Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Bones of The Abdominal Region
Caricato da
yachiru121Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Bones of The Abdominal Region
Caricato da
yachiru121Copyright:
Formati disponibili
www.1aim.
net
Anatomy Tables - Bones of the Abdominal Region
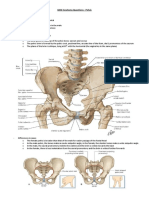
Bone Structure Description Notes paired; the os coxae forms the lateral part of one of three bones the pelvis; it is formed that form the by three fused bones: pelvis ischium, ilium & pubis; also known as the innominate bone acetabulum means vinegar cup; it is the socket for the head of a cup-shaped the femur; it is formed depression in the acetabulum by the: ilium (1/5), lateral surface of ischium (2/5) and pubis the os coxae bone (2/5); the acetabular fossa lies in the floor of the acetabulum it is spanned by the transverse acetabular ligament; the a notch in the acetabular br. of the inferior margin of obturator a. enters the the acetabulum hip joint by passing through the acetabular notch a roughened depression in the center of the acetabulum the ligament of the head of the femur occupies the acetabular fossa
os coxae
acetabular notch
acetabular fossa
lunate the smooth surface of articular surface the of the acetabulum acetabulum
the lunate surface surrounds the acetabular fossa and the acetabular notch obturator means to occlude or stop up, a reference to the fact that the obturator membrane closes the obturator foramen almost completely; a site of attachment for the obturator externus m. and the obturator internus m. one of three bones that form the os coxae: ilium, ischium, pubis; its body forms 1/5 of the acetabulum; its symphyseal surface unites with the pubis of the opposite side to form the pubic symphysis; the superior and inferior pubic rami participate in the formation of the obturator foramen the body of the pubis forms about 1/5 of the acetabulum
obturator foramen
a large foramen formed by the pubic and ischial rami
pubis
an angulated bone the forms the anterior part of the pelvis
body
superolateral portion of the pubis
pubic crest
ridge on the attachment of rectus superior border of abdominis & the superior ramus pyramidalis mm.
pubic tubercle superior ramus
process at the lateral end of pubic crest superior "limb" that passes medially from the body of the pubis
attachment point of the medial end of the inguinal ligament articulates with the superior ramus of the opposite side at the pubic symphysis
pecten
ridge on superior attachment point of the surface of the pectineal ligament superior pubic ramus inferior "limb" that passes inferolaterally from the pubic symphysis groove on the inferior surface of the superior pubic ramus articulates with the ischial ramus to form the ischiopubic ramus; attachment site for the root of the penis (clitoris) marks the area of passage of the obturator vessels and n. in the obturator canal
inferior ramus
obturator groove
ischium
the "V"- shaped one of the three bones bone that forms that form the os coxae: the posteroinferior ilium, ischium, pubis part of the pelvis ischial ramus the limb of the ischium that passes anteriorly and superomedially toward the pubis it articulates with the inferior ramus of the pubis
body
the part of the it articulates with the ischium that ilium and the pubis at participates in the the acetabulum; the
formation of the acetabulum ischial tuberosity the roughened projection that protrudes posteroinferiorly from the body of the ischium
body of the ischium forms 2/5 of the acetabulum it is the site of attachment of the sacrotuberous ligament; it is the site of origin of the inferior gemellus m., quadratus femoris m. and the hamstring mm. (semitendinosus, semimembranosus, long head of biceps femoris, ischiocondylar portion of the adductor magnus) the lesser sciatic notch is converted to the lesser sciatic foramen by the sacrospinous ligament and the sacrotuberous ligament it is the site of attachment of the sacrospinous ligament and the site of origin of the superior gemellus m.
