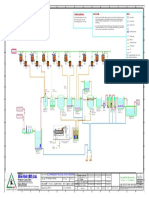
Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Waste Water
Caricato da
christle_agustinDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Waste Water
Caricato da
christle_agustinCopyright:
Formati disponibili
- term applied to any type of water that has been utilized in some capacity that negatively impacts the
quality of the water.
Domestic Wastewater - originates from domestic
household activities, it can also include water that is discharged from commercial and business buildings and institutions, along with ground water. manufacturing process, can be more difficult to treat due to the examination that must take place at an industry-based level. Industrial sources of wastewater contain contaminants such as oils, pharmaceuticals, pesticides, silt, chemicals and other byproducts.
Industrial Wastewater - which originates from the
SANITARY SEWAGE: The spent water from residences
and institutions, carrying body wastes, ablution water, food preparation wastes, laundry wastes, and other waste products of normal living, are classed as domestic or sanitary sewage.
COMMERCIAL WASTES: Liquid-carried wastes from
stores and service establishments serving the immediate community, termed commercial wastes, are included in the sanitary or domestic sewage category if their characteristics are similar to household flows.
SURFACE RUNOFF : It is also known as storm flow or
overland flow, is that portion of precipitation that runs rapidly over the ground surface to a defined channel. Precipitation absorbs gases and particulates from the atmosphere, dissolves and leaches materials from vegetation and soil, suspends matter from the land, washes spills and debris from urban streets and highways, and carries all these pollutants as wastes in its flow to a collection point. Discharges are classified as point-source when they emanate from a pipe outfall, or non-point-source when they are diffused and come from agriculture or unchanneled urban land drainage runoff.
-in order to prevent damage to the outside water
quality or aquatic life, water treatment is performed to restore clarity, remove odor, and remove contaminants from wastewater before it can be safely released into the environment. Usually, wastewater treatment sludge is created during the primary and secondary steps of this process.
is the process of removing the contaminants from sewage and wastewater to produce liquid and solid (sludge) suitable for discharge to the environment or for reuse. It is a form of waste management.
types of Waste Water treatment Biological waste water treatment plants: They use bacteria and other biological matter to break down the waste. Aerobic bacteria- are used in secondary treatment processes. They must have dissolved oxygen present in the water to survive. , the process is called aerobic treatment. Physical /chemical waste water treatment plant: Industrial waste water can contain chemicals that can harm the ecosystem which creates the necessity for a chemical plant to treat this waste. Physical /chemicalwaste water treatment plants use both physical and chemical reactions to treat wastewater.
What are the different steps involved in waste water treatment?
Primary Treatment: As a first step, waste water is screened to physically eliminate objects, like large solids using grates, screens and settling tanks. Some of the solid waste could wreck the treatment plants machinery. Next the wastewater is taken to a primary settling basin where matter can float or sink in the tank.
Secondary Treatment: The remaining water is then sent to the secondary treatment tank where the biological matter, such as bacteria, removes much of the left over suspended matter. These biodegradation processes also takes place in streams, lakes and oceans, but the purification systems in nature can easily be congested with contribution of too much organic waste. Secondary treatment prevents this type ofpollution by degrading most of the organic matter before the water is released into the environment.
Tertiary treatment: This treatment is the final stage before water
can be released into the environment. This is used only where it is needed to protect the receiving waters from excess nutrients. In tertiary treatment, the concentrations of phosphorus or nitrogen are reduced through biological or chemical processes. The treated water, called the effluent, is then disposed of in the environment.
