Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Bones and Cartilages of The Head and Neck
Caricato da
yachiru121Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Bones and Cartilages of The Head and Neck
Caricato da
yachiru121Copyright:
Formati disponibili
www.1aim.
net
Anatomy Tables - Bones and Cartilages of the Head and Neck - Listed Alphabetically
Bone/Cartilage arytenoid cartilage Structure Description a pyramid shaped cartilage located on the superior margin of the cricoid lamina Notes paired; each is connected to the epiglottis above via the aryepiglottic m. and to the thyroid cartilage anteriorly via the vocal ligament; paired arytenoid cartilages are pulled together (adducted) by the arytenoid m. corniculate cartilage is found in the base of the aryepiglottic fold; it is yellow elastic cartilage connected: above to the thyroid cartilage via the inferior horn of the thyroid cartilage, to the conus elasticus, to the arytenoid cartilages which sit atop the lamina; connected below to the first tracheal ring via the cricotracheal ligament
corniculate cartilage
a small cartilage located on the apex of the arytenoid cartilage the inferior & posterior cartilage of the larynx; it forms a complete cartilaginous ring; its arch projects anteriorly and its lamina is broad and flat posteriorly
cricoid cartilage
cuneiform cartilage
small cuneiform cartilage cartilaginous is yellow elastic nodule located in cartilage the aryepiglottic fold the superior part epiglottic cartilage of the larynx is covered by a mucous membrane delicate bone located between the two orbits highly pneumatized bone that contains the ethmoid air cells; forms the fragile medial wall of the orbit
epiglottis
ethmoid
cribriform plate
perforated perforated for portion of passage of the ethmoid bone on olfactory nerves either side of the crista galli superior midline projection of the ethmoid bone into the anterior cranial fossa; it arises between the cribriform plates "cock's comb"; anterior anchor point of the falx cerebri
crista galli
perpendicular plate
midline process forms the superior projecting part of the bony inferiorly into the nasal septum nasal cavity medial projection of the ethmoid bone from the superolateral wall of the nasal cavity portion of the forms the superior nasal meatus below it and the sphenoethmoidal recess above it forms the superior
superior nasal concha
middle nasal
concha
ethmoid bone that projects inferomedially from the lateral wall of the nasal cavity
nasal meatus above it and the middle nasal meatus (which overlies the bulla ethmoidalis and hiatus semilunaris) below it located under cover of the middle nasal concha; middle ethmoidal air cells drain at its apex three groups may be identified: anterior (drain into the hiatus semilunaris in the middle nasal meatus), middle (drain onto the apex of the bulla ethmoidalis in the middle nasal meatus), posterior (drain into the superior nasal meatus) transmits anterior ethmoidal vessels and nerve transmits posterior ethmoidal vessels and nerve receives the frontonasal duct anterosuperiorly, opening of the maxillary sinus posteroinferiorly, and the openings of
bulla ethmoidalis rounded elevation on the lateral wall of the nasal cavity ethmoidal air cells pneumatized spaces (3-18 in number) within the ethmoid bone; located between the orbits
ethmoidal opening in the foramen, anterior medial wall of the orbit ethmoidal foramen, posterior hiatus semilunaris opening in the medial wall of the orbit groove in the ethmoid portion of the lateral nasal wall between the uncinate process below and bulla
ethmoidalis above frontal the anterior bone of the skull which underlies the forehead
the anterior ethmoidal air cells in between articulates with the parietal bone posteriorly; zygomatic, ethmoid and sphenoid bones inferiorly; maxilla, nasal and lacrimal bones anteriorly; it is formed from two ossifications centers which normally fuse in the midline - if they do not fuse, a midline "metopic suture" is the result a very thin portion of the frontal bone which is like an egg shell in thickness
orbital plate
flat portion of frontal that forms the roof of the orbit
foramen cecum
opening near the transmits an anterior end of emissary vein which the crista galli may result in transfer of infectious materials from the nasal cavity to the cranial cavity with resulting meningitis pneumatized space in the frontal bone usually paired; each drains through the frontonasal duct into the uppermost part of the hiatus semilunaris in the middle nasal meatus skin over this region
frontal sinus
superior orbital
arch of bone
margin
above the orbital is supplied by opening branches of the frontal nerve (supraorbital and supratrochlear nn.)