lesser sciatic the notch located notch between the ischial tuberosity and the ischial spine ischial spine the spine that arises just superior to the lesser sciatic notch
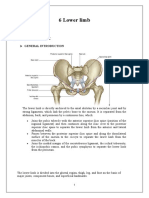
ilium
fan-shaped bone one of three bones that that forms the form the os coxae: lateral ilium, ischium, pubis prominence of the pelvis body the portion of the the body of the ilium
ilium that forms 2/5 of the participates in the acetabulum formation of the acetabulum iliac crest arching superior attachment for edge the ilium abdominal wall that forms the rim muscles of the "fan" broad depression iliac fossa is part of the on the medial false (greater) pelvis surface of the ilium roughened area along the outer edge of the iliac crest spine at the lateral attachment of anterior end of the the inguinal ligament iliac crest spine at the posterior end of the iliac crest position marked by a dimpling of the skin inferior boundary of the iliac fossa; marks the plane of transition from abdominal cavity to pelvic cavity
iliac fossa
iliac tubercle
anterior superior iliac spine posterior superior iliac spine
arcuate line ridge running from anteroinferior to posterosuperior on the inner surface of the ilium sacrum a triangular bone that is the posterior skeletal element forming the pelvis
it is formed by 5 fused vertebrae; the sacrum and two os coxae bones form the pelvis
base
the superior part of the sacrum
the base of the sacrum includes the articular surface for the fifth lumbar vertebra and the superior portion of the two ala the body of the fifth lumbar vertebra sits on the sacral promontory and articulates with it through a symphysis
promontory a projection of the superior part of the sacrum in an anterior direction ala
the lateral portion paired; it projects of the sacrum laterally from the body of the sacrum; it represents the fused costal and transverse processes of the first sacral vertebra an opening in the there are four pairs; anterior surface of each transmits the the sacrum ventral primary ramus of the respective sacral spinal nerve; branches of the lateral sacral aa. Enter the sacral canal through these openings an opening in the there are four pairs; posterior surface each transmits the of the sacrum dorsal primary ramus of the respective sacral spinal nerve
anterior sacral foramina
posterior sacral foramina
sacral canal the opening in the it is the continuation of center of the the vertebral canal at sacrum sacral vertebral levels
sacral hiatus an opening in the posterior surface of the sacrum in the midline
it is a normal feature that results from the failure of fusion of the laminae of the fifth sacral segment (and sometimes the fourth) during development
articular surface
the roughened this surface articulates area located on with the ilium in the the lateral surface sacroiliac articulation of the sacrum the central portion the body is equivalent of the sacrum to the bodies of the other vertebra the superior surface of the sacrum the base of the sacrum articulates with the fifth lumbar vertebra through an intervertebral disk
body
base
coccyx
the most inferior the coccyx results from portion of the the fusion of the four vertebral column coccygeal vertebrae; it may be a single bone or the first coccygeal vertebra may be separated from the other three; it articulates with the fifth sacral segment; coccygeal vertebrae are reduced in complexity, having no pedicles, laminae or spines
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Abrsm PiaAbrsm Piano Grade 2 No Grade 2 2011 2012Documento14 pagineAbrsm PiaAbrsm Piano Grade 2 No Grade 2 2011 2012Podpang Kornchum93% (41)
- Assess Notes Nursing AssessmentDocumento206 pagineAssess Notes Nursing Assessmenttostc100% (7)
- Final Obstetrics and GynacologyDocumento88 pagineFinal Obstetrics and Gynacologysis8100% (2)
- The Influence of Bones and Muscles on FormDa EverandThe Influence of Bones and Muscles on FormValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- The Durability Code Prime Week 1, Day 1 - Lower BodyDocumento4 pagineThe Durability Code Prime Week 1, Day 1 - Lower BodyTomNessuna valutazione finora
- List BonesDocumento38 pagineList Bonesshahera rosdiNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of The Female Pelvis FinalDocumento209 pagineAnatomy of The Female Pelvis FinalMignot Aniley86% (14)