Disinfection: Disinfection kills diseases-causing organisms,
most commonly through chlorination. This step is only performed for water that will be used for human consumption (as opposed to being used for water the lawn, for example)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Metcalf and Eddy Wastewater Engineering Free Download PDFDocumento2 pagineMetcalf and Eddy Wastewater Engineering Free Download PDFAnonymous eKB0qRUpq33% (3)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Thesis M.TechDocumento109 pagineThesis M.TechSonu Dhangar100% (10)
- Beverage-South - Complete ETPDocumento1 paginaBeverage-South - Complete ETPAbinash PatroNessuna valutazione finora
- B.O.Q of Electro-Mechanical Works 9Documento1 paginaB.O.Q of Electro-Mechanical Works 9asdsd dsdaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sulphate-Reducing Bacteria, Their Properties and Methods of Elimination From GroundwaterDocumento6 pagineSulphate-Reducing Bacteria, Their Properties and Methods of Elimination From GroundwaterShabrina Az ZahraNessuna valutazione finora
- Waste Water Treatment Plant Design For Small and Midsized CommunitiesDocumento33 pagineWaste Water Treatment Plant Design For Small and Midsized CommunitieskassyNessuna valutazione finora
- Solid and Liquid Waste ManagementDocumento68 pagineSolid and Liquid Waste ManagementVincent BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimisation of A Method To Extract The Active Coagulant Agent From Jatropha Curcas Seeds For Use in Turbidity RemovalDocumento5 pagineOptimisation of A Method To Extract The Active Coagulant Agent From Jatropha Curcas Seeds For Use in Turbidity RemovalAli MemonNessuna valutazione finora
- Offbeat Harve en KaurDocumento6 pagineOffbeat Harve en KaurMOUNIKA PURETI VP21ARCH0100010Nessuna valutazione finora
- IONE-AA00-PE-CM-0028 Cooling Water Passivation Procedure For BSU - Rev ADocumento21 pagineIONE-AA00-PE-CM-0028 Cooling Water Passivation Procedure For BSU - Rev AYusuf100% (1)
- Additional Tech Details For Polybond STP at DewasDocumento2 pagineAdditional Tech Details For Polybond STP at DewasAnimesh JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Activated Sludge ProcessDocumento53 pagineActivated Sludge ProcessVivek KasarNessuna valutazione finora
- USP For Sobha Developers PDFDocumento1 paginaUSP For Sobha Developers PDFSivapratap SanjeevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ucd Daf: Flotation SeparationDocumento2 pagineUcd Daf: Flotation Separationzhigang dingNessuna valutazione finora
- Hartalega Corporate Social Responsibility (The Edge Billion Dollar Club) FINALDocumento5 pagineHartalega Corporate Social Responsibility (The Edge Billion Dollar Club) FINALPiyu MahatmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Trickling Filters: Trickling Filter at Al Awir WWTPDocumento12 pagineTrickling Filters: Trickling Filter at Al Awir WWTPMostafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Micro ScreenDocumento2 pagineMicro ScreenMARIANessuna valutazione finora
- Rocor NB Liquid 25 LTRDocumento3 pagineRocor NB Liquid 25 LTRpipi929Nessuna valutazione finora
- Operation and Maintenance Manual Amendment City of Snohomish Wastewater Treatment PlantDocumento129 pagineOperation and Maintenance Manual Amendment City of Snohomish Wastewater Treatment PlantjohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Training Laundry WWTUDocumento15 pagineTraining Laundry WWTUSyaiful AkhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Sewage Treatment TechnologyDocumento107 pagineSewage Treatment Technologykmas1612Nessuna valutazione finora
- Alim Knit (BD) LTD.: Recommended Process Flow DiagramDocumento1 paginaAlim Knit (BD) LTD.: Recommended Process Flow DiagramKamrul HasanNessuna valutazione finora
- Field Visit To Water Treatment Plant, AluvaDocumento6 pagineField Visit To Water Treatment Plant, AluvaAdinathNessuna valutazione finora
- Expt 2 Sedimentation IntroductionDocumento4 pagineExpt 2 Sedimentation IntroductionEzekielNessuna valutazione finora
- 2012 01 16cmeapresentationjatiluhur 120118193944 Phpapp01Documento28 pagine2012 01 16cmeapresentationjatiluhur 120118193944 Phpapp01Benny Aryanto SihalohoNessuna valutazione finora
- W-S5014 Algecide PDFDocumento2 pagineW-S5014 Algecide PDFimtiyazNessuna valutazione finora
- Trickling FilterDocumento10 pagineTrickling Filterpriodeep chowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Calculate Septic Tank Size - CivilologyDocumento5 pagineHow To Calculate Septic Tank Size - CivilologyHang ChethaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lohas Wastewater p4Documento1 paginaLohas Wastewater p4Dwinix John CabañeroNessuna valutazione finora
- 007 Inv Es Usa PDFDocumento13 pagine007 Inv Es Usa PDFStajic MilanNessuna valutazione finora