superciliary arch the ridge of bone located deep to the above the orbital eyebrow, blunt margin trauma to this region often results in cuts within the eyebrow glabella midline point between the paired superciliary arches notch in the superior orbital margin occasionally present as a foramen; opening for the passage of the for supraorbital neurovascular bundle the hyoid bone ossifies completely in middle life; the body articulates with the greater horns via cartilage and with the lesser horns via fibrous joints prior to ossification; an important site for muscle attachments (suprahyoid and infrahyoid muscle groups) the body of the
supraorbital notch
hyoid
a "U"-shaped bone consisting of several parts: body, 2 greater horns, 2 lesser horns
body
the middle
portion of the hyoid bone "U"-shaped bone articulates with the greater horns posteriorly greater horn (cornu) posteriorly directed limbs of the "U"-shaped bone each greater horn articulates with the body and lesser horns anteriorly; origin of middle pharyngeal constrictor m. and hyoglossus m. the inferior end of the stylohyoid ligament attaches to the lesser horn it articulates with the maxilla; forms the inferior nasal meatus below it and the middle nasal meatus above it articulates: anteriorly with frontal process of maxilla, superiorly with frontal bone, posteriorly with ethmoid, inferiorly with orbital process of maxilla; forms part of the canal for the nasolacrimal duct
lesser horn (cornu)
articulates with the greater horn at its junction with the body a separate bone on the lateral wall of the nasal cavity
inferior nasal concha
lacrimal
small bone forming part of the medial wall of the orbit
mandible
the U-shaped contains the inferior bone forming the teeth; formed from lower jaw the mesenchyme of the 1st pharyngeal arch, and its
muscles are innervated by the nerve of the 1st arch (mandibular division of cranial nerve V) body the anterior part of the mandible paired halves are fused in the midline at the symphysis menti the two halves of the mandible fuse during the first postnatal year the bone of the chin; mental means relating to the mind, a reference to the act of resting the chin on the hand while thinking (see the sculpture by Rodin: "The Thinker") attachment site for the genioglossus and geniohyoid mm.
symphysis menti the midline symphysis between the two halves of the mandible mental protuberance the projection on the anterior midline of the mandible
mental spines the spines on the (genial tubercles) inner surface of the mandible posterior to the mental protuberance mylohyoid line the ridge running obliquely from posterosuperior to anteroinferior on the medial surface of the body of the mandible
attachment site for the mylohyoid muscle; the submandibular gland is located inferior to this line and the sublingual gland is located
superior to this line mental foramen the opening on the anterior surface of the body of the mandible inferior to the premolar teeth the angled portion of the mandible that joins the posterior portion of the body transmits the mental neurovascular bundle; covered superficially by the depressor anguli oris and depressor labii inferioris mm. it rises nearly vertically from the body; the chondyloid process and the coronoid process extend from the superior end of the ramus; the mandibular foramen is located on the medial surface of the ramus; the medial pterygoid m. attaches to the medial surface and the masseter m. attaches to the lateral surface of the ramus
ramus
angle
the posteroinferior bend formed by the union of the body and the ramus the opening on the medial surface of the ramus it is the opening into the mandibular canal; it transmits the inferior alveolar neurovascular bundle
mandibular foramen
mandibular canal the canal that runs through the body of the mandible
it transmits the inferior alveolar neurovascular bundle from the infratemporal fossa to the mandibular teeth and gingivae it is the attachment site of the inferior end of the sphenomandibular ligament
lingula
the projection of bone medial to the mandibular foramen
coronoid process the process that it is the attachment projects site of the anterosuperiorly temporalis m. from the ramus of the mandible condylar process the rounded process that projects posterosuperiorly from the ramus of the mandible mandibular notch the notch between the coronoid and condylar processes it articulates with the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone
it transmits the masseteric neurovascular bundle from the infratemporal fossa to the deep surface of the masseter m. part of the lateral pterygoid m. inserts into the pterygoid fossa of the mandibular neck
mandibular neck the constriction below the articular chondyle on the chondylar process of the mandible pterygoid fossa of the neck
a shallow part of the lateral depression on the pterygoid m. inserts
anterior surface into the pterygoid of the neck of the fossa of the mandible mandibular neck maxilla bone forming the it forms the inferior midface orbital margin and contains the teeth and maxillary sinus frontal process the part of the maxilla that projects superiorly medial to the orbit it articulates with the nasal bone, the frontal bone and the lacrimal bone; it forms part of medial orbital wall & margin; it forms the anterior part of the canal for the nasolacrimal duct also known as the orbital surface of the maxilla; it contains the infraorbital groove and canal; it forms the roof of the maxillary sinus
orbital process
the part of the maxilla that forms the floor of the orbit
zygomatic process infraorbital groove
the lateral it articulates with projection of the the zygomatic bone maxilla groove in orbital process of the maxilla located in the posterior part of the orbit transmits the infraorbital neurovascular bundle from the infraorbital fissure to the infraorbital canal the direct continuation of the infraorbital groove; transmits the
infraorbital canal canal in orbital process of the maxilla located in the anterior
part of the orbit
infraorbital neurovascular bundle from the infraorbital groove to the infraorbital foramen it transmits the infraorbital neurovascular bundle
infraorbital foramen
opening at the anterior end of the infraorbital canal located inferior to the orbit
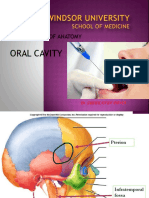
alveolar process "U"-shaped process of bone that holds the maxillary teeth maxillary tuberosity the roughened posterior aspect of the body of the maxilla
contains sockets (alveoli) for the roots of the maxillary teeth the posterior superior alveolar nn. Enter the maxilla directly superior to this structure the cartilaginous part of the nasal septum sits atop this structure
anterior nasal spine
anterior projection of bone in the midline, inferior to the anterior nasal aperture pneumatized hollow center of the body of the maxilla
maxillary sinus
paired; each maxillary sinus drains through the hiatus semilunaris into the middle nasal meatus paired; together, they form the roof of the oral cavity (hard palate) and the floor of the
palatine process
shelf of bone that projects horizontally to meet at the midline in the
intermaxillary suture incisive foramen opening in the midline, posterior to the maxillary incisor teeth
nasal cavity it transmits the terminal branches of the nasopalatine nn. & sphenopalatine aa.; it marks the point of union during development of the primary and secondary palate articulates with the frontal bone superiorly, the frontal process of the maxilla laterally and the contralateral nasal bone medially it articulates superolaterally with the parietal bones through the lambdoid suture, anteroinferiorly with the temporal bone and anteriorly with the body of the sphenoid bone attachment site for the superior pharyngeal constrictor m. it articulates with the petrous part of the temporal bone anteroinferiorly and the parietal bones superolaterally at the lambdoid suture
nasal
thin bone that forms part of the bridge of the nose
occipital
the bone forming the posterior surface of the skull
pharyngeal tubercle
projection located anterior to the foramen magnum the flat, thin portion of the occipital bone located posterior to the foramen magnum
squamous part
external occipital a projection on protuberance the external surface of the squamous part of the occipital bone in the midline inferior nuchal line
it is the attachment site of the ligamentum nuchae and the trapezius m.; its highest point is called the inion
a low ridge that it is an attachment runs transversely site for deep neck on the external muscles surface of the squamous part of the occipital bone inferior to the superior nuchal line a low ridge that runs transversely on the external surface of the squamous part of the occipital bone the opening in the occipital bone posterior to the basal part it is the attachment is the for the trapezius and splenius mm.
