Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Ionisation Energies
Caricato da
stupid gurlzDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Ionisation Energies
Caricato da
stupid gurlzCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1.
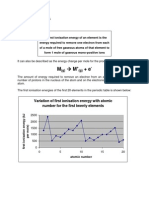
1 Exercise 4 ionisation energies
1. Why does the first ionisation energy of atoms generally increase across a period?
2. Why is the first ionisation energy of boron less than that of beryllium?
3. Why is the first ionisation energy of oxygen less than that of nitrogen?
4. Why do first ionisation energies decrease down a group?
5. Why does helium have the highest first ionisation energy of all the elements?
6. Why is the second ionisation energy of an atom always greater than the first?
7. Why is the second ionisation energy of sodium much greater than the first?
8. Why does atomic size decrease across a period?
9. Why does atomic size increase down a group?
10. Why are cations always smaller than the corresponding atoms?
11. Why are anions always larger than the corresponding atoms?
1.1 Exercise 4
1.
Number of protons increases, shielding stays the same, so attraction of outer electrons to nucleus
increases
2.
Outermost electron in B is 2p, outermost electron in Be is 2s, 2p electron in B better shielded than 2s
electron in Be, so it is less attracted to nucleus
3.
2p electron is paired in O but unpaired in N, so in O there is more repulsion in the orbital which
makes the electron easier to remove
4.
More shells, so more shielding, so attraction of outer electrons to the nucleus decreases
5.
No shielding in 1st period so electrons closely held than in other periods, and more protons than
hydrogen so greater attraction to nucleus
6.
Less electrons, so less electron repulsion
7.
1st electron removed from 3s, second electron removed from 2p so much less shielding
8.
Number of protons increases, shielding stays the same, so attraction of outer electrons to nucleus
increases and they move closer
9.
More shells, so more shielding, so attraction of outer electrons to the nucleus decreases and they are
pushed further away
10.
Less electrons, so less repulsion, so electrons can get closer to the nucleus
11.
More electrons, so more repulsion, so electrons are pushed further away
Mill Hill High School
6.
The values of the first ionisation energies of neon, sodium and magnesium are 2080,
494 and 736 kJ mol1, respectively.
(a)
Explain the meaning of the term first ionisation of an atom.
......................
......................
......................
(2)
(b)
Write an equation to illustrate the process occurring when the second ionisation
energy of magnesium is measured.
......................
......................
(2)
(c)
Explain why the value of the first ionisation energy of magnesium is higher than
that of sodium.
......................
......................
......................
(2)
(d)
Explain why the value of the first ionisation energy of neon is higher than that of
sodium.
......................
......................
......................
(2)
(Total 8 marks)
6.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
Enthalpy change/required when an electron is removed/knocked
out/displaced (Ignore minimum energy)
From a gaseous atom
(could get this mark from equation)
Mg+(g) Mg2+(g) + e
Equation
+
2+
Or Mg (g) + e Mg (g) + 2e State symbols (Tied to M1)
1
1
Increased/stronger nuclear charge or more protons
1
Smaller atom or electrons enter the same shell or same/similar shielding 1
Electron removed from a shell of lower energy or smaller atom or e nearer
nucleus or e removed from 2p rather than from 3s
Less shielding
(Do not accept e from inner shell)
[8]
Mill Hill High School
4.
(a)
Write equations to show the chemical processes which occur when the first and the second
ionisation energies of lithium are measured.
First ionisation energy equation .........................................................................
Second ionisation energy equation .....................................................................
(3)
(b)
(i)
Explain why helium has a much higher first ionisation energy than lithium.
...................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................
(ii)
Explain why beryllium has a higher first ionisation energy than boron.
...................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................
(iii)
Explain why the first ionisation energy of krypton is greater than the first ionisation
energy of bromine.
..............................................................................................................................
..............................................................................................................................
(iv)
Explain why the second ionisation energy of beryllium is greater than the first
ionisation energy.
...................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................
...................................................................................................................
(8)
(Total 11 marks)
4.
