli A EstilloreNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs Acting On Cardiovascular SystemDocumento81 pagineDrugs Acting On Cardiovascular SystemevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Generic / Brand Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indications Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocumento3 pagineGeneric / Brand Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indications Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesJommel Ryan Corpus LumibaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 - A - III Hypertension TreatmentDocumento37 pagineChapter 2 - A - III Hypertension TreatmentEmmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Antihypotensive Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii Ramos Jecino, RN, M.DDocumento28 pagineAntihypotensive Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii Ramos Jecino, RN, M.DFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Top Drugs: 1. ACETAMINOPHEN (Tylenol)Documento12 pagineTop Drugs: 1. ACETAMINOPHEN (Tylenol)epingNessuna valutazione finora
- Antianginal Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii R. Jecino, M.DDocumento31 pagineAntianginal Drugs: Roger Joseph Ii R. Jecino, M.DFranz Earl Niño AlbesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrenergic Antagonists: An Introduction to Alpha and Beta BlockersDocumento64 pagineAdrenergic Antagonists: An Introduction to Alpha and Beta BlockersAneeza AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Amplodipine Drug StudyDocumento1 paginaAmplodipine Drug StudyRai HanahNessuna valutazione finora
- Parkinson's Drugs for Movement ControlDocumento19 pagineParkinson's Drugs for Movement ControlSV SagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Aritmia Dan Kardiotonik Eng UciDocumento36 pagineAritmia Dan Kardiotonik Eng UciUci RamadhantyNessuna valutazione finora
- Coreg (Carvedilol) 6.25mgDocumento3 pagineCoreg (Carvedilol) 6.25mgE100% (2)
- Antiparkinson Agents: Art Hupka, Ph.D. 2009Documento52 pagineAntiparkinson Agents: Art Hupka, Ph.D. 2009Gurjot KaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Effects On Lab Test ResultsDocumento18 pagineEffects On Lab Test Resultsjay5ar5jamorabon5torNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiotonic DrugsDocumento67 pagineCardiotonic DrugsLady Mae Ramos100% (1)
- Activated Charcoal: Adverse EffectsDocumento14 pagineActivated Charcoal: Adverse EffectsAntonetteNessuna valutazione finora
- ICU Pharmacology Guide: Sedatives, Analgesics, Paralytics & PressorsDocumento52 pagineICU Pharmacology Guide: Sedatives, Analgesics, Paralytics & Pressorscoolboy1990Nessuna valutazione finora
- CarvedilolDocumento3 pagineCarvedilolapi-3797941100% (3)
- Lecture 6 Anti HypertensionDocumento40 pagineLecture 6 Anti HypertensionMNGS StudioNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti Parkinson Drugs FinallDocumento36 pagineAnti Parkinson Drugs FinallandrapradeshsseNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacotherapy of Hypertension: Dr. R. Jamuna Rani MD, Professor & HOD, Department of PharmacologyDocumento24 paginePharmacotherapy of Hypertension: Dr. R. Jamuna Rani MD, Professor & HOD, Department of PharmacologyshyamkattiNessuna valutazione finora
- Potassium-Sparing Diuretic Aldacton GuideDocumento8 paginePotassium-Sparing Diuretic Aldacton GuideJoy CalmerinNessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs Used in Cardio Vascular SystemDocumento138 pagineDrugs Used in Cardio Vascular SystemSagun lohalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug ListDocumento30 pagineDrug ListKristineNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacology Reporting-1Documento32 paginePharmacology Reporting-1Mj TalentNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharm Exam ReviewDocumento13 paginePharm Exam ReviewAshleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Propranolol Hydro ChlorideDocumento4 paginePropranolol Hydro Chlorideapi-3797941Nessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding How Anti-Adrenergic Drugs Work to Inhibit the Sympathetic Nervous SystemDocumento21 pagineUnderstanding How Anti-Adrenergic Drugs Work to Inhibit the Sympathetic Nervous SystemMIbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- CARDIO Intensive CareDocumento6 pagineCARDIO Intensive CareDianne Erika MeguinesNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Features and Management of Common PoisonsDocumento33 pagineClinical Features and Management of Common PoisonsTrishenth FonsekaNessuna valutazione finora
