Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Crystalline Materials: Civil & Environmental Engineering E207 Properties of Materials
Caricato da
Archie CabantacDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Crystalline Materials: Civil & Environmental Engineering E207 Properties of Materials
Caricato da
Archie CabantacCopyright:
Formati disponibili
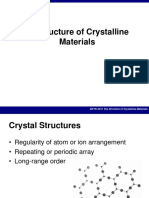
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
CRYSTALLINE MATERIALS
Dr Julia Stegemann Chadwick Building, GM15 Telephone: 020 7679 7370 E-mail: j.stegemann@ucl.ac.uk
Jan-06-1
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Aims
To understand the basic characteristics and structure of crystalline materials, and their relationships with material properties.
Jan-06-2
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Packing
Non dense, random packing
Energy typical neighbor bond length
typical neighbor bond energy
Dense, regular packing
Energy typical neighbor bond length
typical neighbor bond energy
Callister (2003)
Jan-06-3
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Packing
Crystalline materials... atoms pack in ordered 3D arrays typical of: metals many ceramics some polymers Amorphous (noncrystalline) materials... atoms are disordered
crystalline SiO2
noncrystalline SiO2
Callister (2003)
Jan-06-4
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Unit Cells
the smallest repeating volume in a crystal 3 common unit cells in crystalline materials are: Body-centred cubic unit cell (BCC) Face-centred cubic unit cell (FCC) Hexagonal close-packed unit cell (HCP)
Jan-06-5
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Co-ordination Number
= the number of nearest neighbour atoms
Atomic Packing Factor (APF)
= the fraction of the unit cell occupied by atoms APF = volume of atoms in the unit cell unit cell volume
Jan-06-6
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Simple Cubic (SC) Unit Cell
Poor packing rare (only Po)
Callister (2003)
Coordination number = 6
Jan-06-7
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Simple Cubic (SC) Unit Cell
Number of atoms in unit cell 1 =8x 8 =1 a R=0.5a Volume per atom = 4 R3 where R = 1 a 2 3 Volume of cell
Callister (2003)
= a3 APF = 0.52
Jan-06-8
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Body-Centred Cubic (BCC) Unit Cell
Callister (2003)
Examples of BCC materials include: Fe, W, Mo
Jan-06-9
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Face-Centred Cubic (FCC) Unit Cell
Callister (2003)
Examples of FCC materials include: Cu, Al, Ni, Ag, Au
Jan-06-10
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Hexagonal Close-Packed (HCP) Unit Cell
Coordination number = 12 APF = 0.74
Callister (2003)
Examples of HCP materials include: Cd, Mg, Ti, Be
Jan-06-11
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Crystal Density, =
where n A Vc NA nA VcNA
= number of atoms in unit cell = atomic weight (g/mole) = unit cell volume = Avogadros number = 6.023 x 1023 atoms/mole
Jan-06-12
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
SLIP SYSTEMS
In single crystals there are preferred planes where dislocations move, or slip planes. In a slip plane, there are preferred crystallographic directions for dislocation movement, i.e., slip directions. The set of slip planes and directions are known as slip systems. The slip planes and directions are those of highest packing density. The planes are further apart than the atoms within them, and are therefore able to slip more easily relative to one another. Since BCC and FCC crystals have more slip systems as than HCP crystals, there are more ways for dislocation to propagate. Therefore BCC and FCC materials are more ductile than HCP materials.
Jan-06-13
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
ILLUSTRATION OF AN FCC SLIP PLANE AND SLIP DIRECTIONS
Jan-06-14
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Crystallographic Directions
1. Vector passes through origin 2. Length of projection on each axis expressed as unit cell dimensions, in square brackets 3. Negative indices have bar.
Callister (2003)
Jan-06-15
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Miller Indices
Miller Indices are a way of representing the orientation of an atomic plane in a crystal lattice and are defined as the reciprocals of the fractional intercepts which the plane makes with the crystallographic axes.
Jan-06-16
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Determination of Miller Indices (hkl):
1. Plane intersects or is parallel to axes of unit cell 2. Point of intersection with each axis is expressed as number of cell dimensions from unit cell origin 3. For plane parallel to axis, intersection = 4. This yields 3 lengths. Miller indices = reciprocals of these lengths, in parentheses.
