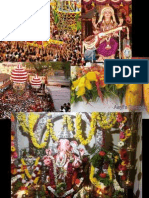Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Diwali
Caricato da
Pankaj AroraDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Diwali
Caricato da
Pankaj AroraCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Diwali, or Deepavali, is one of the biggest Indian festivals and also a major occassion in Nepal.
The festival has great religioussignificance for Hindus, Sikhs, Jains and the Nepalese. In India, Diwali is now considered to be more of a national festival, and is enjoyed by most Indians regardless of faith. Diwali is known as the "Festival of
Lights". This is probably because of the manner in which it is observed. The festival is traditionally celebrated with activities like bursting crackers, lighting rows of candles and diyas (earthen lamps) around individual homes, holding dazzling fireworks display and igniting colourful sparklers.
It is commonly celebrated by decorating homes with lamps and candles,bursting of firecrackers and sparklers, eating sweets and other mouthwatering dishes, praying to Gods and Goddesses, observing religious rituals, wearing new dresses and sending wishes and gifts to one another.
Though the number of days of the celebration of the festival differ with different communities, the actual days of observance of Diwali are common and fall on exactly the same set of days across Nepal and India. Going by the Gregorian calendar, Diwali in India is observed generally in the months of October or November. The festival comes exactly twenty days after Dussehra, another sacred Hindu occassion, and is celebrated for five consecutive days at the end of Hindu month of Ashvin. Diwali is on 5th November, 2010 and 26th October, 2011.
History of diwali
It is since ancient times that Diwali has been celebrated. It is not easy to say now what really was the reason behind its origin. Different people believe different events to be the cause behind this festival. Here are ten mythical and historical reasons that are possibly behind the Diwali (Deepavali) celebrations. The most well known story behind Diwali is in the Ramayana, the great Hindu epic. According to Ramayana, Rama, the prince of Ayodhya was ordered by his father, King Dasharatha, to go away from his country and come back after living in the forest for fourteen years. So Rama went on exile with his devoted wife Sita and faithful brother, Lakshmana. When Ravana, the demon king of Lanka abducted Sita and took her away to his island kingdom of Lanka, Rama fought against and killed Ravana. He rescued Sita and returned to Ayodhya after fourteen years. The people of Ayodhya were very happy to hear of their beloved prince's homecoming. To celebrate Rama's return to Ayodhya, they lit up their houses with earthen lamps (diyas), burst crackers and decorated the entire city in the grandest manner. This is believed to have started the tradition of Diwali. Year after year this homecoming of Lord Rama is commemorated on Diwali with lights, fireworks, bursting of crackers and merriment. The festival gets its name Deepawali, or Diwali, from the rows (avali) of lamps (deepa) that the people of Ayodhya lit to welcome their King. Another well known story related to Diwali history is narrated in the other Hindu epic, Mahabharata. Mahabharata reveals to us how the five royal brothers, the Pandavas, suffered a defeat in the hands of their brothers, the Kauravas, in a game of dice (gambling). As a rule imposed on them, the Pandavas had to serve a term of 13 years in exile. When the period was over, they returned to their birthplace Hastinapura on Kartik Amavashya (the new moon day of the Kartik month). The five Pandava brothers, their mother and their wife Draupadi were honest, kind, gentle and caring in their ways and were loved by all their subjects. To celebrate the joyous occassion of their return to Hastinapura and to welcome back the Pandavas, the common people illuminated their state by lighting bright earthen lamps everywhere. The tradition is believed to have been kept alive through the festival of Diwali, which many believe, is held in remembrance of the Pandava brothers' homecoming. It is also believed that on this very Diwali day, the Goddess of wealth, Lakshmi rose up from the ocean. The Hindu scriptures tell us that long long ago both Devas (gods) and Asuras (demons) were mortal. They had to die sometime or other, like us. But they wanted to live forever. So they churned the ocean to seek Amrita, the nectar of immortality (an event mentioned in the Hindu scriptures as "Samudra-manthan"), during which many divine objects came up. Prime among these was Goddess Lakshmi, the daughter of the king of the milky ocean, who arose on the new moon day (amaavasyaa) of the Kartik month. That very night, Lord Vishnu married her. Brilliant lamps were illuminated and placed in rows to mark this holy occassion. This event is supposed to have given rise to an annual celebration at the same time each year. Even today, Hindus celebrate the birth of the goddess Lakshmi and her marriage to Lord Vishnu on Diwali and seek her blessings for the coming year. The origin of Diwali also refers to the stories narrated in the Hindu Puranas, the primary source of Hindu religious texts.According to the Bhagavata Purana (the most sacred Hindu text), it was on a Kartik day that Lord Vishnu, took on the form of a dwarf (Vaman-avtaara) and defeated King Bali. Bali, or rather King Mahabali, was a powerful demon king who ruled the earth. Once Bali got a boon from Lord Brahma that made him unconquerable. Even gods failed to defeat him in battles. Although a wise and good king otherwise, Mahabali was cruel to the Devas (gods). Finding no way to defeat Bali, the Devas went to Lord Vishnu and insisted him to find a way to stop Bali. Lord Vishnu made a plan. He disguised himself as a short Brahmin and approached Bali for some charity. A largehearted king, Mahabali tried to help the Brahmin. But the whole thing was a trick by Lord Vishnu and ultimately the King had to give up all his kingship and wealth. Diwali celebrates this defeating of Mahabali by Lord Vishnu. The Bhagavata Purana also tells us about Narakasura, an evil demon king who somehow got great powers and conquered both the heavens and earth. Narakasura was very cruel and was a terrible ruler. It is believed that Lord Vishnu killed Narakasura on the day before Diwali and rescued many women whom the demon had locked in his palace. The people of heaven and earth were greatly relieved to have got freedom from the hands of the terrible Narakasura. They celebrated the occassion with muchgrandeur, a tradition that is believed to be alive through the annual observance of Diwali. According to another legend, long ago after the gods lost in a battle with the demons, Goddess Kali took birth from the forehead of Goddess Durga to save heaven and earth from the growing cruelty of the demons. After killing all the devils, Kali lost her control and started killing anyone who came her way which stopped only when Lord Shiva intervened. You all must have seen the well-known picture of Ma Kali, with her tongue hanging out? That actually depicts the moment when she steps on Lord Shiva and stops in horror and repentance. This memorable event has been commemorated ever since by celebrating Kali Puja, which is observed in several parts of India in about the same time as Diwali. Historically it is believed that on a Diwali day in 56 BC King Vikramaditya, the legendary Hindu king of India famed for his wisdom, bravery and large-heartedness, was crowned and declared to be a king. This was marked by a grand celebration by the citizens of Vikramaditya's kingdom celebrated the coronation of their king by lighting up small earthen lamps and that custom still prevails. Many people and even some historians say that this event gave rise to the annual observance of Diwali. Diwali also marks the sacred occasion when on a new moon day of Kartik (Diwali day) Swami Dayananda Saraswati, one of the greatest reformers of Hinduism attained his nirvana (enlightenment) and became 'Maharshi' Dayananda, meaning the great sage Dayananda. In 1875, Maharshi Dayananda founded the Arya Samaj, "Society of Nobles", a Hindu reform movement to purify Hinduism of the many evils it became associated with at that era. Every Diwali, this great reformer is remembered by
Hindus all over India. For Jains, Diwali commemorates the enlightenment of Vardhamana Mahavira(the twenty-fourth and last Tirthankaras of the Jains and the founder of modern Jainism) which is said to have occurred on Oct. 15, 527 B.C. This is one more reason to engage in Diwali celebrations for pious Jains and other than the purpose of commemoration, the festival stands for the celebration of the emancipation of human spirit from earthly desires. For Sikhs, Diwali holds a special significance for it was on a Diwali day that the third Sikh Guru Amar Das institutionalized the festival of lights as an occasion when all Sikhs would gather to receive the Gurus blessings. It was also on a Diwali day in 1619 that their sixth religious leader, Guru Hargobind Ji, who was held by the Mughal Emperor Jahengir in the Gwalior fort, was freed from imprisonment along with 52 Hindu Kings (political prisoners) whom he had arranged to be released as well. And it was also on the same auspicious occasion of Diwali when the foundation stone of the Golden Temple at Amritsar was laid in 1577.
