Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Manual Computing Devices: Pascal'S Calculator
Caricato da
PRINTDESK by DanDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Manual Computing Devices: Pascal'S Calculator
Caricato da
PRINTDESK by DanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
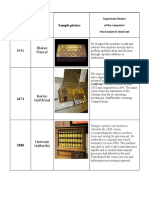
MANUAL COMPUTING DEVICES
PASCAL'S CALCULATOR
Blaise Pascal invented the mechanical calculator in 1642.[1][2] He conceived the idea while trying to help his father who had been assigned the task of reorganizing the tax revenues of the French province of Haute-Normandie ; first called Arithmetic Machine, Pascal's Calculator and later Pascaline, it could add and subtract directly and multiply and divide by repetition.
STEPPED RECKONER
The Step Reckoner (or Stepped Reckoner) was a digital mechanical calculator invented by German mathematician Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz around 1672 and completed in 1694.[1] The name comes from the translation of the German term for its operating mechanism; staffelwalze meaning 'stepped drum'. It was the first calculator that could perform all four arithmetic operations: addition, subtraction, multiplication and division..
DIFFERENCE ENGINE
A difference engine is an automatic, mechanical calculator designed to tabulate polynomial functions. The name derives from the method of divided differences, a way to interpolate or tabulate functions by using a small set of polynomial coefficients. Both logarithmic and trigonometric functions, functions commonly used by both navigators and scientists, can be approximated by polynomials, so a difference engine can compute many useful sets of numbers.
MECHANICAL COMPUTING DEVICES
CALCULATOR
An electronic calculator is a small, portable, usually inexpensive electronic device used to perform the basic operations of arithmetic. Modern calculators are more portable than most computers, though most PDAs are comparable in size to handheld calculators.
COMPUTER
A computer is a general purpose device which can be programmed to carry out a finite set of arithmetic or logical operations. Since a sequence of operations can be readily changed, the computer can solve more than one kind of problem. The essential point of a computer is to implement an idea, the terms of which are satisfied by Alan Turing's Universal Turing machine.
TOTAL DISSOLVED SOLIDS
Total Dissolved Solids (often abbreviated TDS) is a measure of the combined content of all inorganic and organic substances contained in a liquid in: molecular, ionized or micro-granular (colloidal sol) suspended form. Generally the operational definition is that the solids must be small enough to survive filtration through a sieve the size of two micrometer. Total dissolved solids are normally discussed only for freshwater systems, as salinity comprises some of the ions constituting the definition of TDS.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- GNS212 Course MaterialDocumento91 pagineGNS212 Course Materialhafeesadetunji01Nessuna valutazione finora
- APPLICATIONWINDOWSDocumento5 pagineAPPLICATIONWINDOWSAnna Biella Dacaymat PalattaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Solving Techniques and Introduction To C ProgrammingDocumento32 pagineProblem Solving Techniques and Introduction To C ProgrammingAshok KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Based On Principles of OperationDocumento11 pagineBased On Principles of OperationannusainiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 History of Computer by Ibook Development GroupDocumento24 pagineLesson 1 History of Computer by Ibook Development GroupChad Drahc100% (1)
- WAPPDocumento10 pagineWAPPAnna Biella Dacaymat PalattaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Basisto, Rachel Joy - Laboratory 4Documento20 pagineBasisto, Rachel Joy - Laboratory 4Rachel BasistoNessuna valutazione finora
- TimelineDocumento2 pagineTimelineLUZNessuna valutazione finora