superior nuchal line
foramen magnum
it transmits the spinal cord, two vertebral aa., and two spinal accessory nerves
basal part
the portion of the it articulates with occipital bone the body of the located anterior sphenoid bone to the foramen magnum the portion of the occipital bone located lateral to the foramen magnum paired; it is pierced by the hypoglossal canal and the condylar canal
lateral part
hypoglossal
an opening in the paired; it transmits
canal condylar canal
lateral part of the the hypoglossal occipital bone nerve an opening in the paired; it transmits lateral part of the the condylar occipital bone emissary vein
occipital condyle a low, wide paired; it articulates projection from with the atlas the inferior surface of the lateral part of the occipital bone jugular notch a notch located on the anterolateral edge of the lateral part of the occipital bone a chain of three bones in the tympanic cavity (middle ear) connecting the tympanic membrane to the oval window; arranged from lateral to medial: malleus, incus, stapes incus the middle ossicle of the middle ear it forms the posterior margin of the jugular foramen; the temporal bone forms the anterior margin of the jugular foramen the ossicles are joined by synovial articulations that may become arthritic in old age, resulting in conductive deafness
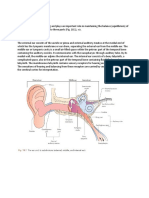
ossicles
articulates with the head of the malleus and the head of the stapes; incus means "anvil"
malleus
the lateral ossicle the manubrium is of the middle ear attached by its handle to the inner surface of the
tympanic membrane at the umbo; its head articulates with the incus; malleus means "hammer" stapes the medial ossicle of the middle ear it articulates with the long process of the incus and its base fills the fenestra vestibuli (oval window); stapes means "stirrup" paired; failure of the perpendicular plates to fuse during development leads to a midline defect (cleft palate) it articulates anteriorly with the maxilla; posteriorly it forms the medial wall of the pterygopalatine fossa and the lateral wall of the nasal cavity; its posterior edge contributes to 1/2 of the sphenopalatine foramen along with the sphenoid bone it forms the sphenopalatine foramen
palatine
the bone that forms the posterior part of the hard palate
perpendicular plate
the vertical portion of the palatine bone located posteriorly on either side of the nasal cavity
sphenopalatine notch
a notch at the posterosuperior margin of the perpendicular plate of the palatine bone
sphenopalatine foramen
an opening in the lateral wall of the nasal cavity formed by the perpendicular plate of the palatine bone and the body of the sphenoid bone a small, superior projection from the perpendicular plate of the palatine bone
it transmits the nasopalatine nerve and the sphenopalatine vessels
orbital process
it forms a small part of the floor of the orbit located posteroinferiorly near the apex
horizontal plate
the portion of the paired; the two palatine bone horizontal plates that forms the meet at the midline posterior 1/3 of the hard palate an opening in the hard palate located medial to the 3rd maxillary molar tooth an opening in the hard palate located posterior to the greater palatine foramen a broad, flat bone forming the lateral surface of the skull it transmits the greater palatine neurovascular bundle; it is an important site for oral anesthesia there may be more than one; it transmits the lesser palatine n. and vessels paired; this bone articulates with the contralateral parietal bone in the midline at the sagittal suture; it articulates anteriorly with frontal bone at
greater palatine foramen
lesser palatine foramen
parietal
coronal suture; it articulates posteriorly with the occipital bone at the lambdoid suture; it articulates inferiorly with the greater wing of the sphenoid bone at the pterion, the squamous part of the temporal bone at the squamous suture and the mastoid part of the temporal bone at the parietomastoid suture inferior temporal an arching ridge line on the external surface of the parietal bone superior temporal line an arching ridge on the external surface of the parietal bone it is an attachment site for the temporalis muscle it is an attachment site for the temporalis muscle and the temporal fascia it transmits the parietal emissary vein, a valveless vein which connects the scalp to the cranial cavity
parietal foramen an opening in the parietal bone located near the sagittal suture
granular foveolae
small pits located for the arachnoid on the inner table granulations of the parietal bone the large anterior connected above to cartilage of the the hyoid bone via
thyroid cartilage
larynx; it has several parts: laminae (2), superior horns (2), inferior horns (2), oblique line, superior thyroid notch,
the thyrohyoid membrane; connected below to the cricoid cartilage via the inferior horn of the thyroid cartilage; connected posteriorly: to the arytenoid cartilage via the vocal ligament and thyroarytenoid m., to the epiglottic cartilage via the thyroepiglottic ligament; it tilts anteriorly to increase the length of the vocal ligament and raise the pitch of the voice the laryngeal prominence is the line of fusion of the two laminae; each lamina is connected superiorly to the hyoid bone by the thyrohyoid membrane it is connected superiorly to the greater horn of the hyoid bone by the lateral thyrohyoid ligament
lamina
a broad flat plate of cartilage forming one side of the thyroid cartilage; two laminae fuse anteriorly in the midline to form the thyroid cartilage the rounded, superior projection of the posterior border of the thyroid lamina
superior horn
inferior horn
the rounded, it is connected inferior inferiorly to the projection of the cricoid cartilage by
posterior border of the thyroid lamina oblique line
the cricothyroid articulation (a synovial joint)
