Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Impaired Skin Integrity
Caricato da
Hanya Bint PotawanDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Impaired Skin Integrity
Caricato da
Hanya Bint PotawanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
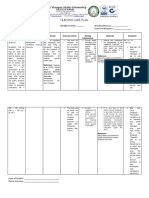
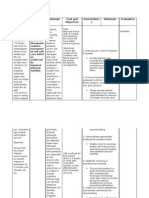
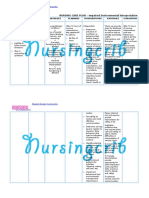
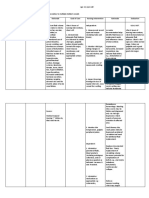
Problem Identified: Impaired skin integrity Nursing Diagnoses: Impaired skin integrity r/t stasis of secretions or drainage secondary
to colostomy. Cause Analysis: Presence of colostomy increases contact of fecal matter around stoma which may result to damage on the surrounding tissues (Doenges, M.E. Nursing Care Plan, 8 ed. p. 338)
Cues Subjective: Dili man siya sakit answered by the patient when asked about his colostomy stump on LLQ of his abdomen. Objective: Colostomy bag in place on LLQ of abdomen with dark red output. Reddish stoma with reddish surrounding skin. Encourage side-lying position with head elevated. Avoid prolonged sitting. Promotes drainage from perineal wound/drains, reducing risk of pooling. Prolonged sitting increases perineal pressure, reducing circulation to wound, and may delay healing. Collaborative: Assisted in irrigating the wound as indicated, using antibiotic solution. May be required to treat preoperative inflammation, infection, or intraoperative contamination. LTO: Within 3 days of nursing interventions, the patient will not develop further symptoms of infection such as pain, swelling and unusual drainage. Large amounts of serous drainage require that Changed dressings as needed. dressings be changed frequently to reduce skin irritation and potential for infection. STO: Within 8 hours of nursing interventions, the patients colostomy bag will be kept clean and drained as indicated. Objectives Independent: Observed wounds, noting characteristics of drainage. Postoperative hemorrhage is most likely to occur during the first 48 hours, whereas infection may develop at any time. Depending on type of wound closure, complete healing may take 6 to 8 months. LTO: After 3 days of nursing interventions, no manifestations of development of further tissue impairment or infection were noted. Nursing Interventions Rationale STO: Within 8 hours of shift, the patients colostomy bag was kept clean and was drained as indicated. Evaluation
th
Reference: Doenges, M.E. (2008). Nursing Care Plan, 8th ed. p. 338
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Impaired Tissue IntegritiyDocumento2 pagineImpaired Tissue IntegritiyPaolo Martin CuaycongNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP PSHDocumento17 pagineNCP PSHMargareth OrtizNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For Ruptured AppendicitisDocumento2 pagineNCP For Ruptured AppendicitisJansen Arquilita RiveraNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Acute PainDocumento3 pagineNCP Acute Painmanoelsterg50% (2)
- Risk For Impaired Skin IntegrityDocumento2 pagineRisk For Impaired Skin Integrityzbestgurl100% (1)
- NCP BPHDocumento8 pagineNCP BPHjyaba0% (1)
- Thyroidectomy NCPDocumento1 paginaThyroidectomy NCPkzbreakerrNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Urinary EliminationDocumento2 pagineImpaired Urinary EliminationMatty-b AskalaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Pain NCPDocumento1 paginaAcute Pain NCPJed AvesNessuna valutazione finora
- NCPDocumento3 pagineNCPJezza RequilmeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ncp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasDocumento4 pagineNcp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasFran LanNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP 2Documento2 pagineNCP 2Neil Abraham Mendoza Lalap100% (2)
- NCP LymphedemaDocumento1 paginaNCP Lymphedemayasira50% (2)
- NCP For CHNDocumento2 pagineNCP For CHNJhielo ArambulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk For Impaired Skin Integrity and Readiness For Enhanced PowerDocumento3 pagineRisk For Impaired Skin Integrity and Readiness For Enhanced PowerdanaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDocumento5 pagineNCP Delayed Wound RecoveryDarkCeades100% (2)
