Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
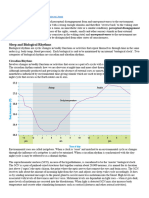
Rest and Sleep
Caricato da
Jastine Diaz0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
47 visualizzazioni2 paginePhysiology of sleep biorhythms(rhythmic biologic clocks) in humans these are controlled from w / in the body and synchronized with environmental factors: light and darkness, gravity, and electromagnetic stimuli. 2 Types of Sleep: 1. NREM Sleepis also referred to as slowwave sleep because the brain waves of a sleeper are slower than those of a person who is awake. Stage IIIdomination of the parasympathetic nervous system causes: -Heart and respiratory rates
Descrizione originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online da Scribd
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoPhysiology of sleep biorhythms(rhythmic biologic clocks) in humans these are controlled from w / in the body and synchronized with environmental factors: light and darkness, gravity, and electromagnetic stimuli. 2 Types of Sleep: 1. NREM Sleepis also referred to as slowwave sleep because the brain waves of a sleeper are slower than those of a person who is awake. Stage IIIdomination of the parasympathetic nervous system causes: -Heart and respiratory rates
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
0 valutazioniIl 0% ha trovato utile questo documento (0 voti)
47 visualizzazioni2 pagineRest and Sleep
Caricato da
Jastine DiazPhysiology of sleep biorhythms(rhythmic biologic clocks) in humans these are controlled from w / in the body and synchronized with environmental factors: light and darkness, gravity, and electromagnetic stimuli. 2 Types of Sleep: 1. NREM Sleepis also referred to as slowwave sleep because the brain waves of a sleeper are slower than those of a person who is awake. Stage IIIdomination of the parasympathetic nervous system causes: -Heart and respiratory rates
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formati disponibili
Scarica in formato DOCX, PDF, TXT o leggi online su Scribd
Sei sulla pagina 1di 2
REST AND SLEEP and is deep, restful sleep & brings a
decrease in physiologic functions.
Rest- implies calmness, relaxation w/out 4 Stages:
emotional stress, & freedom from anxiety. Stage I- very light sleep.
Sleep- an altered state of consciousness in w/c -The person feels drowsy & relaxed
the individual’s perception of & reaction to the - Eyes roll from side to side
environment are decreased. -Heart & respiratory rates drop slightly
-Lasts only a few minutes
Physiology of Sleep Stage II- light deep during w/c body
processes continue to slow down.
Biorhythms- (rhythmic biologic clocks) in
-Eyes are generally still
humans these are controlled from w/in the
-Heart &respiratory rate decrease
body and synchronized w/ environmental
slightly
factors: light & darkness, gravity, &
-Body temperature falls
electromagnetic stimuli.
-Lasts about 10-15 minutes but
Circadian Rhythm- the most familiar biorhythm. constitutes 40%-45% of total sleep.
From Latin circa dies, meaning “about a day.” Stage III- domination of the
parasympathetic nervous system
Circadian Synchronization- when a person’s causes:
biologic clock coincides w/ sleep wake patterns -Heart & respiratory rates & others slow
–the person is awake when the physiologic & further
psychologic rhythms are most inactive. -Sleepers become more difficult to
arouse
Circadian regularity: begins by the third week
-Person is not disturbed by sensory
of life & may be inherited.
stimuli
After 4 months of age: infants enter a 24- hour -Skeletal muscles are very relaxed
cycle (sleep mostly during the night) -Reflexes are diminished
-Snoring may occur
End of 5th/ 6th month: infants sleep wake Stage IV- signals deep sleep, called
patterns are almost like those of adults. delta sleep.
-sleeper’s heart &respiratory rates drop
Stages of Sleep
20%-30% below those exhibited during
Electroencephalogram (EEG)- provides a good waking hours.
picture of what occurs during sleep. -sleeper is very relaxed, rarely moves,
difficult to arouse.
2 Types of Sleep: -eyes usually roll, some dreaming
occurs.
1. NREM Sleep- is also referred to as slow-
wave sleep because the brain waves of 2. REM Sleep- recurs about every 90
a sleeper are slower than the alpha minutes & lasts 5-30 minutes.
&beta waves of a person who is -Dreams take place and remembered,
awake/alert. It’s a sleep during a night, they are consolidated in the memory.
-Brain is highly active & metabolism may
increase as much as 20%.
-Also called paradoxical sleep.
