Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Basal Nuclei & Their Connections
Caricato da
ewijayapalaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Basal Nuclei & Their Connections
Caricato da
ewijayapalaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Neuroscience Module
Basal Nuclei & their Connections
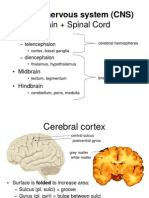
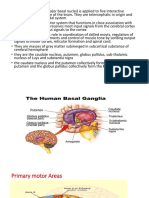
Basal nuclei- collection of masses of grey matter.Situated within each cerebral hemisphere. These nuclei play an important role in the control of posture and voluntary movement. Corpus striatum, amygdaloid nucleus, claustrum. Corpus striatum situated lateral to the thalamus. Internal capsule divide it into two parts. Caudate and lentiform nuclei.
Caudate nucleus C shaped mass. Head, body and tail. Head forms the lateral wall of anterior horn of lateral ventricle.Body forms part of the body of lateral ventricle.Tail continues forwards in the roof of inferior horn of lateral ventricle. It terminates anteriorly in the amygdaloid nucleus. Lentiform nucleus Wedge shaped mass. Related medially to internal capsule and related laterally to external capsule(thin sheet of white matter). It is divided into two parts putamen(laterally) and globus pallidus(medially). Putamen + head of caudate neostriatum.
Amygdaloid nucleus- Situated in temporal lobe close to uncus. Part of the limbic system. Limbic system is concerned with emotion. Claustrum- Thin sheet of grey matter. External capsule separates it from lentiform nucleus. Lateral to claustrum lies the insula. Connections of the corpus striatum Afferent corticostriate, thalamostriate, nigrostriate, brainstem striatal. Efferent striato pallidal and striato nigral.
Corticostriate cerebral cortex caudate&putamen. Largest input from sensory motor cortex. Nmitter glutamate. Thalamostriate thalamus caudate and putamen. Nigrostriate substantia nigra caudate and putamen. Dopamine. Brainstem striatal brain stem caudate and putamen. Serotinin. Inhibitory in function.
Striatopallidal caudate and putamen globus pallidus. N mitter GABA. Striatonigral caudate and putamen substantia nigra. GABA, Ach, substance P. Connections of globus pallidus Afferent striatopallidal(caudate and putamen to globuspallidus. GABA). Efferent pallidofugal. (globuspallidus to thalamic nuclei, subthalamic nuclei and tegmentum of midbrain.)
Functions of the basal nuclei Basal nuclei receive information from cerebral cortex, brainstem, thalamus and sub thalamus. Information is integrated within the corpus striatum and outflow passes back to the same areas. These nuclei can control the muscular movements by influencing the cerebral cortex rather than through direct descending pathways. Parkinsons disease degeneration of neurons in substantianigra, globus pallidus, putamen and caudate nucleus.Decrease dopamine in the corpus striatum. Can present with rigidity, tremor and hypokinesia.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Basal GangliaDocumento4 pagineBasal GangliaOvolime UbodiomNessuna valutazione finora
- Basal GangliaDocumento18 pagineBasal Gangliaआशिष दादाNessuna valutazione finora
- Basal Ganglia: DR Amit Kumar Associate Professor Anatomy CIMSDocumento28 pagineBasal Ganglia: DR Amit Kumar Associate Professor Anatomy CIMSGaurav MadhwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.basal Ganglia-2016 - 082539Documento28 pagine5.basal Ganglia-2016 - 082539sirima makuraNessuna valutazione finora
- Basal Ganglia ExplainedDocumento49 pagineBasal Ganglia ExplainedVincent Lau Bi ShengNessuna valutazione finora
- Basal Nuclei Role in Motor Movement InitiationDocumento8 pagineBasal Nuclei Role in Motor Movement InitiationDang CuevasNessuna valutazione finora
- Basal NucleiDocumento44 pagineBasal NucleiRaj RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Topographic Anatomy of Basal NucleiDocumento44 pagineTopographic Anatomy of Basal NucleiRafique AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Basal GangliaDocumento36 pagineBasal GangliaNguyên KhoaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basal GangliaDocumento8 pagineBasal GangliaDenvic Nove G. BarberoNessuna valutazione finora
- CNS Structure and Function - Anatomy of the Brain and Spinal CordDocumento18 pagineCNS Structure and Function - Anatomy of the Brain and Spinal CordAnna Marthea V.100% (4)
- Pyramidal Tract AND Extrapyramidal TractDocumento23 paginePyramidal Tract AND Extrapyramidal TractKristian CadaNessuna valutazione finora
