Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Write Types of Information Syste1
Caricato da
শেষ রাতের মুসাফিরDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Write Types of Information Syste1
Caricato da
শেষ রাতের মুসাফিরCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1. System Investigation: Understand the business problem or opportunity. 2. System Analysis: Develop an information system solution.
n. Using tools such as data flow diagrams, structured English, or decisions trees. The Role of the IS Department IS workers learn how the current system functions and how it The Information Systems (IS) department is responsible for meets (or fails to meet) the organizations informational needs. designing, building, and managing an organization's 3. System Design: information systems. Develop specification for the H/W,S/W, people network and In years past, the IS department served only the informational data resources and information product. needs of managers. Today, the IS team supports all workers in Use two design methods: 1) Top-down design, in which a business, and supports the business' mission, as well. designers start with the large picture and move to the details of An IS department's tasks include designing, planning, its function. 2) Bottom-up design, in which designers start installing, and maintaining systems; generating reports; and with the details and move to the major functions. cost control. 4. System Implementation: Four conversion methods can be use to move from an old system Role Players in an IS Department to a new one: An IS department can include many members with many different Direct all users stop using the old system and start using the skills. A large IS staff may include: new one. Managers Purchasing Agents Parallel the old system stays in use as increasing amounts of Computer Scientists Security Managers data are processed in the new one. Systems Analysts Trainers Phased users start using the new system, one component at a Programmers User Assistance Architects time. Database Specialists Technical Writers Pilot users at one site use the new system while all other System or Network Managers users keep the old system. Hardware Maintenance Technicians 5. System Maintenance: Use a post implementation review process to monitor, Q: Write the definition of System Development Life Cycle (SDLC)? evaluate, and modify the system. What are the different steps of SDLC? Write each one is details? Ans: System Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is process of conceiving, designing, and implementing, a system by the process of investigation, analysis, design, implementation & maintenance. It is
1) Write types of Information System (IS) with description? Ans: 5 types of IS have. They are: 1. Office automation system or information system in organization: This information system collects, stores and processes data to give an organization real time useful and accurate information. This information system encompasses data gathering information from the people and machines that collect, process, output and store data. Also in the networks that transmit and receive data and the procedures that govern the way data is handled. 2. Transaction Processing System (TPS): A transaction processing system provides a way to collect, process, store, display modify or cancel transactions. Most of these systems allow multiple transactions to take place simultaneously. The data that this system collects is usually stored in databases which can be used to produce reports such as billing, wages, inventory summaries, manufacturing schedules, or check registers. 3. Decision Support System (DSS): A decision support system helps make decisions by working and analyzing data that can generate statistical projections and data models. This system gives support rather than replacing a managers judgment while improving the quality of a managers decision. A DSS helps solve problems while using external data. 4. Management information system (MIS): A management information system is an information system that uses the data collected by the transaction processing system and uses this data to create reports in a way that managers can use it to make routine business decisions in response to problems. Some of the reports that this information system creates are summary, exception and ad hoc reports. All this is done to increase the efficiency of managerial activity. 5. Expert System: An expert system, also known as a knowledge-based system, is a computer system that is designed to analyze data and produce recommendations, diagnosis and decisions that are controlled. An expert system uses computers to foster the way a human brain may process information, learn and remember that information.
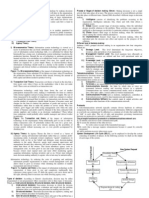
also called IS DEVELOPMENT OR DEVELOPMENT. Different stages of SDLC :1. System investigation. 2. System analysis. 3. System design. 4. System implementation. 5. System maintenance & system support. System investigation
APPLICATION
System analysis
System design
System implementation
System maintenance Write each one is details below:
Q. Define about ERP & SCM system software? What are the different solutions of ERP? How ERP systems work? Ans: ERP: Collects data from many divisions/departments/units located in different countries/branches of a firm for use in nearly all of firms internal business activities is called ERP system software.
