Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Albinism
Caricato da
cikgunita90Descrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Albinism
Caricato da
cikgunita90Copyright:
Formati disponibili
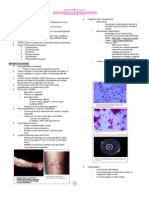
ALBINISM A Lifetime Suffer?
INTRODUCTION Have you ever heard about albinism? Albinism is a defect of melanin production that results in little or no color (pigment). The word albinism itself refers to a group of inherited conditions. It is an inherited condition present at birth. It also sometimes referred to hypopigmentation.
DESCRIPTION It is characterized by a lack of melanin, the pigment that normally gives color to the skin, hair, and eyes. Albinism may affects people from all races in the world. They have inherited altered genes that do not make the usual amounts of a pigment called melanin. However, this is a rare phenomenon. In USA, only one person in 17, 000 has some type of albinism. People usually do not recognize that they have albinism. TYPE OF ALBINISM Many types of albinism exist, all of which involve lack of pigment in varying degrees. Oculocutaneous albinism is a common type of albinism. It will affects the eyes, hair, and skin. The hair and skin will remain completely white throughout life. Everyone with oculocutaneous albinism will experience abnormal flickering movements of eyes which is known as nystagmus and also sensitive to bright light. There may be other eye problems including poor vision and crossed or "lazy" eyes - strabismus .
Other common type of albinism is an ocular albinism. This condition happened when it only affects eyes. The eyes will be lack of colour but hair and skin are normal. The ocular albinism cause more eyes problems than others. CAUSES genetics aspects Albinism is an inherited problem, which is a autosomal recessive disease. It is mainly caused by an alteration in one or more of the genes that are responsible for directing the eyes and skin to produce or distribute melanin. Melanin is a photoprotective pigment that absorbs ultraviolet (UV) light coming from the sun. The skin will not damaged in the presence of the melanin. Sun exposure normally produces a tan, which is an increase in melanin pigment in the skin. Many people with albinism do not have melanin pigment in their skin, do not tan with exposure to the sun, and as a result develop sunburn . as you being mentioned earlier , it is a autosomal recessive disease. What is meant by that? Autusomal recessive disease means that a person must have two copies of the defective gene to show the symptoms of the disease. The child therefore inherits one defective gene responsible for making melanin from each parents. Because the task of making melanin is complex, there are many different types of albinism, involving a number of different genes. It is also possible to inherit one normal gene and one albinism gene. In this case, the one normal gene provides enough information to make some pigment, and the child has normal skin and eye color. The child has one gene for albinism. About one in 70 people are albinism carriers, with one defective gene but no symptoms; they have a 50 percent chance of passing the albinism gene to their child. However, if both parents are carriers with one defective gene each, they have a one in four chance of passing on both copies of the defective gene to the child, who will have albinism. There is also a type of ocular albinism that is carried on the X chromosome and occurs almost exclusively in males because they have only one X chromosome and, therefore, no other gene for the trait to override the defective one.
BIOCHEMICAL ASPECTS Albinism occur when there is an absence of the enzyme tyrosinase, which prevents the synthesis of melanin pigment by pigment-forming cells. These individuals have a very white skin, fine white hair, pink or light blue irises of the eyes, and a variety of other eye disturbances. Various types of localized albinism are characterized by the absence of pigment in specific parts of the body. There is no treatment for albinism.