ridge which a line of muscle descends attachment diagonally from superior to inferior on the lateral surface of the thyroid lamina the line of fusion known to the lay of the thyroid person as the laminae "Adam's apple"; the laryngeal prominence is a secondary sexual characteristic - in postpuberal males the angle of the laryngeal prominence is approximately 90 and in females the angle is approximately 120 the notch at the superior end of the laryngeal prominence an irregularly shaped bone forming the central portion of the skull it is connected to the hyoid bone by the median thyrohyoid ligament it has many parts, including a body, greater wing, lesser wing and pterygoid plates
laryngeal prominence
superior thyroid notch
sphenoid
body
central part of the contains the sphenoid bone sphenoid sinuses; attachment point for
the wings and pterygoid plates sphenoid sinuses pneumatized spaces within the body of the sphenoid bone jugum usually paired; it drains into the sphenoethmoidal recess of the nasal cavity
the anterior-most articulates with the portion of the cribriform plate of sphenoid bone the ethmoid bone the groove for located between the the optic chiasm jugum & the tuberculum sellae canal located at the lateral end of the chiasmatic sulcus and medial to the anterior clinoid process paired; it transmits the optic nerve and the ophthalmic artery from the cranial cavity to the apex of the orbit
chiasmatic sulcus optic canal
tuberculum sellae sella turcica
the anterior limit the middle clinoid of the sella processes project turcica from its lateral ends depression on the superior surface of the body of the sphenoid bone "Turkish saddle"; roughly equivalent to the hypophyseal fossa; area between the tuberculum sellae and the posterior clinoid processes
anterior clinoid process
projection at the the internal carotid medial end of the artery passes medial lesser wing of the to this structure sphenoid bone thin rim of bone bilateral; it forms projecting the posterior margin laterally from the of anterior cranial
lesser wing of the sphenoid
anterior clinoid process
fossa; it articulates anteriorly with the orbital plate of the frontal bone bilateral; it forms the medial part of the floor of the middle cranial fossa, part of temporal fossae laterally, and the posterior part of the lateral wall of orbit; it articulates anteriorly with the zygomatic bone, superiorly with the frontal & parietal bones (at the pterion), posteriorly with the squamous & petrous portions of the temporal bone it transmits the oculomotor nerve, the trochlear nerve, the abducens nerve, branches of ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve, the superior ophthalmic vein and lymphatics from the cranial cavity into the orbit it transmits the maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve
greater wing of the sphenoid
broad plate of bone swinging laterally from the body of the sphenoid bone
superior orbital fissure
slit-like opening between the lesser & greater wings of the sphenoid bone
foramen rotundum
opening in the floor of the middle cranial fossa through the greater wing of
the sphenoid bone foramen ovale opening in the floor of the middle cranial fossa through the greater wing of the sphenoid bone opening in the floor of the middle cranial fossa through the greater wing of the sphenoid bone process of bone that projects inferiorly from undersurface of greater wing of the sphenoid process that projects inferiorly from the junction of the body & greater wing of the sphenoid bone it transmits the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve; it is located between the foramen rotundum and the foramen spinosum it transmits the middle meningeal artery and the meningeal br. of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve V) it is the superior attachment for the sphenomandibular ligament
foramen spinosum
spine of the sphenoid
pterygoid process
it has several parts: lateral & medial pterygoid plates, hamulus, pterygoid fossa, scaphoid fossa; the pterygoid plates are separated by the large pterygoid fossa throughout most of their length, and by the small scaphoid fossa superiorly
lateral pterygoid thin plate of bone it is the attachment plate that projects site of the lateral &
posterolaterally medial pterygoid from the muscles (lateral pterygoid process pterygoid m. on its lateral surface, medial pterygoid m. on its medial surface) medial pterygoid thin plate of bone plate that projects posteriorly from the pterygoid process scaphoid fossa it is the attachment of the superior pharyngeal constrictor m. & the pharygobasilar fascia
an oval it is the site of depression at the origin of the tensor superior end of veli palatini m. the lateral pterygoid plate hook-like projection from the inferior end of the medial pterygoid plate canal that occurs at the junction of the greater wing, the pterygoid process and the body of the sphenoid bone it acts as a pulley for the tendon of the tensor veli palatini m. it transmits the nerve of the pterygoid canal from the pterygoid region to the pterygopalatine fossa
pterygoid hamulus
pterygoid canal
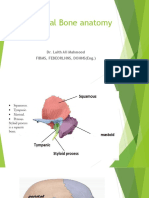
temporal
bone forming the temporal refers the lateral side of the passage of time, skull which is marked by the appearance of gray hair on the side of the head petrous part the hard part of the temporal bone located in it contains the tympanic cavity (middle ear) and the
the floor of the cranial cavity internal acoustic the opening on meatus the posteromedial surface of the petrous part of the temporal bone facial canal a canal which courses through the petrous part of the temporal bone a canal which courses through the petrous part of the temporal bone the process located posteroinferior to the external acoustic meatus
bony labyrinth of the inner ear it transmits the facial n., the vestibulocochlear n., and the labyrinthine a.
