Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Fact Sheet
Caricato da
hsrimediaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Fact Sheet
Caricato da
hsrimediaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
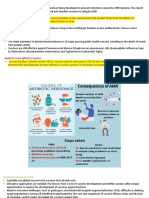
Antibiotic Resistance: Crisis of Thai Peoples Health Situations - Consequences- Measures Presented at the National Seminar on Antibiotic Resistance:
Crisis of Thai Peoples Health 28 - 29 May 2012, at Siam City Hotel, Bangkok, Thailand Antibiotic Resistance Situations Antibiotic resistant infections are emerging infectious diseases, which pose an increasing threat to human health around the world. The National Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance Center, Department of Medical Sciences, Ministry of Public Health reported that there has been a continuing increase of antibiotic resistance rates among many bacteria causing infections in humans. In Thailand, the important antibiotic resistant bacteria are Enterobacteriaceae (such as E.coli), Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumanni. The prevalence of antibiotic resistance among the aforementioned bacteria has been increasing. Acinetobacter baumannii is a major cause of hospital-acquired infections. Most of Acinetobacter baumannii isolates are resistant to carbapenems which are the most potent and the last option for therapy of infections caused by gram negative bacteria. Therefore, we need to return to use colistin which is an old antibiotic developed 50 years ago which is rather toxic agent. Consequences of Antibiotic Resistance The rapid emergence of antibiotic resistance is mainly due to the irrational use of antibiotics, particularly the excessive use of antibiotics in humans and nonhumans. According to the report on manufacture and import of medicines in 2009, it revealed that there was an excessive use of antibiotics among Thai people, accounting for more than 10,000 million baht. The top three most commonly used antibiotics manufactured and imported are penicillins, cephalosporins, and carbapenems. There are more than 100,000 Thai people infected with antibiotic resistant bacteria, 1 million days of extra hospital stay, and 30,000 deaths annually, leading to economic loss of more than 10,000 million baht, excluding losses due to premature deaths.
Measures for Antibiotic Resistance Major measures for containment of antibiotic resistance in Thailand are: 1. All health care facilities must implement strict infection control and prevention measures (such as hand hygiene, isolation precaution) especially for hospitalized patients. 2. All health care facilities must have antibiotic stewardship program to promote rational use of antibiotics. 3. The public should be aware of antibiotic resistance problems and avoid using unnecessary antibiotics especially for minor ailments such as common cold, diarrhea, simple fresh wound. 4. Limit dispensing of antibiotics at pharmacies. 5. Prohibition the use of antibiotics and chemicals either as antimicrobials or growth promoters in feedstuff. .
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Natural Alternatives to Antibiotics: How you can Supercharge Your Immune System and Fight InfectionDa EverandNatural Alternatives to Antibiotics: How you can Supercharge Your Immune System and Fight InfectionNessuna valutazione finora
- Central AcademyDocumento17 pagineCentral AcademyKartikey VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Treatment Issues In... : ENT InfectionsDocumento4 pagineTreatment Issues In... : ENT InfectionsmichaelqurtisNessuna valutazione finora
- Antibiotic StewardshipDocumento6 pagineAntibiotic Stewardshipkyliever100% (1)
- Current World Health DayDocumento8 pagineCurrent World Health DayCityMasterNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Description: Antibiotic ResistanceDocumento2 pagineProject Description: Antibiotic ResistanceVisha MainaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Impacts of Antibiotic ResistanceDocumento3 pagineImpacts of Antibiotic ResistanceSajid RahimNessuna valutazione finora
- Antimicrobial Resistance: 1. Theme For The Joint Programming InitiativeDocumento14 pagineAntimicrobial Resistance: 1. Theme For The Joint Programming InitiativeJimit JaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Use of Antibiotics 2017Documento17 pagineUse of Antibiotics 2017bernard.triciaNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are Antibiotics? How Do Antibiotics Work?Documento13 pagineWhat Are Antibiotics? How Do Antibiotics Work?HusnaaArdiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Overview On Mechanisms of Antibacterial Resistance: Alemayehu Toma, Serawit DeynoDocumento10 pagineOverview On Mechanisms of Antibacterial Resistance: Alemayehu Toma, Serawit DeynowaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry: Investigatory ProjectDocumento16 pagineChemistry: Investigatory ProjectkvNessuna valutazione finora