AGV (automated guided vehicles) Robotics Automated conveyance systems Computerized scheduling and production control CAQ (Computer-aided quality assurance)
SCM: Supply chain management (SCM) is the combination of art and Q: What is the Supply Chain Management Key Issues? Write science that goes into improving the way your company finds the raw some SCM elements? components it needs to make a product or service and deliver it to Ans: Supply Chain Management Key Issues customers. Purchasing Manufacturing Distribution Customer Service/ Different solutions of ERP are: Financial Management Inventory Management Purchasing Sales Management Production Planning Advanced Visual Planning Manufacturing Management A typical ERP system would use multiple component of computer software and hardware to achieve integration ERP delivers a single database that contains all data for the software module
SOURCE MAKE DELIVER SELL Sales
Low purchase price Multiple vendors
Few changeovers Stable schedules Long run lengths
Low inventories Low transportation
High inventories High service levels Regional stocks
Elements of SCM: Strategic Supply Chain Design Resource Acquisition Long Term Planning (1 Year ++) Tactical Production/ Distribution Planning Resource Allocation Medium Term Planning (Qtrly, Monthly) Operational Shipment Scheduling Resource Scheduling Short Term Planning (Weekly,Daily) Q: What is Information flow of SCM? Ans: Information flow of SCM: Information is overriding element Need for databases Master files: Information about customers, products, materials, suppliers, transportation, production and distribution data- do not require frequent processing Q: Define CIM (Computer Integrated Management)? Write Status files- heart of transaction processing- track orders and subsystem of CIM? infrastructure status- updated daily. Essentially using the same information to make all plans right from Ans: CIM: Computer Integrated Management is the integration of the structuring the network to processing every day supply chain tasks. total manufacturing enterprise through the use of integrated systems and data communications coupled with new managerial philosophies that improve organizational and personnel efficiency. Some or all of the following subsystems may be found in a CIM operation: CAD/CAM (Computer-aided design/Computer-aided manufacturing) CAPP (Computer-aided process planning) ERP (Enterprise resource planning) CNC (computer numerical control) machine tools DNC (direct numerical control) machine tools FMS (flexible machining systems) ASRS (automated storage and retrieval systems)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- W1ndm1lls 0f Th3 G0dsDocumento301 pagineW1ndm1lls 0f Th3 G0dsশেষ রাতের মুসাফিরNessuna valutazione finora
- Gas & Electricity BillDocumento1 paginaGas & Electricity Billশেষ রাতের মুসাফিরNessuna valutazione finora
- T.R.Form No.Documento1 paginaT.R.Form No.Md Shahidul KabirNessuna valutazione finora
- Bangladesh Premier LeagueDocumento3 pagineBangladesh Premier Leagueশেষ রাতের মুসাফিরNessuna valutazione finora
- Write Types of Information Syste1Documento2 pagineWrite Types of Information Syste1শেষ রাতের মুসাফিরNessuna valutazione finora
- Creative Questions of Social ScienceDocumento10 pagineCreative Questions of Social Scienceশেষ রাতের মুসাফিরNessuna valutazione finora
- Fahim 1Documento14 pagineFahim 1শেষ রাতের মুসাফিরNessuna valutazione finora
- Write Types of Information Syste1Documento2 pagineWrite Types of Information Syste1শেষ রাতের মুসাফিরNessuna valutazione finora
- Groups, Roles, Norms, and Organizational CultureDocumento4 pagineGroups, Roles, Norms, and Organizational Cultureশেষ রাতের মুসাফিরNessuna valutazione finora
- S/No Outlet Name Retailer Name Retailer Mobile Munber ThanaDocumento12 pagineS/No Outlet Name Retailer Name Retailer Mobile Munber Thanaশেষ রাতের মুসাফিরNessuna valutazione finora
- Barak ObamaDocumento10 pagineBarak Obamaশেষ রাতের মুসাফিরNessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled 1Documento1 paginaUntitled 1শেষ রাতের মুসাফিরNessuna valutazione finora
- To Whom It May ConcernDocumento1 paginaTo Whom It May Concernশেষ রাতের মুসাফিরNessuna valutazione finora
- Focusing Your Evaluation...................................... 4Documento49 pagineFocusing Your Evaluation...................................... 4mohamad-abdul-sater-1406Nessuna valutazione finora