Crackers
Crackers hold a fascination for both young and old alike. Despite a growing anti-cracker campaign, there is no dip in its popularity. When the rocket flies high and burst opens into an umbrella of colourful embers, people from the ground watch this spectacular in awe, the beauty raining down towards them. The children quickly light up a fire wheel which dances on the floor, just as a couple of noisy bombs go off in the background. Every year Diwali arrive in all its sound and sparkle. Each year on the dark night of Diwali, Crackers of varied colors and sounds fill the skies heralding India's favourite festival. Diwali or Deepavali in Sanskrit means "a row of lamps" and fireworks have become a major part of Diwali celebrations. They form a big part of the Diwali budget in households. Firecrackers come in different varieties from the delightfully visual ones to the ear deafening noisy ones. Tradition says that the illumination of homes with lights and the skies with firecrackers is an expression of obeisance to the heavens for the attainment of health, wealth, knowledge, peace and prosperity. Another possible reason and a more scientific one for lighting firecrackers is that the fumes produced by them kill insects and mosquitoes found aplenty after the rains. The standard varieties of firecrackers include the mild flower pots, the electric crackers, the popular ground wheel (commonly called as charka), the high flying rockets, the favourite sparklers and of course the explosive and ear deafening bombs. The colourful twin angles, a new entrant in the cracker market has caught the fancy of many customers. A combination of all the above makes an exclusive festive package which delights young and old alike. Diwali symbolising the triumph of the good over evil continues to be grandiose in spirit and celebrated throughout the country. Firecrackers add to the festivities and as the rows of lamps glow one can hear the crackers go off and see the sparklers being waved by children and adults alike.
In all, I we say that Deepavali is the brightest festival to be celebrated in India. The delicious food associated with the feast makes us feel that this festival must come more often in a year.
"Sabh mil mangal gao re, Sabh mil deep jalao re, Avadh me Ram aaye hai...!"
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Jyotish - The Mystery of Rahu in HoroscopeDocumento161 pagineJyotish - The Mystery of Rahu in Horoscopedayanidhi98% (40)
- Predictive-Astrology by BVB PDFDocumento306 paginePredictive-Astrology by BVB PDFMadhavaKrishna100% (1)
- Mantras of KuberaDocumento1 paginaMantras of KuberasastrologyNessuna valutazione finora
- SaivamDocumento90 pagineSaivamPavan Varma V100% (2)
- Slokas of Lord Shiva With Their MeaningsDocumento6 pagineSlokas of Lord Shiva With Their MeaningsDeepa H100% (8)
- Vishnu AvatarsDocumento116 pagineVishnu AvatarsGaneshru100% (2)
- Stories From Thiruvilaiyadal PuranamDocumento60 pagineStories From Thiruvilaiyadal Puranamsivanands77% (13)
- Mahadev by Narayanan Renuka PDFDocumento105 pagineMahadev by Narayanan Renuka PDFSuryaprakashNessuna valutazione finora
- 15 - Chapter 8 PDFDocumento38 pagine15 - Chapter 8 PDFBunty Mayekar100% (1)
- Diwali FestivalDocumento12 pagineDiwali Festivalapi-204086002Nessuna valutazione finora
- Menaka #039 S Choice - Kavita KaneDocumento173 pagineMenaka #039 S Choice - Kavita Kanepoorvi80% (5)
- Thaipusam 2018Documento21 pagineThaipusam 2018Sivam KrishnanNessuna valutazione finora
