Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Evalution Scheme 2
Caricato da
Udit SrivastavaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Evalution Scheme 2
Caricato da
Udit SrivastavaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
U.P.
TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY, LUCKNOW
STUDY & EVALUATION SCHEME
YEAR III, SEMESTER-V
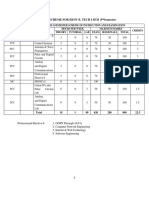
B. Tech. (1)Electronics and Communication Engineering (2) Electronics and (3) Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering Evaluation Scheme PERIODS Course SUBJECT SESSIONAL Code ESE EXAM. L T P CT TA Total THEORY TEC-501 Principles of Communication 3 1 0 30 20 50 100 TEC-502 Analog Integrated Circuits 3 1 0 30 20 50 100 TEC-503 Microprocessors and applications 3 1 0 30 20 50 100 TEC-504 Automatic Control System 3 1 0 30 20 50 100 TEC-505 Antenna & Wave Propagation 3 1 0 30 20 50 100 TEC-551 TEC 552 TEC-553 TEC-554 GP 501 PRACTICAL/TRAINING/PROJECT Communication Lab - I 0 Analog Integrated Circuits Lab 0 Microprocessors Lab 0 Control System Lab 0 General Proficiency Total 15 0 0 0 0 5 2 2 2 2 8 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 50 30 30 30 30 -
S. No.
Subject Total
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 8.
150 150 150 150 150 50 50 50 50 50 1000
YEAR III, SEMESTER-VI
S. No. SUBJECT PERIODS Evaluation Scheme SESSIONAL EXAM. ESE CT TA Total
Course Code
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9.
L T P THEORY TAS-601 Industrial Management 3 1 0 30 20 50 100 TEC-601 Digital Communication 3 1 0 30 20 50 100 TEC-602 Digital Signal Processing 3 1 0 30 20 50 100 TEC-603 VLSI Technology and Design 3 1 0 30 20 50 100 TEC-604 Microwave and Radar Engg. 3 1 0 30 20 50 100 PRACTICAL/TRAINING/PROJECT TEC-651 Communication Lab - II 0 0 2 20 20 30 TEC-652 Digital Signal Processing LAB 0 0 2 20 20 30 TEC-653 Electronics CAD Lab 0 0 2 20 20 30 TEC-654 Microwave Lab 0 0 2 20 20 30 GP-601 General Proficiency - 50 Total 15 5 8 Note- 4 to 6 Weeks Industrial Interaction after VI semester exam to be evaluated in VII semester
Subject Total
150 150 150 150 150 50 50 50 50 50 1000
YEAR III, SEMESTER-V
Syllabus B. Tech. (1)Electronics and Communication Engineering (2) Electronics and (3) Electronics & Telecommunication Engineering
Principles of Communication (TEC-501)
Unit 1 Topic Introduction: Communication Process, Source of Information, Communication channels, base-band and pass-band signals, representation of signal and systems, the modulation process, primary communication resources, analog versus digital communications. 2 Amplitude modulation: Frequency division and time division 1/3 multiplexing, suppressed carrier systems, single side band transmission, amplitude modulation with carrier power, effect of frequency and phase errors in synchronous detection, comparison of various AM systems, vestigial side band transmission. 3 Angle Modulation: Narrow and wide band FM, multiple frequency 1/4 and square wave modulation, linear and non-linear modulation, phase modulation, Demodulation of FM signals, noise reduction. Pulse Modulation: Pulse amplitude modulation, other forms of 1/5 pulse modulation, band width required for transmission PAM signals, Comparison of frequency division and time division multiplexed systems 4 Noise: Different types of noise, noise calculations, equivalent noise 1/6 band width, noise figures, effective noise temperature, noise figure in cascaded stages. 5 Performance of Communication Systems : Noise calculation in 1/7 communication systems, noise in Amplitude Modulated, Angle modulated and Pulse Modulated systems, comparison of coded and un-coded systems Introduction to Information Transmission:Measure of information, 1/8 channel capacity, transmission of continuous signals, exchange of band width for signal to noise ratio, Efficiency of PCM systems Text Book: 1. B. P. Lathi, Communication Systems, BS Publications, Hyderabad, 2004. Reference Book: 1. Simon Haykin, Communication Systems, John Wiley & Sons, 1999, Third Edition. Taub and schilling, Principles of Communication Systems TMH Text Book/ Chapter 2/1 Lectures 06
07
06
06
06
06
05