- Shantanu MajumderDocumento18 pagineShantanu MajumderSyed Mohammad Hasib AhsanNessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5784)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- CHAPTER SEVEN Source SelectionDocumento14 pagineCHAPTER SEVEN Source SelectionTessema TeshomeNessuna valutazione finora
- Draft Bill of Lading for Onion ExportDocumento1 paginaDraft Bill of Lading for Onion Exportsantois1891Nessuna valutazione finora
- Brunel Business School coversheet for online coursework submissionsDocumento17 pagineBrunel Business School coversheet for online coursework submissionsZohaib MehfoozNessuna valutazione finora
- Li & Fung Group 5Documento15 pagineLi & Fung Group 5yogesh85Nessuna valutazione finora
- Merchandising Accounts BasicsDocumento17 pagineMerchandising Accounts BasicsshawtyNessuna valutazione finora
- 111Documento2 pagine111Joyce TenorioNessuna valutazione finora
- Samsung Case StudyDocumento17 pagineSamsung Case Studyshreyam1100% (1)
- Purchasing StrategyDocumento1 paginaPurchasing StrategyRAF RAFNessuna valutazione finora
- Global E-business and Collaboration SystemsDocumento37 pagineGlobal E-business and Collaboration SystemsAshutosh DevpuraNessuna valutazione finora
- Logistics Management Sourcing: Özgür Kabak, PH.DDocumento20 pagineLogistics Management Sourcing: Özgür Kabak, PH.Dsathya priyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analyzing a Trading Company's Supply ChainDocumento3 pagineAnalyzing a Trading Company's Supply ChainVasco TorgalNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparison of Dell and Zara Supply ChainDocumento3 pagineComparison of Dell and Zara Supply ChainPart Khatsig AlexanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 6 - Inventory CycleDocumento42 pagineLesson 6 - Inventory CycleUnnamed homosapienNessuna valutazione finora
- CIM Still The Solution For Manufacturing Industry PDFDocumento13 pagineCIM Still The Solution For Manufacturing Industry PDFAbid YusufNessuna valutazione finora
- Measuring Product CostsDocumento71 pagineMeasuring Product CostsNitin100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical Supply Chain and Inventory Management Strategies PDFDocumento13 paginePharmaceutical Supply Chain and Inventory Management Strategies PDFRizky AzizahNessuna valutazione finora
- Managerial Economics Chapter 7 MCQsDocumento10 pagineManagerial Economics Chapter 7 MCQsMuhammad AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Nist Ir 7622Documento99 pagineNist Ir 7622FedScoop100% (1)
- Supply Chain & TCIDocumento12 pagineSupply Chain & TCInil_71Nessuna valutazione finora
- Certification in Humanitarian Supply Chain Management (CHSCM) Competence Model. Final Version 2007Documento28 pagineCertification in Humanitarian Supply Chain Management (CHSCM) Competence Model. Final Version 2007Kareem AqeelNessuna valutazione finora
- VIVO ReportDocumento16 pagineVIVO ReportKashif Raza100% (3)
- Transformation Head/ Senior Level Professional Logistics - Supply Chain Management - Team Building & LeadershipDocumento2 pagineTransformation Head/ Senior Level Professional Logistics - Supply Chain Management - Team Building & LeadershipRITHIN.rNessuna valutazione finora
- Adding Value To Corporate Recruitment: Carlos Jordán de Urries Talent Search ConsultantDocumento8 pagineAdding Value To Corporate Recruitment: Carlos Jordán de Urries Talent Search ConsultantCarlos Jordan de UrriesNessuna valutazione finora
- SIPOCDocumento27 pagineSIPOCAlex Vincent100% (1)
- Bài Báo 2 Developing MRP II Systems - A Case Study at HT Company.Documento20 pagineBài Báo 2 Developing MRP II Systems - A Case Study at HT Company.ANH PHẠM THỊ LANNessuna valutazione finora
- Audi N Suzuki PDFDocumento12 pagineAudi N Suzuki PDFSrikant SahuNessuna valutazione finora
- Walmart Case - Group 5Documento11 pagineWalmart Case - Group 5Rushi AbheeshaiNessuna valutazione finora
- 1FS - Basic Warehouse Inbound Processing From SupplierDocumento60 pagine1FS - Basic Warehouse Inbound Processing From SupplierKaiser Ka100% (1)
- International Logistics and DistributionDocumento12 pagineInternational Logistics and DistributionshobineelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment: Financial Management - 1Documento8 pagineAssignment: Financial Management - 1Rahul SinghNessuna valutazione finora