Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Karl Fischer - New
Caricato da
fadlysuriansyahDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Karl Fischer - New
Caricato da
fadlysuriansyahCopyright:
Formati disponibili
3 2000
Advances in Analytical Chemistry
Latest Developments of Karl Fischer Reagents More Convenience and less Toxicity
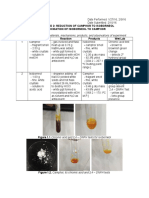
Karl Fischer Titration The Karl Fischer titration is a widely used titrimetric method for water determination in various substances. The determination of water is important to check the product quality and to assure even chemical and physical properties of the product. In the pharmaceutical industry for example a stable water content is important for intermediate powders which are formed to tablets. When the powder is too dry, the tablets crumble, when it is too wet, the tablets will stick to the blister foil. The loss-on-drying often used is not suitable for a variety of samples since it determines all volatile material and not only the water content. Karl Fischers Original Reagents In 1935 the German chemist Karl Fischer (figure 2) needed a method for moisture determination in sulphur dioxide. He mixed a reagent containing pyridine, sulphur dioxide and iodine according to the Bunsen equation without the excess of water. He formulated [1]: 2 H2O + SO2 + 2 Py + I2 H2SO4 + 2HI*Py
Py = pyridine
He validated the reagent by adding known amounts of water but never attempted to modify his formulation. In the next 40 years the Karl Fischer titration was slightly modified, but there was no significant progress. The KF titration was disliked by the laboratory technicians since it was difficult to determine the end-point, the reagent contained pyridine and was malodorous. First Generation of Pyridine-free Karl Fischer Reagents In the beginning of the 80s Eugen Scholz at Riedel-de Han in Germany started investigations on KF reagents. The objective was to develop a reagent without the pyridine odour. After a few months he formulated the following reaction equation [2]: 1. step SO2 + MeOH + B MeSO3- + HB+ 2. step MeSO3- + H2O + I2 + 2 B MeSO4- + 2 HB+ + 2 IB = Base
4
Figure 1: Titration curves A= 2 component reagent, pyridine-free B= 1 component reagent, pyridine-free C= 1 component reagent, containing pyridine
mg H2O
(2a)
3
(2b)
1 T [min]
(1)
He discovered that the methanol takes 0 part in the reaction forming the methyl sulphite, one active species in the KF titration. As Anders Cedergren noticed some years before the pyridine was just a buffering agent and not a reactive part [3]. According to the results it was possible to replace the unpleasant pyridine with the odourless imidazole. The second advantage
Contents: Theory of Karl Fischer titration Reagents for general use Reagent for special applications Non-toxic Karl Fischer reagents
a member of the Sigma-Aldrich Family
of the imidazole is its higher basicity which leads to a faster reaction speed and more stable endpoints (figure 1). Within a short period of time, various reagents for general use in one-component titration, two-component titration and coulometric titration had been formulated. Second Generation of Pyridine-free Karl Fischer Reagents: Specialities Water determination in a variety of different products had been possible at that point. But there were still a large group of samples which underwent side reactions with the ingredients of the KF reagents. Acids and bases change the pH which supports side reactions [4], and fats and oils do not dissolve. A very typical side reaction is the generation of ketals from ketones and methanol. During this reaction water is formed and causes false results and fading end-points (figures 3 + 4). Typical acetal formation (3)
Therefore, it was necessary to develop reagents which did not undergo side reactions while keeping their reactivity. Systematic investigations of various organic solvents showed that halogenated alcohols react according to equation (2a) and do not form by-products with carbonyl compounds as (3), [2]. Chloroform also has a positive effect on the KF titration and in addition it dissolves a variety of compounds which are insoluble in methanol. In coulometric determination, the conductivity of such compounds generates problems. Chloroform has a very low dielectric constant, thereby making it impossible to form a coulometric reagent based on pure chloroform. On the other hand, a suitable alcohol is necessary to keep the exact stochiometry of the Karl Fischer reaction. A conductivity of at least 10 mS/cm is also required in the reagent. Trifluoroethanol is the solution: it improves the conductivity and does not undergo side reactions. Third Generation of Karl Fischer Reagents: environmentally friendly In the late 80s health and environment became important points in public discussion. Carbontetrachloride, which was part of all commercial coulometric catholytes for KF titration, was forbidden in the USA because of its cancerogenity. Halogenated hydrocarbons became more expensive to dispose. Therefore attempts were made to remove these solvents from KF reagents. Unfortunately, we found that they were needed as reaction partners, not only as solvents. Carbontetrachloride and chloroform were reduced in the cathodic KF reaction [5]. CCl4 + 2 e + 1 H+ HCCl3 + Cl
-
Figure 2: Karl Fischer
R C R O+
CH 3OH CH 3OH
R C R
OCH 3 + H 2O OCH 3
Figure 3: Titration of acetone in methanol, no end-point found
V [ml reagent] 10
8 6
(4a) (4b)
HCCl3 + 2 e + 1 H+ H2CCl2 + Cl
a
T [min] 2 4 6 8
4 2 0
Figure 4: Titration of acetone in HYDRANAL-Working Medium K, stable end-point found
V [ml reagent] 8
These reductions form electrochemical inert products (chloride, chloroform and methylene chloride) which could not be oxidised at the anode. In a catholyte without halogenated hydrocarbons, methyl sulphite is reduced. The reduction products diffuse into the anode compartment of the coulometric cell where they act as water. We found that ammonium salts can be used as a reactive agent in KF catholytes. In this case, hydrogen ions are reduced to hydrogen which evaporates out of the cell and does not disturb the anodic reaction. For analysis of ketones the halogenated alcohols can be replaced by glycol ethers and long chain alcohols.
