Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Edc Exp
Caricato da
srisairampolyDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Edc Exp
Caricato da
srisairampolyCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Fundamentals of Electronics (9051)
Experiment No. 2
EXPERIMENT No. 2
1.0 Title :
To identify various active and passive electronic components.
2.0 Prior concepts :
Solids are classified as insulators, conductors and
semiconductors. Insulators : Insulators are those substances, which do not allow the passage of electric current through them. In terms of energy band, the valance band is full while the conduction band is empty. The energy gap between valance band and conduction band is 15eV. Eg. wood, glass. Conductors : Conductors are those substances which easily allow the passage of electric current through them. In terms of energy band, the valance band and conduction band overlap each other eg. Copper, aluminium. Semiconductors : Semiconductors are those substances whose electrical conductivity lies between conductors and insulators. In terms of energy band, the valance band is almost filled and conduction band is almost empty. Further the energy gap between valance and conduction band is very small i.e. 1.1eV. eg. Germanium and silicon. Following points shall be explained by teacher before starting of experiment i) Ohms law ii) Concept of voltage/current.
3.0 New concepts :
Proposition 1 : Passive Components They require external energy source for their operation e.g. Resistors Capacitors, Inductors etc. Passive components Require External energy source
Resistor
Capacitor
Inductor
Proposition 2 : Active Components They do not require any external energy source for their operation e.g. Diode, Zener diode, Transistor, FET, UJT, SCR, DIAC, TRIAC, Photodiode, photo-transistor etc. Active componens
Require
No external energy source
Diode
Transistor
FET
UJT
SC
Photo-transistor
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
-7-
Fundamentals of Electronics (9051)
Experiment No. 2
Proposition 4 : Identify different terminals of the components and find their type, numeric code, specifications and ratings. Refer data book for ratings and specifications. Terminals
Identification of components
Type No.
Specifications
Ratings Resistors : They are passive electronic components mainly used for controlling flow of electric current and providing desired amount of voltage in electronic circuits.
Resistors
Types
Functions
Symbol
Unit
NonLinear
Linear
Controlling flow of electric current Providing desired amount of Voltage in electronic circuit
Ohm ()
Inductors : They are passive electronic components used to minimize the alternating current while permitting the flow of direct current. Inductors
Types
Functions
Symbol
Unit Henry (H)
Fixed inductor
Variable inductor
Minimize A.C. Permit DC
Capacitors : They are passive electronic components which have an ability to charge or store energy.
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
-8-
Fundamentals of Electronics (9051)
Experiment No. 2
Capacitors
Types
Functions
Symbols (Fixed)
Unit
1. Fixed Capacitor 2. Variable Capacitor
To block DC To pass AC signal
Farad (F)
(Variable)
Diode : It is a unidirectional semi-conductor component with two terminals, Anode and Cathode. Silver ring on some diodes indicates cathode. Diode
Terminals
Types
Functions
Symbol
Anode
Cathode
Zener diode Varactor diode Rectifier diode
For rectification As a switch
+ A
Schottkey diode Tunnel diode Light emitting diode Photodiode
Zener Diode : It is properly doped crystal diode, which is reverse biased and has a sharp break down voltage Zener Diode
Terminals
Functions
Symbol
Anode
Cathode
To regulate voltage
Transistor :- Transistor is a three terminal semi conductor device with terminals emitter, base, and collector and two types such as PNP & NPN Some commonly used transistors in electronic circuit are BEL 147, BEL187, BC147, BF167, AC127, BD115, CL100, SK100, 2SC2131. There are two types of transistors such as NPN and PNP. Identification of terminals is as per package.
