Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Frequency Modulation & DEMOD
Caricato da
Shathis KumarDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Frequency Modulation & DEMOD
Caricato da
Shathis KumarCopyright:
Formati disponibili
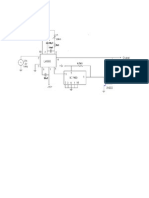
FREQUENCY MODULATION AND DEMODULATION AIM: 1. To construct Frequency modulator and demodulator circuit and to study its waveforms.
EQUIPMENTS REQUIRED: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. IC XR2206 IC NE565 Resistor -5k,50K,100K,1k Capacitors -0.001uf,22uf,10 uf Signal generator -(0-2)MHz CRO -30MHz Regulated power supply
THEORY: Frequency modulation uses the information signal, Vm(t) to vary the carrier frequency within some small range about its original value. Here are the three signals in mathematical form:
Information: Vm(t) Carrier: Vc(t) = Vco sin ( 2 p fc t + f ) FM: VFM (t) = Vco sin (2 p [fc + (Df/Vmo) Vm (t) ] t + f)
We have replaced the carrier frequency term, with a time-varying frequency. We have also introduced a new term: Df, the peak frequency deviation. In this form, you should be able to see that the carrier frequency term: fc + (Df/Vmo) Vm (t) now varies between the extremes of fc - Df and fc + Df. The interpretation of Df becomes clear: it is the farthest away from the original frequency that the FM signal can be. Sometimes it is referred to as the "swing" in the frequency. We can also define a modulation index for FM, analogous to AM: b = Df/fm , where fm is the maximum modulating frequency used. The simplest interpretation of the modulation index, b, is as a measure of the peak frequency deviation, Df. In other words, b represents a way to express the peak deviation frequency as a multiple of the maximum modulating frequency, fm, i.e. Df = b fm. Example: suppose in FM radio that the audio signal to be transmitted ranges from 20 to 15,000 Hz (it does). If the FM system used a maximum modulating index, b, of 5.0, then the frequency would "swing" by a maximum of 5 x 15 kHz = 75 kHz above and below the carrier frequency.
FM DEMODULATION In fm demodulators, the intelligence to be recovered is not in amplitude variations; it is in the variation of the instantaneous frequency of the carrier, either above or below the center frequency. The detecting device must be constructed so that its output amplitude will vary linearly according to the instantaneous frequency of the incoming signal. Several types of fm detectors have been developed and are in use, but in this section you will study three of the most common: (1) the phase-shift detector, (2) the ratio detector, and (3) the gated-beam detector. PROCEDURE: 1. 2. 3. 4. The circuit connections are given as per the circuit diagram. The message signal is given as input and the output wave is viewed in the CRO The graphs are plotted for the FM wave. The FM wave is given as input to the demodulation circuit and the output demodulated signal is obtained. 5. The graph is also plotted for demodulation RESULT: Thus the frequency modulation and demodulation circuits are constructed and the waveforms are observed.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Electronics and Communication Lab Manual PDFDocumento41 pagineElectronics and Communication Lab Manual PDFtesterNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsDa EverandAnalysis and Design of Multicell DC/DC Converters Using Vectorized ModelsNessuna valutazione finora
- FM DelieveredDocumento46 pagineFM DelieveredFaizan Ashraf100% (1)
- Unit-I: Introduction To Communication SystemDocumento107 pagineUnit-I: Introduction To Communication SystemSivaKumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Build Your Own Low-Power Transmitters: Projects for the Electronics ExperimenterDa EverandBuild Your Own Low-Power Transmitters: Projects for the Electronics ExperimenterValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (4)
- 1 and 2 NotesDocumento65 pagine1 and 2 NotesMylavarapu SriprithamNessuna valutazione finora
- Newnes Radio and Electronics Engineer's Pocket BookDa EverandNewnes Radio and Electronics Engineer's Pocket BookNessuna valutazione finora
- Amplitude Modulation1Documento44 pagineAmplitude Modulation1Dilbagh SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Adc QB 2020Documento14 pagineAdc QB 2020priyaroopaNessuna valutazione finora