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Communication and Computer NetworksDocumento13 pagineCommunication and Computer NetworksVikram RaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Adc Lesson PlanDocumento2 pagineAdc Lesson PlanKalaimani ThirugnanamNessuna valutazione finora
- ExtcDocumento48 pagineExtcSagar KuchekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Ece203 Modulation-Techniques Eth 1.20 Ac29 PDFDocumento2 pagineEce203 Modulation-Techniques Eth 1.20 Ac29 PDFRanjith KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Mona SharmaDocumento80 pagineMona SharmachotushNessuna valutazione finora
- Calicut University - Viii Semester Ece Btech 2004 SyllabusDocumento19 pagineCalicut University - Viii Semester Ece Btech 2004 SyllabusRakesh GopalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus EXTC Sem 7 Rev. (MU)Documento31 pagineSyllabus EXTC Sem 7 Rev. (MU)Anurag RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Aei-5th & 6TH Sem23062008Documento44 pagineAei-5th & 6TH Sem23062008War MachineNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance Analysis of OFDM For 4G Wireless Systems Under Various Fading ChannelsDocumento4 paginePerformance Analysis of OFDM For 4G Wireless Systems Under Various Fading ChannelsJuan Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- B.tech MDU Syllabus (ECE) 3yrDocumento22 pagineB.tech MDU Syllabus (ECE) 3yrbtechkarloNessuna valutazione finora
- RD THDocumento18 pagineRD THMukul MahadikNessuna valutazione finora
- JNTUH Syllabus 2013 M.tech Communication SysDocumento26 pagineJNTUH Syllabus 2013 M.tech Communication SysSRINIVASA RAO GANTANessuna valutazione finora
- Course Plan: Francis Xavier Engineering College Department of Electronics and Communication Course PlanDocumento3 pagineCourse Plan: Francis Xavier Engineering College Department of Electronics and Communication Course PlanImmanuel VinothNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Switching Systems Course ContentDocumento31 pagineDigital Switching Systems Course ContentravimhattiNessuna valutazione finora
- CS6301 - Analog and Digital Communication (ADC) PDFDocumento122 pagineCS6301 - Analog and Digital Communication (ADC) PDFparantnNessuna valutazione finora
- Dcrust ECE 4th YearDocumento16 pagineDcrust ECE 4th YearRahulPoriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mobile Communication Systems: University of Mumbai Scheme of Instruction and Evaluation (R2007)Documento27 pagineMobile Communication Systems: University of Mumbai Scheme of Instruction and Evaluation (R2007)Vignesh AigalNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus & Scheme For M.Tech. (ECE)Documento27 pagineSyllabus & Scheme For M.Tech. (ECE)Siddharth SidNessuna valutazione finora
- BTech ECE Semester-6Documento15 pagineBTech ECE Semester-6Arighna BasakNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Communication Syllabus 2016-2020Documento4 pagineAnalog Communication Syllabus 2016-2020yogesh zalteNessuna valutazione finora
- EC6402 Communication Theory PDFDocumento166 pagineEC6402 Communication Theory PDFparantn0% (1)
- 00 - Mobile Communication (404189) - Syllabus - OKDocumento32 pagine00 - Mobile Communication (404189) - Syllabus - OKvydeoNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus Ece 5 8 Reg2001Documento25 pagineSyllabus Ece 5 8 Reg2001api-3748534100% (3)
- Principles of Communication (3-0-2)Documento3 paginePrinciples of Communication (3-0-2)Anil MarsaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Communication & Data CommunicationDocumento88 pagineElectronic Communication & Data CommunicationGuruKPO100% (2)
- Modeling of Power Line Communications Using MIMO Coding Scheme For Indoor SystemDocumento11 pagineModeling of Power Line Communications Using MIMO Coding Scheme For Indoor SystemNoorianah LollmahamodNessuna valutazione finora
- GITAM-ECE-4 TH Yr SyllabusDocumento41 pagineGITAM-ECE-4 TH Yr SyllabusSanthosh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Syllabus MECCE Syllabus FinalDocumento14 pagineSyllabus MECCE Syllabus FinalPhilip G GeojiNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication SystemsDocumento51 pagineCommunication SystemsKinza MallickNessuna valutazione finora