- Historical Development of Computers FSC 113Documento15 pagineHistorical Development of Computers FSC 113amodusofiat77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Computer: Introduction To Computer: Created By: Rafique KhakiDocumento35 pagineComputer: Introduction To Computer: Created By: Rafique KhakiMir ArsalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Introdution To Computers and LogicDocumento45 pagineUnit 1 Introdution To Computers and Logicjoemar cadampogNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is ComputerDocumento8 pagineWhat Is ComputerElissa HornejasNessuna valutazione finora
- History of ComputingDocumento53 pagineHistory of ComputingMocmoc SalihNessuna valutazione finora
- Patawaran, Jezreel C, BSCE 1F, Activity 2, Microsoft PowerpointDocumento49 paginePatawaran, Jezreel C, BSCE 1F, Activity 2, Microsoft PowerpointPatawaran JezreelNessuna valutazione finora
- Aksu - GSS 211 (2015Documento86 pagineAksu - GSS 211 (2015Joseph Israel100% (1)
- History of ComputersDocumento118 pagineHistory of ComputersDima BurkovichNessuna valutazione finora
- Index Unit - 1 Content Page No H C Generation OF Computers Types of ComputersDocumento46 pagineIndex Unit - 1 Content Page No H C Generation OF Computers Types of Computerspsaravanan1985Nessuna valutazione finora
- 9th Class Computer Science Important QuestionsDocumento19 pagine9th Class Computer Science Important QuestionsTahir MehmoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Minor Project Report On Computers - Assignment On Computer and Its ApplicationsDocumento37 pagineMinor Project Report On Computers - Assignment On Computer and Its ApplicationsNikhil Dhawan0% (1)
- History of Computer and Generations of Computer.: S2F18BSEN0029Documento33 pagineHistory of Computer and Generations of Computer.: S2F18BSEN0029Nabeel Riasat Riasat AliNessuna valutazione finora
- All About ComputersDocumento4 pagineAll About ComputersjosedenniolimNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Digital ElectronicsDocumento63 pagineIntroduction To Digital ElectronicsPearl Anne ManilaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Adelphi College 2Documento2 pagineThe Adelphi College 2Emilie Ann SumalloNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes 9thDocumento10 pagineNotes 9thabqureshiNessuna valutazione finora
- LIE - History of ComputerDocumento88 pagineLIE - History of ComputerJustin Acuña DungogNessuna valutazione finora
- Law On Partnership ReviewerDocumento29 pagineLaw On Partnership ReviewerClyde SaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer NotesDocumento49 pagineComputer NotesAnb BajwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Document 4Documento22 pagineDocument 4Aditya RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculator: Mechanical Calculator Calculator (Disambiguation)Documento8 pagineCalculator: Mechanical Calculator Calculator (Disambiguation)Jef PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro To ComputingDocumento50 pagineIntro To ComputingJhierry Elustrado FrancoNessuna valutazione finora
- History of ComputerDocumento34 pagineHistory of ComputerChristine Jane RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- 1st Quarter ICT Lesson 1-4Documento83 pagine1st Quarter ICT Lesson 1-4John SeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 9 Computer Book Federal Board MergedDocumento120 pagineClass 9 Computer Book Federal Board MergedMunib Ahmad100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Class 9 Computer Book Federal BoardDocumento29 pagineChapter 1 Class 9 Computer Book Federal BoardBaaghi Talha100% (4)
- GST100 Complete Material-1Documento147 pagineGST100 Complete Material-1Lovina Tam BelabriNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Lieracy Lecture NotesDocumento54 pagineComputer Lieracy Lecture NotesnkayomocNessuna valutazione finora
- Calculator - WikipediaDocumento16 pagineCalculator - Wikipediayanachii22Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamental Concept of ComputerDocumento7 pagineFundamental Concept of ComputerML MariaWengNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 OopDocumento15 pagineModule 1 OopAdonisNessuna valutazione finora
- Evolution and Generation of Computers: Samuel KizitoDocumento69 pagineEvolution and Generation of Computers: Samuel KizitoShankar ThakareNessuna valutazione finora