Callister (2003)
Jan-06-17
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Other planes
Callister (2003)
Jan-06-18
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Linear density (LD)
1-D density along line through crystal structure LD = length of line occupied by atoms length of line
Jan-06-19
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Planar density (PD)
2-D density across a plane through crystal structure PD = area of atoms in plane plane area
Jan-06-20
10
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Crystal Structure
Body-centred cubic Face-centred cubic Hexagonal close-packed
Number of slip systems
12 12 3
FCC metals are soft at all temperatures BCC metals brittle at low T (slip planes not close packed) HCP metals tend to be brittle (few slip planes)
Jan-06-21
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
POLYCRYSTALS AND OTHER DEFECTS
Jan-06-22
11
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Polycrystals
most engineering materials are polycrystals crystal sizes range from 1 nm to 2 cm single crystals in a polycrystalline material are known as grains.
1 mm
Nb-Hf-W plate with an electron beam weld (Callister, 2003) Jan-06-23
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Microscopic View of Progressive Crystallisation of Unit Cells t1 t2
Callister (2003)
t3
t4
Jan-06-24
12
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Single vs Polycrystals
Single Crystals
E (diagonal) = 273 GPa
properties vary with direction: anisotropy e.g., modulus of elasticity, E, in BCC iron:
E (edge) = 125 GPa
200 mm
Polycrystals
isotropic, if grains are random e.g., Epolycrystalline iron = 210 GPa
Callister (2003)
anisotropic, if grains are directionally oriented, i.e., textured
Jan-06-25
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Dislocations
linear (1-D) defect in crystalline solids. 3 types: edge screw mixed
Jan-06-26
13
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Edge Dislocation
Callister (2003)
Jan-06-27
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
An edge dislocation comprises an extra half plane of atoms within the crystal lattice. Above the line of the edge dislocation, the bonds between the crystal atoms are in compression. Below the line of the edge dislocation the bonds are in tension. This tension and compression distortion of the lattice decreases with distance from the dislocation line. The Burgers vector denotes the magnitude of the distortion of the crystal lattice and indicates the direction in which slip can occur. For an edge dislocation, the direction of the Burgers vector is perpendicular to the dislocation line.
Jan-06-28
14
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Screw Dislocation:
upper region is sheared relative to the lower region
Callister (2003)
A view from above shows the windings of the screw
Jan-06-29
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Mixed Dislocation
Callister (2003)
Jan-06-30
15
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Point Defects
Vacancy
distortion of planes
distortion of planes
selfinterstitial
Callister (2003)
Jan-06-31
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Solid Solution
Callister (2003)
Substitutional (e.g., alloy of Cu in Ni)
Interstitial alloy (e.g., alloy of C in Fe)
Jan-06-32
16
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Learning Outcomes
To be able to describe the structure of single crystal and polycrystalline materials To be able to calculate atomic packing factor, linear and planar density To be able to describe directions and planes in crystal structures using vectors and Miller indices To be able to describe the nature of defects and dislocations in crystal structures
Jan-06-33
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
Recommended Reading
Domone, P.L. & Illston, J.M. (2001), Eds., Construction Materials: Their Nature and Behaviour, 3rd edition, Spon Press, London.
Chapters 8. Physical Metallurgy
Chapters 3/ The Structure of Crystalline Solids 4.1-4.5/ Imperfections in Solids 7.1-7.4/ Dislocations and Slip Systems
Callister, W.D. (2003), Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction, 6th edition, John Wiley and Sons, Inc. (includes CD-ROM)
Jan-06-34
17
CIVIL & ENVIRONMENTAL ENGINEERING E207 PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS
On-Line Learning Exercise
Introduction to Dislocations http://www.doitpoms.ac.uk/tlplib/dislocations/
Jan-06-35
18
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Structure of Crystalline Solids: Issues To Address..Documento35 pagineThe Structure of Crystalline Solids: Issues To Address..Razman BijanNessuna valutazione finora