- Ec8395 Ce Notes 2Documento127 pagineEc8395 Ce Notes 2makNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Structure: 4 Periods Which Includes Library, e - Learning, Internet and PresentationDocumento16 pagineCourse Structure: 4 Periods Which Includes Library, e - Learning, Internet and PresentationMuhammadSajidNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Syllabus: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Virasit Imtawil Semester: 2 /2016 Dr. Puripong SuthisopapanDocumento3 pagineCourse Syllabus: Assoc. Prof. Dr. Virasit Imtawil Semester: 2 /2016 Dr. Puripong SuthisopapanMixer TanatsanNessuna valutazione finora
- Dcs Course FileDocumento50 pagineDcs Course FilerajeshchitikenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sem 2Documento7 pagineSem 2Ajay KatageriNessuna valutazione finora
- EC8394 Analog and Digital Communication TechniquesDocumento18 pagineEC8394 Analog and Digital Communication TechniquesEzhil Azhahi.AM Assistant ProfessorNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment No.1: 1. AIM: 2. EquipmentDocumento7 pagineExperiment No.1: 1. AIM: 2. EquipmentNilesh RathoreNessuna valutazione finora
- ACS Lab Manual 1546926763Documento49 pagineACS Lab Manual 1546926763vinay minsuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ei Elective PDFDocumento18 pagineEi Elective PDFtushardkdNessuna valutazione finora
- CS Syllabus 2012 Admissions OnwardsDocumento78 pagineCS Syllabus 2012 Admissions OnwardsAnurag DeterminedNessuna valutazione finora
- Ecesem8 2022Documento188 pagineEcesem8 2022Sathiyavani VaradharajNessuna valutazione finora
- 7th & 8th Sem SyllabusDocumento33 pagine7th & 8th Sem SyllabusAkshay BharadwajNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Syllabus - Anna University Tirunelveli 5-8 SemestersDocumento93 pagineFinal Syllabus - Anna University Tirunelveli 5-8 SemestersVijay SwarupNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE-2019-23-SYLLABUS III Year I SemesterDocumento22 pagineECE-2019-23-SYLLABUS III Year I SemesterNani SaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Plan for Communication EngineeringDocumento4 pagineLecture Plan for Communication EngineeringkhananuNessuna valutazione finora
- Signal Integrity: From High-Speed to Radiofrequency ApplicationsDa EverandSignal Integrity: From High-Speed to Radiofrequency ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Next Generation Wireless Communications Using Radio over FiberDa EverandNext Generation Wireless Communications Using Radio over FiberNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Communications: Courses and Exercises with SolutionsDa EverandDigital Communications: Courses and Exercises with SolutionsValutazione: 3 su 5 stelle3/5 (2)
- Wireless Multi-Antenna Channels: Modeling and SimulationDa EverandWireless Multi-Antenna Channels: Modeling and SimulationNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Communications Networks and SystemsDa EverandPrinciples of Communications Networks and SystemsNevio BenvenutoNessuna valutazione finora
- Delay-Doppler Communications: Principles and ApplicationsDa EverandDelay-Doppler Communications: Principles and ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Wireless Receiver Architectures and Design: Antennas, RF, Synthesizers, Mixed Signal, and Digital Signal ProcessingDa EverandWireless Receiver Architectures and Design: Antennas, RF, Synthesizers, Mixed Signal, and Digital Signal ProcessingNessuna valutazione finora
- Software Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationDa EverandSoftware Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationNessuna valutazione finora
- Wireless Communications: Algorithmic TechniquesDa EverandWireless Communications: Algorithmic TechniquesNessuna valutazione finora
- Cross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionDa EverandCross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionNessuna valutazione finora
- Handbook of Visual CommunicationsDa EverandHandbook of Visual CommunicationsHseuh-Ming HangNessuna valutazione finora
- Partial-Update Adaptive Signal Processing: Design Analysis and ImplementationDa EverandPartial-Update Adaptive Signal Processing: Design Analysis and ImplementationNessuna valutazione finora
