Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Foot Drop
Caricato da
Saravanan SridharanDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Foot Drop
Caricato da
Saravanan SridharanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
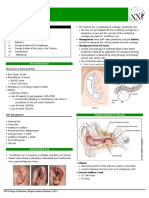
Footdrop Approach Bilateral LMN Peripheral neuropathy (see peripheral neuropathy) UMN Cord lesion Unilateral Once dorsiflexion
flexion impaired Check eversion (Common peroneal nerve = dorsiflex and eversion) Check inversion and plantarflex = posterior tibial nerve If foot drop and inversion and eversion is lost with normal plantarflexion, then L5 nerve root If all gone = posterior tibial+common peroneal, sciatic nerve or plexus/roots Knee flexion intact Go to sensory Peripheral neuropathy Common peroneal nerve palsy (sensory loss over dorsum of the foot) Determine if common peroneal nerve or Deep branch only or The superficial branch only If knee flexion weak, test hip abduction and internal rotation and intact Go to sensory Sciatic nerve If hip abduction and internal rotation is weak Go to sensory Nil = anterior horn cell L4 and L5 dermatome = plexus or root Once site is located, go for the cause Note walking aids Questions Common peroneal nerve palsy (L4 and L5) Anatomy the sciatic nerve divides at the popliteal fossa into the tibial and common peroneal nerves The posterior tibial nerves effects plantar flexion and inversion of the foot The common peroneal nerves winds round the neck of the fibula, covered by s/c tissue and skin only and prone to extrinsic compression It then divides into the Superficial branch: foot everters and sensation to lateral calves and dorsum of the foot Deep branch : toe dorsiflexors and dorsiflexion of the ankle and sensation to the first interdigital web space
Therefore wasting of the peroneous and anterior tibialis muscles; weakness of dorsiflexion of the foot and eversion; foot drop and high steppage gait and loss of sensory over the lateral aspect of the calf and dorsum of the foot Causes of mononeuropathy (3 Sx and 3 Medical causes) Trauma Surgical Compression at the neck of the fibula (habitual leg crossing, cast, brace) Infection Leprosy Inflammatory CIDP Ischaemic - Vasculitis Part of mononeuritis multiplex (Endo, AI, infection, infiltrative and cancer) Ix = NCT and EMG Mx PT/OT 90 degrees splint at night Sx for severed nerve or excision of ganglion Sciatic nerve (L4 L5 S1 S2) Weakness of the knee flexion also Knee jerk is intact but ankle jerks affected and plantar response absent (for common peroneal nerve, all reflexes intact) L5 nerve root Weakness of hip abduction and internal rotation as well as loss of foot inversion (cf with common peroneal nerve)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Normal Paediatric Lab ValuesDocumento6 pagineNormal Paediatric Lab ValuesRITESH SINGH100% (1)
- Sas PDFDocumento2 pagineSas PDFWisnu Surya WardhanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hip Exam-RevDocumento3 pagineHip Exam-RevJennifer LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- InflexibleYogis Flexibility GuideDocumento111 pagineInflexibleYogis Flexibility GuideSarah ChalhoubNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiencing Dance - From Student To Dance Artist (PDFDrive)Documento262 pagineExperiencing Dance - From Student To Dance Artist (PDFDrive)kristof100% (2)
- What Is The History of Reflexology?Documento2 pagineWhat Is The History of Reflexology?Yolanda AllendeNessuna valutazione finora
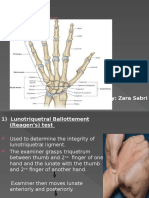