- DEI Class - Basal Ganglion, Substantia Nigra, PallidumDocumento26 pagineDEI Class - Basal Ganglion, Substantia Nigra, PallidumSiddharth SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Parts of The BrainDocumento106 pagineParts of The BrainbechichemelissaNessuna valutazione finora
- Models of BrainDocumento28 pagineModels of Brainnironkushbhuyan2002Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Are The Basal Ganglia?Documento53 pagineWhat Are The Basal Ganglia?Gursangeetkaur2010Nessuna valutazione finora
- Basal GangliaDocumento20 pagineBasal GangliaUloko Christopher100% (1)
- Basal Ganglia ModifiedDocumento34 pagineBasal Ganglia ModifiedNada MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- Basal Ganglia: Dr. Mohanad R. AlwanDocumento35 pagineBasal Ganglia: Dr. Mohanad R. Alwanmohanad11Nessuna valutazione finora
- Basal GangliaDocumento11 pagineBasal GangliaSTEVEN OKURUTNessuna valutazione finora
- My Basal GangliaDocumento18 pagineMy Basal GangliaPriya GKNessuna valutazione finora
- Basal Ganglia 1Documento7 pagineBasal Ganglia 1Nala MelegritoNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuroana Mod4 Basal Ganglia 1Documento12 pagineNeuroana Mod4 Basal Ganglia 1Danielle HayagNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous SystemDocumento125 pagineNervous SystemGIRLLYN BURZONNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Basal ganglia 2022Documento39 pagine5 Basal ganglia 2022Gregory WigginsNessuna valutazione finora
- Basal Ganglia: Corpus StriatumDocumento5 pagineBasal Ganglia: Corpus StriatumJohann Sebastian CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Biopsych ReviewDocumento83 pagineBiopsych Reviewapi-421695293Nessuna valutazione finora
- Basal GangliaDocumento32 pagineBasal GangliaManisanthosh Kumar100% (2)
- Basal Ganglia AnatomyDocumento17 pagineBasal Ganglia AnatomyEnoch MordecaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Basal GangliaDocumento17 pagineBasal GangliaSnehal SawantNessuna valutazione finora
- Basal Ganglia & CerebellumDocumento77 pagineBasal Ganglia & Cerebellumyasrul izadNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture (17) Basal GangliaDocumento13 pagineLecture (17) Basal GangliaAkashNessuna valutazione finora
- Psychosomatics: Nervous System: Miguel Agustin ST Francisco, RPM, Mpsy CandDocumento29 paginePsychosomatics: Nervous System: Miguel Agustin ST Francisco, RPM, Mpsy CandRalph Christian ZorillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuroanatomical and Neurophysiological Bases of Behavior LecDocumento53 pagineNeuroanatomical and Neurophysiological Bases of Behavior Lecstephen allan ambalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basal Ganglia: Sridharan Neelamegan MMCDocumento23 pagineBasal Ganglia: Sridharan Neelamegan MMCRetrocasualty Find OutNessuna valutazione finora
- SARAF PUSAT DAN OTONOMDocumento72 pagineSARAF PUSAT DAN OTONOMellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Wk. 3 - Brain N Endocrine SystemDocumento47 pagineWk. 3 - Brain N Endocrine SystemShayyy JacksonNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 - Cerebellum, Diencephalon, Basal NucleiDocumento60 pagine8 - Cerebellum, Diencephalon, Basal Nucleib.ozyurek84Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biopsychology and the BrainDocumento61 pagineBiopsychology and the BrainJupiter BassettNessuna valutazione finora
- The Nervous SystemDocumento54 pagineThe Nervous Systemeleldev100% (2)
- Cerebrum DR Premanand BDocumento20 pagineCerebrum DR Premanand BOmcar patilNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Shift - NL Basal Ganglia - 2. Caudate NucleusDocumento4 pagine3 Shift - NL Basal Ganglia - 2. Caudate NucleusJOVI ANNE MACARAEGNessuna valutazione finora
- Thalamus 130624023852 Phpapp02Documento37 pagineThalamus 130624023852 Phpapp02Dr Abdulkadir Aminu DaudaNessuna valutazione finora
- CerebrumDocumento38 pagineCerebrumAuza Moses IbrahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Brain (Encephalon) : DR - Nirajan NeupaneDocumento26 pagineBrain (Encephalon) : DR - Nirajan NeupaneShyam SubediNessuna valutazione finora
- DR Alexandra MihailescuDocumento23 pagineDR Alexandra MihailescuAdelina ZaicescuNessuna valutazione finora
- Basal GangliaDocumento29 pagineBasal Gangliaapi-19916399Nessuna valutazione finora
- Brainstem Anatomy - Pons, Midbrain & Key StructuresDocumento24 pagineBrainstem Anatomy - Pons, Midbrain & Key StructuresjabirNessuna valutazione finora
- Brain and Behavior Psychology DiplomaDocumento27 pagineBrain and Behavior Psychology DiplomaDilindri GunasenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous System - All NotesDocumento6 pagineNervous System - All NotesJNessuna valutazione finora