it transmits the facial n. from the internal acoustic meatus to the stylomastoid foramen it transmits the internal carotid a. and the internal carotid plexus of nerves into the cranial cavity it projects inferiorly from the junction of the petrous and squamous parts of the temporal bone; it contains the mastoid air cells that open into tympanic cavity through the mastoid antrum
carotid canal
mastoid process
tegmen tympani thin plate of bone located on the floor forming the roof of the middle of the tympanic cranial fossa cavity jugular fossa a depression on the posterior surface of the it forms the anterior margin of the jugular foramen; the
petrous part of the temporal bone styloid process the spike of bone that projects inferiorly from the petrous part of the temporal bone
occipital bone forms the posterior margin of the jugular foramen it is the attachment site for the stylohyoid, styloglossus and stylopharyngeus mm. and the stylomandibular and stylohyoid ligaments the medial 1/3 of the external acoustic meatus is bony and the lateral 2/3 is formed by cartilage it extends medially from the surface to the tympanic membrane; it allows sound to reach the tympanic membrane; the medial 1/3 of the external acoustic meatus is bony and the lateral 2/3 is formed by cartilage
tympanic part
the part of the temporal bone consisting of the external acoustic meatus and the tympanic ring
external acoustic the opening in meatus the lateral surface of the temporal bone
tympanic ring
the rim of bone it is the attachment surrounding the site of the tympanic medial end of the membrane external acoustic meatus the thin flat portion of the temporal bone it articulates with the parietal bone and the greater wing
squamous part
that constitutes the side of the skull above the ear zygomatic process the projection of bone that arises anterior to the external acoustic meatus
of the sphenoid bone at the squamous suture it articulates with the temporal process of the zygomatic bone to form the zygomatic arch
mandibular fossa the depression it articulates with located medial to the condylar process the origin of the of the mandible zygomatic process articular tubercle an inferior projection located anterior to the mandibular fossa vomer thin plate of bone forming the posteroinferior part of the nasal septum dislocations of the temporomandibular joint result when the mandibular condyle slides anterior to this structure articulates superiorly with the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone and the body of the sphenoid bone; articulates inferiorly with the palatine processes of the maxilla and the horizontal plate of the palatine bone wormian bones are variable in occurrence and are especially common at the junction of the squamous suture
wormian bone
small irregular bone that occurs between sutures of the skull
and the lambdoid suture zygomatic the bone that forms the cheek the zygomatic bone is frequently fractured in blows to the side of the orbit; the temporal fascia attaches to the zygomatic arch it articulates with the zygomatic process of the temporal bone to form the zygomatic arch it forms the inferior part of the lateral orbital margin and the anteroinferior part of the lateral orbital wall; it articulates with the frontal bone anteriorly and the greater wing of the sphenoid bone posteriorly it forms the lateral part of the inferior orbital margin and the anterolateral part of the orbital floor; it articulates with the maxilla it transmits the zygomaticofacial n.