E
6
a
2
T [min] 0 2 4 6 8
Forth Generation of Karl Fischer Reagents: non-hazardous Environmentally friendly is not automatically also friendly for mankind. A lot of KF reagents have still been based on methanol. Methanol is considered toxic and displays the skull and crossbone on the label. Our next goal was to make a reagent line which protects the people in the lab as good as possible from the danger of hazardous chemicals. For the HYDRANAL-Composite products, the one-component reagents for the volumetric titration this has already been done in the late 80s. These reagents contain a long-chain ether as solvent, the diethylenglycol monoethyl ether which is non-toxic and not easy flammable. Since the base imidazole buffers the acid sulphur dioxide, the reagent is not irritant for skin or eyes. Particular studies have been made under GMP conditions to prove these properties. The remaining reagents were the two-component reagents for volumetric titration and the coulometric reagents which all contained methanol as main ingredient. Methanol has a close-related brother in chemical understanding, the ethanol. Ethanol has not been used in the past for Karl Fischer reagents for two reasons. First, the reaction rate of the Karl Fischer reaction in pure ethanol is very slow. Secondarily, the electrochemical behaviour varies from the methanol, the conductivity is lower, that hinders the suitability in a coulometric reagent. The first problem could be dissolved by speeding-up the ethanol. Special salts are added to the solvent which increase the reaction speed in ethanol and do not disturb the Karl Fischer titration. Based on this technique the two component reagents HYDRANAL-Solvent E and HYDRANAL-Titrant E as well as the working medium HYDRANAL-CompoSolver could be developed [6] (see also figure 5). The conductivity for a coulometric reagent mainly consisting of ethanol could be adjusted to the a/m requirements by using special additives. This knowledge led to HYDRANAL-Coulomat E. As additional benefit this reagent can be used as anolyte and as catholyte as well for the cell with diaphragm. A special catholyte reagent is no longer necessary. Plenty of formulations and mixtures are created around the described reagents in order to make the Karl Fischer titration as convenient as possible.
All these investigations caused a better understanding of the complicated mechanisms of Karl Fischer reactions and led to Karl Fischer reagents which were more stable, had better accuracy and less safety risks than the obscure mixture Karl Fischer had published in 1935.
3,5
Reagent Consumption [ml]
3 2,5 2 1,5 1 0,5 0
Ethanol CompoSolver
End-point CompoSolver 0 0,5 1 1,5 2 2,5 3 3,5 4
End-point pure ethanol 4,5
time [min]
Figure 5: Titration curve pure ethanol, delayed titration Titration curve HYDRANALCompoSolver; rapid titration
References
[1] Fischer, K.; Neues Verfahren zur massanalytischen Bestimmung des Wassergehaltes von Flssigkeiten und festen Krpern, Angew. Chemie, 48, 394, 1935 [2] Scholz, E.; Karl Fischer Titration, Springer Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, Tokyo, 1983 [3] Cedergren, A.; Reaction Rates between Water and Karl Fischer Reagent Talanta, 21, 265, 1974 [4] Wuensch, G., Schoeffski, K.; Die Iodierende Nebenreaktion im Karl Fischer System, Anal. Chimica Acta, 239, 283, 1990 [5] Scholz, E.; Karl Fischer Coulometry - the Cathode Reaction, Fresenius J.Anal. Chem., 348, 269, 1994 [6] Hoffmann, H.; Karl-Fischer-Reagenz enthaltend Ethanol als alkoholische Komponente, European Patent Application 98121169.1; 1998.
over 20 years experience in Karl Fischer Titration
Please ask for your personal copy of our HYDRANAL-Manual.