- Physical Examination of The Wrist and Hand. DanielDocumento34 paginePhysical Examination of The Wrist and Hand. DanielCut DianafitriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Qualitative Biomechanical Analysis To IMPROVE TRAININGDocumento28 pagineQualitative Biomechanical Analysis To IMPROVE TRAININGThor Manlangit100% (2)
- A Simple Guide to Ankle Dislocation, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsDa EverandA Simple Guide to Ankle Dislocation, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- Ulnar Nerve EntrapmentDocumento4 pagineUlnar Nerve Entrapmentnavneetsingh86Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bones and Joints TBDocumento19 pagineBones and Joints TBmichaelcylNessuna valutazione finora
- Trans Oto 14 ENT EmergenciesDocumento8 pagineTrans Oto 14 ENT EmergenciesAbegail IbañezNessuna valutazione finora
- EssayDocumento2 pagineEssayFelipe AndinoNessuna valutazione finora
- HealingHabit24-Have A Foot Reflex RegularlyDocumento4 pagineHealingHabit24-Have A Foot Reflex RegularlyJyles SirabNessuna valutazione finora
- LaserDocumento8 pagineLaserALİ YAVUZ KARAHANNessuna valutazione finora
- Pain and Pain Gate Control MechanismDocumento17 paginePain and Pain Gate Control MechanismKapil LakhwaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Lumbar SpineDocumento67 pagineLumbar Spineeashoor100% (4)
- Trismus: Normal Jaw FunctionDocumento5 pagineTrismus: Normal Jaw FunctionKumaran Bagavathi RagavanNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary MRI Knee ImagingDocumento17 pagineSummary MRI Knee ImagingSoban DaudNessuna valutazione finora
- Ankle Examination Orthopaedics McraeDocumento6 pagineAnkle Examination Orthopaedics McraeHafizah HoshniNessuna valutazione finora
- Menisectomy Case StudyDocumento3 pagineMenisectomy Case StudyMiggy SikatNessuna valutazione finora
- Tests of Examination of CervicalDocumento10 pagineTests of Examination of CervicalAde Yahya NasutionNessuna valutazione finora
- Special Tests For WristDocumento13 pagineSpecial Tests For WristSaif Ahmed LariNessuna valutazione finora
- 0011 The Real ReflexologyDocumento2 pagine0011 The Real ReflexologyWAGNER PAULONNessuna valutazione finora
- Rough DraftDocumento12 pagineRough Draftapi-248853282Nessuna valutazione finora
- Leg Ankle Orthopaedic Conditions FinalDocumento26 pagineLeg Ankle Orthopaedic Conditions Finalangel bolfriNessuna valutazione finora
- Nerve Injuries Diagnosis, Evaluation and ManagementDocumento80 pagineNerve Injuries Diagnosis, Evaluation and ManagementjothiNessuna valutazione finora
- Facialpain 150204113108 Conversion Gate01Documento51 pagineFacialpain 150204113108 Conversion Gate01Muhammad IrfanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cervical Spine CYRIAXDocumento16 pagineCervical Spine CYRIAXCarlos TavaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Knee Case Study 1Documento4 pagineKnee Case Study 1superhoofy7186100% (1)
- Fracture Colles Rehabilitation Advice Following WristDocumento4 pagineFracture Colles Rehabilitation Advice Following WristfaprilisaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Arnadi Fraktur & DislokasiDocumento77 pagineDr. Arnadi Fraktur & DislokasiPuji Yunisyah RahayuNessuna valutazione finora
- Traumatic Optic Neuropathy - Prof. N. KarthikeyanDocumento22 pagineTraumatic Optic Neuropathy - Prof. N. KarthikeyanDobrin_Nicolai_8219Nessuna valutazione finora
- H10 Reflexology Infographic 10AM-4 Curativo SansaitDocumento1 paginaH10 Reflexology Infographic 10AM-4 Curativo SansaitGwen Heather CurativoNessuna valutazione finora
- CTEV-Hanum Maftukha ADocumento30 pagineCTEV-Hanum Maftukha ADevi Fitri AryaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Tendon Injuries of Hand: DR Saumya AgarwalDocumento101 pagineTendon Injuries of Hand: DR Saumya AgarwaltesfahuntekletilahunNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoulder Knee WristDocumento110 pagineShoulder Knee Wriststevebravo81100% (1)