temporal process the portion of the zygomatic bone that projects posteriorly
frontal process
the portion of the zygomatic bone that projects superiorly and medially
maxillary process
the part of the zygomatic bone that projects medially
zygomaticofacial a small opening foramen on the lateral surface of the zygomatic bone
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Anatomy of The HeadDocumento24 pagineAnatomy of The HeadAbdul Nasifh Bn Hamsa100% (1)
- Chapter 139 Anatomy of The Skull Base Temporal Bone External Ear and Middle Ear Larry G Duckert - CompressDocumento12 pagineChapter 139 Anatomy of The Skull Base Temporal Bone External Ear and Middle Ear Larry G Duckert - CompressWudieNessuna valutazione finora
- 06 Lec 11 12 Anatomy First YearDocumento13 pagine06 Lec 11 12 Anatomy First YearS:M:ENessuna valutazione finora
- Lec 6 Anatomy First StageDocumento36 pagineLec 6 Anatomy First Stagespo9equtabaNessuna valutazione finora
- Found 903118732 4683Documento2 pagineFound 903118732 4683Bogdan Robert CNessuna valutazione finora
- 28 Temporal Bone (Done)Documento7 pagine28 Temporal Bone (Done)Ayah HyasatNessuna valutazione finora
- Interior of SkullDocumento11 pagineInterior of SkullUnaiza Siraj100% (1)
- Middle Cranial FossaDocumento5 pagineMiddle Cranial Fossaalexandra663Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomia TemporalDocumento17 pagineAnatomia TemporalClaudia HeiderNessuna valutazione finora
- The Infratemporal FossaDocumento5 pagineThe Infratemporal FossaxxyumeNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied AnatomyDocumento14 pagineApplied AnatomySumit PrinjaNessuna valutazione finora
- Growth and Development of Cranial Base: SeminarDocumento34 pagineGrowth and Development of Cranial Base: SeminarMNSNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy 2-1 - Lecture One (HEAD & NECK)Documento21 pagineAnatomy 2-1 - Lecture One (HEAD & NECK)Abod AbodNessuna valutazione finora
- Temporal BoneDocumento20 pagineTemporal BoneHuynh NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Aa AnatomyDocumento109 pagineAa AnatomyshailendraNessuna valutazione finora
- Sphenoid BoneDocumento76 pagineSphenoid BoneLALITH SAI KNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture Medskull - ModofiedDocumento88 pagineLecture Medskull - ModofiedNikolai SamaniegoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture 7 Anatomy First YearDocumento8 pagineLecture 7 Anatomy First Yearspo9equtabaNessuna valutazione finora
- Temporal Bone RadioantomyDocumento43 pagineTemporal Bone RadioantomyRavindra MuzaldaNessuna valutazione finora
- Temporal BoneDocumento104 pagineTemporal Bonekatnev100% (1)
- Jaw and Temporomandibu Lar Joint: Drg. Shanty Chairani, M. SiDocumento62 pagineJaw and Temporomandibu Lar Joint: Drg. Shanty Chairani, M. Sihola holaNessuna valutazione finora
- Osteology of Maxilla & Mandible Muscles of MasticationDocumento26 pagineOsteology of Maxilla & Mandible Muscles of MasticationJaveria KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of The EarDocumento10 pagineAnatomy of The EarJP SouaidNessuna valutazione finora
- ანატომია ზეპირიDocumento22 pagineანატომია ზეპირიmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cavities of The Neuro and ViscerocraniumDocumento79 pagineCavities of The Neuro and ViscerocraniumSchönberger AlbertNessuna valutazione finora
- AnatomyDocumento15 pagineAnatomyAdeleye John AdebolaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nasal AnatomyDocumento23 pagineNasal AnatomyArchanaShenoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Temporal Fossa: DR V.O UkwenyaDocumento22 pagineTemporal Fossa: DR V.O UkwenyaIdowu SolomonNessuna valutazione finora
- Bones of The Upper LimbDocumento14 pagineBones of The Upper Limbyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Aprimaion Angulo PontocerebelosoDocumento64 pagineAprimaion Angulo PontocerebelosoLuis Carlos Avellaneda CurchoNessuna valutazione finora
- Osta Diagrams Facial Part of HeadDocumento22 pagineOsta Diagrams Facial Part of HeadslyfoxkittyNessuna valutazione finora
- Paranasal Sinus Anatomy - Overview, Gross Anatomy, Microscopic AnatomyDocumento12 pagineParanasal Sinus Anatomy - Overview, Gross Anatomy, Microscopic AnatomyKienlevy100% (1)
- The Foramen Magnum: Albert L. Rhoton, JR., M.DDocumento39 pagineThe Foramen Magnum: Albert L. Rhoton, JR., M.Dbodeadumitru9261100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Ear PDFDocumento12 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of The Ear PDFDeshini Balasubramaniam83% (6)
- DR PriyankaDocumento107 pagineDR PriyankakobexNessuna valutazione finora
- Temporal Bone AnatomyDocumento39 pagineTemporal Bone AnatomymizmuzNessuna valutazione finora
- Part 2 The Nose, Paranasal Sinuses and PharnyxDocumento12 paginePart 2 The Nose, Paranasal Sinuses and PharnyxLauraDernNessuna valutazione finora
- Skeletal System4Documento1 paginaSkeletal System4Elisha DienteNessuna valutazione finora
- Surgical Anatomy of Mandible: Department of Oral and Maxilofacial SurgeryDocumento92 pagineSurgical Anatomy of Mandible: Department of Oral and Maxilofacial SurgerySAMEENANessuna valutazione finora