-Sleeper may be difficult to arouse/ may wake
spontaneously
-Muscle tone is depressed
-Gastric secretions increase
-Heart a& respiratory rates often irregular
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Rest and Sleep ReviewerDocumento3 pagineRest and Sleep ReviewerJo Marchianne PigarNessuna valutazione finora
- INTROPSY Reviewer - Chapters 4-6Documento17 pagineINTROPSY Reviewer - Chapters 4-6jonaxx enthusiastNessuna valutazione finora
- Sleep Disorders - Lecture Notes 13: Clinical Psychology (Bournemouth University)Documento10 pagineSleep Disorders - Lecture Notes 13: Clinical Psychology (Bournemouth University)rupal aroraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapte 4 SleepDocumento4 pagineChapte 4 SleepMarco RagaNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 4 - Sleep - Psychological Health and WellbeingDocumento42 paginePart 4 - Sleep - Psychological Health and Wellbeingapi-642709499Nessuna valutazione finora
- Riverside College, Inc. Department of Physical Therapy Physiology01Documento6 pagineRiverside College, Inc. Department of Physical Therapy Physiology01Neonil Dequina CaceresNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit - I BPDocumento32 pagineUnit - I BPJenifa BaluNessuna valutazione finora
- Sleep Disorders Lecture NotesDocumento9 pagineSleep Disorders Lecture Notesrupal aroraNessuna valutazione finora
- Psych 111 Chapter 4 ConsciousnessDocumento3 paginePsych 111 Chapter 4 ConsciousnessGamboa, Manuella BrittanyNessuna valutazione finora
- Stages of SleepDocumento1 paginaStages of Sleepapi-461452779Nessuna valutazione finora
- Abnormal PsychologyDocumento23 pagineAbnormal PsychologySimon RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- SleepDocumento14 pagineSleepmoiezsatyaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Consciusness and Its Altered StateDocumento5 pagineConsciusness and Its Altered StatePAULINA GABRIELLE H. GAMIDONessuna valutazione finora
- INTRO TO PSYCH Chapter 5 NotesDocumento7 pagineINTRO TO PSYCH Chapter 5 Notescharity villanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rest & Sleep: Fundamental Components of WellbeingDocumento61 pagineRest & Sleep: Fundamental Components of WellbeingtitafungoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sleep: Kalpana.K Assistant ProfessorDocumento23 pagineSleep: Kalpana.K Assistant Professorkalpana KuppurajNessuna valutazione finora
- Biological Rhythms, Sleep Architecture and Functions in 40 CharactersDocumento28 pagineBiological Rhythms, Sleep Architecture and Functions in 40 CharactersWwwanand111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sleep and RestDocumento85 pagineSleep and RestJann ericka Jao100% (2)
- Sleeping and Dreaming - PPTX Filename UTF 8sleeping and DreamingDocumento39 pagineSleeping and Dreaming - PPTX Filename UTF 8sleeping and DreamingMary Claire BagioenNessuna valutazione finora
- Physiology of Sleep and ConsciousnessDocumento40 paginePhysiology of Sleep and ConsciousnessZobayer AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit - IV States of ConsciousnessDocumento2 pagineUnit - IV States of Consciousnessiamsathya2005Nessuna valutazione finora
- Circadian Rhythm: I.A. Eka WidiastutiDocumento56 pagineCircadian Rhythm: I.A. Eka WidiastutiAinun MahtobNessuna valutazione finora
- MODULE 7: Sleep & Dreams Consciousness Dreaming: MaligroDocumento3 pagineMODULE 7: Sleep & Dreams Consciousness Dreaming: MaligroIubel MaligroNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro To Psych Chapter 5-8 NotesDocumento26 pagineIntro To Psych Chapter 5-8 Notescharity villanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Psychology Module FinalsDocumento36 paginePsychology Module FinalsIrishNessuna valutazione finora
- Modules 14 and 15 PsychDocumento4 pagineModules 14 and 15 PsychSarah AsifNessuna valutazione finora
- States of ConsciousnessDocumento71 pagineStates of ConsciousnesskatNessuna valutazione finora
- States of ConsciousnessDocumento87 pagineStates of ConsciousnessMegan Horswood Morrow100% (1)
- Sleep: Non-Rapid Eye Movement Sleep (NREM Sleep) Rapid Eye Movement Sleep (REM Sleep)Documento4 pagineSleep: Non-Rapid Eye Movement Sleep (NREM Sleep) Rapid Eye Movement Sleep (REM Sleep)Sudarsan VeeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Sleep and Dreams ReviewerDocumento10 pagineSleep and Dreams ReviewerElieNessuna valutazione finora
