Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Tshooting I
Caricato da
CoNnie AwangDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Tshooting I
Caricato da
CoNnie AwangCopyright:
Formati disponibili
IMS 453 Troubleshooting
1.0
TROUBLESHOOTING (Hardware & Software problem)
Loose connection A loose connection between a computer and a component can give the appearance of hardware failure. You should always make sure components are securely connected to the computer. Power fluctuations One of the most common causes of hardware failure is repeated exposure to power fluctuations, such as spikes, surges and blackouts. You can connect a computer to an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) to protect the computer from power fluctuations. Dust and dirt Dust and dirt inside a computer are common causes of hardware failure. Dust and dirt can cause increased temperatures and short-circuiting inside a computer. You should clean a computer on a regular basis to keep hardware in good working order. Component Age Many components simply fail after they have been used for several years. Components such as hard drives, floppy drives and fans, which contain moving parts eventually wear out. If properly maintained, most computer components can last 5 years or more. Heat All computer components generate heat as they operate. If the temperature in a computer gets too high, hardware failures can occur. To prevent overheating, you should always ensure that a computer has adequate ventilation and that the fan opening at the back of the computer is not blocked.
Defective media
IMS 453 Troubleshooting Defective storage media, such as a floppy disk or type cartridge, can give the appearance of a failed storage device. You should try using a different floppy disk or tape cartridge to determine whether the media or the device is at fault. Defective component Defects can cause a component to fail when it is first installed in a computer or after only a short period of use. Although the quality and reliability of new components have increased in recent years, up to 10 percent of new components may be defective when they are purchased. Check the manual The first step in troubleshooting a hardware problem is to check the documentation for the computer or device for troubleshooting information. Manuals usually provide detailed information about the most common problems. Check connections A loose connection is a common cause of hardware problems. Make sure the components are securely connected to the computer. Check the driver Most computer components require software, called a driver to operate. You should ensure you are using the correct and most up-to-date driver for the component you think is causing the problem. Test multiple possibilities Testing multiple possibilities can help you find the cause of a problem. For example, if a floppy drive cannot access data on a floppy disk, the problem may be cause by the driver on the disk. To find the cause, try using another disk. If the floppy drive cannot access data on the second disk, the drive is likely the cause of the problem.
Try another component You can try using another component to troubleshoot a problem. For example, if you think the video card is malfunctioning, try replacing it with a video card you know
IMS 453 Troubleshooting works properly. Of the problem stops, the original video card is likely the cause of the problem. Move and remove component Moving and removing components can help you troubleshoot a problem. For example, if you suspect an expansion card is causing a problem, first try moving the card to another expansion slot. If the problem stops, it may be due to the original expansion slot. If the problem persists, you can remove the expansion card and restart the computer to see if the problem still exists. If the problem stops, it is likely due to the expansion cards. Tools Bootable rescue disk. Flat-head screwdriver (slotted) Philips-head screwdriver (bunga) Torx screwdriver (Allign key) Tweezers for picking pieces of paper Chip extractor to remove chip Extractor, a spring-loaded device that looks likes a hypodermic needle. Multimeter to check the power output. Ground bracelet. Antistatic bags to store. Pen and paper to taking notes Utility software. Virus detection software on disk. Compressed air (sembur habuk) Drive cleaner Brush
Protect Yourself, Hardware and Software The most common threat to hardware electrostatic discharge (ESD) known as static electricity. A ground bracelet, is worn on your wrist and is grounded to a ground mat, computer case of a ground prong of wall outlet.
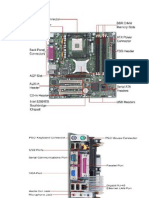
IMS 453 Troubleshooting Troubleshooting on Coprocessor 1. Many manufactures provide diagnostics on diskette for the microprocessor that can be used for great advantage. 2. Be sure you software is aware of a newly installed numeric coprocessor. You might have to reinstall the software or set certain software parameters to indicate the presence of the coprocessor. 3. Do you have two video cards installed in your system? They may not be correctly configured. Such a situation can cause apparent CPU problems. 4. If after trying the above you conclude that the CPU or motherboard is defective, try replacing the CPU, then the motherboard. This should be your last resort. 5. If you are running DOS version 6.0 or higher, you can use the msd command to obtain info about the processor. Troubleshooting on Hard Drive 6. Check the cables (including the power cable) to see that they are
properly and securely connected. You might also try replacing the control and data cables. In the dry and dusty environment inside the computer, cables tend to be crack. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Ensure that the jumpers are set correctly. If an error like Disk not found is displayed, rerun the setup program. An error like Missing command interpreter means that a valid copy Try reseating the disk controller card (remove and install it). Persistent grinding noises are the sign of a bad disk or possibly a Use the DOS defrag command as a free compaction tool to If you are running DOS version 6.0 or higher, you can use the msd
of command.com doest not exist in the root directory of the hard disk.