- NCPDocumento3 pagineNCPeun kyung shinNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocumento2 pagineImpaired Skin IntegrityRoseben SomidoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Making (Ulcerative Colitis & Crohn's Disease)Documento2 pagineNCP Making (Ulcerative Colitis & Crohn's Disease)R Hornilla ArcegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ncp-Readiness For Enhanced Knowledge Related To Preoperative CareDocumento1 paginaNcp-Readiness For Enhanced Knowledge Related To Preoperative CareAce Dioso Tubasco50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Student Nurse: Diestro, Angela Mae BSN 2BDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plan Student Nurse: Diestro, Angela Mae BSN 2BAngela Mae DiestroNessuna valutazione finora
- BPH NCPDocumento1 paginaBPH NCPJayson BenitezNessuna valutazione finora
- NCPDocumento2 pagineNCPDidith AbanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan For Impaired Environmental Interpretaion NCPDocumento4 pagineNursing Care Plan For Impaired Environmental Interpretaion NCPderic100% (2)
- NCP HemoDocumento2 pagineNCP HemoJigs HechNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP HemothoraxDocumento3 pagineNCP Hemothoraxroseonabreeze0% (2)
- NCP Acute PainDocumento5 pagineNCP Acute PainMicah Jonah Elicaño0% (1)
- Disturbed Body ImageDocumento3 pagineDisturbed Body Imagenura100% (1)
- Diarrhea Care PlanDocumento2 pagineDiarrhea Care Planzepoli_zepoly6232100% (1)
- Fernando - NCP & Drud Study (Colostomy)Documento4 pagineFernando - NCP & Drud Study (Colostomy)Cyril Joy N. FernandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept MapDocumento2 pagineConcept Mapjunifer laynoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP - Impaired Skin IntegrityDocumento4 pagineNCP - Impaired Skin IntegrityColette Marie PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Llacer FdarDocumento2 pagineLlacer FdarRaidis PangilinanNessuna valutazione finora
- Cholecystectomy Nursing Care Plan: Intraoperative Problem: Risk For AspirationDocumento1 paginaCholecystectomy Nursing Care Plan: Intraoperative Problem: Risk For AspirationJess GoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP: Acute GastroenteritisDocumento3 pagineNCP: Acute GastroenteritishauteanicoleNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 pagineAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationRomeo Avecilla CabralNessuna valutazione finora
- NafarinDocumento2 pagineNafarinianecunar100% (2)
- Cancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For InfectionDocumento2 pagineCancer Nursing Care Plan (NCP) - Risk For InfectionAngie MandeoyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity IntoleranceDocumento2 pagineActivity IntolerancedohbleNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation: VIII. Nursing Care PlanDocumento1 paginaAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation: VIII. Nursing Care PlanKriz_sakuradreamNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Plan Intervention Evaluation Subjective Data: "Masakit Po Yung Sa Short Term: IndependentDocumento2 pagineProblem Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Plan Intervention Evaluation Subjective Data: "Masakit Po Yung Sa Short Term: IndependentkyawNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet#2-Maintaining Asepsis: Medical Asepsis Includes All Practices Intended To Confine A SpecificDocumento4 pagineWorksheet#2-Maintaining Asepsis: Medical Asepsis Includes All Practices Intended To Confine A SpecificCj MayoyoNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Epidural HemDocumento32 pagineNCP Epidural HemKatrina PonceNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning ImplementationDocumento4 pagineAssessment Diagnosis Planning ImplementationMG PolvorosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation GoalDocumento2 pagineAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation GoalI Am SmilingNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Short Term Short TermDocumento2 pagineAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective Short Term Short TermFrancis Xavier S. MendezNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Impaired Skin IntegrityDocumento2 pagineNCP Impaired Skin IntegrityAubrey SungaNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Acute Pain FURUNCOLOSISDocumento2 pagineNCP Acute Pain FURUNCOLOSISMaria Imogen MilambilingNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk For Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocumento5 pagineRisk For Ineffective Tissue PerfusionElle Oranza100% (1)