SYMPTOMS clinical Signs of albinism are usually appear in the skin, hair and eye color. There are also symptoms showing vision impairments. Although the most recognizable form of albinism results in milky white skin, skin pigmentation can range from white to brown, and may be nearly the same as that of parents or siblings without albinism. For some people with albinism, skin pigmentation never changes. For others, melanin production may begin or increase during childhood and adolescence, resulting in slight changes in pigmentation. With exposure to the sun, some people may develop freckles,
moles, with or without pigment, large freckle-like spots (lentigines) and also the ability to tan Hair Hair color can range from very white to brown. Eye color can range from very light blue to brown and may change with age. The lack of pigment in the colored part of the eyes (irises) makes them somewhat translucent. This means that the irises can't completely block light from entering the eye. Because of this translucence, very light-colored eyes may appear red in some lighting. This occurs because you're seeing light reflected off the back of the eye and passing back out through the iris again similar to red eye that occurs in a flash photograph. Signs and symptoms of albinism related to eye function include rapid, involuntary back-and-forth movement of the eyes (nystagmus). There will be also an inability of both eyes to stay directed at the same point or to move in unison (strabismus) or extreme nearsightedness or farsightedness. Another symptom is sensitivity to light (photophobia) and astigmatism. DIAGNOSIS Genetic testing offers the most accurate way to diagnose albinism. This testing is proven if the person have a family history of albinism. It is also useful for certain groups of people who are known to get the disease. Doctor may also diagnose the condition based on the appearance of the skin, hair, and eyes. An ophthalmologist should perform a electroretinogram test, which can reveal vision problems related to albinism. A visual evoked potentials test can be very useful when the diagnosis is uncertain.
TREATMENT The goal of treatment is to relieve symptoms. Treatment depends on the severity of the disorder.
Treatment involves protecting the skin and eyes from the sun, reducing sunburn risk by avoiding the sun, using sunscreen, and covering up completely with clothing when exposed to the sun. We may use sunscreen that have a high sun protection factor (SPF), sunglasses (UV protected) may relieve light sensitivity. Glasses are often prescribed to correct vision problems and eye position. Eye muscle surgery is sometimes recommended to correct abnormal eye movements (nystagmus).
UNIVERSITI PENDIDIKAN SULTAN IDRIS SEMESTER 2 SESI 2011/2012
PRINCIPLES IN BIOCHEMISTRY SBK 3013
ASSIGNMENT INDIVIDUAL ARTICLE
NAME : NOOR HAJAH SANITA BT MOHD SATAR MATRIC NUM : D20091035086 TITLE : ALBINISM
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- AlbinismDocumento6 pagineAlbinismWanJienNessuna valutazione finora
- Albinism EssayDocumento1 paginaAlbinism EssayMeer BabanNessuna valutazione finora
- AlbinismDocumento27 pagineAlbinismEnitsirk Yag Escleto TemplonuevoNessuna valutazione finora
- Albinism Classification, Clinical.23Documento4 pagineAlbinism Classification, Clinical.23Danny WongNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Alkaptonuria? Highlights: SymptomsDocumento4 pagineWhat Is Alkaptonuria? Highlights: SymptomsJustin PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Glaucoma: Mohd Roslee Bin Abd GhaniDocumento42 pagineGlaucoma: Mohd Roslee Bin Abd GhaniSaha DirllahNessuna valutazione finora
- Iron Deficiency AnemiaDocumento5 pagineIron Deficiency AnemiaLoiegy PaetNessuna valutazione finora
- Stem Cells EssayDocumento4 pagineStem Cells EssayalskjdhhNessuna valutazione finora
- Diamond-Blackfan Anemia Is A DisorderDocumento22 pagineDiamond-Blackfan Anemia Is A DisorderDarem SoNessuna valutazione finora