power supply. enhance disk performance. command to obtain info about the disk devices. Eg: Attrib.exe, Chkdsk.exe, edit.com emm386.exe , fdisk.exe, format.com , scandisk.exe , sys.com , Himem.sys , undelete.exe
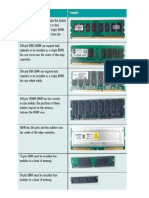
Troubleshooting on Memory 14. Be sure that any memory chips you have added are properly seated in their holders. Beware of curried pins.
IMS 453 Troubleshooting 15. 16. 17. Are SIMM or DIMM modules properly seated? Remove and reinstall each one. Make sure the SIMMs have correct or consistent part numbers. For example, if there are four installed SIMMs, they usually must be the same size. If you are running DOS version 6.0 or higher, you can use the mem command to obtain info about the system memory. Eg: MEM /C \MORE , MEM /C >PRN , MEMMAKER /UNDO Troubleshooting on Power Supply 18. 19. 20. 21. The most common sign of a bad or inadequate power supply will be surging noises coming from hard disk or repeated disk failures on the floppy disk. Check the power supply directly with a multimeter. Fan be sure it is working. A damaged fan can caused the computer to overheat, which can destroy the power supply. Use only power supplies specifically designed for your type of computer.
Connect a UPS 22. Before connecting a UPS, turn off the computer and monitor. Unplug the computers power cable from the electrical outlet and plug it into the outlet on the UPS 23. 24. 25. Unplug the monitors power power cable from the electrical outlet and plug it into the outlet on the UPS Plug the power cable from the UPS into an electrical outlet. Turn on the UPS.
Troubleshooting on Monitor 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. Check the contrast and brightness before assuming the screen is faulty. Be sure that the software you are running is aware of the current video configuration. Try reseating the video card (remove and reinstall it) Beware of bad power supplies affecting display performance. Do not leave monitor on when not in use because this practice can reduce the life of the monitor and cause permanent ghost images on the screen. DOS command, placed in the autoexec.bat file by you or by installation software, can affect the screen display. Check autoexec.bat such commands and verify that they make sense in computer configuration: Eg - Mode mo80 (sets display as monochrome 80)
IMS 453 Troubleshooting - Mode co80 (sets display as color 80 columns) - Mode co40 32. 33. Try moving the video card to a different slot. Take advantage of any diagnostic / setup software supplied with your video card. THERE ARE SEVERAL COMMON CAUSES OF HARDWARE FAILURE. BEING AWARE OF THE CAUSES OF HARDWARE ARE FAILURE CAN HELP YOU AVOID PROBLEM. No of beeps 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ERROR Codes Error Number 101 199 201 - 299 301 399 601 699 901 999 1101 1199 1701 1799 Problem System board error RAM error Keyboard error Floppy drive error Printer port error Serial port error Hard drive error Problem Memory error Memory error Memory error System time error CPU error Keyboard controller error CPU error Video card error BIOS error CMOS error Cache memory error
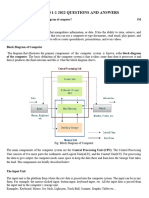
What is an IRQ ? An IRQ is really an interrupt Request line. In the case of expansion board, and it is an actual contact (finger) on the board, and it is a corresponding pin in the sockets on the bus connected by a trace on the motherboard. A device sends a interrupt to the motherboards interrupt circuitry by changing the voltage level on the interrupt request line. This voltage change acts via interrupt controller circuitry to interrupt the processor to service the device needing the CPU attention. Simply put, if for example, a seriap port
IMS 453 Troubleshooting is receiving data from a MODEM, it can wait until its buffer overflows for the CPU to come to its assistance. The CPU will then temporally store the program and data it is working on in an area of memory know as the stack and load a routing (program) to service the interrupting device, service the device (move the data out of its buffer) and then restore the program and then restore the program and it was previously working on and resume what is was doing. A CPU can be interrupted many times a seconds a marvelously complicated affair when one considers that a CPU can be working on one interrupt request and be interrupt in this task by still another IRQ request of a higher priority, and that it usually does all of this juggling without losing a beat or data. IRQ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 USUAL FUNCTION / DEVICE System Timer Keyboard 2nd IRQ controller COM2 : COM1 : Free (Used by LPT2 : or sound card) Floppy Disk LPT1 Real Time Clock (RTC) Free (May be labeled/appear as IRQ2) Free (often used by sound cards) Free PS/2 mouse Math coprocessor on CPU (used) Primary IDE Secondary IDE
DMA DMA stands for Direct Memory Access. DMA allows computer peripherals to communicate directly with computers RAM memory, by passing the processor. With DMA, peripherals work faster and use less processor power. In modern computers, DMA access is negotiated by the computers BIOS during startup, or by the operating system. Computer has a limited number of DMA channels available, but modern computers rarely run out.