- Festkörper Probleme: Plenary Lectures of the Divisions Semiconductor Physics, Surface Physics, Low Temperature Physics, High Polymers, Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics, of the German Physical Society, Münster, March 19–24, 1973Da EverandFestkörper Probleme: Plenary Lectures of the Divisions Semiconductor Physics, Surface Physics, Low Temperature Physics, High Polymers, Thermodynamics and Statistical Mechanics, of the German Physical Society, Münster, March 19–24, 1973Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ch-27.1 Basic Concepts On Structure of SolidsDocumento39 pagineCh-27.1 Basic Concepts On Structure of SolidsJyotilal SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- SSD - L02 - Review On CrystallographyDocumento25 pagineSSD - L02 - Review On CrystallographysumonNessuna valutazione finora
- Metallurgical Achievements: Selection of Papers Presented at the Birmingham Metallurgical Society's Diamond Jubilee Session, 1963-1964Da EverandMetallurgical Achievements: Selection of Papers Presented at the Birmingham Metallurgical Society's Diamond Jubilee Session, 1963-1964W. O. AlexanderNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter+4+ +Imperfections+in+CrystalsDocumento25 pagineChapter+4+ +Imperfections+in+Crystalspramod_kNessuna valutazione finora
- Iron - Crystal Structure - Intro To Redox ReactionsDocumento35 pagineIron - Crystal Structure - Intro To Redox ReactionsHiểu Lam NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch-27.1 Basic Concepts On Structure of SolidsDocumento39 pagineCh-27.1 Basic Concepts On Structure of SolidsManojNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch-27.1 Basic Concepts On Structure of SolidsDocumento45 pagineCh-27.1 Basic Concepts On Structure of SolidsdSGDASUDNessuna valutazione finora
- 06 - Uet FM LecDocumento48 pagine06 - Uet FM LecAbcNessuna valutazione finora
- CHPT 5: Imperfections in Solids: Issues To Address..Documento27 pagineCHPT 5: Imperfections in Solids: Issues To Address..Asim TheTru BlueNessuna valutazione finora
- Material Lecture 4 DefectsDocumento44 pagineMaterial Lecture 4 Defectsdareen180732Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Materials Science and Engineering: Prepared By: Eng. Khaled BasheerDocumento22 pagineIntroduction To Materials Science and Engineering: Prepared By: Eng. Khaled BasheerCommon StoriesNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystal Structure and PropertiesDocumento29 pagineCrystal Structure and PropertiesfrancjagadeeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Notes of Engineering MaterialsDocumento7 pagineLecture Notes of Engineering Materialsahsan888100% (1)
- Structures of Crystalline SolidsDocumento25 pagineStructures of Crystalline SolidsTarun KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic Bonding: Classic Model: Ionic Lattice, Conduction Electrons Gas" (Fermi)Documento8 pagineAtomic Bonding: Classic Model: Ionic Lattice, Conduction Electrons Gas" (Fermi)goron_antonNessuna valutazione finora
- MSM - Unit No. 1 NotesDocumento25 pagineMSM - Unit No. 1 NotesPratik SaindanePatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 1Documento112 pagineLecture 1RAMA KRISHNA CHAVANessuna valutazione finora
- Ch-27.1 Basic Concepts On Structure of SolidsDocumento39 pagineCh-27.1 Basic Concepts On Structure of SolidsVinit Khaiwal100% (1)
- Manufacturing Science and MetallurgyDocumento47 pagineManufacturing Science and MetallurgyAppu bjNessuna valutazione finora
- Enrichment of AISI 316L Steel Surface Layer With Rare Earth Elements Using Ion BeamsDocumento3 pagineEnrichment of AISI 316L Steel Surface Layer With Rare Earth Elements Using Ion BeamsSuresh JeevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure of Engineering MaterialsDocumento12 pagineStructure of Engineering Materialsjust_killing_pplNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Material: Subject NameDocumento25 pagineIndustrial Material: Subject NameHamza SaeedNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystal Imperfection CH 4Documento44 pagineCrystal Imperfection CH 4anapguerraNessuna valutazione finora
- Material Science and EngineeringDocumento14 pagineMaterial Science and Engineeringanne calabasaNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Engineering Materials: Unit No 01Documento69 pagineBasics of Engineering Materials: Unit No 01VijayParaskarNessuna valutazione finora
- Universitatea Transilvaania Facultatea S.I.M Profil I.S.I. Grupa 3331Documento9 pagineUniversitatea Transilvaania Facultatea S.I.M Profil I.S.I. Grupa 3331Robert PrinceNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystal Properties and Growth of Semiconductors-Lecture-1Documento13 pagineCrystal Properties and Growth of Semiconductors-Lecture-1A.K.M.TOUHIDUR RAHMANNessuna valutazione finora