- PHENYLKETONURIADocumento4 paginePHENYLKETONURIAmarsiel03Nessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Lymphoblastic LeukemiaDocumento25 pagineAcute Lymphoblastic Leukemiaapi-396564080Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hyperphosphatemia and HypophosphatemiaDocumento15 pagineHyperphosphatemia and HypophosphatemiaHari Prasad KNessuna valutazione finora
- Four Types of Artificial Family Planning MethodsDocumento2 pagineFour Types of Artificial Family Planning MethodsGershee April Cardona100% (1)
- Chapter 50 Vision and HearingDocumento7 pagineChapter 50 Vision and HearingAlmer OstreaNessuna valutazione finora
- Night BlindnessDocumento18 pagineNight BlindnessNicholas RedlyNessuna valutazione finora
- OsteomalaciaDocumento16 pagineOsteomalaciasyukkurNessuna valutazione finora
- General Principles of Hereditary DiseasesDocumento17 pagineGeneral Principles of Hereditary DiseasesrutwickNessuna valutazione finora
- Gasa Sa Gugma: Reflection PaperDocumento2 pagineGasa Sa Gugma: Reflection PaperAll NewtNessuna valutazione finora
- Awareness of Kirkuk Technical Institute Female Students Regarding Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)Documento9 pagineAwareness of Kirkuk Technical Institute Female Students Regarding Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS)Central Asian StudiesNessuna valutazione finora
- MalnutritionDocumento5 pagineMalnutritionCarlo Pasaol Alang Jr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Red Blood Cell Anomalies: Elliptocytes & Oval MacrocyteDocumento12 pagineRed Blood Cell Anomalies: Elliptocytes & Oval MacrocyteSHUPATUSSAI100% (1)
- Different Methods of Family PlanningDocumento8 pagineDifferent Methods of Family PlanningFamela LauzonNessuna valutazione finora
- AnaemiaDocumento15 pagineAnaemiaAnik SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Megaloblastic AnaemiaDocumento11 pagineMegaloblastic AnaemiaJesmin_36Nessuna valutazione finora
- Definition of PneumoniaDocumento4 pagineDefinition of PneumoniaEmylia Ananda PutriNessuna valutazione finora
- CyclosporineDocumento3 pagineCyclosporineraki9999Nessuna valutazione finora
- Types of LeukemiaDocumento4 pagineTypes of LeukemiawizardebmNessuna valutazione finora
- Subcutaneous & Systemic MycosesDocumento7 pagineSubcutaneous & Systemic MycosesDee GeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Lithium ToxicityDocumento28 pagineLithium ToxicityReejan PaudelNessuna valutazione finora
- AlbinismDocumento3 pagineAlbinismNaim ElmasriNessuna valutazione finora
- Epilepsy in Pregnancy JatuDocumento57 pagineEpilepsy in Pregnancy Jatuninjahattori1Nessuna valutazione finora
- 02 - Examination of Blood and Bone Marrow HematologyDocumento3 pagine02 - Examination of Blood and Bone Marrow Hematologyhamadadodo7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Obstetric Maneuvers For Shoulder Dystocia and Associated Fetal MorbidityDocumento5 pagineObstetric Maneuvers For Shoulder Dystocia and Associated Fetal MorbidityBill HarmanNessuna valutazione finora
- DiarrheaDocumento44 pagineDiarrheaAnonymous P2CDF5uic1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Gurrea LV Sec.2c Ncm105 Mod2Documento4 pagineGurrea LV Sec.2c Ncm105 Mod2Lovely GurreaNessuna valutazione finora
- Screening Test For Phagocytic Engulfment: DiapedesisDocumento2 pagineScreening Test For Phagocytic Engulfment: DiapedesisBianca ANessuna valutazione finora
- RP-Case History of A Child With Sickle Cell Anemia in IndiaDocumento5 pagineRP-Case History of A Child With Sickle Cell Anemia in IndiaMarie Kelsey Acena MacaraigNessuna valutazione finora
- Amyotrophic Lateral SclerosisDocumento6 pagineAmyotrophic Lateral SclerosisJohnjohn MateoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pancytopenia Secondary To Bacterial SepsisDocumento16 paginePancytopenia Secondary To Bacterial Sepsisiamralph89Nessuna valutazione finora
- BACTERIA CULTURE PRES Rev1Documento28 pagineBACTERIA CULTURE PRES Rev1Jendie BayanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chelsea Amman Pku Case StudyDocumento37 pagineChelsea Amman Pku Case Studyapi-365955738Nessuna valutazione finora
- Neurofibromatosis 1Documento10 pagineNeurofibromatosis 1Minelle Sanchez InsoNessuna valutazione finora
- Malnutrition in Children: Pediatric NursingDocumento59 pagineMalnutrition in Children: Pediatric Nursingflex gy100% (1)