- Sleep and Rest PatternDocumento70 pagineSleep and Rest PatternAitzaz IjazNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4 (Consciousness)Documento29 pagineLecture 4 (Consciousness)NURUL FARHANA BINTI IMRAN -Nessuna valutazione finora
- Harvard Health Guide to Sleep Stages and CyclesDocumento11 pagineHarvard Health Guide to Sleep Stages and CyclesMariaNessuna valutazione finora
- 5da402f11a983 - Lecture 5.2Documento34 pagine5da402f11a983 - Lecture 5.2lengers poworNessuna valutazione finora
- PSY 1 - Understanding States of ConsciousnessDocumento10 paginePSY 1 - Understanding States of ConsciousnessShaira Mae CababaNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Arc 1 - Project 3Documento3 pagineResearch Arc 1 - Project 3api-593346566Nessuna valutazione finora
- Consciousness and Its Altered StateDocumento45 pagineConsciousness and Its Altered StateWendell Castro Marabe Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Psych Chapter 9 HeheDocumento11 paginePsych Chapter 9 Hehemadeline.carter22Nessuna valutazione finora
- States of ConsciousnessDocumento3 pagineStates of ConsciousnessJoanne TolopiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5Documento1 paginaChapter 5Glydel Cris SualNessuna valutazione finora
- Sleep NituDocumento10 pagineSleep NituAakriti BhanjoNessuna valutazione finora
- How the Brain Experiences Sleep and DreamsDocumento3 pagineHow the Brain Experiences Sleep and DreamsVianca EpinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 - ConsciousnessDocumento13 pagineChapter 4 - ConsciousnessCamilleNessuna valutazione finora
- Psychology Chapter 7Documento3 paginePsychology Chapter 7cardenass100% (1)
- Rest and SleepDocumento6 pagineRest and SleepkcamillebautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 03 - Conciousness (Reading Chapter 5) A) Biology of SleepDocumento8 pagineLecture 03 - Conciousness (Reading Chapter 5) A) Biology of SleeptanyatewaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sleep PresentationDocumento25 pagineSleep PresentationmonicaNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 07Documento57 pagineCH 07DoinaOlarescuNessuna valutazione finora
- Rest and SleepDocumento11 pagineRest and Sleepdlneisha61Nessuna valutazione finora
- Sleep and WakingDocumento36 pagineSleep and WakingPayal MulaniNessuna valutazione finora
- States of Brain Activity-: Sleep, Brain Waves, Epilepsy, PsychosesDocumento60 pagineStates of Brain Activity-: Sleep, Brain Waves, Epilepsy, PsychosesashupathakaNessuna valutazione finora
- ConsciousnessDocumento43 pagineConsciousnessSaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Finals PhysiopsychDocumento8 pagineFinals PhysiopsychVerna TrillanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch. 5 Consciousness and Its Altered States (Student's Copy)Documento30 pagineCh. 5 Consciousness and Its Altered States (Student's Copy)Red MistNessuna valutazione finora
- Sleep - Biological RhythmsDocumento5 pagineSleep - Biological RhythmsAsad ullahNessuna valutazione finora
- Psy - Mod 3Documento25 paginePsy - Mod 3Daev Thara RanjithNessuna valutazione finora
- Sleep: Altaf Qadir KhanDocumento28 pagineSleep: Altaf Qadir KhanAhmad Irtaza AdilNessuna valutazione finora
- Sleep and its disturbances: An overviewDocumento83 pagineSleep and its disturbances: An overviewSatbir GillNessuna valutazione finora
- GRP. 2 -3B Sleep and Biological Rhythm Neurological DisorderDocumento161 pagineGRP. 2 -3B Sleep and Biological Rhythm Neurological DisorderHUSHTINE ANGEL EDRALINNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study - Paracetamol Ambroxol, Ascorbic Acid, CefuroximeDocumento4 pagineDrug Study - Paracetamol Ambroxol, Ascorbic Acid, Cefuroximeapi-3701489100% (12)
- Social Science (Religion)Documento5 pagineSocial Science (Religion)Jastine DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Creative Name TagDocumento3 pagineCreative Name TagJastine DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Child Abuse JournalDocumento1 paginaChild Abuse JournalJastine DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- A Choice Between Life and DeathDocumento2 pagineA Choice Between Life and DeathJastine DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- CHN - Written ReportDocumento3 pagineCHN - Written ReportJastine DiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Tack Welding PowerPointDocumento94 pagineTack Welding PowerPointCheerag100% (1)