(a)
(b)
First ionisation energy equation
Li(g) Li+(g) + e (1)
Second ionisation energy equation
Li+(g) Li2+(g) e (1)
tate symbols (1)
(i)
Hes electron in 1s (1)
closer to nucleus (or no shielding) (1)
(or converse argument for Li)
(ii)
Bes outer electron in 2s (1)
lower in energy than 2p (1)
(iii)
more protons (1)
or increased nuclear charge
attracting electrons in the same {shell/orbital/subshell/energy level (1)
or similar shielding
(iv)
Electron removed from positive ion (1)
which attracts the electron more (1)
(allow for 2nd electron nearer to the nucleus)
8
[11]
Mill Hill High School
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Electrons in Atoms.Documento62 pagineElectrons in Atoms.Md.Tanjim reza TurjoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 111 Week Three Notes BDocumento7 pagineChem 111 Week Three Notes BnyachiosirNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionisation Energy Q& A SampleDocumento2 pagineIonisation Energy Q& A SampleShalu Princess DikshNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 13 Ionisation EnergiesDocumento6 pagine2 13 Ionisation EnergiesRobertLiu100% (2)
- Che Chapter 3Documento7 pagineChe Chapter 3lisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic Table and PeriodicityDocumento11 paginePeriodic Table and Periodicityakeemoluwadamilare623Nessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet BenzenaDocumento5 pagineWorksheet BenzenaRizky KurniawatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionisation EnergyDocumento6 pagineIonisation EnergyAathifa ThowfeekNessuna valutazione finora
- Patterns of First Ionisation Energies in The Periodic TableDocumento7 paginePatterns of First Ionisation Energies in The Periodic TableRugen RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionisation EnergyDocumento12 pagineIonisation Energyhahajing1980Nessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Chemistry Notes UNIT 4Documento9 pagineEngineering Chemistry Notes UNIT 4Nivetha ENessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Commonly Asked QuestionsDocumento28 pagineUnit 1 Commonly Asked Questionssofia begumNessuna valutazione finora
- Topic 1 - Atomic StructureDocumento4 pagineTopic 1 - Atomic Structurejulian maltoNessuna valutazione finora
- AS Level Summary-Unit 1Documento11 pagineAS Level Summary-Unit 1Filiz Kocayazgan ShanablehNessuna valutazione finora
- 11c Classification, Periodicity (Class Notes)Documento20 pagine11c Classification, Periodicity (Class Notes)RAJEEV KARAKOTINessuna valutazione finora
- A-Level Chemistry NotesDocumento10 pagineA-Level Chemistry NotesHannah Bryson-JonesNessuna valutazione finora
- HL Electron Configuration and The Periodic TableDocumento12 pagineHL Electron Configuration and The Periodic TableMarilee HuntNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionization Energy and Electron AffinityDocumento9 pagineIonization Energy and Electron AffinityKhan AaghaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Unit 1 Edexcel Notes (AS Level)Documento1 paginaChemistry Unit 1 Edexcel Notes (AS Level)--------100% (1)
- Ionisation Energy EdexcelDocumento5 pagineIonisation Energy EdexcelKevin The Chemistry Tutor100% (1)
- 08 Physics 11se Ch08Documento42 pagine08 Physics 11se Ch08pecan_lisa38Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3 2 Physical PropertiesDocumento4 pagine3 2 Physical PropertiesNguyenHoangMinhDucNessuna valutazione finora
- A - Level Inorganic Chemistry 2-1Documento171 pagineA - Level Inorganic Chemistry 2-1kitderoger_391648570Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ion EnergiesDocumento4 pagineIon EnergiesNamratha NairNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Objectives: Periodic TrendsDocumento9 pagineUnit Objectives: Periodic Trendsmartin mulengaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 - Atomic StructureDocumento9 pagineChapter 1 - Atomic Structureleonide357Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ionization EnergyDocumento69 pagineIonization EnergyVisalakshi Venkat100% (2)