IMS 453 Troubleshooting DMA 0 1 Bus line No 8/16 bit Typical Default Use Memory refresh Sound card (low DMA) Other common uses None SCSI host adapters, ECP parallel ports, tape accelerator cards, network 2 3 8/16 bit 8/16 bit Floppy Disk controller Non cards, voice modems Tape accelerator cards ECP parallel ports, adapter, tape
SCSI
host cards,
accelerator
sound card (low DMA), network cards, voice modems, hard disk controller on 4 5 6 7 No 16 bit only 16 bit only 16 bit only None: Cascade old PC/XT for None SCSI host adapters, network card Sound cards (high DMA), network card Sound cards (high DMA), network card
DMAs 0 3 Sound card (high DMA) None None
Check for viruses Software problems may be caused by a computer virus. You can use an anti-virus to check the computer for viruses. Most anti-virus programs also include a virus removal features when it found virus. Check the updates Software manufactures often create minor software updates, called patches or service pack, to fix known bugs and problems with the software. You can check the software manufactures web site to see if a patch or service pack exists that fixes your problem. Reinstall software If problem occurs only when you use s specific program, you may able to correct the problem by reinstalling the software. Reinstalling software replaces the program files on the computer with a new copy. If the cause of a problem is deleted or corrupted program files, reinstalling the software may correct the problem. Uninstall software If you suspect the problems you are experiencing are caused by a particular software, you can remove the software to see if the problems stop. Most software come with a
IMS 453 Troubleshooting utility that lets you uninstall the program. Some operating systems, such as Windows ME and Windows 2000 also include an uninstall utility where you can use to uninstall the software. Reinstall Operating System If you are experiencing problems with many of the programs installed on a computer, the operating system may be caused of the problems. An operating system can become corrupted when system files are accidentally deleted or damaged. Reinstalling the operating system may resolve the problems. Safe Mode Safe Mode is troubleshooting tool for windows, much like the command line switches were for Windows 3.X. Safe Mode allows access into Windows using unlu the most basic drivers. Autoexec.bat and Config.sys are not loaded. To get into Safe Mode, Start / Restart you computer and as soon as you see the Starting Window 9X text, hit the F8 key, Choose option 3, Safe Mode.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- How to Build a Computer: The Best Beginner's Guide to Building Your Own PC from Scratch!Da EverandHow to Build a Computer: The Best Beginner's Guide to Building Your Own PC from Scratch!Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Comprehensive Guide About Computers and TechnologyDa EverandA Comprehensive Guide About Computers and TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- IT Essentials: PC Hardware and SoftwareDocumento109 pagineIT Essentials: PC Hardware and Softwarempo36985100% (2)
- Why Is My Computer So Slow?: Computer Tips and Solutions, #1Da EverandWhy Is My Computer So Slow?: Computer Tips and Solutions, #1Nessuna valutazione finora
- AM Loop AntennasDocumento8 pagineAM Loop AntennasSaung SunnahNessuna valutazione finora
- 3500B and 3500B High Displacement Generator Sets Electrical SystemDocumento2 pagine3500B and 3500B High Displacement Generator Sets Electrical SystemAliHabesNessuna valutazione finora
- Linked PDFDocumento4.282 pagineLinked PDFDariusz DNessuna valutazione finora
- Administrator and Helpdesk Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesDa EverandAdministrator and Helpdesk Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be Asked: Job Interview Questions SeriesNessuna valutazione finora