- Anatomy of The Female PelvisDocumento60 pagineAnatomy of The Female PelvisMignot AnileyNessuna valutazione finora
- Hip Joint Anatomy - Overview, Gross AnatomyDocumento14 pagineHip Joint Anatomy - Overview, Gross AnatomyZuraedha ZamilNessuna valutazione finora
- AstmDocumento29 pagineAstmMohd Zulfadli Mohamad IzaraeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Alan Dundes Into The EndzoneDocumento15 pagineAlan Dundes Into The Endzonev6mazda6100% (3)
- Cardiogenic ShockDocumento21 pagineCardiogenic ShockIslamOteshNessuna valutazione finora
- Obstetrics and Gynecology Ebook Notes PDFDocumento89 pagineObstetrics and Gynecology Ebook Notes PDFGaurav ShyamaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Bacteriology ReviewDocumento47 pagineBacteriology ReviewDeti ParidlahNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Hip BoneDocumento8 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of The Hip BoneBeGie MamBaNessuna valutazione finora
- Presented By, Mrs - Amita Shilpa GottliebDocumento42 paginePresented By, Mrs - Amita Shilpa GottliebGiritama IrwantoroNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Hip BoneDocumento2 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of The Hip BoneNkk Aqnd MgdnglNessuna valutazione finora
- Positioning, Staggering and Who Covers What Shot in Doubles by - Gigi Fernandez TennisDocumento11 paginePositioning, Staggering and Who Covers What Shot in Doubles by - Gigi Fernandez TennisHUy100% (1)
- Curs Pelvis PerineuDocumento101 pagineCurs Pelvis PerineuCiprianTeodorulNessuna valutazione finora
- Cat and Mouse StoryDocumento28 pagineCat and Mouse Storyعبد الرحمن100% (3)
- Maternal Pelvis Fetal Skull PDFDocumento13 pagineMaternal Pelvis Fetal Skull PDFAnuradha Maurya100% (2)
- Occupational ProfileDocumento21 pagineOccupational Profileapi-308033434100% (1)
- Sphenoid BoneDocumento76 pagineSphenoid BoneLALITH SAI KNessuna valutazione finora
- Female PelvisDocumento7 pagineFemale PelvissubashikNessuna valutazione finora
- Seminar On Female Pelvis and Pelvic FloorDocumento11 pagineSeminar On Female Pelvis and Pelvic FloorJasmin SabnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hose Management Guide: SN: Agc Lines Group - AttachmentDocumento42 pagineHose Management Guide: SN: Agc Lines Group - AttachmentJose luis Consuegra100% (1)
- Callan Kids Level1bDocumento10 pagineCallan Kids Level1bThanh TranNessuna valutazione finora
- HandbookDocumento60 pagineHandbookyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bones of The Pelvis and PerineumDocumento6 pagineBones of The Pelvis and Perineumyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bones of The Lower LimbDocumento15 pagineBones of The Lower Limbyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- By DR M Vijaya BhushanamDocumento26 pagineBy DR M Vijaya Bhushanamwar_ruinzNessuna valutazione finora
- Bones of The Back RegionDocumento9 pagineBones of The Back Regionyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bones of The The RegionDocumento51 pagineBones of The The RegionjazzyNessuna valutazione finora
- Gluteal RegionDocumento66 pagineGluteal Regionashley nicholeNessuna valutazione finora
- Lower LimbDocumento25 pagineLower LimbNandhana Kattuparambil SunojNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Tables For Today's Topic: Bones of The Abdominal WallDocumento12 pagineAnatomy Tables For Today's Topic: Bones of The Abdominal WallRocci Jack ParseNessuna valutazione finora
- A 7Documento2.234 pagineA 7Rao AfrasiabNessuna valutazione finora
- Pdfs/residency/anatomy/ Normal-Anatomy-And-Physiology-Of-The-Female-PelvisDocumento34 paginePdfs/residency/anatomy/ Normal-Anatomy-And-Physiology-Of-The-Female-PelvisMohamed FarahatNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Research Paper PelvisDocumento4 pagineAnatomy Research Paper PelvisBasil AdeelNessuna valutazione finora
- 6 Lower LimbDocumento19 pagine6 Lower LimbMOHAMMED BIN BAREKNessuna valutazione finora
- LowerLimbExam NurDocumento108 pagineLowerLimbExam Nuralina nguynNessuna valutazione finora
- Region of The HipDocumento16 pagineRegion of The HipMosa AljohaniNessuna valutazione finora
- The Back: Cortez Gomez Lucas VillafuerteDocumento53 pagineThe Back: Cortez Gomez Lucas VillafuerteFlorenze Laiza Donor LucasNessuna valutazione finora