- Delay-Doppler Communications: Principles and ApplicationsDa EverandDelay-Doppler Communications: Principles and ApplicationsNessuna valutazione finora
- ObjectivesDocumento22 pagineObjectivesMohd YasirNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Electrical Engineering Analog and Digital CommunicationDocumento4 pagineDepartment of Electrical Engineering Analog and Digital CommunicationAleena KanwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Frequency ModulationDocumento46 pagineFrequency Modulationkrejish100% (1)
- ANLOG Communication Full Manual...Documento54 pagineANLOG Communication Full Manual...ydsraju100% (1)
- Theory:-: Experiment No-1 Objective Apparatus RequiredDocumento23 pagineTheory:-: Experiment No-1 Objective Apparatus RequiredAnand SantNessuna valutazione finora
- INTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Lab3Documento8 pagineINTRODUCTION TO COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Lab3tetraprimigNessuna valutazione finora
- 3ECE-AC Lab ManualDocumento62 pagine3ECE-AC Lab ManualShannon DunnNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Commn FinalDocumento39 pagineAnalog Commn FinalYash AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Pulse Amplitude Modulation and Demodulation - Google SearchDocumento30 paginePulse Amplitude Modulation and Demodulation - Google SearchHasan SkNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 15: Frequency Modulation: Purpose and DiscussionDocumento4 pagineExperiment 15: Frequency Modulation: Purpose and Discussionhamizan maulanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment of Amplitude Modulation and Angle ModulationDocumento3 pagineAssignment of Amplitude Modulation and Angle ModulationRhelf Mae ValenciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acl-03-04 - Exp-01-C PR PDFDocumento6 pagineAcl-03-04 - Exp-01-C PR PDFDESMALANILS48Nessuna valutazione finora
- Angle Modulation All 0Documento64 pagineAngle Modulation All 0Yanyan100% (1)
- Equency ModulationDocumento9 pagineEquency Modulationabdhakm92Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anna University Engineering Question Bank: Home About Us Downloads Answers Upload Contact USDocumento42 pagineAnna University Engineering Question Bank: Home About Us Downloads Answers Upload Contact USChenthil KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab-Report Analogue Communications: Amplitude ModulationDocumento11 pagineLab-Report Analogue Communications: Amplitude ModulationmahinNessuna valutazione finora
- BATCH 2018-2022 Submitted By: SubmittedtoDocumento27 pagineBATCH 2018-2022 Submitted By: SubmittedtoshantanuNessuna valutazione finora
- COMMUNICATIONS LAB. Experiment #3: Frequency Modulation / DemodulationDocumento2 pagineCOMMUNICATIONS LAB. Experiment #3: Frequency Modulation / DemodulationaliNessuna valutazione finora
- EC6512 CSLab ManualDocumento42 pagineEC6512 CSLab ManualBalaji VenkatNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Manual: Principles of Communication System LabDocumento30 pagineLaboratory Manual: Principles of Communication System LabAbhishekNessuna valutazione finora
- BandwidthDocumento25 pagineBandwidthlvsaruNessuna valutazione finora
- DC Lab ManualDocumento54 pagineDC Lab ManualAbhimanyu YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- CommunicationDocumento44 pagineCommunicationNilupul WijeratneNessuna valutazione finora
- Module - 06 FM Transmitter and ReceiverDocumento13 pagineModule - 06 FM Transmitter and ReceiverAmin Wahid100% (1)
- (Ebook) US Army Electronics Course - FM Radio Transmitters MM0323Documento175 pagine(Ebook) US Army Electronics Course - FM Radio Transmitters MM0323João HenriqueNessuna valutazione finora
- B.SC Electronics D2 P4 (2020) SolutionsDocumento15 pagineB.SC Electronics D2 P4 (2020) SolutionsShubham KeshriNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog and Digital Communication Important Questions AnswersDocumento21 pagineAnalog and Digital Communication Important Questions AnswersMehboob Khokhar75% (4)
- ECE 401L Lab5Documento10 pagineECE 401L Lab5mrpatilNessuna valutazione finora