- Essence of SkandaDocumento101 pagineEssence of Skandahariharv50% (2)
- Holi FestivalDocumento8 pagineHoli FestivalMayra rosas salazarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ketu and Its Forms (4 PGS)Documento4 pagineKetu and Its Forms (4 PGS)simonloongNessuna valutazione finora
- Mys Dasara PDFDocumento2 pagineMys Dasara PDFmsulgadleNessuna valutazione finora
- Ujjain's Ancient Mahakali Temple and the Legend of King VikramadityaDocumento13 pagineUjjain's Ancient Mahakali Temple and the Legend of King Vikramadityaexpertjatak0% (1)
- Murugan Worship in SkandapuranamDocumento15 pagineMurugan Worship in SkandapuranamShanmugam Piramanayagam100% (1)
- Study On Kumbh Mela AllahabadDocumento81 pagineStudy On Kumbh Mela Allahabadneelfearless75% (8)
- Yathiraja SaptatiDocumento291 pagineYathiraja Saptatiajiva_rts100% (3)
- WW May Hari Raya Puasa Activity Sheet - 230511 - 181540Documento10 pagineWW May Hari Raya Puasa Activity Sheet - 230511 - 181540David LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Prepositions Consolidated (Vetrumai Urubu)Documento23 paginePrepositions Consolidated (Vetrumai Urubu)Nidhi ShriyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Festivals of India - A Guide to Celebrations Across RegionsDocumento25 pagineFestivals of India - A Guide to Celebrations Across RegionsjtikyaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Dhanvantari EmpowermentmanualDocumento5 pagineDhanvantari EmpowermentmanualAditya Narain MullaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hindu Wedding Ceremony GuideDocumento3 pagineHindu Wedding Ceremony Guidekuldip1951Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bharatnatyam DanceDocumento2 pagineBharatnatyam DanceRahul KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- An Essay On Diwali - Deepawali The Festival of Lights - Stories PubDocumento4 pagineAn Essay On Diwali - Deepawali The Festival of Lights - Stories PubNachu edamNessuna valutazione finora
- DiwaliDocumento22 pagineDiwaliUmageswari MohanNessuna valutazione finora
- Kanu PidiDocumento6 pagineKanu PidiT Sampath KumaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Celebrate Dussehra FestivalDocumento4 pagineCelebrate Dussehra FestivalMeghna PorwalNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Ravana Temples in IndiaDocumento3 pagine6 Ravana Temples in IndiaSuryajeeva SuresNessuna valutazione finora
- Devi Karumari AmmanDocumento5 pagineDevi Karumari AmmanbulbtommyNessuna valutazione finora
- Holi: The Festival of Colours: (By-Satya Mahapatra)Documento4 pagineHoli: The Festival of Colours: (By-Satya Mahapatra)satya mahapatraNessuna valutazione finora
- Tamil TranslationDocumento3 pagineTamil TranslationKamali KannanNessuna valutazione finora
- PUJA and ViVARANADocumento49 paginePUJA and ViVARANAKurumeti Naga Surya Lakshmana KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Namostute Namostute - Ma Durga PrayerDocumento1 paginaNamostute Namostute - Ma Durga PrayerAlok Kumar100% (1)
- South Indian Villages FinalDocumento17 pagineSouth Indian Villages FinalRichard ClarkeNessuna valutazione finora
- DeepawaliDocumento28 pagineDeepawaliNicholas FrazierNessuna valutazione finora
- Diwali Festival Traditions and SignificanceDocumento3 pagineDiwali Festival Traditions and SignificanceSushil Khatwani100% (1)
- 64 Kalas: Udaka VadyaDocumento2 pagine64 Kalas: Udaka VadyaShreyash JayewarNessuna valutazione finora