- Eee 508Documento95 pagineEee 508OrtyomNessuna valutazione finora
- 630 Imperfections - 2020 - EN - ZdravkovDocumento12 pagine630 Imperfections - 2020 - EN - ZdravkovЧавдар ПенеловNessuna valutazione finora
- lectut-MTN-513-pdf-Structure of Crystalline CeramicsDocumento53 paginelectut-MTN-513-pdf-Structure of Crystalline CeramicsAkash AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Microstructure MaterialsDocumento8 pagineMicrostructure Materialsweda walata heduwaNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEM0013 Slides pt1 PDFDocumento30 pagineCHEM0013 Slides pt1 PDFAdar DeslolNessuna valutazione finora
- Noncrystalline Materials: 8.1 GasesDocumento24 pagineNoncrystalline Materials: 8.1 GasesmuawizzatNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Fundamentals of Electronic DevicesDocumento77 pagine2 Fundamentals of Electronic DevicesResy ApolinarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Metals: Effects of Rare Earth (Ce and La) On Steel Corrosion Behaviors Under Wet-Dry Cycle Immersion ConditionsDocumento14 pagineMetals: Effects of Rare Earth (Ce and La) On Steel Corrosion Behaviors Under Wet-Dry Cycle Immersion ConditionsThanhluan NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal of Crystal Growth: S. Dhanuskodi, T.C. Sabari GirisunDocumento6 pagineJournal of Crystal Growth: S. Dhanuskodi, T.C. Sabari GirisunRama GaurNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystal Defects: 1.0 Learning ObjectivesDocumento5 pagineCrystal Defects: 1.0 Learning ObjectivesstevenkoNessuna valutazione finora
- Other Sources.: A4 Sheet Papers Submission Date - August 26, 27 and 28, 2019Documento5 pagineOther Sources.: A4 Sheet Papers Submission Date - August 26, 27 and 28, 2019Anas MuhammedNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastic Deformation of MetalsDocumento42 paginePlastic Deformation of MetalsNaresh DeshpandeNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 - Plastic Deformation of Single CrystalDocumento42 pagine04 - Plastic Deformation of Single Crystalshanthakumar100% (1)
- (BKTK) - 2-The Structure of CrystalDocumento24 pagine(BKTK) - 2-The Structure of CrystalMnemosyneNessuna valutazione finora
- The Chemistry of Engineering Materials 20192020Documento19 pagineThe Chemistry of Engineering Materials 20192020potassiumNessuna valutazione finora
- Imperfection in Solid: Mahfodzah MD PadziDocumento44 pagineImperfection in Solid: Mahfodzah MD PadziIzzat IkramNessuna valutazione finora
- Galvanic Corrosion Behavior of Orthodontic Archwire Alloys Coupled To Bracket Alloys.Documento7 pagineGalvanic Corrosion Behavior of Orthodontic Archwire Alloys Coupled To Bracket Alloys.maparmerNessuna valutazione finora
- CV1013 - SteelDocumento103 pagineCV1013 - SteelAsh KongNessuna valutazione finora
- Ceramic Lecture 22 - 23Documento41 pagineCeramic Lecture 22 - 23KlanaWijayaNessuna valutazione finora
- EM Unit I 21-22Documento154 pagineEM Unit I 21-22Gayatri KanwadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Segregation Effects Iii Welded Stairless Steels: Pinstech/Npd-121Documento26 pagineSegregation Effects Iii Welded Stairless Steels: Pinstech/Npd-121Lenin CórdovaNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 - Crystal Structures of MetalsDocumento8 pagine03 - Crystal Structures of MetalsJant Erbert GarbosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 - Crystal Imperfection and DeformationDocumento36 pagineChapter 3 - Crystal Imperfection and DeformationViet NguyenHoangNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2Documento70 pagineChapter 2劉德信Nessuna valutazione finora
- Nuclear Engineering Department Ion ChannelingDocumento11 pagineNuclear Engineering Department Ion Channelingحسين عمريNessuna valutazione finora
- Additional Course Material: Ceramic MaterialsDocumento16 pagineAdditional Course Material: Ceramic Materialssayhigaurav07Nessuna valutazione finora
- High Temperature MaterialsDocumento120 pagineHigh Temperature MaterialsshakeelahmadjsrNessuna valutazione finora
- Elastic-Plastic Load Carrying Capacity of Steel MembersDocumento3 pagineElastic-Plastic Load Carrying Capacity of Steel MembersArupananda PrustyNessuna valutazione finora
- From Diffraction To Structure: 3.012 Fund of Mat Sci: Structure - Lecture 19Documento30 pagineFrom Diffraction To Structure: 3.012 Fund of Mat Sci: Structure - Lecture 19kishorkumarn8212Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ischebeck - Lizzi Lecture - Design of Direct Drilled and Continuous Flush Grouted Micropiles TITANDocumento40 pagineIschebeck - Lizzi Lecture - Design of Direct Drilled and Continuous Flush Grouted Micropiles TITANDaniel Rioja GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drying Shrinkage NoteDocumento1 paginaDrying Shrinkage NoteyuancchanNessuna valutazione finora