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION -9-
Fundamentals of Electronics (9051)
Experiment No. 2
Transistor
Types
Terminals
Functions
Symbols
NPN
PNP
Emitter
Amplifying signal Base Collector As a Switch As a regulator B
C B
E NPN
E PNP
Unijunction transistor (UJT) : It is a semiconductor device with three terminals i.e. emitter E, base-1, base-2. It is basically used for switching, pulse generation and saw tooth generation. UJT
Terminals
Functions
Symbol
Switching Emitter Base 1 Base 2 Oscillator
B2
B1
Field Effect Transistor (FET) : It is three terminal, unidirectional semiconductor device in which current conduction is by one type carrier i.e. electrons or holes. It has three terminals-Source, Drain & Gate. It is of two types N channel & P channel. As FET has high input impedance and low noise-level, it is used for amplification.
Field effect transistor (FET)
Terminals
Types
Functions
Symbols
Drain Source
Gate
P-channel N-channel
As a buffer amplifier As RF amplifier G As oscillator
G S S N-channel P-channel
Silicon Controlled Rectifier (SCR) : It is a three terminal unidirectional component having Anode, Cathode & Gate.
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION - 10 -
Fundamentals of Electronics (9051)
Experiment No. 2
SCR
Terminals
Functions Switching
Symbol
Anode
Cathode
Gate
Rectification As static conductor For power control For speed control Gate
Anode
Cathode
DIAC : It is a two terminaled, three layered bi-directional device which can be switched from its OFF state to ON state for either polarity of applied voltage. It is one of the switching devices, which is used to tigger TRAIC.
DIAC
Terminals
Functions To trigger TRIAC
Symbol
MT1
MT2
TRIAC : It is a three terminal bi-directional semi-conductor device, which can control alternating current in load. TRIAC
Terminals
Functions
Symbol
As electronic ON & OFF Switch MT1 MT2 Gate For controlling alternating current in load Rectification Photo Diode : It is a light sensitive diode with two terminals Anode & Cathode. It is formed by embedding a PN junction in a clear plastic capsule. The light is permitted to fall on one surface of the capsule and is focused on the PN junction with the help of focusing lens. The remaining sides of the capsule are pained black or enclosed in metallic case.
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
- 11 -
Fundamentals of Electronics (9051)
Experiment No. 2
Photo diode
Terminals
Functions In alarm system
Symbol
Anode
Cathode
In optical -communication In Counter system In character-recognition In encoder A K
Phototransistor : It is light sensitive transistor with three terminals Emitter, Base & Collector. It is usually connected in common emitter configuration with base open. The radiation is concentrated on the region near collector junction.
Phototransistor
Terminals
Functions
Symbol
Emitter
Base
Punch card readers Collector Lighting controls in highways Level indication Relays
4.0 Learning Objectives :
Intellectual Skills : To discriminate the given components in three groups like photo sensitive, Low power & High power (Thyristor) components. To label each group and identify the different components in it. Motor Skills : Ability to observe the given components & identify their terminals. Ability to list the components with their ratings, specification, referring data manuals. Ability draw the symbols for different electronic components in the group under observation.
5.0 Apparatus :
Components such as resistors, capacitors, inductors, diode, Zener diode transistor, UJT, FET, SCR, TRIAC & DIAC and photosensitive components like photo diode & phototransistor.
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
- 12 -
Fundamentals of Electronics (9051)
Experiment No. 2
6.0 Diagram :
Carbon resistor Diode Electrolytic capacitor
Zener diode
7.0 Stepwise Procedure :
1. Observe the given components. 2. Discriminate the components in three groups. 3. List the components of each group and draw their symbolic representation. 4. Note down the type, number, Specifications and ratings of the components.
8.0
Observations :
Sr. No 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12 13 Component Type Functions Symbol Rating/value Units
9.0
Questions :
Write answers to Q ----- Q ---- Q ---- Q -- Q -- (The question numbers to be alloted by teacher. 1. How to identify anode and cathode of diode from its physical appearance? 2. What is active devices? Give any four examples of it. 3. Draw the characteristics of zener diode in forward bias?