- Clinical Features and Diagnosis of FracturesDocumento43 pagineClinical Features and Diagnosis of FracturesChenna Kesava100% (2)
- Glossopharyngeal NeuralgiaDocumento36 pagineGlossopharyngeal NeuralgiaGeetha SoundaryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocumento7 pagineCarpal Tunnel SyndromeNeecel PastoralNessuna valutazione finora
- Claw HandDocumento23 pagineClaw HandAditya Pratama Saanin100% (1)
- Knee Joint Inj and AspirationsDocumento2 pagineKnee Joint Inj and AspirationsUmmu Nur FathonahNessuna valutazione finora
- Cervical PalpationDocumento22 pagineCervical Palpationpraveen100% (12)
- Ankylosing SpondylitisDocumento19 pagineAnkylosing SpondylitisZulhida YuniNessuna valutazione finora
- OOT ROP: Oleh Indri Dan IrwanDocumento15 pagineOOT ROP: Oleh Indri Dan IrwanFarahEzzlynn100% (1)
- Olfactory PathwayDocumento6 pagineOlfactory PathwayJean Pierre Chastre LuzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lumbar Spine CYRIAXDocumento34 pagineLumbar Spine CYRIAXCarlos Tavares100% (1)
- FR MaxillaDocumento5 pagineFR MaxillaJeane SuyantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscle and LigamentDocumento15 pagineMuscle and LigamentPadma VidyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Significance of History Taking Oral SurgeryDocumento32 pagineSignificance of History Taking Oral SurgeryFourthMolar.com0% (1)
- Spondylosis2 PDFDocumento13 pagineSpondylosis2 PDFdrwarigitNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigger FingersDocumento13 pagineTrigger FingersJunarto Putra TandiarrangNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 - Introduction To The Orthopedics (Updated)Documento11 pagine1 - Introduction To The Orthopedics (Updated)Dahir Sani YaAmeerNessuna valutazione finora
- Carpal Tunnel SyndromeDocumento1 paginaCarpal Tunnel SyndromekenthepaNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 AxillaDocumento31 pagine4 AxillaRamesh KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Peripheral Nerve Injury and Repair: Adam Osbourne, 5th Year MedicineDocumento5 paginePeripheral Nerve Injury and Repair: Adam Osbourne, 5th Year Medicineayrahma29Nessuna valutazione finora
- Facial Nerve & Trigeminal NerveDocumento25 pagineFacial Nerve & Trigeminal NerveRafiur RahmanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bab 6 HandDocumento36 pagineBab 6 HandMichael John TedjajuwanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Imaging of Salivary GlandsDocumento87 pagineImaging of Salivary GlandsWalaa Mohamed Hamed100% (1)
- Causes of Hearing LossDocumento2 pagineCauses of Hearing LossTitaniasAppleNessuna valutazione finora
- Facial Nerve Paralysis 2Documento44 pagineFacial Nerve Paralysis 2Omowole GbengaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lumbar Radicular Pain: PathophysiologyDocumento4 pagineLumbar Radicular Pain: PathophysiologynetifarhatiiNessuna valutazione finora
- OSTEOMYELITISDocumento5 pagineOSTEOMYELITISArafat Masud Niloy100% (1)
- What Is Dry Needling MaDocumento6 pagineWhat Is Dry Needling MaElanghovan ArumugamNessuna valutazione finora
- A Simple Guide to Meniscus with Acl Injury, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsDa EverandA Simple Guide to Meniscus with Acl Injury, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNessuna valutazione finora
- StomasDocumento4 pagineStomasSaravanan Sridharan100% (1)
- Myasthenia GravisDocumento2 pagineMyasthenia GravisSaravanan SridharanNessuna valutazione finora
- Renal IndicesDocumento6 pagineRenal IndicesSaravanan SridharanNessuna valutazione finora