- About Antibiotic Resistance: What Is The Problem?Documento4 pagineAbout Antibiotic Resistance: What Is The Problem?Primelift Safety Resources LimitedNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review of Use of AntibioticsDocumento15 pagineA Review of Use of AntibioticsInternational Medical Publisher0% (1)
- Ntibiotic: AntibioticsDocumento14 pagineNtibiotic: AntibioticsVinayKumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Antibiotic PolicyDocumento35 pagineAntibiotic PolicyArpita Garg100% (2)
- The Role of Clinical Pharmacist in Combating Antibiotic ResistanceDocumento4 pagineThe Role of Clinical Pharmacist in Combating Antibiotic ResistanceAnto BijuNessuna valutazione finora
- Antibiotic Resistance: Key FactsDocumento5 pagineAntibiotic Resistance: Key Factssehyoun.fNessuna valutazione finora
- Argumentative Research EssayDocumento5 pagineArgumentative Research Essayckjennings6100% (1)
- What To Know About AntibioticsDocumento11 pagineWhat To Know About Antibioticsmuhammad aslam100% (1)
- AMR Hindu July 2022 Special EditionDocumento7 pagineAMR Hindu July 2022 Special EditionAditya KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Antibiotic Resistance: Audience-Senior Medical Officers Venue-Pune Date - 9 May 2011Documento42 pagineAntibiotic Resistance: Audience-Senior Medical Officers Venue-Pune Date - 9 May 2011J NuchinNessuna valutazione finora
- 1200-Article Text-3659-1-10-20220523Documento9 pagine1200-Article Text-3659-1-10-20220523mishbahNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 69: Odontogenic Infections Larry J. PetersonDocumento14 pagineChapter 69: Odontogenic Infections Larry J. PetersonAhmad EidNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento4 pagineUntitledMwamba MutaleNessuna valutazione finora
- 1-Intro. Antibiotic Oct 14th 2018-ModifiedDocumento23 pagine1-Intro. Antibiotic Oct 14th 2018-ModifiedLeena AlateeqNessuna valutazione finora
- Antibiotic Resistance and The Susceptibility of Bacteria LabDocumento19 pagineAntibiotic Resistance and The Susceptibility of Bacteria LabsciencystuffNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti Biotic WhoDocumento4 pagineAnti Biotic WhoWelfredo Jr YuNessuna valutazione finora
- Antibiotics EditedDocumento7 pagineAntibiotics EditedamnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecec 03 00052Documento4 pagineEcec 03 00052Matiyas ZewdeNessuna valutazione finora
- 7-Introduction To AntibioticsDocumento18 pagine7-Introduction To Antibioticssunny kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal of Infection and ChemotherapyDocumento13 pagineJournal of Infection and ChemotherapydrnguyenbvtkNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal Infectious DiseasesDocumento2 pagineJournal Infectious DiseasesPhoebeKatezPiedraCampasasNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnostic Microbiology in Antibiotic PolicyDocumento46 pagineDiagnostic Microbiology in Antibiotic Policytummalapalli venkateswara raoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sas Hes032 8Documento8 pagineSas Hes032 8Jose Melmar Autida AutenticoNessuna valutazione finora
- Prevention and ControlDocumento3 paginePrevention and ControlABHINASH BERIHANessuna valutazione finora
- Biofilms in Infection Prevention and Control: A Healthcare HandbookDa EverandBiofilms in Infection Prevention and Control: A Healthcare HandbookValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (1)
- Doubek Essay Antibiotic ResistanceDocumento1 paginaDoubek Essay Antibiotic ResistanceJirka DoubekNessuna valutazione finora
- What Are AntibioticsDocumento31 pagineWhat Are Antibiotics1211988610Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Project ReportDocumento15 pagineBiology Project ReportOmsai GarNessuna valutazione finora
- Science 24Documento3 pagineScience 24gabyvaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti Microbial ResistanceDocumento5 pagineAnti Microbial Resistanceprashanth naik naikNessuna valutazione finora
- The Treasure Called AntibioticsDocumento2 pagineThe Treasure Called AntibioticsBenamrane MarwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Moving Towards A Multisectoral Approach To Tackling Antimicrobial ResistanceDocumento2 pagineMoving Towards A Multisectoral Approach To Tackling Antimicrobial ResistancepikasNessuna valutazione finora
- By:Ruma Daniel Hendry Kyambogo University Bsc. Human Nutrition and Dietetics. (Yr Two) TEL: 0755514951/0786224870 EmailDocumento12 pagineBy:Ruma Daniel Hendry Kyambogo University Bsc. Human Nutrition and Dietetics. (Yr Two) TEL: 0755514951/0786224870 EmailRUMA DANIEL HENDRYNessuna valutazione finora
- Safe and Clean Care: Infection Prevention and Control for Health and Social Care StudentsDa EverandSafe and Clean Care: Infection Prevention and Control for Health and Social Care StudentsNessuna valutazione finora
- AMR Manual WHO Input (Optional)Documento18 pagineAMR Manual WHO Input (Optional)Saltuk KoçyiğitNessuna valutazione finora