- Srilasri Swaprakasananda Theertha Avadhootha (Gurugaru)Documento2 pagineSrilasri Swaprakasananda Theertha Avadhootha (Gurugaru)RB joshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Upanyasam Compilation Final Dushyant Sridhar SwamiDocumento47 pagineUpanyasam Compilation Final Dushyant Sridhar SwamisgganeshinNessuna valutazione finora
- PDF Book 1Documento127 paginePDF Book 1Shree Krishna0% (1)
- Festivals of IndiaDocumento4 pagineFestivals of Indiaamol Akolkar ( amolpc86)Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Cult to Salvage Mankind: The Jagannath Cult of Orissa Reflects Joy and CelebrationDocumento167 pagineA Cult to Salvage Mankind: The Jagannath Cult of Orissa Reflects Joy and CelebrationRoderick2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Being A GSBDocumento5 pagineBeing A GSBuvkini100% (1)
- The Color Rituals of RajasthanDocumento4 pagineThe Color Rituals of RajasthanTanisha VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Representation of Fauna in Indian Jewellery: Dr. Gomathi Gowda & G. Lenin BabuDocumento6 pagineRepresentation of Fauna in Indian Jewellery: Dr. Gomathi Gowda & G. Lenin BabuTJPRC PublicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Lord Kubera & Goddess Mahalakshmi MantraDocumento1 paginaLord Kubera & Goddess Mahalakshmi MantraHarsh ChadhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ezhur Chetty and Caste System in IndiaDocumento70 pagineEzhur Chetty and Caste System in IndiaSShaNessuna valutazione finora
- Classical DanceDocumento16 pagineClassical Danceরজতশুভ্র করNessuna valutazione finora
- Goa Folk DancesDocumento3 pagineGoa Folk DancesSallyCabsNessuna valutazione finora
- Astamatricka Dance of PatanDocumento29 pagineAstamatricka Dance of PatanMin Bahadur shakya100% (1)
- Cult Mah PDFDocumento83 pagineCult Mah PDFjoy parimalaNessuna valutazione finora
- BharatanatyamDocumento9 pagineBharatanatyamPushpa B SridharanNessuna valutazione finora
- GarbaDocumento2 pagineGarbaBrajesh SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Janakpurdham The Ancient MithilaDocumento24 pagineJanakpurdham The Ancient MithilaLordgrg Ghotane100% (1)
- Worksheet Culture in MalaysiaDocumento1 paginaWorksheet Culture in MalaysiashahrizazillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Abishegam Substances Benefits GodsDocumento2 pagineAbishegam Substances Benefits GodsGomatam Hari PriyaNessuna valutazione finora
- NaimisharanyaDocumento5 pagineNaimisharanyaT M Santhosh Kumar100% (1)
- Alagar Koil Temple & Mandooga Maharishi FestivalDocumento7 pagineAlagar Koil Temple & Mandooga Maharishi FestivalsathyarNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian HauntingDocumento81 pagineIndian HauntingVivek AnandNessuna valutazione finora
- The Sabar Tradition in Shri Jagannath CultureDocumento3 pagineThe Sabar Tradition in Shri Jagannath CulturemanNessuna valutazione finora
- 13 Chapter 4Documento42 pagine13 Chapter 4indrani royNessuna valutazione finora
- Angala Parameshwari MaaDocumento3 pagineAngala Parameshwari MaasharathVEMNessuna valutazione finora
- Thirugnanasambandar - Panuval Pathigam - Thiru Nedungalam - 1Documento13 pagineThirugnanasambandar - Panuval Pathigam - Thiru Nedungalam - 1krishvidhya2000100% (5)
- Different Food Habits in Different Festivals in KarnatakaDocumento4 pagineDifferent Food Habits in Different Festivals in KarnatakanayanNessuna valutazione finora
- 108 Names of MahalaxmiDocumento3 pagine108 Names of MahalaxmiBalrajGoulikarNessuna valutazione finora