- Trial and Error: When You Find A Faulty: Diagnosing Computer SystemsDocumento14 pagineTrial and Error: When You Find A Faulty: Diagnosing Computer SystemsBarbara M. Cachero100% (1)
- 1 GE TG Frame 6B IM PlanningDocumento6 pagine1 GE TG Frame 6B IM PlanningJorge LuisNessuna valutazione finora
- Brush Wear GuideDocumento3 pagineBrush Wear GuideSomkene MbakweNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Reasons Why Pcs Crash U Must KnowDocumento7 pagine10 Reasons Why Pcs Crash U Must Knowsivadashxyz8066Nessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Reasons Why Pcs Crash U Must Know?: Prabhu.D (3 - Year Cse-B)Documento5 pagine10 Reasons Why Pcs Crash U Must Know?: Prabhu.D (3 - Year Cse-B)prabhusctNessuna valutazione finora
- Varun 2003Documento17 pagineVarun 2003amuljuneNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Reasons Why PCs CrashDocumento7 pagine10 Reasons Why PCs CrashPragathesh RajagopalNessuna valutazione finora
- First: 10 Reasons Why Pcs Crash U Must KnowDocumento13 pagineFirst: 10 Reasons Why Pcs Crash U Must KnowEP GanzonNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Reasons Why PCs Crash U Must KnowDocumento5 pagine10 Reasons Why PCs Crash U Must Knowpawan_battulaNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnosing Computer Systems: Egil M. TabangcuraDocumento22 pagineDiagnosing Computer Systems: Egil M. TabangcuraPlazo AngelicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Troubleshooting For The Non-TechnicianDocumento59 pagineTroubleshooting For The Non-TechnicianaufcheNessuna valutazione finora
- Troubleshooting MotherboardsDocumento4 pagineTroubleshooting Motherboardsdawit demeNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnosing Computer Systems PC DiagnosingDocumento4 pagineDiagnosing Computer Systems PC DiagnosingVon AlvarezNessuna valutazione finora
- COM216 Week2Documento8 pagineCOM216 Week2Suopriye Hart100% (1)
- Diagnosing Computer SystemsDocumento23 pagineDiagnosing Computer Systemsrossan.abadNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnosing Computer Systems and NetworksDocumento6 pagineDiagnosing Computer Systems and NetworksAxel RamirezNessuna valutazione finora
- Com 216 Introduction To Computer Trouble Shooting 1Documento38 pagineCom 216 Introduction To Computer Trouble Shooting 1Olabiyi FawazNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Reasons Why PCs Crash U Must KnowDocumento5 pagine10 Reasons Why PCs Crash U Must KnowAppu bjNessuna valutazione finora
- PC Troubleshooting ThesisDocumento7 paginePC Troubleshooting Thesiscjzarbkef100% (2)
- MotherboardDocumento8 pagineMotherboardstendley busanNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic TroubleShootingDocumento4 pagineBasic TroubleShootingNelvin DondonillaNessuna valutazione finora
- COM 226 - Computer Troubleshooting Handout PrintDocumento68 pagineCOM 226 - Computer Troubleshooting Handout PrintOluwafisayo B. AyoadeNessuna valutazione finora
- TroubleshootingDocumento25 pagineTroubleshootingoladokunstephen6Nessuna valutazione finora
- Omputer Ardware Ervicing: C H S NC IiDocumento71 pagineOmputer Ardware Ervicing: C H S NC IiRaymoon Twopass DaysNessuna valutazione finora
- Dell Dimension-4600 Service Manual En-UsDocumento44 pagineDell Dimension-4600 Service Manual En-Usfernando1641991Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anti StaticDocumento11 pagineAnti Staticalcan9071Nessuna valutazione finora
- User ManualDocumento13 pagineUser ManualRicardo TavellaNessuna valutazione finora
- Zaria Poly Computer Troubleshooting II TheoryDocumento146 pagineZaria Poly Computer Troubleshooting II TheoryAbdallah AbdallahNessuna valutazione finora
- Omputer Ardware Ervicing: C H S NC IiDocumento71 pagineOmputer Ardware Ervicing: C H S NC Ii4u2cb4icNessuna valutazione finora
- CSS11 SSLM QTR3 WK7Documento8 pagineCSS11 SSLM QTR3 WK7EllenJoy CeroUyNessuna valutazione finora