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
- 13 -
Fundamentals of Electronics (9051)
Experiment No. 2
4. Write the components which require external energy source for their operation. 5. FET is called field effect transistor, Explain ? 6. Draw the symbol of diode used for regulating voltage. 7. From the symbols shown below, identify the types of diodes. a) b)
8. Differentiate between SCR and Triac on the basis of terminals and function. 9. Why SCR is called unidirectional device? 10. Input circuit of FET is connected in reverse bias, Give the reason. 11. Write any four specifications of zener diode and BJT. 12. Write the name of component which have ability to store charge. 13 Write the name of device which has in build diode and two resistors. 14. Why UJT is called uni junction transistor. 15. In what respect LED is different form ordinary PN junction diode ? 16. Name the different components of the following circuit
(Space for answers)
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
- 14 -
Fundamentals of Electronics (9051)
Experiment No. 2
_________________ Signature of teacher
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION - 15 -
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Advanced Data Structures Lab ManualDocumento65 pagineAdvanced Data Structures Lab ManualsrisairampolyNessuna valutazione finora
- System On ModuleDocumento21 pagineSystem On ModulesrisairampolyNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuit Thoery Lab ManualDocumento57 pagineCircuit Thoery Lab ManualsrisairampolyNessuna valutazione finora
- DsaDocumento112 pagineDsadgbooklover0766571100% (3)
- ADVERTISINGDocumento25 pagineADVERTISINGsrisairampolyNessuna valutazione finora
- NetDocumento13 pagineNetsrisairampolyNessuna valutazione finora
- 14 Watermelon DayDocumento28 pagine14 Watermelon DaysrisairampolyNessuna valutazione finora
- Mentor CardPage2Documento1 paginaMentor CardPage2srisairampolyNessuna valutazione finora
- V SEMESTER Appeared in Month: YearDocumento1 paginaV SEMESTER Appeared in Month: YearsrisairampolyNessuna valutazione finora
- Simultaneous Fusion, Compression, and Encryption of Multiple ImagesDocumento7 pagineSimultaneous Fusion, Compression, and Encryption of Multiple ImagessrisairampolyNessuna valutazione finora
- Information Entropy Measure For Evaluation of Image Quality: Du-Yih Tsai, Yongbum Lee, and Eri MatsuyamaDocumento10 pagineInformation Entropy Measure For Evaluation of Image Quality: Du-Yih Tsai, Yongbum Lee, and Eri MatsuyamasrisairampolyNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Architecture NotesDocumento320 pagineComputer Architecture NotesgireeshkrNessuna valutazione finora
- Extra Curricular Activities Student RecordDocumento1 paginaExtra Curricular Activities Student RecordsrisairampolyNessuna valutazione finora
- S AesDocumento5 pagineS AessrisairampolyNessuna valutazione finora
- SathyaDocumento1 paginaSathyasrisairampolyNessuna valutazione finora
- Sequential Circuits-Class NotesDocumento41 pagineSequential Circuits-Class NotessrisairampolyNessuna valutazione finora
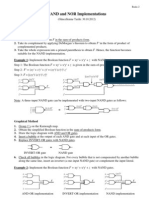
- NAND NOR ImplementationDocumento3 pagineNAND NOR Implementationsrisairampoly50% (2)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Analytica Chimica Acta: Kamil Strzelak, Agnieszka Czajkowska, Robert KonckiDocumento9 pagineAnalytica Chimica Acta: Kamil Strzelak, Agnieszka Czajkowska, Robert Konckibelqis ratuNessuna valutazione finora