- CH-2 Amplitude (Linear) ModulationDocumento38 pagineCH-2 Amplitude (Linear) Modulationelias asefaNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment Number 1 Amplitude Modulation & DemodulationDocumento3 pagineExperiment Number 1 Amplitude Modulation & DemodulationAlasadNessuna valutazione finora
- EC6512 Communication System Lab ManualDocumento52 pagineEC6512 Communication System Lab ManualSalai Kishwar JahanNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 2 FMDocumento33 pagineChapter 2 FMSazali HusinNessuna valutazione finora
- Comm Lab Exp3Documento2 pagineComm Lab Exp3Ahmed MashhoorNessuna valutazione finora
- 2-FM MOD DemodDocumento8 pagine2-FM MOD Demodsmilyboy2904Nessuna valutazione finora
- 08-Com101 AMDocumento11 pagine08-Com101 AMHồng HoanNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Modulation: DefinitionsDocumento40 pagineIntroduction To Modulation: DefinitionsBruno SonzogoNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Bank (I and II)Documento4 pagineQuestion Bank (I and II)Anonymous 4u5XkWGONessuna valutazione finora
- Analog and Digital CommunicationDocumento20 pagineAnalog and Digital CommunicationnofeelingrahulNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Communication Lab Manual PDFDocumento21 pagineAnalog Communication Lab Manual PDFAjeet BhardwajNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog and Digital Communication Systems: The Transmission of Information Is Called CommunicationDocumento71 pagineAnalog and Digital Communication Systems: The Transmission of Information Is Called Communication20-403 TejashwiniNessuna valutazione finora
- AmplitudeModulation PDFDocumento85 pagineAmplitudeModulation PDFKevin Fer CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- FM LectureDocumento33 pagineFM Lectureemg sivanNessuna valutazione finora
- CS1 - Unit 1 - FMDocumento34 pagineCS1 - Unit 1 - FMAjay ANessuna valutazione finora
- 4-1 Amplitude ModulationDocumento19 pagine4-1 Amplitude ModulationMubiru RodneyNessuna valutazione finora
- CS File-1Documento19 pagineCS File-1Shruti NarangNessuna valutazione finora
- ADC QB SolutionsDocumento15 pagineADC QB Solutionssandeep kumar yadavNessuna valutazione finora
- Adc Lab Manual STUDENTDocumento59 pagineAdc Lab Manual STUDENTramNessuna valutazione finora
- Turbo Codes 1. Concatenated Coding System: RS Encoder Algebraic Decoder Layer 2Documento27 pagineTurbo Codes 1. Concatenated Coding System: RS Encoder Algebraic Decoder Layer 2Shathis KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- BCH Codes: BCH (Bose - Chaudhuri - Hocquenghem) Codes Form A LargeDocumento16 pagineBCH Codes: BCH (Bose - Chaudhuri - Hocquenghem) Codes Form A LargeShathis KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- The Reed-Solomon Codes (RS Codes) Are Nonbinary Cyclic CodesDocumento10 pagineThe Reed-Solomon Codes (RS Codes) Are Nonbinary Cyclic CodesShathis KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Maximum Likelihood Decoding of Convolutional CodesDocumento45 pagineMaximum Likelihood Decoding of Convolutional CodesShathis KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2Documento14 pagine2whirryNessuna valutazione finora
- Pre Emphasis and de EmphasisDocumento2 paginePre Emphasis and de EmphasisShathis Kumar50% (2)
- Study of GMSK NewDocumento3 pagineStudy of GMSK NewShathis KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp. No.10 Simulation of Bask, BFSK and BPSK Aim:: Amplitude Shift KeyingDocumento6 pagineExp. No.10 Simulation of Bask, BFSK and BPSK Aim:: Amplitude Shift KeyingShathis KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- PN SeqDocumento8 paginePN SeqShathis KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Pam, PPM, PWMDocumento9 paginePam, PPM, PWMShathis Kumar100% (2)
- Line Coding TechniquesDocumento1 paginaLine Coding TechniquesShathis KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Amplitude Modulation and DemodulationDocumento2 pagineAmplitude Modulation and DemodulationShathis KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp. No.11 Simulation of M-Ary Ask, FSK and PSK Aim:: CommstartupDocumento3 pagineExp. No.11 Simulation of M-Ary Ask, FSK and PSK Aim:: CommstartupShathis KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Block Code Generation Matlab Program:: EXNO: 10 (A)Documento8 pagineBlock Code Generation Matlab Program:: EXNO: 10 (A)Shathis KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp - No.5 Pulse Code