- Reflection Paper My Sisters KeeperDocumento1 paginaReflection Paper My Sisters KeeperAllyson VillarealNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study-Molar PregnancyDocumento14 pagineCase Study-Molar Pregnancysimbarashe tangwadzana100% (1)
- 4 HemophiliaDocumento5 pagine4 HemophiliaMary Rose F. MalaluanNessuna valutazione finora
- Patho DSDocumento10 paginePatho DSJesselyn CampitNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Lymphoblastic LeukemiaDocumento22 pagineAcute Lymphoblastic Leukemiaحسن محمدNessuna valutazione finora
- AUBF Renal DiseasesDocumento3 pagineAUBF Renal DiseasesAngela LaglivaNessuna valutazione finora
- Amlodipine Captopril MetronidazoleDocumento5 pagineAmlodipine Captopril Metronidazolekhrysty1506Nessuna valutazione finora
- Vaccination Chart: National Immunization Schedule For New BornDocumento20 pagineVaccination Chart: National Immunization Schedule For New BornsmilealwplzNessuna valutazione finora
- LEIOMYOMADocumento14 pagineLEIOMYOMARANessuna valutazione finora
- Geriatric Module 1Documento19 pagineGeriatric Module 1Cherry Joyce Basco100% (1)
- ALKAPTONURIADocumento15 pagineALKAPTONURIAJean Claude Balancio100% (1)
- g6pd BrochureDocumento2 pagineg6pd BrochureMaha GaberNessuna valutazione finora
- Nitrogen Metabolism: Nitrate AssimilationDocumento3 pagineNitrogen Metabolism: Nitrate AssimilationSalsabila LuqyanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pheochromocytoma and HomoeopathyDocumento13 paginePheochromocytoma and HomoeopathyDr. Rajneesh Kumar Sharma MD HomNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Activity No. 1 - Hemoglobin DeterminationDocumento2 pagineLab Activity No. 1 - Hemoglobin DeterminationChelsea Padilla Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- AMLDocumento19 pagineAMLquerokeropi100% (1)
- Information and Communication Technology in Science Data LoggingDocumento15 pagineInformation and Communication Technology in Science Data Loggingcikgunita90Nessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation Iwb MiraDocumento11 paginePresentation Iwb Miracikgunita90Nessuna valutazione finora
- Information and Communication Technology in Science: MembersDocumento11 pagineInformation and Communication Technology in Science: Memberscikgunita90Nessuna valutazione finora
- Enzyme IwbDocumento9 pagineEnzyme Iwbcikgunita90Nessuna valutazione finora
- Solar Energy History All Beganppt RealDocumento31 pagineSolar Energy History All Beganppt Realcikgunita90Nessuna valutazione finora
- Group Members: Naziratul Asyikin Mohd Sam Noramira Binti Ahmad Tajuddin Noor Hajah Sanita Mohd SatarDocumento8 pagineGroup Members: Naziratul Asyikin Mohd Sam Noramira Binti Ahmad Tajuddin Noor Hajah Sanita Mohd Satarcikgunita90Nessuna valutazione finora
- Title Right-Handed and Left HandledDocumento7 pagineTitle Right-Handed and Left Handledcikgunita90Nessuna valutazione finora
- Edited Tropical Rain Forest Group 7Documento39 pagineEdited Tropical Rain Forest Group 7cikgunita90Nessuna valutazione finora
- Slide MacroDocumento20 pagineSlide Macrocikgunita90Nessuna valutazione finora
- Information and Communication Technology in Science Data LoggingDocumento12 pagineInformation and Communication Technology in Science Data Loggingcikgunita90Nessuna valutazione finora
- Information and Communication Technology in Science Data LoggingDocumento12 pagineInformation and Communication Technology in Science Data Loggingcikgunita90Nessuna valutazione finora
- Examples AntibioticsDocumento7 pagineExamples Antibioticscikgunita90Nessuna valutazione finora
- Information and Communication Technology in Science Data LoggingDocumento12 pagineInformation and Communication Technology in Science Data Loggingcikgunita90Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kitchen ProjectDocumento31 pagineKitchen ProjectAwan PutihNessuna valutazione finora
- Report VitagenDocumento4 pagineReport Vitagencikgunita90Nessuna valutazione finora
- Roti Canai Oh Roti CanaiDocumento4 pagineRoti Canai Oh Roti Canaicikgunita90Nessuna valutazione finora
