Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Atomic Structure
Caricato da
vennicesumoDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Atomic Structure
Caricato da
vennicesumoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
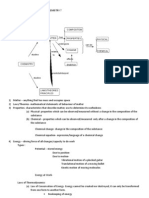
. ATOMIC STRUCTURE ENERGY LEVELS Electrons possess energies to counteract the nuclear pull.
Energies not of any amounts however but quantized energies, (energy levels) . ) 1 K ) 2 L ) 3 M ) 4 N ) 5 O ) 6 P ) 7 Q
Ordering of energy levels : 1< 2<
3<
4 ..
Electrons tend to occupy energy level of low energy state 2n2 = maximum number of electrons in an energy level . 2) 8) 18) 32) 50) 72) 98)
Example Kr 36 Ca20 2) 2) 8) 8) 18) 8) 8) 2) Why ?
SUBLEVELS OF ENERGY Electrons are not only restricted to certain energy levels, 1.7 but they are also restricted to certain sublevels of energy called orbitals.
Kinds of orbitals
Kinds s p d f
Types 1 3 5 7
Designations s Px Py Pz D d d d d
Maximum number of es 2 6 10 14
F f f f f f f
S orbital starts on the 1st and present at all higher energy levels P orbital starts on the 2nd and present at all higher energy levels D orbital starts on the 3rd and at all higher energy levels F orbital starts on the 4th and present at all higher energy levels. . s) s p) s, p, d) s, p, d, f ) ..
Ordering of Orbitals s < p < d < f
Ca 20 s2)
s2 p6)
s2p6)
s2)
Orbital space or region in the atom where an electron is probably located.
Properties of an Electron
ELECTRON charged repel each other maximally to be stable spins around produces magnetic field whose polarity depends upon direction of spin; thus as they spin in opposite directions, they atrract each other
ELECTRONIC CONFIGURATION Distribution of the electrons of a given atom into their respective energy levels and orbitals.
electron
n l
energy level
type of orbital
Rules : 1. Aufbau Building Up Principle Aufbau Guide : 1 s 2 S p 3 S P d 4 s p d f 5 s p d f 6 s p d 7 s p
1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p 6s 4f 5d 6p 7s 5f 6d 7p Electrons tend to occupy energy level and orbital of low energy states. 2. Pauli Exclusion Principle Two electrons can occupy a given orbital at the same time provided they are of opposite spins. 3. Hunds Rule Degenerated orbitals (types of orbitals) within the same energy level are of equal energies. Electrons occupy them one at a time before they would pair. Example: Ca 20 1s2 2s2 2px2 2py2 2pz2 3s2 3px2 3py2 3pz2 4s2
QUANTUM NUMBERS An electron of a given atom can be described by four quantum numbers 1. Principal Quantum Number (n)- describes the relative distance of the electron from the nucleus N= 1,2,3,4.,5,6,7, 2. Azimuthal Quantum Number (l)- describes the kind of orbital where the electron occupies L= 0..(n-1) 3. Magnetic Quantum Number (m)= describes the type of orbital where the electron is. M= l (l-1) 0.(l-1) l 4. Spin Quantum number (s)= describes the direction of the spin of an electron S= +1/2 = clockwise direction -1/2=counterclockwise direction
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Ge F-Class Gek111895Documento2 pagineGe F-Class Gek111895gopinathsampath0% (2)
- Heat Exchangers-Principles and Design Rev1 PDFDocumento68 pagineHeat Exchangers-Principles and Design Rev1 PDFroyNessuna valutazione finora
- Piping Stress AnalysisDocumento36 paginePiping Stress AnalysisSugumar S100% (1)
- Corrosion and Its Control NFDocumento93 pagineCorrosion and Its Control NFAayu JainNessuna valutazione finora
- Air Cooled Heat Exchangers - BrochureDocumento16 pagineAir Cooled Heat Exchangers - Brochurenorthstarleo100% (1)
- 6 InertingDocumento9 pagine6 InertingHasan CosalevNessuna valutazione finora
- GMAW GuideDocumento21 pagineGMAW GuidewhoopsoopsNessuna valutazione finora