- Hotel invoice summary 40 charsDocumento5 pagineHotel invoice summary 40 charsUdit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nielsen Featured Insights Understanding Indias FMCG ShopperDocumento8 pagineNielsen Featured Insights Understanding Indias FMCG ShopperUdit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Distributor Audit GuidelinesDocumento3 pagineDistributor Audit GuidelinesUdit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Book Name Author NameDocumento2 pagineBook Name Author NameUdit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Animal Testing in Cosmetics IndustryDocumento3 pagineAnimal Testing in Cosmetics IndustryUdit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Primary OrderDocumento1 paginaPrimary OrderUdit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Recharge Invoice 1799487247Documento1 paginaRecharge Invoice 1799487247Udit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 1Documento1 paginaWeek 1Udit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Export: S.No. /year 2009-2010 2010-2011 2011-2012 2012-2013 2013-2014Documento2 pagineExport: S.No. /year 2009-2010 2010-2011 2011-2012 2012-2013 2013-2014Udit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Export CountriesDocumento46 pagineExport CountriesUdit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- About The EmbassyDocumento2 pagineAbout The EmbassyUdit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- India - Cuba Relations 1. Trade StatisticsDocumento7 pagineIndia - Cuba Relations 1. Trade StatisticsUdit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- 169305Documento95 pagine169305Udit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- ICreate Executive Summary Proposal Doc 2015Documento2 pagineICreate Executive Summary Proposal Doc 2015Bhanu PratapNessuna valutazione finora
- Export: S.No. /year 2009-2010 2010-2011 2011-2012 2012-2013 2013-2014Documento2 pagineExport: S.No. /year 2009-2010 2010-2011 2011-2012 2012-2013 2013-2014Udit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Iran 2Documento5 pagineIran 2Udit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Plan of Action: Group: Anand (48) Yogesh Jaiswal (93) Dhruba Jyoti Bhuyan (64) Udit SrivastavaDocumento1 paginaPlan of Action: Group: Anand (48) Yogesh Jaiswal (93) Dhruba Jyoti Bhuyan (64) Udit SrivastavaUdit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- P 1 ToastmasterDocumento1 paginaP 1 ToastmasterUdit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Iran 1Documento2 pagineIran 1Udit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Weak Litmus Test: Winter 2011Documento2 pagineA Weak Litmus Test: Winter 2011Udit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Workshop On Six Sigma Green Belt Workshop On Six Sigma Green BeltDocumento1 paginaWorkshop On Six Sigma Green Belt Workshop On Six Sigma Green BeltUdit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- What The Experts Say: Power CuesDocumento5 pagineWhat The Experts Say: Power CuesUdit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lessons For Budding EntrepreneursDocumento1 paginaLessons For Budding EntrepreneursUdit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Iran 1Documento2 pagineIran 1Udit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- I Tod AssignmentDocumento4 pagineI Tod AssignmentUdit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- 20 Symbolic Images That Nreflect The Reality in The WorldDocumento30 pagine20 Symbolic Images That Nreflect The Reality in The WorldUdit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Subhiksha MICA SochDocumento41 pagineSubhiksha MICA SochChiranjiv KarkeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Club MembershipDocumento12 pagineFinal Club MembershipUdit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Plan of Action: Group: Anand (48) Yogesh Jaiswal (93) Dhruba Jyoti Bhuyan (64) Udit SrivastavaDocumento1 paginaPlan of Action: Group: Anand (48) Yogesh Jaiswal (93) Dhruba Jyoti Bhuyan (64) Udit SrivastavaUdit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- 20 Symbolic Images That Nreflect The Reality in The WorldDocumento30 pagine20 Symbolic Images That Nreflect The Reality in The WorldUdit SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tatoo Java Themes PDFDocumento5 pagineTatoo Java Themes PDFMk DirNessuna valutazione finora