- Online PC Repair Guide and PC ManualDocumento28 pagineOnline PC Repair Guide and PC ManuallxjvwkknNessuna valutazione finora
- C H S NC Ii: Omputer Ardware ErvicingDocumento66 pagineC H S NC Ii: Omputer Ardware ErvicingJaime CanchelaNessuna valutazione finora
- ProjectDocumento3 pagineProjectEniolorunda LoveNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 4 Css4 ReportDocumento19 pagineGroup 4 Css4 ReportLaikha SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Day 2Documento27 pagineDay 2trustphli73Nessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Computer System ErrorDocumento7 pagineTypes of Computer System ErrorKenneth Santos100% (7)
- Hardware Problems: Blank MonitorsDocumento2 pagineHardware Problems: Blank MonitorsDwight AsetreNessuna valutazione finora
- A+ TestDocumento23 pagineA+ TestLittlejohnny22027Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cpws Ar20 All Units Questions & AnswersDocumento80 pagineCpws Ar20 All Units Questions & AnswersSudheerNessuna valutazione finora
- TextDocumento2 pagineTextJaymar Kevin EviaNessuna valutazione finora
- Handout 4Documento4 pagineHandout 4jarelleNessuna valutazione finora
- Com 214Documento27 pagineCom 214pius nojiriNessuna valutazione finora
- System Config 311Documento10 pagineSystem Config 311Unknown UserNessuna valutazione finora
- Differences Related To Computer MaintenanceDocumento5 pagineDifferences Related To Computer MaintenanceAlpesh ThesiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Troubleshooting of ComputerDocumento11 pagineTroubleshooting of ComputerAlpesh ThesiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Q3 Module-5 CSS9 San-Jacinto-NHSDocumento6 pagineQ3 Module-5 CSS9 San-Jacinto-NHSJohn Benedick BelverNessuna valutazione finora
- Dimension-8400 Service Manual En-UsDocumento47 pagineDimension-8400 Service Manual En-UsJames Richard RoblesNessuna valutazione finora
- Monaco Institute of Business & Computer Science Diploma in Software EngineeringDocumento5 pagineMonaco Institute of Business & Computer Science Diploma in Software EngineeringKwizera AndrewNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Will Not StartDocumento48 pagineComputer Will Not StartAlan MosoNessuna valutazione finora
- CMP 104 - Module 2Documento13 pagineCMP 104 - Module 2Aritesoma ENessuna valutazione finora
- CHS NC2 ReviewerDocumento14 pagineCHS NC2 ReviewerCo YiskāhNessuna valutazione finora
- Computing Fundamentals Module Lesson 3 Maintaining and Protecting HardwareDocumento31 pagineComputing Fundamentals Module Lesson 3 Maintaining and Protecting HardwareAnb BajwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Top Ten Computer ComponentsDocumento11 pagineTop Ten Computer ComponentsEizen LuisNessuna valutazione finora
- The SSD Optimization Guide for Windows 7 & Windows 8.1 Edition 2018Da EverandThe SSD Optimization Guide for Windows 7 & Windows 8.1 Edition 2018Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fixing Common Computer Problems: A Comprehensive Troubleshooting GuideDa EverandFixing Common Computer Problems: A Comprehensive Troubleshooting GuideNessuna valutazione finora
- The Calculation of RAMDocumento3 pagineThe Calculation of RAMCoNnie AwangNessuna valutazione finora
- Ram PicDocumento1 paginaRam PicCoNnie AwangNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap8-10 - IRQ & DMADocumento8 pagineChap8-10 - IRQ & DMACoNnie AwangNessuna valutazione finora
- Step To Install PCDocumento1 paginaStep To Install PCCoNnie AwangNessuna valutazione finora
- Pic PCDocumento1 paginaPic PCCoNnie AwangNessuna valutazione finora
- PC Degree - Writing Skills 2Documento3 paginePC Degree - Writing Skills 2CoNnie AwangNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap13-14 - Troubleshooting S & HDocumento28 pagineChap13-14 - Troubleshooting S & HCoNnie AwangNessuna valutazione finora