Modulation AimDocumento4 pagineExp - No.5 Pulse Code Modulation AimShathis KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 6.delta ModulationDocumento3 pagine6.delta ModulationShathis KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Equency SynthesizerDocumento3 pagineEquency SynthesizerShathis KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.time Division MultiplexingDocumento3 pagine4.time Division MultiplexingShathis KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 FSK ModulationDocumento3 pagine1 FSK ModulationSivaranjani RavichandranNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Ask ModulationDocumento3 pagine2 Ask ModulationSivaranjani RavichandranNessuna valutazione finora
- MPMC Lab Program Solutions: Label Mnemonics Add N NumbersDocumento3 pagineMPMC Lab Program Solutions: Label Mnemonics Add N NumbersShathis KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Curriculum Manual PDFDocumento150 pagineDigital Curriculum Manual PDFSwift SavageNessuna valutazione finora
- SS Signals and Systems PRESENTATIONDocumento212 pagineSS Signals and Systems PRESENTATIONARAVIND100% (1)
- TA2003Documento7 pagineTA2003calinsatNessuna valutazione finora
- 5991 3162enDocumento11 pagine5991 3162enMRousstiaNessuna valutazione finora
- HP Esa-L1500a Spectrum Analyzer - User's and Calibration GuideDocumento325 pagineHP Esa-L1500a Spectrum Analyzer - User's and Calibration GuideSanyel SaitoNessuna valutazione finora
- Freecom2x Manual enDocumento24 pagineFreecom2x Manual enOzNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQs On AMDocumento10 pagineMCQs On AMNajeeb Muhammad HasniNessuna valutazione finora
- B.Tech Model Papers 2019 20Documento54 pagineB.Tech Model Papers 2019 20SYAMALANessuna valutazione finora
- SG 1240Documento2 pagineSG 1240Ryan BlazerNessuna valutazione finora
- AVR300 (SM) PDFDocumento91 pagineAVR300 (SM) PDFJory2005Nessuna valutazione finora
- BSC Comp SC - CBCSS Syllabus PDFDocumento42 pagineBSC Comp SC - CBCSS Syllabus PDFSooraj krishnan v.sNessuna valutazione finora
- Scanner and Ham Radio FrequenciesDocumento67 pagineScanner and Ham Radio Frequenciessrtmedic100% (7)
- Precision Waveform Generator/Voltage Controlled Oscillator FeaturesDocumento12 paginePrecision Waveform Generator/Voltage Controlled Oscillator FeaturesCharles Tineo0% (1)
- Data StructuresDocumento72 pagineData StructuresDrHarman Preet SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- APH Thesis Kurt PeekDocumento101 pagineAPH Thesis Kurt PeekkurtpeekNessuna valutazione finora
- Yaesu FT-7800R Operation ManualDocumento80 pagineYaesu FT-7800R Operation ManualYayok S. Anggoro100% (1)
- Sony HCD Bx9, Dx9Documento70 pagineSony HCD Bx9, Dx9Eduardo Jesus MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- EE 390 - Introduction To Communication Systems: Special NoticesDocumento3 pagineEE 390 - Introduction To Communication Systems: Special NoticesÁngelMorenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Aiwa Cx-jpk33 SMDocumento78 pagineAiwa Cx-jpk33 SMSergio Daniel BarretoNessuna valutazione finora
- Radio RCD 510: Wiring DiagramDocumento6 pagineRadio RCD 510: Wiring DiagramHaji RashidNessuna valutazione finora
- Bose Lifestyle 5 Service Manual PDFDocumento70 pagineBose Lifestyle 5 Service Manual PDFboroda2410100% (4)
- Rt490 Eng ManualDocumento9 pagineRt490 Eng ManualLucian CarabetNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Communication Computer Networks Notes BCA PDFDocumento20 pagineData Communication Computer Networks Notes BCA PDFHemalatha S Chinnu100% (2)
- Service Manual: Fm/Am Compact Disc PlayerDocumento48 pagineService Manual: Fm/Am Compact Disc PlayerLeandro PimentelNessuna valutazione finora
- AM ProjectDocumento30 pagineAM ProjectMariam muhsenNessuna valutazione finora
- EMI Innovations Texas InstrumentsDocumento18 pagineEMI Innovations Texas InstrumentsJUAN SEBASTIAN DIAZ BERDECIANessuna valutazione finora
- 47 PDFDocumento2 pagine47 PDFSaravananSelvarajNessuna valutazione finora
- Sem-4 CSEDocumento7 pagineSem-4 CSEdattpatel2020Nessuna valutazione finora
- FM Bugger Circuit Final Project CorrDocumento42 pagineFM Bugger Circuit Final Project CorrEmmanuel M RaimiNessuna valutazione finora
- Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsDa EverandMicrosoft Azure Infrastructure Services for Architects: Designing Cloud SolutionsNessuna valutazione finora
- ITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationDa EverandITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- CCNA Certification Study Guide, Volume 2: Exam 200-301Da EverandCCNA Certification Study Guide, Volume 2: Exam 200-301Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxDa EverandHacking: A Beginners Guide To Your First Computer Hack; Learn To Crack A Wireless Network, Basic Security Penetration Made Easy and Step By Step Kali LinuxValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (67)
- Hacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.Da EverandHacking Network Protocols: Complete Guide about Hacking, Scripting and Security of Computer Systems and Networks.Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Evaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsDa EverandEvaluation of Some Websites that Offer Virtual Phone Numbers for SMS Reception and Websites to Obtain Virtual Debit/Credit Cards for Online Accounts VerificationsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- The Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionDa EverandThe Compete Ccna 200-301 Study Guide: Network Engineering EditionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (4)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C01 ExamDa EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C01 ExamValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Cybersecurity: The Beginner's Guide: A comprehensive guide to getting started in cybersecurityDa EverandCybersecurity: The Beginner's Guide: A comprehensive guide to getting started in cybersecurityValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Palo Alto Networks: The Ultimate Guide To Quickly Pass All The Exams And Getting Certified. Real Practice Test With Detailed Screenshots, Answers And ExplanationsDa EverandPalo Alto Networks: The Ultimate Guide To Quickly Pass All The Exams And Getting Certified. Real Practice Test With Detailed Screenshots, Answers And ExplanationsNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical TCP/IP and Ethernet Networking for IndustryDa EverandPractical TCP/IP and Ethernet Networking for IndustryValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (2)
- Cybersecurity: A Simple Beginner’s Guide to Cybersecurity, Computer Networks and Protecting Oneself from Hacking in the Form of Phishing, Malware, Ransomware, and Social EngineeringDa EverandCybersecurity: A Simple Beginner’s Guide to Cybersecurity, Computer Networks and Protecting Oneself from Hacking in the Form of Phishing, Malware, Ransomware, and Social EngineeringValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (40)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamDa EverandAWS Certified Solutions Architect Study Guide: Associate SAA-C02 ExamNessuna valutazione finora
- Set Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNDa EverandSet Up Your Own IPsec VPN, OpenVPN and WireGuard Server: Build Your Own VPNValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Computer Networking: The Complete Beginner's Guide to Learning the Basics of Network Security, Computer Architecture, Wireless Technology and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCENT, and CCNA)Da EverandComputer Networking: The Complete Beginner's Guide to Learning the Basics of Network Security, Computer Architecture, Wireless Technology and Communications Systems (Including Cisco, CCENT, and CCNA)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (4)
- ITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationDa EverandITIL® 4 Create, Deliver and Support (CDS): Your companion to the ITIL 4 Managing Professional CDS certificationNessuna valutazione finora
- Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Systems Architecture and DesignDa EverandOpen Radio Access Network (O-RAN) Systems Architecture and DesignNessuna valutazione finora
- CWNA Certified Wireless Network Administrator Study Guide: Exam CWNA-108Da EverandCWNA Certified Wireless Network Administrator Study Guide: Exam CWNA-108Nessuna valutazione finora
- Microsoft Certified Azure Fundamentals Study Guide: Exam AZ-900Da EverandMicrosoft Certified Azure Fundamentals Study Guide: Exam AZ-900Nessuna valutazione finora