- Second Law of EntrophyDocumento22 pagineSecond Law of EntrophyMia Betia BalmacedaNessuna valutazione finora
- Inbound 9092675230374889652Documento14 pagineInbound 9092675230374889652Sean Andrew SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Vidura College Marketing AnalysisDocumento24 pagineVidura College Marketing Analysiskingcoconut kingcoconutNessuna valutazione finora
- Variable Speed Pump Efficiency Calculation For Fluid Flow Systems With and Without Static HeadDocumento10 pagineVariable Speed Pump Efficiency Calculation For Fluid Flow Systems With and Without Static HeadVũ Tuệ MinhNessuna valutazione finora
- AtmDocumento6 pagineAtmAnkit JandialNessuna valutazione finora
- Oblicon SampleDocumento1 paginaOblicon SamplelazylawatudentNessuna valutazione finora
- Equipment, Preparation and TerminologyDocumento4 pagineEquipment, Preparation and TerminologyHeidi SeversonNessuna valutazione finora
- Laws of MotionDocumento64 pagineLaws of MotionArnel A. JulatonNessuna valutazione finora
- S2 Retake Practice Exam PDFDocumento3 pagineS2 Retake Practice Exam PDFWinnie MeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chicago Electric Inverter Plasma Cutter - 35A Model 45949Documento12 pagineChicago Electric Inverter Plasma Cutter - 35A Model 45949trollforgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Determination of Vitamin C in FoodsDocumento11 pagineDetermination of Vitamin C in FoodsDalal Shab JakhodiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2002, Vol.86, Issues 4, Hospital MedicineDocumento221 pagine2002, Vol.86, Issues 4, Hospital MedicineFaisal H RanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Course: Citizenship Education and Community Engagement: (8604) Assignment # 1Documento16 pagineCourse: Citizenship Education and Community Engagement: (8604) Assignment # 1Amyna Rafy AwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Control SystemsDocumento269 pagineControl SystemsAntonis SiderisNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Portfolio (Aashi Singh)Documento18 pagineComputer Portfolio (Aashi Singh)aashisingh9315Nessuna valutazione finora
- Your Inquiry EPALISPM Euro PalletsDocumento3 pagineYour Inquiry EPALISPM Euro PalletsChristopher EvansNessuna valutazione finora
- Development of Rsto-01 For Designing The Asphalt Pavements in Usa and Compare With Aashto 1993Documento14 pagineDevelopment of Rsto-01 For Designing The Asphalt Pavements in Usa and Compare With Aashto 1993pghasaeiNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Like-Love - Hate and PronounsDocumento3 paginePractice Like-Love - Hate and PronounsangelinarojascnNessuna valutazione finora
- The Sound Collector - The Prepared Piano of John CageDocumento12 pagineThe Sound Collector - The Prepared Piano of John CageLuigie VazquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Binomial ExpansionDocumento13 pagineBinomial Expansion3616609404eNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Important Methods Used For Studying Comparative EducationDocumento35 pagine5 Important Methods Used For Studying Comparative EducationPatrick Joseph63% (8)
- Russian Tea Market Growth and Brand PreferenceDocumento6 pagineRussian Tea Market Growth and Brand PreferenceKing KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- WWW - Istructe.pdf FIP UKDocumento4 pagineWWW - Istructe.pdf FIP UKBunkun15Nessuna valutazione finora
- Programming Manual Magic 308/616-CLI Quick ReferenceDocumento16 pagineProgramming Manual Magic 308/616-CLI Quick ReferencekrishnamarajublrNessuna valutazione finora
- Term Sheet: Original Borrowers) Material Subsidiaries/jurisdiction) )Documento16 pagineTerm Sheet: Original Borrowers) Material Subsidiaries/jurisdiction) )spachecofdz0% (1)
- VL2019201000534 DaDocumento2 pagineVL2019201000534 DaEnjoy LifeNessuna valutazione finora
- 'K Is Mentally Ill' The Anatomy of A Factual AccountDocumento32 pagine'K Is Mentally Ill' The Anatomy of A Factual AccountDiego TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- Numerical Methods: Jeffrey R. ChasnovDocumento60 pagineNumerical Methods: Jeffrey R. Chasnov2120 sanika GaikwadNessuna valutazione finora
- Finance at Iim Kashipur: Group 9Documento8 pagineFinance at Iim Kashipur: Group 9Rajat SinghNessuna valutazione finora