- Common Surface Defects of Wire Rod and Steel Bar and Treatment MethodsDocumento4 pagineCommon Surface Defects of Wire Rod and Steel Bar and Treatment Methodsdofan thrimavithanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Study of Rate of Evaporation of LiquidsDocumento18 pagineStudy of Rate of Evaporation of Liquidsrohinrohin78% (9)
- Modeling The Oxygen Diffusion of Nanocomposite-Based Food Packaging FilmsDocumento10 pagineModeling The Oxygen Diffusion of Nanocomposite-Based Food Packaging FilmsbhuniakanishkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Materials Science and Engineering ADocumento7 pagineMaterials Science and Engineering ALuan CaetanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Essentials of Materials Science and Engineering Si Edition 3rd Edition Askeland Solutions ManualDocumento11 pagineEssentials of Materials Science and Engineering Si Edition 3rd Edition Askeland Solutions Manualjeffreyhayesagoisypdfm100% (13)
- ECD en HGH Temp WellsDocumento162 pagineECD en HGH Temp WellsWalter MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abhishek Thakur Xi-F 15 Physics Project File: Mechanical Properties of FluidsDocumento14 pagineAbhishek Thakur Xi-F 15 Physics Project File: Mechanical Properties of FluidsAbhishek ThakurNessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Properties of NanomaterialsDocumento23 paginePhysical Properties of NanomaterialsNaveed UR RehmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal of Constructional Steel Research Volume 103 Issue 2014 (Doi 10.1016 - j.jcsr.2014.08.006) Hu, Hong-Song Nie, Jian-Guo Eatherton, Matthew R. - Deformation Capacity of Concrete-Filled Steel PDocumento11 pagineJournal of Constructional Steel Research Volume 103 Issue 2014 (Doi 10.1016 - j.jcsr.2014.08.006) Hu, Hong-Song Nie, Jian-Guo Eatherton, Matthew R. - Deformation Capacity of Concrete-Filled Steel PPrapa KaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Vapor Deposition ChemicalDocumento30 pagineVapor Deposition ChemicalJohn JosephNessuna valutazione finora
- MP 211: Fluid Mechanics Tutorial No.1: Fluid PropertiesDocumento2 pagineMP 211: Fluid Mechanics Tutorial No.1: Fluid PropertiesGabrielNessuna valutazione finora
- DING-Smart and Functional Polymers (2019) PDFDocumento308 pagineDING-Smart and Functional Polymers (2019) PDFJuanManuelAmaroLuisNessuna valutazione finora
- Goud-Umashankar2018 Article InterfaceShearStrengthPropertiDocumento14 pagineGoud-Umashankar2018 Article InterfaceShearStrengthPropertiJPDGLNessuna valutazione finora
- Gaussian Optics ExerciseDocumento2 pagineGaussian Optics ExerciseManar MansourNessuna valutazione finora
- Carpenter Stainless Type 430: IdentificationDocumento4 pagineCarpenter Stainless Type 430: Identificationumesh sengarNessuna valutazione finora
- Long ColumnDocumento27 pagineLong ColumnAnnamalai VaidyanathanNessuna valutazione finora
- LaserDocumento27 pagineLaserskNessuna valutazione finora
- Challenges in PavementsDocumento23 pagineChallenges in PavementsSomeshwar Rao ThakkallapallyNessuna valutazione finora
- 3-Introduction To Dynamic AnalysisDocumento16 pagine3-Introduction To Dynamic Analysiskenny lieNessuna valutazione finora
- Concrete Slabs Strengthened With Basalt Fibres - Experimental Tests ResultsDocumento8 pagineConcrete Slabs Strengthened With Basalt Fibres - Experimental Tests ResultsBanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pedot:pss/go Nanocomposite For Indoor Co2 SensorDocumento9 paginePedot:pss/go Nanocomposite For Indoor Co2 SensorIJAR JOURNALNessuna valutazione finora
- Hemp in Construction - Shanaka2Documento31 pagineHemp in Construction - Shanaka2kbkshanakaNessuna valutazione finora
- C 2 - Singly Reinforced BeamsDocumento32 pagineC 2 - Singly Reinforced BeamsRekanNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal of FerrocementDocumento130 pagineJournal of FerrocementValentina Roncancio GuizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 10 TemperatureDocumento12 pagineChapter 10 TemperatureGiovanni SlackNessuna valutazione finora
- (1967-1) The Influence of Mass Transfer On Liquid Film BreakdownDocumento15 pagine(1967-1) The Influence of Mass Transfer On Liquid Film BreakdownClarissa OlivierNessuna valutazione finora
- Material Specification HS-70: Coiled TubesDocumento13 pagineMaterial Specification HS-70: Coiled TubesAlbertus TardiaNessuna valutazione finora
- READING COMPREHENSION, Group 2Documento63 pagineREADING COMPREHENSION, Group 2CakrabhuwanaNessuna valutazione finora