- B 22-Rs-Anatomy - Saq AnswersDocumento22 pagineB 22-Rs-Anatomy - Saq Answersapi-516879364Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anterior and Posterior Petrosectomy Seminar 13 Jan 2021 DR Abhinav 2Documento76 pagineAnterior and Posterior Petrosectomy Seminar 13 Jan 2021 DR Abhinav 2Tamajyoti GhoshNessuna valutazione finora
- Oral CavityDocumento82 pagineOral Cavitydavid100% (1)
- ЧерепDocumento34 pagineЧерепbekafop813Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomical Considerations of Periodontal Surgery: SeminarDocumento30 pagineAnatomical Considerations of Periodontal Surgery: SeminarshravaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Fracture of The Mandible (Repaired)Documento67 pagineFracture of The Mandible (Repaired)Arafat Masud NiloyNessuna valutazione finora
- Exterior and Middle EarDocumento26 pagineExterior and Middle EarAndra BauerNessuna valutazione finora
- Head and NeckDocumento63 pagineHead and Neckbayenn100% (1)
- Left Maxilla. Outer Surface. : See Enlarged ImageDocumento5 pagineLeft Maxilla. Outer Surface. : See Enlarged Imageparveen41Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Ear: Head & Neck Unit - مسعسلا ليلج رديح .دDocumento20 pagineThe Ear: Head & Neck Unit - مسعسلا ليلج رديح .دStevanovic StojaNessuna valutazione finora
- External EarDocumento3 pagineExternal EarbarbacumlaudeNessuna valutazione finora
- The Larynx: StructureDocumento7 pagineThe Larynx: StructureJohn DroughtNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of The SkullDocumento3 pagineAnatomy of The SkullYeraldin EspañaNessuna valutazione finora
- Headandneck SkullDocumento27 pagineHeadandneck SkullKarla PappaNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Cranial CavityDocumento35 pagineIntroduction To Cranial CavityexoNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Infratemporal FossaDocumento7 pagine7 Infratemporal FossaAaaNessuna valutazione finora
- HN Infections Pic 2011 11Documento35 pagineHN Infections Pic 2011 11Oriza Aridilah FitraNessuna valutazione finora
- Lowerlimb (Repaired)Documento132 pagineLowerlimb (Repaired)Muhammad Farukh IbtasamNessuna valutazione finora
- The Adductor Muscles of the Jaw In Some Primitive ReptilesDa EverandThe Adductor Muscles of the Jaw In Some Primitive ReptilesNessuna valutazione finora
- A New Species of Heteromyid Rodent from the Middle Oligocene of Northeast Colorado with Remarks on the SkullDa EverandA New Species of Heteromyid Rodent from the Middle Oligocene of Northeast Colorado with Remarks on the SkullNessuna valutazione finora
- Bacteriology ReviewDocumento47 pagineBacteriology ReviewDeti ParidlahNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Pelvis ReviewDocumento20 pagineAnatomy Pelvis Reviewyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Assess Notes Nursing AssessmentDocumento206 pagineAssess Notes Nursing Assessmenttostc100% (7)
- Anatomy and Physiology I Fall 2009 Exam I Study GuideDocumento1 paginaAnatomy and Physiology I Fall 2009 Exam I Study Guideyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Thorax ReviewDocumento18 pagineAnatomy Thorax Reviewyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- AP Review NotesDocumento15 pagineAP Review Notesyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- API Review Muscles f2009Documento1 paginaAPI Review Muscles f2009yachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Lower Extr ReviewDocumento12 pagineAnatomy Lower Extr Reviewabuzeid5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology Unit III: Objectives/RationaleDocumento16 pagineAnatomy and Physiology Unit III: Objectives/Rationaleyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Abdomin ReviewDocumento24 pagineAnatomy Abdomin Reviewmooni2009Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Head ReviewDocumento34 pagineAnatomy Head ReviewJordan BrooksNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Levels and Planes ReviewDocumento3 pagineAnatomy Levels and Planes Revieware4erNessuna valutazione finora
- A P1 Review Test 4Documento1 paginaA P1 Review Test 4yachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- First Aid ManualDocumento225 pagineFirst Aid ManualHugo MartinsNessuna valutazione finora
- Bones of The Lower LimbDocumento15 pagineBones of The Lower Limbyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bones of The Abdominal RegionDocumento7 pagineBones of The Abdominal Regionyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bones of The Pelvis and PerineumDocumento6 pagineBones of The Pelvis and Perineumyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bones of The Upper LimbDocumento14 pagineBones of The Upper Limbyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Tables - Bones of The Thorax: Bone Structure Description Notes RibDocumento3 pagineAnatomy Tables - Bones of The Thorax: Bone Structure Description Notes Ribyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bones of The Back RegionDocumento9 pagineBones of The Back Regionyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- DEPED 2012 - K TO 12 - Learning DR VillanezaDocumento32 pagineDEPED 2012 - K TO 12 - Learning DR Villanezayachiru121100% (1)
- DEPED 2012 - K TO 12 - Where Are We Now, K in K To 12Documento21 pagineDEPED 2012 - K TO 12 - Where Are We Now, K in K To 12yachiru121100% (1)