- Standard Syllabus For ECEDocumento5 pagineStandard Syllabus For ECESeshu TadivakaNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Manual: Tester Lps04: DC Characteristics of Fiber Optic Leds, Pin Photodiode and PhototransistorDocumento17 pagineLaboratory Manual: Tester Lps04: DC Characteristics of Fiber Optic Leds, Pin Photodiode and Phototransistorramakris79Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ijarcc 79Documento3 pagineIjarcc 79MithunNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Sensors: Gaurav Sharma Electrical Engineering IEC University, BaddiDocumento17 pagineIntroduction To Sensors: Gaurav Sharma Electrical Engineering IEC University, BaddiPrabhjot SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Sensors: Presented by SYNAJIE JohnDocumento10 pagineSensors: Presented by SYNAJIE JohnLeKing KJNessuna valutazione finora
- Wireless Transmission of Telemetry Data Via Laser BeamDocumento4 pagineWireless Transmission of Telemetry Data Via Laser BeamBijay MaharjanNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Circuit SymbolsDocumento13 pagineElectronic Circuit SymbolsMerlin QuipaoNessuna valutazione finora
- PLC Controlled Automatic Bottle Filling SystemDocumento44 paginePLC Controlled Automatic Bottle Filling SystemSheryar ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- Seat Belt Tension SensorsDocumento5 pagineSeat Belt Tension SensorsAhamed Lebbe FaizNessuna valutazione finora
- Phototransistor-Ired Data BookDocumento72 paginePhototransistor-Ired Data BookvishunjeetNessuna valutazione finora
- Optoelectronics: Wave Nature of LightDocumento41 pagineOptoelectronics: Wave Nature of LightEbenezer AkpariboNessuna valutazione finora
- Optical Communication Project PDFDocumento34 pagineOptical Communication Project PDFge120120100% (1)
- Improved Bit Error Rate Evaluation For Optically Pre-Amplified Free-Space Optical Communication Systems in Turbulent AtmosphereDocumento8 pagineImproved Bit Error Rate Evaluation For Optically Pre-Amplified Free-Space Optical Communication Systems in Turbulent AtmosphereAbisayo AladelobaNessuna valutazione finora
- Photodetector Operation TypesDocumento15 paginePhotodetector Operation TypesKhyati ZalawadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2. Basic Sensors and Principles: 2.1 Displacement MeasurementsDocumento26 pagineChapter 2. Basic Sensors and Principles: 2.1 Displacement MeasurementsIlavarasan TamizhNessuna valutazione finora
- Position SensorsDocumento24 paginePosition SensorsTadese AtomssaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mellesgriot Photodiode 3Documento1 paginaMellesgriot Photodiode 3norbertscribdNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics of Semiconductors DevicesDocumento33 paginePhysics of Semiconductors DevicesKwesiam SamNessuna valutazione finora
- Special Purpose DiodesDocumento90 pagineSpecial Purpose DiodesRafi Rebal ShaikNessuna valutazione finora
- FL3H7CDocumento5 pagineFL3H7CHoàngTrầnNessuna valutazione finora
- Line Follower Robot Using ArduinoDocumento13 pagineLine Follower Robot Using Arduinolizhi2012Nessuna valutazione finora
- Visible Light Communication (VLC)Documento35 pagineVisible Light Communication (VLC)narasimhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ir Music Transmitter and Reciever Project ReportDocumento40 pagineIr Music Transmitter and Reciever Project ReportVaddi Vishwanath Kaushik100% (1)
- OG Operator Guide Advia 2120iDocumento470 pagineOG Operator Guide Advia 2120iEstie Kiriwenno100% (1)
- Vedantu Neet Ug Material Part 2Documento41 pagineVedantu Neet Ug Material Part 2PrateekNessuna valutazione finora
- Detector de Humo-Alk-V - 02-2014 PDFDocumento2 pagineDetector de Humo-Alk-V - 02-2014 PDFArthur Alexis Buitron DurandNessuna valutazione finora
- Color SensorDocumento14 pagineColor SensorNguyễn HiếuNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Sensors and Transducers (Carstens, 1993) BMKDocumento417 pagineElectrical Sensors and Transducers (Carstens, 1993) BMKRyan DuttNessuna valutazione finora
- Sanet - ST - Optical Fiber CommunicationsDocumento474 pagineSanet - ST - Optical Fiber Communicationskabi6713Nessuna valutazione finora