- Chemistry Semester 1 Final Study Guide KeyDocumento7 pagineChemistry Semester 1 Final Study Guide Keyalexanderhdinh50% (2)
- Ionization EnergyDocumento8 pagineIonization EnergyHafiza Sikder AnishaNessuna valutazione finora
- AQA A Level Chemistry Unit 1 NotesDocumento17 pagineAQA A Level Chemistry Unit 1 NotesMuadh Chati100% (1)
- PeriodicityDocumento6 paginePeriodicityNetkoNessuna valutazione finora
- Electron Configuration and The Periodic PropertiesDocumento4 pagineElectron Configuration and The Periodic Propertiesapi-240883010Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 - Electrons in AtomsDocumento32 pagineChapter 2 - Electrons in AtomsFandyNessuna valutazione finora
- Amit Bikram Mishra - BSCH201Documento10 pagineAmit Bikram Mishra - BSCH201Amit Bikram MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ebenezer Matric .Hr. Sec. School: 1.what Is Ionization Energy?Documento3 pagineEbenezer Matric .Hr. Sec. School: 1.what Is Ionization Energy?r karthickNessuna valutazione finora
- Inorganic Chemistry NotesDocumento105 pagineInorganic Chemistry NotesOdongo TonnyNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of Elements & Periodic Table: Iind PartDocumento31 pagineClassification of Elements & Periodic Table: Iind PartKeshan PaudelNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem Topic 2 and 3Documento4 pagineChem Topic 2 and 3aliyaahsnahNessuna valutazione finora
- Ionisation Energy ClassDocumento13 pagineIonisation Energy ClassKordell McShineNessuna valutazione finora
- PeriodicTable and Trends DPDocumento109 paginePeriodicTable and Trends DPSurya NairNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Trends in The Periodic TableDocumento4 pagine5 Trends in The Periodic TableCris CorsinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 8 Atomic Structure - Notes...Documento7 pagineGrade 8 Atomic Structure - Notes...Antonita100% (1)
- Ionization Energy Trend in The Periodic TableDocumento3 pagineIonization Energy Trend in The Periodic TableOluwabamire OreoluwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 Periodic Table (SUEC) AnswerDocumento12 pagineChapter 3 Periodic Table (SUEC) AnswerLee AustinNessuna valutazione finora
- AtomsDocumento5 pagineAtomsjijigox479Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ionization Energy Cape Unit 1Documento21 pagineIonization Energy Cape Unit 1Shanice JohnsonNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento27 pagineUntitledFatimah AgboolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tanapp Tcm18-410hurDocumento5 pagineTanapp Tcm18-410hurNguh FabriceNessuna valutazione finora
- Classification of ElementsDocumento74 pagineClassification of ElementsJimit Patel BankNessuna valutazione finora
- Document From Michi?Documento55 pagineDocument From Michi?audrey abaasaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 - Structure of The AtomDocumento11 pagineChapter 4 - Structure of The AtomA.BensonNessuna valutazione finora
- 3.1.1 Periodicity: Classification of Elements in S, P, D BlocksDocumento5 pagine3.1.1 Periodicity: Classification of Elements in S, P, D BlocksstudierNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial Chapter 2 - AsnwDocumento6 pagineTutorial Chapter 2 - AsnwyvcgNessuna valutazione finora
- A Level Inorganic Chemistry NotesDocumento95 pagineA Level Inorganic Chemistry NotesnaluwairoericjohnNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem Inorganic A'levelDocumento95 pagineChem Inorganic A'levelAlvin HavinzNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1: Structure, Bonding and Main Group ChemistryDocumento7 pagineUnit 1: Structure, Bonding and Main Group ChemistryJosh ColeNessuna valutazione finora
- Is Nuclear Energy Safe? -Nuclear Energy and Fission - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksDa EverandIs Nuclear Energy Safe? -Nuclear Energy and Fission - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNessuna valutazione finora