- Using Abaqus To Model Delamination in Fiber-Reinforced Composite MaterialsDocumento18 pagineUsing Abaqus To Model Delamination in Fiber-Reinforced Composite MaterialsdashatanliNessuna valutazione finora
- Kelton Calculation DetailsDocumento17 pagineKelton Calculation DetailsronziesNessuna valutazione finora
- SolutionsDocumento5 pagineSolutionsvennicesumoNessuna valutazione finora
- GasesDocumento2 pagineGasesvennicesumoNessuna valutazione finora
- Periodic TableDocumento4 paginePeriodic TablevennicesumoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mole ConceptDocumento2 pagineMole ConceptvennicesumoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical BondsDocumento6 pagineChemical BondsvennicesumoNessuna valutazione finora
- Dipole Induced Dipole: CH C O CHDocumento4 pagineDipole Induced Dipole: CH C O CHvennicesumoNessuna valutazione finora
- Formula Writing NomenclatureDocumento3 pagineFormula Writing NomenclaturevennicesumoNessuna valutazione finora
- Composition Has Undergoes Relates Can BeDocumento3 pagineComposition Has Undergoes Relates Can BevennicesumoNessuna valutazione finora
- 101 CompositionDocumento3 pagine101 CompositionvennicesumoNessuna valutazione finora
- Refrigerant Selection and Environmental ImpactsDocumento67 pagineRefrigerant Selection and Environmental Impactsdamola2realNessuna valutazione finora
- Wassce / Waec Chemistry Syllabus: 1. Structure of The AtomDocumento30 pagineWassce / Waec Chemistry Syllabus: 1. Structure of The AtomJesse Lartey100% (1)
- Chem 16.1 ReviewerDocumento7 pagineChem 16.1 ReviewerCindy ChengNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 4a Solar ThermalDocumento34 pagineLecture 4a Solar ThermalTze Long GanNessuna valutazione finora
- PHYS101L Report 3 Tables GraphsDocumento1 paginaPHYS101L Report 3 Tables GraphsKarylle AquinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Laws of MotionDocumento5 pagineLaws of Motionkatie4834Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pipeline JournalDocumento68 paginePipeline Journal구용찬Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cie626 2 Fema 356Documento35 pagineCie626 2 Fema 356Ricardo Wong MontoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2005-021 MotwaniDocumento6 pagine2005-021 Motwanialexander100% (1)
- COOLPLUS-Water Cooled Heat ExchangerDocumento10 pagineCOOLPLUS-Water Cooled Heat ExchangerCOOLPLUS OIL COOLERNessuna valutazione finora
- Energy Loss and Straggling ConceptsDocumento33 pagineEnergy Loss and Straggling ConceptsyounessinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Duct Velocity D - 928 PDFDocumento7 pagineDuct Velocity D - 928 PDFTeo Pei SanNessuna valutazione finora
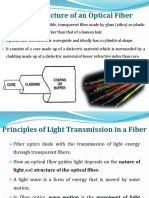
- Optical Fiber Structure & Light TransmissionDocumento83 pagineOptical Fiber Structure & Light Transmissionece Ms.G.Bhargavi100% (1)
- Elink For Windows: List of Pages in This Trip KitDocumento20 pagineElink For Windows: List of Pages in This Trip KitgiganticvisNessuna valutazione finora
- Ra 51350Documento32 pagineRa 51350lcandoNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.fluid Mechanics-1-10Documento10 pagine6.fluid Mechanics-1-10Vijeesh VijayalayamNessuna valutazione finora
- Arches and CablesDocumento21 pagineArches and CablesAriel Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Ip21 Hw10 SolDocumento4 pagineIp21 Hw10 Sol吳昭亮Nessuna valutazione finora
- Activity Session 5 Earth Science ConseminoDocumento32 pagineActivity Session 5 Earth Science ConseminoFatimah D. Rubin-Cansancio100% (2)
- SR07 SeriesDocumento8 pagineSR07 SeriesSumit JadhavNessuna valutazione finora
- Designand Performanceof Soft Ground Improvement Using PVDwithandwithout Vacuum ConsolidationDocumento17 pagineDesignand Performanceof Soft Ground Improvement Using PVDwithandwithout Vacuum ConsolidationShadabNessuna valutazione finora