- FemalepelvispptDocumento42 pagineFemalepelvispptYeni LaelasariNessuna valutazione finora
- Bony Pelvis, Inguinal Canal, Inguinal HerniasDocumento12 pagineBony Pelvis, Inguinal Canal, Inguinal HerniasDanielNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.2 20hip 20anatomyDocumento85 pagine1.2 20hip 20anatomyKhushboo IkramNessuna valutazione finora
- Worku Antomy and Physiology of Reproductive OrganDocumento206 pagineWorku Antomy and Physiology of Reproductive OrganMignot AnileyNessuna valutazione finora
- The Pelvic Girdle: By/Dr - Abdisamad Omar AliDocumento30 pagineThe Pelvic Girdle: By/Dr - Abdisamad Omar AliSAKARIYE MAXAMEDNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy CaseDocumento2 pagineAnatomy CaseNaomi NicoleNessuna valutazione finora
- Bony Pelvis and Pelvic FloorDocumento73 pagineBony Pelvis and Pelvic Floormamai elijahNessuna valutazione finora
- Posterior Cervical Anatomy and Surgical ApproachesDocumento11 paginePosterior Cervical Anatomy and Surgical ApproachesVõ Văn Phúc ToànNessuna valutazione finora
- Os CoxaeDocumento11 pagineOs CoxaeKNessuna valutazione finora
- Osteology BonesDocumento48 pagineOsteology BonesÂhmęd ĐoolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Bones of The Upper LimbDocumento14 pagineBones of The Upper Limbyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- LP - nr.2-dr. Ispas The Columna Vertebralis: The Corpus Vertebrae (Vertebral Body) Possesses An Upper and A Lower SurfaceDocumento7 pagineLP - nr.2-dr. Ispas The Columna Vertebralis: The Corpus Vertebrae (Vertebral Body) Possesses An Upper and A Lower Surfaceinna3003Nessuna valutazione finora
- Scapula HumerusDocumento7 pagineScapula HumerussujsamNessuna valutazione finora
- Lower LimbpostgDocumento79 pagineLower LimbpostgBuya kasahunNessuna valutazione finora
- ЧерепDocumento34 pagineЧерепbekafop813Nessuna valutazione finora
- Last's Anatomy - Pelvis Annotated Question BankDocumento90 pagineLast's Anatomy - Pelvis Annotated Question BankHarriott MaixnerNessuna valutazione finora
- Back Pain PDFDocumento40 pagineBack Pain PDFsana shiekhNessuna valutazione finora
- The Pelvis: Assignment OnDocumento40 pagineThe Pelvis: Assignment OnSubhada GosaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Bones of Lower Limb: 1. Pelvic Bone (Hip Bone)Documento9 pagineBones of Lower Limb: 1. Pelvic Bone (Hip Bone)Zaid AbdulqadirNessuna valutazione finora
- April 12 Bony PelvisDocumento43 pagineApril 12 Bony PelvisFranz SalazarNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemDocumento41 pagineAnatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemMahad Maxamed AxmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Pelvis: Navigation SearchDocumento8 paginePelvis: Navigation SearchHelen McClintockNessuna valutazione finora
- The Female Pelvis: Namasinga JoyceDocumento79 pagineThe Female Pelvis: Namasinga JoyceNamaganda NajjatiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Pelvic GirdleDocumento22 pagineThe Pelvic GirdleJudithNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 17 PelvicDocumento21 pagineChapter 17 PelvicpoNessuna valutazione finora
- Articulations of The PelvisDocumento4 pagineArticulations of The PelvisSiva ShanmugamNessuna valutazione finora
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocumento36 pagineOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreYoAmoNYCNessuna valutazione finora
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocumento36 pagineOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreabctutorNessuna valutazione finora
- Middle Cranial FossaDocumento5 pagineMiddle Cranial Fossaalexandra663Nessuna valutazione finora
- API Review Muscles f2009Documento1 paginaAPI Review Muscles f2009yachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Thorax ReviewDocumento18 pagineAnatomy Thorax Reviewyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology I Fall 2009 Exam I Study GuideDocumento1 paginaAnatomy and Physiology I Fall 2009 Exam I Study Guideyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Levels and Planes ReviewDocumento3 pagineAnatomy Levels and Planes Revieware4erNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Lower Extr ReviewDocumento12 pagineAnatomy Lower Extr Reviewabuzeid5Nessuna valutazione finora