- Integrated CircuitDocumento1 paginaIntegrated CircuitCoNnie AwangNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap8-10 - Storage Device Supporting Hard Drives 1Documento30 pagineChap8-10 - Storage Device Supporting Hard Drives 1CoNnie AwangNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap8-10 - Storage Devices & Planning Support 2Documento38 pagineChap8-10 - Storage Devices & Planning Support 2CoNnie AwangNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap7 Managing MemoryDocumento49 pagineChap7 Managing MemoryCoNnie AwangNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap3 - How Software & Hardware Working TogetherDocumento33 pagineChap3 - How Software & Hardware Working TogetherCoNnie AwangNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap8-10 - IRQ & DMADocumento8 pagineChap8-10 - IRQ & DMACoNnie AwangNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap4-5 System BoardDocumento86 pagineChap4-5 System BoardCoNnie AwangNessuna valutazione finora
- NMB RT 8200wDocumento2 pagineNMB RT 8200wSergio Diaz PereiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Dp-II Series Um en v1.0Documento19 pagineDp-II Series Um en v1.0hanspktNessuna valutazione finora
- LG Lfu850Documento35 pagineLG Lfu850Ventas RobertsNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual Del Operador Jt2720Documento183 pagineManual Del Operador Jt2720yonatahanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 5 - Sync GeneratorDocumento4 pagineLab 5 - Sync GeneratorzawirNessuna valutazione finora
- LHR TechnicalDocumento548 pagineLHR TechnicalJulio AltamiranoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ribblex Price ListDocumento22 pagineRibblex Price ListDipen patraNessuna valutazione finora
- Siemens Scalance w788x 748 1 en UsDocumento40 pagineSiemens Scalance w788x 748 1 en UsMichealNessuna valutazione finora
- 942006-001 TQP-RS Manual Rev2Documento40 pagine942006-001 TQP-RS Manual Rev2week redNessuna valutazione finora
- Opengear User Manual3.6 - OldDocumento261 pagineOpengear User Manual3.6 - OldnaveenvarmainNessuna valutazione finora
- Ams Plus - Ams CL Plus - Ams Co Plus Self-Venting Version: AMSA PLUSDocumento40 pagineAms Plus - Ams CL Plus - Ams Co Plus Self-Venting Version: AMSA PLUSSanty MontalvoNessuna valutazione finora
- Lista Partes NP3FDocumento3 pagineLista Partes NP3FWilliam ValenciaNessuna valutazione finora
- HP Laptop 15-Bs0xxDocumento124 pagineHP Laptop 15-Bs0xxmanoj14febNessuna valutazione finora
- EasyPact EZC EZC100F3080Documento5 pagineEasyPact EZC EZC100F3080Rizal PrasetyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mriya SII NE88 (Automatic Chrono)Documento1 paginaMriya SII NE88 (Automatic Chrono)SRI, Lda.Nessuna valutazione finora
- EDP - DSP-90 - Air - NEXTDocumento2 pagineEDP - DSP-90 - Air - NEXTmongojerryNessuna valutazione finora
- Flyer Chillers TCX and TCADocumento2 pagineFlyer Chillers TCX and TCAjdbNessuna valutazione finora
- Question: Describe The 8085 Programming Model in Detail. Answer: Following Is The Answer To The Above QuestionDocumento9 pagineQuestion: Describe The 8085 Programming Model in Detail. Answer: Following Is The Answer To The Above QuestionSidh SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Hih 060216Documento337 pagineHih 060216Asif IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- MLVS0402L Series Engineering Specification: ScopeDocumento8 pagineMLVS0402L Series Engineering Specification: ScopecafosokNessuna valutazione finora
- IE EBM112 DLT1227 18 aEN 001Documento32 pagineIE EBM112 DLT1227 18 aEN 001Matias Van Balen BlankenNessuna valutazione finora
- Tech Description CB Rev01Documento7 pagineTech Description CB Rev01hnphuocNessuna valutazione finora
- 2RMLB SDocumento7 pagine2RMLB SjckrishnahNessuna valutazione finora
- 65646-Item-Brochure Dynapac DRS120DDocumento5 pagine65646-Item-Brochure Dynapac DRS120DUri RocabadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter7 Powerfeed SystemDocumento27 pagineChapter7 Powerfeed SystemYAKUBU A. AROGENessuna valutazione finora