- Weight of An Adult BrainDocumento5 pagineWeight of An Adult BrainjisarafaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Neural Control and CoordinationDocumento60 pagineNeural Control and CoordinationDivya Agarawal100% (1)
- Diencephalon, Basal Ganglia, Limbic SystemDocumento56 pagineDiencephalon, Basal Ganglia, Limbic SystemJoaquin GuillermoNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 2: The Extrapyramidal System. The CerebellumDocumento42 pagineTopic 2: The Extrapyramidal System. The Cerebellumprashant singhNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Lecture 4 - ThalamusDocumento49 pagineAnatomy Lecture 4 - ThalamusBISMARCK BANAHENE BOAHENENessuna valutazione finora
- The Limbic System: An Overview of Key Structures and FunctionsDocumento54 pagineThe Limbic System: An Overview of Key Structures and FunctionsJuan Enrique Toro PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurotransmitters LectureDocumento22 pagineNeurotransmitters LectureKrystal LaiNessuna valutazione finora
- EEG Block Diagram, Electrodes and Their PlacementDocumento57 pagineEEG Block Diagram, Electrodes and Their Placementbathula hariniNessuna valutazione finora
- Psychopharmacology: Understanding How Drugs Affect the BrainDocumento29 paginePsychopharmacology: Understanding How Drugs Affect the BrainChris ZantiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdomen - Vasculature of GutDocumento33 pagineAbdomen - Vasculature of GutewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdomen - Small Bowel, Large Bowel & PancreaseDocumento17 pagineAbdomen - Small Bowel, Large Bowel & PancreaseewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdomen - Pancrease & Extrahepatic Biliary SystemDocumento25 pagineAbdomen - Pancrease & Extrahepatic Biliary SystemewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anterior Abdominal WallDocumento20 pagineAnterior Abdominal WallewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mouth, Pharynx, Tongue, OesophagusDocumento35 pagineMouth, Pharynx, Tongue, OesophagusewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdomen Abdominal CavityDocumento18 pagineAbdomen Abdominal CavityewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdomen & Pelvis - Ureters, Bladder & MicturitionDocumento43 pagineAbdomen & Pelvis - Ureters, Bladder & MicturitionewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdomen & Pelvis - Adrenal GlandDocumento21 pagineAbdomen & Pelvis - Adrenal GlandewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdomen & Pelvis - Stomach and DuodenumDocumento43 pagineAbdomen & Pelvis - Stomach and DuodenumewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdomen & Pelvis - PancreasDocumento13 pagineAbdomen & Pelvis - PancreasewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abdomen & Pelvis - Anatomy of Kidney2004Documento26 pagineAbdomen & Pelvis - Anatomy of Kidney2004ewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- OesophagusDocumento16 pagineOesophagusewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Skeletal TissueDocumento26 pagineSkeletal TissueewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- 01.introduction Digestive TractDocumento21 pagine01.introduction Digestive TractewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gut MotilityDocumento15 pagineGut MotilityewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Histology of SkinDocumento33 pagineHistology of SkinH R A K Kulathilaka75% (4)
- Epithelia of The Digestive TractDocumento18 pagineEpithelia of The Digestive TractewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Urinary SystemDocumento52 pagineUrinary SystemewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular TissueDocumento27 pagineMuscular TissueewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Skeletal Tissue2005Documento40 pagineSkeletal Tissue2005ewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Red Blood Cell 15-11-2004Documento26 pagineRed Blood Cell 15-11-2004ewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of The CellDocumento30 pagineStructure of The CellewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Organization of Vascular SystemDocumento31 pagineOrganization of Vascular SystemewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lymphatic TissueDocumento49 pagineLymphatic TissueewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nervous SystemDocumento36 pagineNervous SystemRukshan RanatungaNessuna valutazione finora