- EarlycomputingdevicesDocumento3 pagineEarlycomputingdevicesZio BronaNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer History HandoutDocumento3 pagineComputer History HandoutMary Jane Climaco GamoseNessuna valutazione finora
- CC101 - Evolution of ComputingDocumento33 pagineCC101 - Evolution of Computingjaydee nazNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.1.1 Characteristics of Computers: Speed: The Computers Process Data at An Extremely Fast Rate, at Millions or BillionsDocumento17 pagine1.1.1 Characteristics of Computers: Speed: The Computers Process Data at An Extremely Fast Rate, at Millions or BillionsPratibha JhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer 9th ClasschapterDocumento48 pagineComputer 9th ClasschapterSalman ZaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 1Documento10 pagineChap 1Atiq JuttNessuna valutazione finora
- NCM 110 LectureDocumento3 pagineNCM 110 LectureGenesis PalangiNessuna valutazione finora
- Fit IDocumento10 pagineFit IMadasu BalnarsimhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Fanda MentalsDocumento148 pagineComputer Fanda MentalsJager JacksonNessuna valutazione finora
- IT BeginerDocumento10 pagineIT Beginershantanu dasNessuna valutazione finora
- CalculatorDocumento7 pagineCalculatorNo Copyright Audio StoreNessuna valutazione finora
- ITT Project1Documento71 pagineITT Project1Aashish Makkar0% (1)
- CSC 200Documento10 pagineCSC 200timothyosaigbovo3466Nessuna valutazione finora
- CS101 - Intro2Computing - Part 1Documento2 pagineCS101 - Intro2Computing - Part 1rayden22Nessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of ComputerDocumento8 pagineClassification of Computertrxxx.axxNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Computer, Any of A Class of Devices Capable of SolvingDocumento3 pagineDigital Computer, Any of A Class of Devices Capable of SolvingkeithevaristoNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Role in Modern AccountingDocumento10 pagineComputer Role in Modern AccountingSanjeet Kumar100% (6)
- Basic Computer Skills: M.SC Economics IDocumento44 pagineBasic Computer Skills: M.SC Economics IAmara AwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Tools Used in AgricultureDocumento4 pagineTools Used in AgriculturePRINTDESK by Dan100% (1)
- Type of ForceDocumento3 pagineType of ForcePRINTDESK by DanNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are Context CluesDocumento1 paginaWhat Are Context CluesPRINTDESK by DanNessuna valutazione finora
- Map Eeeh EeeeDocumento82 pagineMap Eeeh EeeePRINTDESK by DanNessuna valutazione finora
- Why The English Teacher Died at ChristmasDocumento3 pagineWhy The English Teacher Died at ChristmasPRINTDESK by DanNessuna valutazione finora
- Why The Sky Is HighDocumento2 pagineWhy The Sky Is HighPRINTDESK by DanNessuna valutazione finora
- The PartingDocumento2 pagineThe PartingPRINTDESK by Dan67% (3)
- What Is The Different Kinds of MedicineDocumento2 pagineWhat Is The Different Kinds of MedicinePRINTDESK by DanNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are The Importance of Element in Life and in IndustryDocumento1 paginaWhat Are The Importance of Element in Life and in IndustryPRINTDESK by Dan75% (4)
- Low and High BiodiversityDocumento14 pagineLow and High BiodiversityPRINTDESK by DanNessuna valutazione finora
- by Mhae On ArtsDocumento24 pagineby Mhae On ArtsPRINTDESK by DanNessuna valutazione finora
- Foundations of Values FormationDocumento9 pagineFoundations of Values FormationPRINTDESK by Dan100% (1)
- The Barangay As A Unit of SocietyDocumento1 paginaThe Barangay As A Unit of SocietyPRINTDESK by DanNessuna valutazione finora
- Medicinal PlantsDocumento5 pagineMedicinal PlantsPRINTDESK by DanNessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular GeneticsDocumento3 pagineMolecular GeneticsPRINTDESK by DanNessuna valutazione finora
- NewtonDocumento3 pagineNewtonPRINTDESK by DanNessuna valutazione finora
- Climate Variability and Climate Chang1Documento2 pagineClimate Variability and Climate Chang1PRINTDESK by Dan100% (1)
- How Chemistry Related To Other ScienceDocumento1 paginaHow Chemistry Related To Other SciencePRINTDESK by Dan100% (2)