- ICU Pharmacology: Sedatives Analgesics Paralytics PressorsDocumento51 pagineICU Pharmacology: Sedatives Analgesics Paralytics Pressorsdevi trismiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Angina Pharmacology YeahDocumento16 pagineAngina Pharmacology YeahMuhammad AfifuddinNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiovascular Agents: Mrs. Michelle A. Iduria, RN, MAN LecturerDocumento131 pagineCardiovascular Agents: Mrs. Michelle A. Iduria, RN, MAN LecturerNiala AlmarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharm Exam #3 Review: Diuretics, Heart Failure Drugs, Lipids, ElectrolytesDocumento293 paginePharm Exam #3 Review: Diuretics, Heart Failure Drugs, Lipids, ElectrolytesTrish HồNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 MG Iv BidDocumento17 pagine5 MG Iv BidhanzreinherNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento70 pagineDrug Studyjahmaicao50% (2)
- Generic Name: Frequent (10%) Baseline Assessment Antiemetic (Assess Intervention/EvaluationDocumento11 pagineGeneric Name: Frequent (10%) Baseline Assessment Antiemetic (Assess Intervention/EvaluationIrene Soriano BayubayNessuna valutazione finora
- Antiarrhytmic Talk For ResidenDocumento90 pagineAntiarrhytmic Talk For ResidenMusa yohanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Digoxin Drug CardDocumento1 paginaDigoxin Drug CardMahsa Ahmadzadeh100% (2)
- Heart FailureDocumento37 pagineHeart FailureNashita NowshinNessuna valutazione finora
- Ca ChannelDocumento30 pagineCa ChannelKency DoneyNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam 3 Study Guide PharmacologyDocumento23 pagineExam 3 Study Guide PharmacologymmonsonfNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcDa EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNessuna valutazione finora
- Fast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteDa EverandFast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteNessuna valutazione finora
- NURS 20172 Crisis InterventionDocumento26 pagineNURS 20172 Crisis Interventionp_dawg100% (3)
- Module 6 - Infant Bath Pediatric Care Pre-Reading00Documento4 pagineModule 6 - Infant Bath Pediatric Care Pre-Reading00p_dawgNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Lab Semester 4Documento3 pagineFinal Lab Semester 4p_dawgNessuna valutazione finora
- Surgical Client CareDocumento58 pagineSurgical Client Carep_dawg100% (1)
- Drug CardsDocumento16 pagineDrug Cardsp_dawg100% (7)
- Health Teaching Plan - Wound Care and DressingDocumento6 pagineHealth Teaching Plan - Wound Care and Dressingp_dawg100% (2)
- Elder Abuse and Neglect Can Be Broadly Categorized Into Five CategoriesDocumento1 paginaElder Abuse and Neglect Can Be Broadly Categorized Into Five Categoriesp_dawgNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1Documento7 pagineChapter 1p_dawg0% (1)
- Pharmacology Nursing ReviewDocumento19 paginePharmacology Nursing Reviewp_dawg50% (2)
- Annotated BibliographyDocumento6 pagineAnnotated Bibliographyp_dawg100% (1)
- Generic Name: Acetaminophen Brand Name: Tylenol: ActionDocumento22 pagineGeneric Name: Acetaminophen Brand Name: Tylenol: Actionp_dawg100% (14)
- AssignmentDocumento7 pagineAssignmentp_dawgNessuna valutazione finora
- Tracheostomy Suctioning and CareDocumento7 pagineTracheostomy Suctioning and Carep_dawgNessuna valutazione finora
- BloodDocumento64 pagineBloodp_dawgNessuna valutazione finora
- AssignmentDocumento7 pagineAssignmentp_dawgNessuna valutazione finora
- Generic Name: Acetaminophen Brand Name: Tylenol: ActionDocumento22 pagineGeneric Name: Acetaminophen Brand Name: Tylenol: Actionp_dawg100% (14)