- Solar EnergyDocumento9 pagineSolar Energycikgunita90Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kitchen ProjectDocumento9 pagineKitchen Projectcikgunita90Nessuna valutazione finora
- Guidelines For High Flow Oxygen Therapy (AIRVO ) On The WardsDocumento11 pagineGuidelines For High Flow Oxygen Therapy (AIRVO ) On The WardsBurhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Complete Workbook - How To Radiate 1000 Watt PresenceDocumento39 pagineComplete Workbook - How To Radiate 1000 Watt PresenceAditya AdiNessuna valutazione finora
- Removable Partial Denture OcclusionDocumento17 pagineRemovable Partial Denture OcclusionJhuselle Patrice de MesaNessuna valutazione finora
- HandTumors PDFDocumento1 paginaHandTumors PDFniteenkardiNessuna valutazione finora
- Restless Leg Syndrome: The Most Common Disorder You Have Never Heard Of."Documento20 pagineRestless Leg Syndrome: The Most Common Disorder You Have Never Heard Of."Maulida Manurung100% (1)
- BioDocumento36 pagineBioDHQ Hospital ChiniotNessuna valutazione finora
- Colour TherapyDocumento23 pagineColour Therapynelkon505100% (6)
- The Compassion Fatigue and Resilience Connection A Survey of Resilience Compassion Fatigue Burnout and Compassion Satisfaction Among Trauma Responders 1522 4821 17 165 PDFDocumento9 pagineThe Compassion Fatigue and Resilience Connection A Survey of Resilience Compassion Fatigue Burnout and Compassion Satisfaction Among Trauma Responders 1522 4821 17 165 PDFMarc Andreo MalalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Stroke RehabilitationDocumento43 pagineStroke RehabilitationHashini Vjkmr100% (4)
- Emergency DrugsDocumento47 pagineEmergency DrugsBesimanNessuna valutazione finora
- BetterBack Posture Ebook CompressDocumento60 pagineBetterBack Posture Ebook Compress123100% (2)
- Learning: Concepts, Principles and Nature!Documento15 pagineLearning: Concepts, Principles and Nature!amrendrakr090% (1)
- Anesthesia For Cesarean SectionDocumento84 pagineAnesthesia For Cesarean SectionssamaddNessuna valutazione finora
- Bee Propolis May Improve Fertility in Women With en Dome Trios IsDocumento2 pagineBee Propolis May Improve Fertility in Women With en Dome Trios Isapi-3723677Nessuna valutazione finora
- Access To Dental CareDocumento29 pagineAccess To Dental CareNilusha93Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hemophilia BDocumento2 pagineHemophilia BHoger AmediNessuna valutazione finora
- Herioux Jeffyn MP PDFDocumento34 pagineHerioux Jeffyn MP PDFthenimadhavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Master of Arts in Counseling (MAC) : Practicum ManualDocumento36 pagineMaster of Arts in Counseling (MAC) : Practicum ManualMark StigerNessuna valutazione finora
- CompletepdfDocumento10 pagineCompletepdfReha NilNessuna valutazione finora
- Comfortrac Cervical ManualDocumento12 pagineComfortrac Cervical Manualsigilum_deiNessuna valutazione finora
- PTOSISDocumento3 paginePTOSISprasad_ssrk1967396Nessuna valutazione finora
- (English) The Secret of Becoming Mentally Strong - Amy Morin - TEDxOcala (DownSub - Com)Documento14 pagine(English) The Secret of Becoming Mentally Strong - Amy Morin - TEDxOcala (DownSub - Com)Maulana Yazid Al AnnuriNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 59 - Antiemetic AgentsDocumento11 pagineChapter 59 - Antiemetic AgentsJonathonNessuna valutazione finora
- High Risk B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Interim Maintenance IIDocumento1 paginaHigh Risk B-Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Interim Maintenance IIRitush MadanNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study For OligohydramniosDocumento7 pagineCase Study For Oligohydramniosbjhilario86% (14)
- GynecologyDocumento50 pagineGynecologyPhilips55100% (4)
- Physician Order SheetDocumento4 paginePhysician Order SheetResci Angelli Rizada-NolascoNessuna valutazione finora
- Research DefindersDocumento12 pagineResearch DefindersJeffrey ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- June 2007-NPT 5-Questions and RationaleDocumento16 pagineJune 2007-NPT 5-Questions and RationaleLarissa AquinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Draft GCDocumento15 pagineFinal Draft GCHusnal Taufiq ZulkernainNessuna valutazione finora