Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Answer 1
Caricato da
drjisharDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Answer 1
Caricato da
drjisharCopyright:
Formati disponibili
a) What are the advantages of the prone position?
Increase in FRC Changes in diaphragmatic excursions Improved ventilationperfusion matching
All these can significantly improve oxygenation in the prone position. This technique has been utilized for treatment of refractory hypoxaemia and in early acute respiratory distress syndrome 7080% of patients turned prone initially benefit from improved oxygenation. Other benefit -Surgical access for certain procedures eg neurosurgery, surgery on the back. Etc
b) What problem may be encountered by a patient in the prone position undergoing a lumbar microdiscectomy? Prone position is associated with airway ,breathing,circulatory and pressure related problems. These can be avoided if adequate steps are taken Airway Accidental extubation is a problem.Difficulty in accessing the airway and reintubation Swelling of the tongue and mouth can cause potential airway obstruction and delayed extubation. The mechanism is assumed to be obstruction of venous drainage from the head and neck secondary to excessive flexion of the neck. The subsequent increase in hydrostatic pressure causes the equivalent of dependent oedema.
Breathing Increase in external pressure on the chest leading to reduced thoracic compliancerequiring high airway pressure and can cause barotrauma
circulatory Cardiac index in one study dropped by an average of 24%. This was mainly as a result of decreasing stroke volume with little change in heart rate. Pressure on the abdomen can cause high intra-abdominal pressure which can cause inferior vena caval compression, reduced venous return and subsequent poor cardiac output.
Pressure related injuries Direct pressure can cause occlusion to an arterial supply or venous drainage Occlusion to the venous drainage, or any generalised rise in venous pressure will raise the IOP, as will use of a head-down position. MAP may be reduced either by deliberate hypotension or abdominal compression. If ocular perfusion pressure is too low to adequately perfuse the eyes then ischaemic damage will result Nerve injury--Chest support can compress nerves in the axilla. Direct compression of the ulnar nerve in the cubital tunnel Indirect compression of the axillary neurovascular bundle by axial pressure from the humerus. nerves exiting at the superior orbital fissure are at risk, Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh.
Excess pressure on the nose and eyes. The dorsum of the foot as well as knees, pelvic area,breasts, axilla, elbows and face are all at risk of pressure necrosis in this position. Others--The lower limbs are at increased risk of compartment syndrome in the tuck position, where both knees and hips are flexed. Arterial blood flow and MAP decrease, and limb pressure increases. This can result in rhabdomyolysis and compartment syndrome, which when complicated by renal failure can be
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Varicose VeinsDocumento37 pagineVaricose VeinsJavier SaadNessuna valutazione finora
- Varicose Case ProformaDocumento2 pagineVaricose Case ProformaSneha Naulakha100% (1)
- 03 Retinal Vascular Occlution - Dr. Darwan Triyono, SP.MDocumento28 pagine03 Retinal Vascular Occlution - Dr. Darwan Triyono, SP.MDissa Yulianita SuryaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmacy Latin Terms and AbbreviationsDocumento11 paginePharmacy Latin Terms and AbbreviationsAngeli GregorioNessuna valutazione finora
- Central Venous PressureDocumento39 pagineCentral Venous PressureJelly Rose Bajao Otayde100% (2)
- Sanaani Nur Hathi M. Nso Jugular Venous Oximetry Staff Nurse 1Documento7 pagineSanaani Nur Hathi M. Nso Jugular Venous Oximetry Staff Nurse 1Nur SanaaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Astrology Eileen NaumanDocumento13 pagineMedical Astrology Eileen NaumansrivathsalNessuna valutazione finora
- Science - G9 - Week 2 (Lessons-4-6)Documento46 pagineScience - G9 - Week 2 (Lessons-4-6)Rhyan Zero-four BaluyutNessuna valutazione finora
- Transport of Oxygen and Carbon DioxideDocumento45 pagineTransport of Oxygen and Carbon DioxideNamithaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Variceal Bleeding in CirrhoticsDocumento8 paginePathophysiology of Variceal Bleeding in Cirrhoticsanon_914506742Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biology: Practice WorksheetsDocumento20 pagineBiology: Practice Worksheetsদেবব্রত মন্ডলNessuna valutazione finora
- Leg EdemaDocumento13 pagineLeg Edemacamila perillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 42 Circulation and Gas ExchangeDocumento16 pagineChapter 42 Circulation and Gas ExchangeBeck MicksNessuna valutazione finora
- Esophageal Varices - Part I: Pathophysiology, Diagnostics, Conservative Treatment and Prevention of BleedingDocumento8 pagineEsophageal Varices - Part I: Pathophysiology, Diagnostics, Conservative Treatment and Prevention of BleedingSesilia RosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bleeding Control Lesson 01 HandoutDocumento25 pagineBleeding Control Lesson 01 HandoutjvanelslanderNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Notes: Cie IgcseDocumento64 pagineBiology Notes: Cie Igcsehamza96Nessuna valutazione finora
- DVTDocumento46 pagineDVTLuqman ArifNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Class X Biology - Life Processs Key NotesDocumento18 pagineCBSE Class X Biology - Life Processs Key NotesBhavesh DesaiNessuna valutazione finora
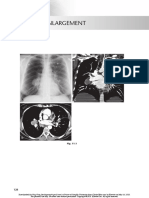
- Hilar EnlargementDocumento19 pagineHilar EnlargementGriggrogGingerNessuna valutazione finora
- Insuficienta Venoasa CronicaDocumento15 pagineInsuficienta Venoasa CronicaSimona IonitaNessuna valutazione finora
- BloodDocumento7 pagineBloodpravinambadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Med 1 Block 2 - Wet Lab NotesDocumento36 pagineMed 1 Block 2 - Wet Lab NotesluckyNessuna valutazione finora
- Imaging Tutorial - Differential Diagnosis of Bright Lesions On Diffusion-Weighted MR Images - RadioGraphicsDocumento163 pagineImaging Tutorial - Differential Diagnosis of Bright Lesions On Diffusion-Weighted MR Images - RadioGraphicsNatalia E PenagosNessuna valutazione finora
- Difference Between Adult and Fetal CirculationDocumento6 pagineDifference Between Adult and Fetal CirculationRaquel M. MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Obstructive Shock Pediatric - Journal PDFDocumento3 pagineObstructive Shock Pediatric - Journal PDFGerald SweinslionNessuna valutazione finora
- Brier Ley 2020Documento8 pagineBrier Ley 2020kemoNessuna valutazione finora
- LESSON 7 Capillary Puncture Equipment and ProcedureDocumento3 pagineLESSON 7 Capillary Puncture Equipment and ProcedureAlthea EspirituNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 1 PRS ListDocumento6 pagineWeek 1 PRS ListAnonymous E9kQDbflONessuna valutazione finora
- Physical Assessment Part 3 Assignment - SuzukiDocumento21 paginePhysical Assessment Part 3 Assignment - SuzukiNANAMI BOLIGOR SUZUKINessuna valutazione finora
- Just Go With The FlowDocumento2 pagineJust Go With The FlowIRIS50% (2)