- Kerning and Brudzinski-MeningitaDocumento2 pagineKerning and Brudzinski-MeningitaDobre CristinaNessuna valutazione finora
- CrutchDocumento135 pagineCrutchYahia Tawfeek AlkilanyNessuna valutazione finora
- Thoracic and Lumbar Pain and Stiffness - M. Suresh SchlangerDocumento26 pagineThoracic and Lumbar Pain and Stiffness - M. Suresh Schlangerscason9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Orif Patella Fracture Rehab ProtocolDocumento1 paginaOrif Patella Fracture Rehab ProtocolHanna RikaswaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Va SPH Guidebook For Facility Champions and CoordinatorsDocumento166 pagineVa SPH Guidebook For Facility Champions and CoordinatorsjonoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ot Goals NuevoDocumento157 pagineOt Goals NuevoElbania PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- 0868 Upper Limb OrthosesDocumento68 pagine0868 Upper Limb OrthosesJose Jaramillo100% (1)
- Module in MidtermDocumento19 pagineModule in MidtermPaulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Anatomy 7th Edition Martini Test BankDocumento45 pagineHuman Anatomy 7th Edition Martini Test Banklaeliacaixpoyf100% (29)
- DOPS Revision - Orthopaedic TestingDocumento38 pagineDOPS Revision - Orthopaedic TestingDr-Syed Hammad Hussain-GilaniNessuna valutazione finora
- (REHAB) Supplemental UE, LE, and Spine Special Tests (B2022)Documento8 pagine(REHAB) Supplemental UE, LE, and Spine Special Tests (B2022)Jolaine ValloNessuna valutazione finora
- Knee OsteoarthritisDocumento21 pagineKnee OsteoarthritisSEAN JERIMIAH AGBAYANINessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Pain and Impaired Skin Integrity PostopDocumento9 pagineAcute Pain and Impaired Skin Integrity PostopKach Kurrs0% (1)
- Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita-Dr S P DasDocumento7 pagineArthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita-Dr S P DasSheel GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- סיכום לבוחן מבואות ברדיוגרפיהDocumento6 pagineסיכום לבוחן מבואות ברדיוגרפיהLubi Dubi DooNessuna valutazione finora
- 123 - PE1 - Lesson Proper For Week 15Documento9 pagine123 - PE1 - Lesson Proper For Week 15Mark Jerome AlbanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Management of Limb Injuries in Adults and Children Over 2 YearsDocumento17 pagineManagement of Limb Injuries in Adults and Children Over 2 YearsjustforuroNessuna valutazione finora
- Rehab Med Recalls PDFDocumento4 pagineRehab Med Recalls PDFmpcsoletaNessuna valutazione finora
- Analisa Gerak: W. Prasasti Mutiadesi, M.DDocumento54 pagineAnalisa Gerak: W. Prasasti Mutiadesi, M.DSastiy MutiadesieNessuna valutazione finora
- Lower Extremity Prosthesis Part IIDocumento98 pagineLower Extremity Prosthesis Part IIsjs6r8wwv9Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hamstring Strain Injuries JOSPTDocumento18 pagineHamstring Strain Injuries JOSPTHugo FalquetoNessuna valutazione finora
- CASE REPORT Hip DislocationDocumento42 pagineCASE REPORT Hip DislocationvereriNessuna valutazione finora
- ShoulderDocumento17 pagineShoulderNehaNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 QEC SlidesDocumento34 pagine5 QEC SlidesKLINIK UNG CENDERAWASIHNessuna valutazione finora
- Musculoskeletal System AssessmentDocumento75 pagineMusculoskeletal System AssessmentRolinette DaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Ryan J. Warth, Peter J. Millett Auth. Physical Examination of The Shoulder An Evidence-Based ApproachDocumento280 pagineRyan J. Warth, Peter J. Millett Auth. Physical Examination of The Shoulder An Evidence-Based ApproachAndrei R Lupu100% (1)