- Glandular TissueDocumento16 pagineGlandular TissueewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscular Tissue - Skelital MuscleDocumento23 pagineMuscular Tissue - Skelital MuscleewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Epithelial TissueDocumento68 pagineEpithelial TissueH R A K KulathilakaNessuna valutazione finora
- Histology of SkinDocumento33 pagineHistology of SkinH R A K Kulathilaka75% (4)
- Epithelia of The Digestive TractDocumento18 pagineEpithelia of The Digestive TractewijayapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Wildlife Awareness CentreDocumento3 pagineWildlife Awareness CentreVarun TankNessuna valutazione finora
- The Nutrient Evaluation of Fermented Rice Bran As Poultry FeedDocumento3 pagineThe Nutrient Evaluation of Fermented Rice Bran As Poultry FeedmaskrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm A194Documento3 pagineAstm A194luizz100% (1)
- Extended Essay NorhanDocumento23 pagineExtended Essay NorhanAbed ZaghalNessuna valutazione finora
- General Biology QuizDocumento2 pagineGeneral Biology QuizQueng ElediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anaphy - CellDocumento3 pagineAnaphy - CellrhmanipolNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 09 Sum MT PoriferaDocumento17 pagine02 09 Sum MT PoriferaMudasir AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- LN Med Bact Final PDFDocumento444 pagineLN Med Bact Final PDFPrince HimansuNessuna valutazione finora
- Kla DeterminationDocumento23 pagineKla DeterminationJokanoe LertNessuna valutazione finora
- Mathematically Based Management of Fermentations: Saccharomyces Sp. Batch Propagations andDocumento144 pagineMathematically Based Management of Fermentations: Saccharomyces Sp. Batch Propagations andleon felipe toroNessuna valutazione finora
- Test Smiles 2 Periudha 2Documento4 pagineTest Smiles 2 Periudha 2JolandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch.2.2 Ecological Pyramid WorksheetDocumento2 pagineCh.2.2 Ecological Pyramid Worksheet무루파털뭉치Nessuna valutazione finora
- d20 Adamant Entertainment PosthumanDocumento27 pagined20 Adamant Entertainment Posthumanjoaam100% (3)
- Khan Academy Cellular Development QuestionsDocumento3 pagineKhan Academy Cellular Development QuestionsLoraNessuna valutazione finora
- Particles of MatterDocumento9 pagineParticles of MatterFatema KhatunNessuna valutazione finora
- Applications of Biotechnology in Food TechnologyDocumento7 pagineApplications of Biotechnology in Food TechnologyJhon NeverNessuna valutazione finora
- The Differences Between The Germ Theory and The Terrain TheoryDocumento3 pagineThe Differences Between The Germ Theory and The Terrain Theorytesla2008Nessuna valutazione finora
- Managing Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases - Past, Present and FutureDocumento6 pagineManaging Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases - Past, Present and FutureNICOLASNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Disabilities Summary1Documento11 pagineLearning Disabilities Summary1fordmayNessuna valutazione finora
- 4th Quarter Exam'17Documento15 pagine4th Quarter Exam'17cattleya abello100% (1)
- Microorganism Identification MethodsDocumento29 pagineMicroorganism Identification MethodsAlmoatazbellah AbdallahNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid & Electrolyte Management in Neonates: Critical Aspect of Care of High Risk InfantsDocumento78 pagineFluid & Electrolyte Management in Neonates: Critical Aspect of Care of High Risk Infantsdrhemantparakh100% (1)
- Social Network Influence On YouthDocumento3 pagineSocial Network Influence On YouthKhairun NisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dragon Fruit Growth on BAP Concentration and Germination Age In VitroDocumento7 pagineDragon Fruit Growth on BAP Concentration and Germination Age In VitroAzmi NadhifNessuna valutazione finora
- Phytostabilization of Nickel by The Zinc and Cadmium Hyperaccumulator SolanumDocumento7 paginePhytostabilization of Nickel by The Zinc and Cadmium Hyperaccumulator SolanumYogi PernandaNessuna valutazione finora
- JurnalDocumento7 pagineJurnalDangdut ManiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Classification (Porifera-Echinodermata)Documento164 pagineAnimal Classification (Porifera-Echinodermata)9415697349Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hsm7n Continuum Modeling in The Physical SciencesDocumento238 pagineHsm7n Continuum Modeling in The Physical SciencesSF1234567890Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ballistic StretchingDocumento14 pagineBallistic Stretchingapi-351172625Nessuna valutazione finora
- Practice 0612 - Endangered SpeciesDocumento10 paginePractice 0612 - Endangered SpeciesMai LinhNessuna valutazione finora