- Temple FestivesDocumento66 pagineTemple FestivesVan MathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Dikshitar's Navagraha kritis: Angaraka kriti analysis and translationDocumento16 pagineDikshitar's Navagraha kritis: Angaraka kriti analysis and translationSrinivaas GanesanNessuna valutazione finora
- Sikh Festival DiwaliDocumento2 pagineSikh Festival DiwaliPoorvKumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Diwali Festival of Lights ExplainedDocumento22 pagineDiwali Festival of Lights ExplainedArxhenta ÇupiNessuna valutazione finora
- History of Diwali: Deepavali Indian Festivals Significance A NationalDocumento2 pagineHistory of Diwali: Deepavali Indian Festivals Significance A NationalPankaj AroraNessuna valutazione finora
- About IITDocumento9 pagineAbout IITPankaj AroraNessuna valutazione finora
- About IITDocumento9 pagineAbout IITPankaj AroraNessuna valutazione finora
- ISEET Syllabus 2013 For Main and Advance ExamsDocumento2 pagineISEET Syllabus 2013 For Main and Advance ExamsPankaj AroraNessuna valutazione finora
- Kalidasar's VaraMangalashtakamDocumento4 pagineKalidasar's VaraMangalashtakambhagavathi.muruganpillai6851Nessuna valutazione finora
- Srimad BhagavataDocumento64 pagineSrimad BhagavataRasakali SatyapujariNessuna valutazione finora
- Lakshmi - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento5 pagineLakshmi - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaymadhukumarNessuna valutazione finora
- LifcoZine - Volume 1 Issue 2Documento15 pagineLifcoZine - Volume 1 Issue 2lifcobooksNessuna valutazione finora
- POWER As AMRIT in The Eternal Struggle Between Hinduism and Buddhism in CambodiaDocumento17 paginePOWER As AMRIT in The Eternal Struggle Between Hinduism and Buddhism in CambodiaudayNessuna valutazione finora
- Kumbh Mela: Mass Hindu Pilgrimage Where Millions Bathe in Holy RiversDocumento10 pagineKumbh Mela: Mass Hindu Pilgrimage Where Millions Bathe in Holy RiversKoushik DebNessuna valutazione finora
- Mahashivrathri - KSDocumento17 pagineMahashivrathri - KSSeshadrinathNessuna valutazione finora
- Churning of The OceanDocumento1 paginaChurning of The OceanDay FriendsNessuna valutazione finora
- Indian ManagementDocumento4 pagineIndian Managementkitty1969Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kumbh MelaDocumento6 pagineKumbh MelaShan PrabhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Raam Naam - The Only Solution to World ProblemsDocumento17 pagineRaam Naam - The Only Solution to World ProblemsreenaashuNessuna valutazione finora
- Who Is The Strong-Armed Monkey Who Chur PDFDocumento26 pagineWho Is The Strong-Armed Monkey Who Chur PDFSovannrath VarNessuna valutazione finora
- Anurag Sagar GenesisDocumento40 pagineAnurag Sagar GenesiscpbhatnagarNessuna valutazione finora
- Matsya Kurma Varaha Narasimha Vamana Parashurama: Go To TopDocumento6 pagineMatsya Kurma Varaha Narasimha Vamana Parashurama: Go To TopNARENDRA KUMARNessuna valutazione finora
- Padma Purana Vol 07 Uttara KhandaDocumento392 paginePadma Purana Vol 07 Uttara KhandaMantas Jey100% (1)
- Lessons From Samudra Manthan Lila - 1Documento2 pagineLessons From Samudra Manthan Lila - 1Leena PurohitNessuna valutazione finora
- Symbolism of Samudra Manthan (Churning of The Ocean)Documento1 paginaSymbolism of Samudra Manthan (Churning of The Ocean)Pablo PalaciosNessuna valutazione finora
- ThiruvellaraiDocumento36 pagineThiruvellaraiajiva_rtsNessuna valutazione finora