- DEPED 2012 - K TO 12 - MTB RationaleDocumento30 pagineDEPED 2012 - K TO 12 - MTB Rationaleyachiru121100% (3)
- DEPED 2012 - Classroom DR VillanezaDocumento17 pagineDEPED 2012 - Classroom DR Villanezayachiru121100% (1)
- DEPED - The K To 12 Basic Education Programv2 - 2012Documento38 pagineDEPED - The K To 12 Basic Education Programv2 - 2012yachiru121100% (1)
- DEPED 2012 - K TO 12 - L1-L2-L3-Dr. GironDocumento56 pagineDEPED 2012 - K TO 12 - L1-L2-L3-Dr. Gironyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- DEPED 2012 - Assessment in Kinder Mam VioletaDocumento54 pagineDEPED 2012 - Assessment in Kinder Mam Violetayachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- DEPED - K To 12 Assessment & Rating - 2012Documento44 pagineDEPED - K To 12 Assessment & Rating - 2012yachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- HandbookDocumento53 pagineHandbookyachiru121Nessuna valutazione finora
- Q1. (A) The Diagram Shows A Microphone Being Used To Detect The Output From ADocumento10 pagineQ1. (A) The Diagram Shows A Microphone Being Used To Detect The Output From ASivmi MalishaNessuna valutazione finora
- ACF5950 - Assignment # 7 Semester 2 2015: The Business Has The Following Opening Balances: Additional InformationDocumento2 pagineACF5950 - Assignment # 7 Semester 2 2015: The Business Has The Following Opening Balances: Additional InformationkietNessuna valutazione finora
- Soil Biotechnology (SBT) - Brochure of Life LinkDocumento2 pagineSoil Biotechnology (SBT) - Brochure of Life Linkiyer_lakshmananNessuna valutazione finora
- CrewmgtDocumento36 pagineCrewmgtDoddy HarwignyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro To Psychological AssessmentDocumento7 pagineIntro To Psychological AssessmentKian La100% (1)
- ArticleDocumento5 pagineArticleJordi Sumoy PifarréNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample SWMSDocumento4 pagineSample SWMSJuma KavesuNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Records in Family PracticeDocumento22 pagineMedical Records in Family PracticenurfadillahNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Ror The First TermDocumento29 pagineRevision Ror The First TermNguyễn MinhNessuna valutazione finora
- Compartment SyndromeDocumento14 pagineCompartment SyndromedokteraanNessuna valutazione finora
- G1 Series User Manual Ver. 1.2Documento101 pagineG1 Series User Manual Ver. 1.2unedo parhusip100% (1)
- Rules For State Competitions and Iabf Approved TournamentsDocumento56 pagineRules For State Competitions and Iabf Approved TournamentsQuality management systems documentsNessuna valutazione finora
- Appendix B - Distance Tables - Metric Units PDFDocumento15 pagineAppendix B - Distance Tables - Metric Units PDFitisINessuna valutazione finora
- Senior Project RiceberryDocumento76 pagineSenior Project RiceberryIttisak PrommaNessuna valutazione finora
- Join Our Telegram Channel: @AJITLULLA: To Get Daily Question Papers & SolutionsDocumento24 pagineJoin Our Telegram Channel: @AJITLULLA: To Get Daily Question Papers & SolutionsNaveen KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- HVAC (Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning) : SRS PrecautionsDocumento1 paginaHVAC (Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning) : SRS PrecautionssoftallNessuna valutazione finora
- Cultivation Vaderstad Manual 2017Documento128 pagineCultivation Vaderstad Manual 2017deroryNessuna valutazione finora
- Alex Eubank GGIIDocumento40 pagineAlex Eubank GGIIOliver Sleiman94% (16)
- CONTROLTUB - Controle de Juntas - New-Flare-Piping-Joints-ControlDocumento109 pagineCONTROLTUB - Controle de Juntas - New-Flare-Piping-Joints-ControlVss SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Paper Specific Instructions:: GATE Chemical Engineering MSQ Paper - 1Documento11 paginePaper Specific Instructions:: GATE Chemical Engineering MSQ Paper - 1Mayank ShelarNessuna valutazione finora
- NRF Nano EthicsDocumento18 pagineNRF Nano Ethicsfelipe de jesus juarez torresNessuna valutazione finora
- ALL102-Walker Shirley-Unemployed at Last-The Monkeys Mask and The Poetics of Excision-Pp72-85Documento15 pagineALL102-Walker Shirley-Unemployed at Last-The Monkeys Mask and The Poetics of Excision-Pp72-85PNessuna valutazione finora
- Bhert - EoDocumento2 pagineBhert - EoRose Mae LambanecioNessuna valutazione finora
- Multi-Wing Engineering GuideDocumento7 pagineMulti-Wing Engineering Guidea_salehiNessuna valutazione finora
- Interviewing Skill Workshop (KAU)Documento54 pagineInterviewing Skill Workshop (KAU)DrKomal KhalidNessuna valutazione finora
- Adsorbents and Adsorption Processes For Pollution ControlDocumento30 pagineAdsorbents and Adsorption Processes For Pollution ControlJoao MinhoNessuna valutazione finora
- Not Really A StoryDocumento209 pagineNot Really A StorySwapnaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Critical Appreciation of Ode To NightingaleDocumento3 pagineA Critical Appreciation of Ode To NightingaleBaloch Karawan100% (2)
- Nutrition & You - Chapter 6Documento40 pagineNutrition & You - Chapter 6Bridget KathleenNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of Fire SprinklerDocumento21 pagineBasics of Fire SprinklerLeo_1982Nessuna valutazione finora