- NCP Impaired SkinDocumento2 pagineNCP Impaired Skinarjay2306_obcq100% (1)
- NCPDocumento8 pagineNCPJoseph Anthony Benitez VerzosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisDocumento3 pagineNursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisJashAnia MarIe EvArdo FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Betty Impaired Skin IntegrityDocumento2 pagineBetty Impaired Skin IntegrityBenjie DimayacyacNessuna valutazione finora
- "May Mga Sugat Ako.": As Verbalized by The PatientDocumento6 pagine"May Mga Sugat Ako.": As Verbalized by The Patientedifier_moonNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Diagnosis For TonsillitisDocumento3 pagineNursing Diagnosis For TonsillitisVaneca Go67% (9)
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocumento9 pagineImpaired Skin IntegrityJamila Angeli Valle100% (2)
- Impaired Skin IntegrityDocumento2 pagineImpaired Skin IntegrityBethel OlivaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Nephro NCP2Documento2 pagineNephro NCP2hannahNessuna valutazione finora
- Actual Nursing Care Plan 2Documento16 pagineActual Nursing Care Plan 2Alyanna Evangelista100% (2)
- NCPDocumento4 pagineNCPbjhilario100% (1)
- Herbal MedicinesDocumento6 pagineHerbal MedicinesHanya Bint PotawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Verbal and or Written CommunicationDocumento2 pagineImpaired Verbal and or Written CommunicationHanya Bint Potawan100% (1)
- Ineffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionDocumento3 pagineIneffective Cerebral Tissue PerfusionHanya Bint Potawan88% (25)
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocumento2 pagineImpaired Physical MobilityHanya Bint PotawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Herbal MedicinesDocumento6 pagineHerbal MedicinesHanya Bint PotawanNessuna valutazione finora
- BSN - 4C: PresentorsDocumento52 pagineBSN - 4C: PresentorsHanya Bint Potawan100% (1)
- MSHC Ordr PRC FormatDocumento4 pagineMSHC Ordr PRC FormatHanya Bint PotawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Rhu Day 1 RequirementsDocumento4 pagineRhu Day 1 RequirementsHanya Bint PotawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Schizophrenia UndifferentiatedDocumento88 pagineSchizophrenia UndifferentiatedHanya Bint Potawan75% (4)
- Rhu Day 1 RequirementsDocumento4 pagineRhu Day 1 RequirementsHanya Bint PotawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Rhu Day 1 RequirementsDocumento4 pagineRhu Day 1 RequirementsHanya Bint PotawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Jose Rizal: 'Those Who Cannot See Where They Came From Will Never Get To Where They Are Going.'Documento55 pagineJose Rizal: 'Those Who Cannot See Where They Came From Will Never Get To Where They Are Going.'Anne Ginez BilledoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hanieyah Guro OR DR PRC FormatDocumento4 pagineHanieyah Guro OR DR PRC FormatHanya Bint PotawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Psychotropic DrugsDocumento49 paginePsychotropic DrugsHanya Bint PotawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Angina PectorisDocumento2 pagineAngina PectorisHanya Bint PotawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Breathing PatternDocumento1 paginaImpaired Breathing PatternHanya Bint PotawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pa Tho Physiology - Type 1 Diabetes (Hanieyah Guro)Documento1 paginaPa Tho Physiology - Type 1 Diabetes (Hanieyah Guro)Hanya Bint PotawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Akiya - DiphtheriaDocumento52 pagineAkiya - DiphtheriaHanya Bint PotawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocumento2 pagineImpaired Gas ExchangeHanya Bint PotawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocumento2 pagineIneffective Airway ClearanceHanya Bint PotawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Dopamine HydrochlorideDocumento1 paginaDopamine HydrochlorideJoannes SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- DT - Feb 4Documento2 pagineDT - Feb 4Hanya Bint PotawanNessuna valutazione finora
- DOH Officials Directory Execom MembersDocumento2 pagineDOH Officials Directory Execom MembersHanya Bint PotawanNessuna valutazione finora