- Stressors and Coping Mechanisms of Psychologically Distressed MSU-IIT StudentsDocumento22 pagineStressors and Coping Mechanisms of Psychologically Distressed MSU-IIT StudentsDarleen Rizel CalumbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Class I Type 3 Malocclusion Using Simple Removable AppliancesDocumento5 pagineManagement of Class I Type 3 Malocclusion Using Simple Removable AppliancesMuthia DewiNessuna valutazione finora
- Environmental Hazards For The Nurse As A Worker - Nursing Health, & Environment - NCBI Bookshelf PDFDocumento6 pagineEnvironmental Hazards For The Nurse As A Worker - Nursing Health, & Environment - NCBI Bookshelf PDFAgung Wicaksana100% (1)
- Resume - K MaclinDocumento3 pagineResume - K Maclinapi-378209869Nessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Sleep Disorders and Their ClassificationDocumento6 pagineUnderstanding Sleep Disorders and Their ClassificationAh BoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Rosemont Hill Health CenterDocumento14 pagineRosemont Hill Health CenterMona SahooNessuna valutazione finora
- Labcorp: Patient ReportDocumento4 pagineLabcorp: Patient ReportAsad PrinceNessuna valutazione finora
- MicroMaxx 3.3 UG ENG P06435-02B e 1 - 1Documento200 pagineMicroMaxx 3.3 UG ENG P06435-02B e 1 - 1Waheed MidoNessuna valutazione finora
- Repair of Obstetric Perineal LacerationsDocumento7 pagineRepair of Obstetric Perineal LacerationsadriantiariNessuna valutazione finora
- Remark: (Out Patient Department)Documento7 pagineRemark: (Out Patient Department)Tmiky GateNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 6 - LP Modeling ExamplesDocumento36 pagineWeek 6 - LP Modeling ExamplesCharles Daniel CatulongNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro To MycologyDocumento8 pagineIntro To Mycologycamille chuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Context & Interested Party AnalysisDocumento6 pagineContext & Interested Party AnalysisPaula Angelica Tabia CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Steps To The Perfect PICO Search White PaperDocumento9 pagine7 Steps To The Perfect PICO Search White PaperNurkhasanah 71Nessuna valutazione finora
- Proximal Humerus Fractures Epidemiology and TrendsDocumento5 pagineProximal Humerus Fractures Epidemiology and TrendsHelena Sofia Fonseca Paiva De Sousa TelesNessuna valutazione finora
- Interactive CME Teaching MethodsDocumento5 pagineInteractive CME Teaching MethodsROMSOPNessuna valutazione finora
- Influence of Social Capital On HealthDocumento11 pagineInfluence of Social Capital On HealthHobi's Important BusinesseuNessuna valutazione finora
- The Tocqueville Review/La Revue Tocqueville, Vol. XXVII, N° 2 - 2006Documento16 pagineThe Tocqueville Review/La Revue Tocqueville, Vol. XXVII, N° 2 - 2006Valente EnacheNessuna valutazione finora
- Soft Drinks in India: Euromonitor International February 2022Documento27 pagineSoft Drinks in India: Euromonitor International February 2022Gayathri22394Nessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction 1 Esoteric HealingDocumento20 pagineIntroduction 1 Esoteric HealingChicowski Caires100% (1)
- Role of Imaging in RhinologyDocumento223 pagineRole of Imaging in RhinologyDr. T. Balasubramanian100% (2)
- Lauren Tickner #StrengthFeed Training Guide - 129 PagesDocumento129 pagineLauren Tickner #StrengthFeed Training Guide - 129 PagessimplyjimbojimNessuna valutazione finora
- Life Threatening Rhythm: Presenter: Muhammad Najmuddin Bin Hussain 2. Wan Muhammad Nasirudin Bin Wan YusoffDocumento17 pagineLife Threatening Rhythm: Presenter: Muhammad Najmuddin Bin Hussain 2. Wan Muhammad Nasirudin Bin Wan YusoffWan NasirudinNessuna valutazione finora
- 4bi1 - Jan22 2b QPDocumento28 pagine4bi1 - Jan22 2b QPXIN PEINessuna valutazione finora
- Handbook of Laboratory Animal Science - Vol IIIDocumento319 pagineHandbook of Laboratory Animal Science - Vol IIICarlos AlmeidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gurr2011-Probleme Psihologice Dupa Atac CerebralDocumento9 pagineGurr2011-Probleme Psihologice Dupa Atac CerebralPaulNessuna valutazione finora
- BDD Fact SheetDocumento2 pagineBDD Fact SheetKeen ZeahNessuna valutazione finora
- Perioperative NursingDocumento8 paginePerioperative NursingGil Platon Soriano100% (3)
- TuDocumento382 pagineTuAndra NiculaeNessuna valutazione finora