- 5.periodicity - AnswersDocumento7 pagine5.periodicity - AnswersAnshu MovvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem Test RevisionDocumento10 pagineChem Test RevisionmaddieNessuna valutazione finora
- Hand-Out 1Documento5 pagineHand-Out 1Mae ZelNessuna valutazione finora
- Atomic StructureDocumento92 pagineAtomic StructureYuenHei KwokNessuna valutazione finora
- Merryland High School (Physics) PDFDocumento3 pagineMerryland High School (Physics) PDFVictor LusibaNessuna valutazione finora
- Skema Pemarkahan Kertas 2 Kimia ParwahDocumento9 pagineSkema Pemarkahan Kertas 2 Kimia ParwahJamuna RaniNessuna valutazione finora
- ZJC Longhorn Secondary Chemistry FORM 2Documento259 pagineZJC Longhorn Secondary Chemistry FORM 2takudzwa misileNessuna valutazione finora
- Jee M A PDFDocumento54 pagineJee M A PDFVarun UpadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- DOE-HDBK-1015 - 1-92 DOE Fundamentals Handb - Fundamentals HandbookDocumento262 pagineDOE-HDBK-1015 - 1-92 DOE Fundamentals Handb - Fundamentals HandbookjuanmoczoNessuna valutazione finora
- Solid State Physics PPT - Compatibility ModeDocumento124 pagineSolid State Physics PPT - Compatibility ModeBibhu Prasad SahooNessuna valutazione finora
- Grade 9 Chemistry Block PlanDocumento9 pagineGrade 9 Chemistry Block Planapi-354019245Nessuna valutazione finora
- Harold Searles The Nonhuman Environment in Normal Development and SchizophreniaDocumento463 pagineHarold Searles The Nonhuman Environment in Normal Development and Schizophreniaadam100% (11)
- Chap 4 SolutionsDocumento36 pagineChap 4 Solutions황인우Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3RD Quarter AssessmentsDocumento6 pagine3RD Quarter AssessmentsLorraine DonioNessuna valutazione finora
- Therapy Physics - Review - Part 1 PDFDocumento62 pagineTherapy Physics - Review - Part 1 PDFcarlosqueiroz7669100% (3)
- Living in The Environment 18th Edition Miller Solutions ManualDocumento35 pagineLiving in The Environment 18th Edition Miller Solutions Manualbombyciddispelidok100% (22)
- Dalton's Atomic TheoryDocumento7 pagineDalton's Atomic TheoryMhyr Pielago CambaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric Field and Potential (Etc.)Documento280 pagineElectric Field and Potential (Etc.)TudorNessuna valutazione finora
- Terms:: Lowest Energy Orbitals of Electrons of Electron CloudDocumento7 pagineTerms:: Lowest Energy Orbitals of Electrons of Electron CloudMineey Mo100% (1)
- 2ND Quarter Science ExamDocumento2 pagine2ND Quarter Science ExamTRANKZ100% (2)
- Lab Report PhysDocumento1 paginaLab Report Physcozyolo23Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physics of Plasma: Plasma and It's Different KindsDocumento15 paginePhysics of Plasma: Plasma and It's Different KindsToka ElnaggarNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre TestDocumento2 paginePre TestGhem EmeloNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic Table NotesDocumento8 paginePeriodic Table NotesThanabalan MunuswamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESODocumento6 pagineChemical Bond Physics and Chemistry ESOurgazuNessuna valutazione finora
- Color Encyclopedia of GemstonesDocumento332 pagineColor Encyclopedia of Gemstonesnecca00790% (31)
- Chemistry Notes For Students SECONDARY SDocumento70 pagineChemistry Notes For Students SECONDARY Skcgno72Nessuna valutazione finora
- Entertainment Computing: Harits Ar Rosyid, Matt Palmerlee, Ke ChenDocumento9 pagineEntertainment Computing: Harits Ar Rosyid, Matt Palmerlee, Ke ChenAlpyh ZahrohNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Sample Syllabus 4 Id 1029721v1 PDFDocumento20 pagineChemistry Sample Syllabus 4 Id 1029721v1 PDFWong Weng SiongNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Objectual PhilosophyDocumento284 pagineIntroduction To Objectual PhilosophyAurel RusuNessuna valutazione finora
- Final ReviewDocumento41 pagineFinal Reviewmr.dogbunzNessuna valutazione finora
- Tema 3. Chemical BondingDocumento68 pagineTema 3. Chemical Bondingkarthik tvkNessuna valutazione finora