Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
TENECTEPLASE (Metalyse®) Protocol: Wentworth Area Health Service
Caricato da
illusionilluTitolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
TENECTEPLASE (Metalyse®) Protocol: Wentworth Area Health Service
Caricato da
illusionilluCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Wentworth Area Health Service
TENECTEPLASE (Metalyse) Protocol
TENECTEPLASE (Metalyse) Protocol
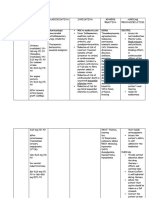
Indication: Thrombolytic treatment of acute myocardial infarction (within 12 hours of symptom onset) Dosage: Based on body weight. One dose only. Maximum = 10,000 IU (50mg) Body weight (kg) <60kg 60 - 69 kg 70 - 79 kg 80 89 kg 90 kg
Note: 1000 IU = 5mg
Tenecteplase (IU) 6000 7000 8000 9000 10 000
Dose (mg) 30 35 40 45 50
Volume of reconstituted solution (mL) 6 7 8 9 10
Route: IV bolus injection Dilution: Reconstitute with complete volume of pre-filled WFI using vial OR needle. Using vial: Screw pre-filled syringe to the vial adapter. Use the spike on the vial adapter to penetrate the vial stopper. Push syringe down SLOWLY. (See pictogram inside box) Using needle: Push the syringe plunger down SLOWLY to avoid foaming. SWIRL GENTLY. DO NOT SHAKE. Invert vial with syringe attached, transfer appropriate volume of reconstituted solution (5mg/mL) into syringe. Colourless/pale yellow CLEAR solution must be obtained. Compatibility: 0.9% sodium chloride. Incompatibility: Glucose (dextrose) solution. Do not mix with other drugs. Administration: IV bolus over 5 - 10 seconds Presentation: Vials (powder for reconstitution) 40 mg (8,000 IU) (plus 8 mL WFI prefilled syringe, vial adapter and needle for reconstitution) 50 mg (10,000 IU) (plus 10 mL WFI prefilled syringe, vial adapter and needle for reconstitution) Reconstituted solution contains tenecteplase 5mg/mL (1000 U/mL).
Wentworth Area Health Service
TENECTEPLASE (Metalyse) Protocol
Stability: Any unused solution must be discarded. o Reconstituted solution can be kept at 2-8 C for 24 hours OR 8 hours at room temperature. Storage: Store at room temperature. Protect from light. Contraindication: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Precaution: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Above 70 years old Bleeding Arrhythmias Cholesterol embolization Arterial and venous punctures should be minimized Readministration with tenecteplase has not been evaluated, hence should be done with caution. Active internal bleeding or known bleeding predisposition History of cerebrovascular accident Intracranial and intraspinal surgery or trauma within 2 months Intracranial neoplasm Arteriovenous malformation or aneurysm Severe uncontrolled hypertension (systolic180mmHg diastolic >110mmHg)
Adverse Effects: Minor bleeding (22%), major bleeding (4.7%), stroke (1.8%), intracranial haemorrhage (0.9%), reperfusion arrhythmias, allergic reactions (< 1%), anaphylaxis (<0.1%), cholesterol embolizations (rare) Monitoring Parameters: ECG (reperfusion arrhythmias) Neurological examinations (for intracranial bleed) Vital signs (HR, BP) Evidence of bleeding (e.g. haematuria) Coagulation parameters (APTT, platelets) - do not predict bleeding episodes (coagulation tests may be unreliable) Hematocrit/haemoglobin (bleeding)
Cost:
$1722.00 (40mg vial with solvent) $1818.00 (50mg vial with solvent)
Comments: Tenecteplase (rTNKtpa) and alteplase (rTPA) have similar clinical efficacy for thrombolysis after myocardial infarction, (similar mortality and intracranial haemorrhage rates). However, advantages of TNK include ease and rapidity of administration, longer half-life, greater fibrin specificity, and lower non-cerebral bleeding rates.