- StewardshipDocumento19 pagineStewardshipJorge David LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- The Efficacy of Piper Betle Linn Against Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus and Vancomycin-Resistant EnterococcusDocumento21 pagineThe Efficacy of Piper Betle Linn Against Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus and Vancomycin-Resistant EnterococcusClaire GonoNessuna valutazione finora
- Antibiotics BrochureDocumento2 pagineAntibiotics Brochureidno1008Nessuna valutazione finora
- Amoxicillin: A Broad Spectrum Antibiotic: Review ArticleDocumento8 pagineAmoxicillin: A Broad Spectrum Antibiotic: Review ArticlebooksdiversNessuna valutazione finora
- The Myth of Antibiotics: Complete The Course' Won'T Stop Resistance, Researchers SayDocumento10 pagineThe Myth of Antibiotics: Complete The Course' Won'T Stop Resistance, Researchers SayMf FonsecaNessuna valutazione finora
- EsaiDocumento4 pagineEsaiismimasyithahNessuna valutazione finora
- Prophylactic Use of Anti-Microbial Agents: Presented By: Jagir R. Patel Assistant ProfessorDocumento18 pagineProphylactic Use of Anti-Microbial Agents: Presented By: Jagir R. Patel Assistant ProfessorJagirNessuna valutazione finora
- Dapus 2 8101-20729-3-PBDocumento10 pagineDapus 2 8101-20729-3-PBLidya DiandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Why Antibiotics Should Not Be OverusedDocumento10 pagineWhy Antibiotics Should Not Be Overusedoicfbd100% (3)
- AAW 2018 PowerPoint PresentationDocumento60 pagineAAW 2018 PowerPoint PresentationAgung RahmadaniNessuna valutazione finora
- E - Enterobacter Species: EskapDocumento2 pagineE - Enterobacter Species: EskapOscar Moisés López SanabioNessuna valutazione finora
- Vol 6 No 3Documento149 pagineVol 6 No 3hsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vol 6 No 3Documento149 pagineVol 6 No 3hsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal of Health Systems ResearchDocumento169 pagineJournal of Health Systems ResearchhsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal of Health Systems ResearchDocumento169 pagineJournal of Health Systems ResearchhsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vol 6 No 3Documento149 pagineVol 6 No 3hsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vol 6 No 4Documento156 pagineVol 6 No 4hsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal of Health Systems ResearchDocumento169 pagineJournal of Health Systems ResearchhsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal of Health Systems ResearchDocumento169 pagineJournal of Health Systems ResearchhsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vol 6 No 1Documento140 pagineVol 6 No 1hsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vol 6 No 1Documento140 pagineVol 6 No 1hsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fact SheetDocumento2 pagineFact SheethsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vol 6 No 1Documento140 pagineVol 6 No 1hsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fact SheetDocumento2 pagineFact SheethsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- THailand UCS Achievement and ChallengesDocumento124 pagineTHailand UCS Achievement and ChallengeshsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vol 5 No 4Documento187 pagineVol 5 No 4hsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vol 6 No 1Documento140 pagineVol 6 No 1hsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Publish 2011Documento41 paginePublish 2011hsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Published Researches in The Year 2010Documento16 paginePublished Researches in The Year 2010hsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- UniversalDocumento114 pagineUniversalhsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- THailand UCS Achievement and ChallengesDocumento124 pagineTHailand UCS Achievement and ChallengeshsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Published Researches in The Year 2009Documento17 paginePublished Researches in The Year 2009hsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vol 5 No 4Documento187 pagineVol 5 No 4hsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Published Researches in The Year 2009Documento17 paginePublished Researches in The Year 2009hsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vol 5 No 4Documento187 pagineVol 5 No 4hsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Published Research 4Documento3 paginePublished Research 4hsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Title: Health Equity and Human Rights of The Stateless Hill Tribes in ThailandDocumento9 pagineTitle: Health Equity and Human Rights of The Stateless Hill Tribes in ThailandhsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- UniversalDocumento114 pagineUniversalhsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- UniversalDocumento114 pagineUniversalhsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Title: Health Equity and Human Rights of The Stateless Hill Tribes in ThailandDocumento9 pagineTitle: Health Equity and Human Rights of The Stateless Hill Tribes in ThailandhsrimediaNessuna valutazione finora