- First Aid ManualDocumento225 pagineFirst Aid ManualHugo MartinsNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology Unit III: Objectives/RationaleDocumento16 pagineAnatomy and Physiology Unit III: Objectives/Rationaleyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- AP Review NotesDocumento15 pagineAP Review Notesyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Head ReviewDocumento34 pagineAnatomy Head ReviewJordan BrooksNessuna valutazione finora
- Bones of The Upper LimbDocumento14 pagineBones of The Upper Limbyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- DEPED - The K To 12 Basic Education Programv2 - 2012Documento38 pagineDEPED - The K To 12 Basic Education Programv2 - 2012yachiru121100% (1)
- DEPED 2012 - K TO 12 - MTB RationaleDocumento30 pagineDEPED 2012 - K TO 12 - MTB Rationaleyachiru121100% (3)
- Anatomy Tables - Bones of The Thorax: Bone Structure Description Notes RibDocumento3 pagineAnatomy Tables - Bones of The Thorax: Bone Structure Description Notes Ribyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bones and Cartilages of The Head and NeckDocumento27 pagineBones and Cartilages of The Head and Neckyachiru121100% (1)
- DEPED 2012 - K TO 12 - Learning DR VillanezaDocumento32 pagineDEPED 2012 - K TO 12 - Learning DR Villanezayachiru121100% (1)
- DEPED 2012 - K TO 12 - L1-L2-L3-Dr. GironDocumento56 pagineDEPED 2012 - K TO 12 - L1-L2-L3-Dr. Gironyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- DEPED 2012 - Classroom DR VillanezaDocumento17 pagineDEPED 2012 - Classroom DR Villanezayachiru121100% (1)
- DEPED - K To 12 Assessment & Rating - 2012Documento44 pagineDEPED - K To 12 Assessment & Rating - 2012yachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- GHCPregistrationform 2012Documento1 paginaGHCPregistrationform 2012yachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- HandbookDocumento53 pagineHandbookyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- HandbookDocumento48 pagineHandbookyachiru121100% (1)
- DTH Tubex Specification Sheet EnglishDocumento1 paginaDTH Tubex Specification Sheet EnglishkrishkpeNessuna valutazione finora
- Guia Alpes SuicosDocumento12 pagineGuia Alpes SuicosbjotadfNessuna valutazione finora
- Albert R Kopsick Bio AwardsDocumento1 paginaAlbert R Kopsick Bio Awardsark6of7Nessuna valutazione finora
- Memphis Travel GuideDocumento16 pagineMemphis Travel Guideapi-664453460Nessuna valutazione finora
- English & Songs - Ejercicios de Inglés Con Letras de Canciones en Inglés - Listening ExercisesDocumento2 pagineEnglish & Songs - Ejercicios de Inglés Con Letras de Canciones en Inglés - Listening ExercisesdancruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Great Yoga PDFDocumento24 pagineGreat Yoga PDFGuyenne NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Gensou Narratograph 13.10.2023Documento219 pagineGensou Narratograph 13.10.2023Всевид Альбертович РуденкоNessuna valutazione finora
- BVA Masters 2022 VýsledkyDocumento102 pagineBVA Masters 2022 VýsledkyJan PotůčekNessuna valutazione finora
- KGE2000 TiDocumento2 pagineKGE2000 TifernandollorentegNessuna valutazione finora
- Basketball Defense Syracuse 2-3 ZoneDocumento3 pagineBasketball Defense Syracuse 2-3 ZoneEmmanuel SaravasNessuna valutazione finora
- Dana 60-F Dana 60 Dana 70Documento2 pagineDana 60-F Dana 60 Dana 70Zé MirtoNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Learn Kung Fu at HomeDocumento8 pagineHow To Learn Kung Fu at Homesunita barwarNessuna valutazione finora
- HOPE 4 - Q4 - Week6Documento2 pagineHOPE 4 - Q4 - Week6Maria Mae L. OrioqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Jammie's DietDocumento6 pagineJammie's DietStefi CohenNessuna valutazione finora
- Kit de Montaje para CilindrosDocumento2 pagineKit de Montaje para CilindrossandraNessuna valutazione finora
- 2611657-t2k - NPC Generator v1.1.7Documento18 pagine2611657-t2k - NPC Generator v1.1.7AntônioNessuna valutazione finora
- Catálogo Ingersoll RandDocumento21 pagineCatálogo Ingersoll RandLukas EzequielNessuna valutazione finora
- Inclusive Education A2 Case StudyDocumento8 pagineInclusive Education A2 Case Studyapi-408345354Nessuna valutazione finora
- Active Passive VoiceDocumento7 pagineActive Passive VoiceParth RathodNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 PPP4 Keys To Transcriptions in The BookDocumento6 pagine2 PPP4 Keys To Transcriptions in The Booksandrago75Nessuna valutazione finora