Wentworth Area Health Service
TENECTEPLASE (Metalyse) Protocol
References:
Metalyse Product Information, MIMS Online 2004. MICROMEDEX(R) Healthcare Series Vol. 121 expires 9/2004 Llevadot J., Giugliano R., Antman E. Bolus Fibrinolytic Therapy in Acute Myocardial Infarction. JAMA 2001: 286(4) p442-449
COMPILED BY COMMITTEE RESPONSIBLE DATE REVISED DATE EFFECTIVE REVIEW DATE
Ms R Dey, Intensive Care Pharmacist ICU management committee July 2004 August 2004 July 2007
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Physical Education: Quarter 3 - Module 3b: Festival DanceDocumento14 paginePhysical Education: Quarter 3 - Module 3b: Festival DanceSolrac LeunamNessuna valutazione finora
- Modified Rood's Approach and Ability of Independent Selfcare in Haemorrhagic Stroke Patients of Assam, IndiaDocumento6 pagineModified Rood's Approach and Ability of Independent Selfcare in Haemorrhagic Stroke Patients of Assam, Indianandhini raguNessuna valutazione finora
- Aspirin Drug StudyDocumento4 pagineAspirin Drug StudyNikael Patun-ogNessuna valutazione finora
- ENLS V4.0 ICH Manuscript FINAL PDFDocumento15 pagineENLS V4.0 ICH Manuscript FINAL PDFkoko komarudinNessuna valutazione finora
- MSU-Iligan Institute of Technology: Nursing Health Assessment IDocumento1 paginaMSU-Iligan Institute of Technology: Nursing Health Assessment IJhon Jade PalagtiwNessuna valutazione finora
- Cerebrolysin in Patients With Hemorrhagic StrokeDocumento7 pagineCerebrolysin in Patients With Hemorrhagic StrokeZeynep Emirhan ŞenyüzNessuna valutazione finora
- Management Acute StrokeDocumento108 pagineManagement Acute StrokeratuhamimNessuna valutazione finora
- TutorialDocumento18 pagineTutorialEllya Syahfitri 2108125983Nessuna valutazione finora
- ESO Guideline TIADocumento24 pagineESO Guideline TIASiti ZulaikhahNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrotherapy Stroke ChinaDocumento7 pagineHydrotherapy Stroke China黃姵儒Nessuna valutazione finora
- Neurology revision-2015: Benztropine side effects & status epilepticus treatmentsDocumento99 pagineNeurology revision-2015: Benztropine side effects & status epilepticus treatmentsPaz Vida100% (7)
- Perspective: New England Journal MedicineDocumento3 paginePerspective: New England Journal Medicinedwi adiNessuna valutazione finora
- Stroke (Brain Attack)Documento16 pagineStroke (Brain Attack)Nhayr Aidol100% (1)
- MCQ Continuum Stroke 2Documento10 pagineMCQ Continuum Stroke 2Vita Kusuma RahmawatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Kwah Dan Diong, 2014Documento1 paginaKwah Dan Diong, 2014heruNessuna valutazione finora
- Rle RequirementDocumento101 pagineRle RequirementJe KirsteneNessuna valutazione finora
- Vascular Lesions of the Brain Classification and TreatmentDocumento6 pagineVascular Lesions of the Brain Classification and TreatmentAlyssa NadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuroanesthesia and Outcomes: Evidence, Opinions, and Speculations On Clinically Relevant TopicsDocumento7 pagineNeuroanesthesia and Outcomes: Evidence, Opinions, and Speculations On Clinically Relevant TopicsenriquegarciagalianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pappas' Pysiology of The Cell ManualDocumento66 paginePappas' Pysiology of The Cell ManualVeres AndrásNessuna valutazione finora
- Lufkin Heat stress programDocumento7 pagineLufkin Heat stress programmohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- KW 15 AbstractsDocumento1.129 pagineKW 15 AbstractsShloime-Batsheva Dalezman100% (1)
- Mirror Therapy and PTDocumento14 pagineMirror Therapy and PTCaity AngellNessuna valutazione finora
- Hemorrhagic Transformation After Cerebral InfarctionDocumento14 pagineHemorrhagic Transformation After Cerebral InfarctionAlyk Tumayan CalionNessuna valutazione finora
- Anthony Hans HL Biology Ia Database WM PDFDocumento12 pagineAnthony Hans HL Biology Ia Database WM PDFYadhira IbañezNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 1 and 2. Introduction To LinguisticsDocumento35 pagineWeek 1 and 2. Introduction To LinguisticsAngel Joy MeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Home care and self-care measures after a strokeDocumento1 paginaHome care and self-care measures after a strokeYESSAMIN GUADIZNessuna valutazione finora
- Cerebrovascular Accident I. General Medical Background A. DefinitionDocumento11 pagineCerebrovascular Accident I. General Medical Background A. Definitionner100% (1)
- Consent Carotid StentingDocumento13 pagineConsent Carotid StentingAbhinav GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- CNS NotesDocumento103 pagineCNS NotesrileyNessuna valutazione finora
- Development of Robots For Rehabilitation Therapy T PDFDocumento13 pagineDevelopment of Robots For Rehabilitation Therapy T PDFManuel Fernando BallesterosNessuna valutazione finora