- StressDocumento2 pagineStressPRINTDESK by DanNessuna valutazione finora
- Project in English IV Book Report: Ma. Jamaica V. de GuzmanDocumento7 pagineProject in English IV Book Report: Ma. Jamaica V. de GuzmanPRINTDESK by DanNessuna valutazione finora
- Contribution of Chemistry ToDocumento1 paginaContribution of Chemistry ToPRINTDESK by DanNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 7 Term 1 Computer Science NotesDocumento26 pagineGrade 7 Term 1 Computer Science NotesOmari JnrNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Key: Chapter 1: Know Your ComputerDocumento10 pagineAnswer Key: Chapter 1: Know Your ComputerHung Nguyen DoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2 Part 1 - History of ComputerDocumento37 pagineLesson 2 Part 1 - History of ComputerJohnpatrick SongcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Charles BabbageDocumento12 pagineCharles BabbageNazzir Hussain Hj MydeenNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecutre-2 Evolution of ComputersDocumento26 pagineLecutre-2 Evolution of ComputersEren JeagerNessuna valutazione finora
- Challenge of Artificial IntelligenceDocumento230 pagineChallenge of Artificial IntelligenceDragosNessuna valutazione finora
- Abacus: Napier BoneDocumento3 pagineAbacus: Napier BoneAayushNessuna valutazione finora
- The Innovators SummaryDocumento4 pagineThe Innovators SummaryTony AstroNessuna valutazione finora
- Ada Byron and Her Contributions To Early Computer Science PSSOH 2018Documento4 pagineAda Byron and Her Contributions To Early Computer Science PSSOH 2018Titilayo Deborah CadmusNessuna valutazione finora
- The Mechanical AgeDocumento4 pagineThe Mechanical AgenoelNessuna valutazione finora
- AKOTODocumento3 pagineAKOTOCHOLOENessuna valutazione finora
- TechnoDocumento17 pagineTechnoMa Sonia JorgeNessuna valutazione finora
- 1premech Mech AgeDocumento22 pagine1premech Mech AgeEver BelloteNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 7 CBC Computer Science Note SlidesDocumento73 pagineGrade 7 CBC Computer Science Note SlidesRaphael Leyson100% (1)
- The History of Mathematical TablesDocumento372 pagineThe History of Mathematical Tablesresty100% (1)
- Basics of Computer by Rajiv KhanaDocumento268 pagineBasics of Computer by Rajiv Khanatariqghayyur2100% (2)
- Information Age: Instr. Jeremiah G. PedralDocumento31 pagineInformation Age: Instr. Jeremiah G. PedralMac VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- SSC I Computer Science NOTES by Usman JavedDocumento82 pagineSSC I Computer Science NOTES by Usman JavedOsman JavaidNessuna valutazione finora
- A CalculatorDocumento18 pagineA CalculatorRohit MakhijaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Information and Computer TechnologyDocumento3 pagineIntroduction To Information and Computer Technologywendrei marquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Class XI Evolution of ComputerDocumento9 pagineClass XI Evolution of ComputerJaveriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Uk About Uk Inventions in The Mexican ContextDocumento22 pagineUk About Uk Inventions in The Mexican ContextJoel RezaNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem SpaceDocumento281 pagineProblem SpaceozorgnaxNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Computer: Basic Computing Periods: Week 3 Living in The IT Era Maria Michelle VinegasDocumento41 pagineHistory of Computer: Basic Computing Periods: Week 3 Living in The IT Era Maria Michelle VinegasMary Ianne Therese GumabongNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 вариантDocumento3 pagine2 вариантalmady176Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture1 History of ComputersDocumento30 pagineLecture1 History of ComputersDoc AlexNessuna valutazione finora
- Living in The I.T Era Module 2Documento18 pagineLiving in The I.T Era Module 2Aivee GatzzNessuna valutazione finora
- Nptel AI Week 1Documento83 pagineNptel AI Week 1Renu TyagiNessuna valutazione finora
- Comp7 Sept Exam 1st SetDocumento3 pagineComp7 Sept Exam 1st SetHazel Joy LusellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To ComputingDocumento5 pagineIntroduction To ComputingRaishelly SyNessuna valutazione finora