- Unit 12Documento28 pagineUnit 12p_dawg100% (1)
- L Sit ProgramDocumento23 pagineL Sit Programdebo100% (1)
- EV3110 SIA Group ReportDocumento38 pagineEV3110 SIA Group ReportWill MyatNessuna valutazione finora
- OCPD: Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocumento4 pagineOCPD: Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentRana Muhammad Ahmad Khan ManjNessuna valutazione finora
- B29061KDocumento13 pagineB29061KMeethuanNessuna valutazione finora
- PEMEDocumento1 paginaPEMERajesh MohananNessuna valutazione finora
- NHS Trust PolicyDocumento52 pagineNHS Trust Policyver_at_workNessuna valutazione finora
- Promoting The Rights of Children E3Documento15 paginePromoting The Rights of Children E3api-236865763Nessuna valutazione finora
- Repair of Obstetric Perineal LacerationsDocumento7 pagineRepair of Obstetric Perineal LacerationsadriantiariNessuna valutazione finora
- Lucas MattoonDocumento1 paginaLucas Mattoonapi-248178524Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fertilizer Use by Crop in The Islamic Republic of IranDocumento78 pagineFertilizer Use by Crop in The Islamic Republic of Iransiamak77Nessuna valutazione finora
- TuDocumento382 pagineTuAndra NiculaeNessuna valutazione finora
- Legalizing abortion in the Philippines for women's health and rightsDocumento2 pagineLegalizing abortion in the Philippines for women's health and rightsRosario Antoniete R. Cabilin100% (1)
- Appendix - 6 - Site Logistics PlanDocumento16 pagineAppendix - 6 - Site Logistics PlanRamesh BabuNessuna valutazione finora
- Environment in Palestine 1Documento28 pagineEnvironment in Palestine 1YOSEF DERDESAWENessuna valutazione finora
- Sdera Demo Lesson DVD Worksheet 2021Documento2 pagineSdera Demo Lesson DVD Worksheet 2021api-396577001Nessuna valutazione finora
- Getting HSE Right A Guide For BP Managers 2001Documento62 pagineGetting HSE Right A Guide For BP Managers 2001Muhammad Labib Subhani0% (1)
- Curriculum Map Grade 9 Health: T (N .) M U T C C S P S C S A A R I C V Quarter 1Documento5 pagineCurriculum Map Grade 9 Health: T (N .) M U T C C S P S C S A A R I C V Quarter 1joan niniNessuna valutazione finora
- Tugas Parafrase Jurnal MIPKI (Revisi) - Rizka Amalia Hutami - 150510160235Documento2 pagineTugas Parafrase Jurnal MIPKI (Revisi) - Rizka Amalia Hutami - 150510160235RizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Interactive CME Teaching MethodsDocumento5 pagineInteractive CME Teaching MethodsROMSOPNessuna valutazione finora
- Maturity-Onset Diabetes of The Young (MODY) : Genetic and Clinical CharacteristicsDocumento5 pagineMaturity-Onset Diabetes of The Young (MODY) : Genetic and Clinical CharacteristicsSarah AgustinNessuna valutazione finora
- Radiographic Cardiopulmonary Changes in Dogs With Heartworm DiseaseDocumento8 pagineRadiographic Cardiopulmonary Changes in Dogs With Heartworm DiseaseputriwilujengNessuna valutazione finora
- Method Development and Validation For Estimation of Moxifloxacin HCL in Tablet Dosage Form by RP HPLC Method 2153 2435.1000109Documento2 pagineMethod Development and Validation For Estimation of Moxifloxacin HCL in Tablet Dosage Form by RP HPLC Method 2153 2435.1000109David SanabriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Context & Interested Party AnalysisDocumento6 pagineContext & Interested Party AnalysisPaula Angelica Tabia CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Pregnancy Calendar For DogsDocumento3 paginePregnancy Calendar For DogsVina Esther FiguraNessuna valutazione finora
- Cutting and TailoringDocumento90 pagineCutting and Tailoringhamba_dahNessuna valutazione finora
- UKA: When Would I Do It?Documento35 pagineUKA: When Would I Do It?neareastspineNessuna valutazione finora
- BDD Fact SheetDocumento2 pagineBDD Fact SheetKeen ZeahNessuna valutazione finora
- Master Plan for Trivandrum City 2021-2031Documento21 pagineMaster Plan for Trivandrum City 2021-2031Adhithy MenonNessuna valutazione finora
- RPNDocumento21 pagineRPNAruna Teja Chennareddy43% (7)
- Fitness WalkingDocumento60 pagineFitness WalkingJC LeriaNessuna valutazione finora