-Manual
Eugen Scholz Reagents for Karl Fischer Titration
for technical help for Karl Fischer titration please contact our HYDRANAL-Laboratory Ms Helga Hoffmann Tel: ++49 5137 8238 353 Fax: ++49 5137 8238 698 Email: hhoffman@eurnotes.sial.com
Sigma-Aldrich
Your favorite analytical research associate
More than 20,000 analytical products and 2,000 applications from all the Sigma-Aldrich brands have been brought together in one place. They have been organized by analytical technique. If you browse the on-line catalogue or search by keyword, name, CAS#, or application, you will be able to find the products you need.
www.sigma-aldrich.com/analytical
A Member of the Sigma-Aldrich Family
Biochemicals and Reagents for Life Science Research
Organics and Inorganics for Chemical Synthesis
Speciality Chemicals and Analytical Reagents for Research
Laboratory Chemicals and Reagents for Research and Analysis
Chromatography Products for Analysis and Purification
DGE
6.2000 / 56
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Lab8 PDFDocumento5 pagineLab8 PDFgb-sarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Bruttel - Water Determination by Karl Fischer TitrationDocumento81 pagineBruttel - Water Determination by Karl Fischer TitrationFernanda LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Determination by Karl FischerTitrationDocumento81 pagineWater Determination by Karl FischerTitrationtraffik100% (1)
- ABC of Karl Fischer Titration: in Theory and PracticeDocumento23 pagineABC of Karl Fischer Titration: in Theory and PracticeSandi VicoNessuna valutazione finora
- Synthesis of An Alkyl HalideDocumento4 pagineSynthesis of An Alkyl HalideClyde Co SorianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal (Karl Fischer)Documento3 pagineJournal (Karl Fischer)jumi jumdailNessuna valutazione finora
- 2-28!3!14 Oxidation ReductionDocumento11 pagine2-28!3!14 Oxidation ReductionNadine Harajli HamzehNessuna valutazione finora
- Anisole SynthesisDocumento6 pagineAnisole SynthesisManoj Tiwari0% (1)
- REACTIONS OF HYDROCARBONSDocumento6 pagineREACTIONS OF HYDROCARBONSAnn Gelé100% (1)
- Aliphatic Compounds: Dihydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and DerivativesDa EverandAliphatic Compounds: Dihydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and DerivativesNessuna valutazione finora
- Aliphatic Compounds: Trihydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and Derivatives, Penta- and Higher Polyhydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and Derivatives; Saccharides, Tetrahydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and DerivativesDa EverandAliphatic Compounds: Trihydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and Derivatives, Penta- and Higher Polyhydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and Derivatives; Saccharides, Tetrahydric Alcohols, Their Oxidation Products and DerivativesNessuna valutazione finora
- KF ChemicalsDocumento52 pagineKF ChemicalsKevin FriasNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review of New Developments in The Friedel Crafts Alkylation From Green Chemistry To Asymmetric CatalysisDocumento24 pagineA Review of New Developments in The Friedel Crafts Alkylation From Green Chemistry To Asymmetric CatalysisNicolas LoonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Quantitative Determination of WaterDocumento23 pagineQuantitative Determination of WaterApurba Sarker Apu100% (1)
- Experiment 2: AROMATIC SIDE-CHAIN OXIDATION: PHTHALIC ACID FROM XYLENEDocumento4 pagineExperiment 2: AROMATIC SIDE-CHAIN OXIDATION: PHTHALIC ACID FROM XYLENEPrincess Alyssa Abid0% (1)
- GEMs ID90Documento8 pagineGEMs ID90Andre PNessuna valutazione finora
- Friedel CraftsDocumento8 pagineFriedel CraftsAhmed MashalyNessuna valutazione finora
- 961 Efficient Method Going From OH To Cle3b0Documento3 pagine961 Efficient Method Going From OH To Cle3b0Wolmir NemitzNessuna valutazione finora
- The Karl Fischer Reaction: StoichiometryDocumento3 pagineThe Karl Fischer Reaction: StoichiometrygoparsucoNessuna valutazione finora
- Preparation and Purification of An Alkyl Halide FRDocumento6 paginePreparation and Purification of An Alkyl Halide FRCamille GrefaldiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 4 Alcohol - 2011-2Documento8 pagineLab 4 Alcohol - 2011-2Miisty Raiyen HallNessuna valutazione finora
- The Oxidation of Alcohols and Ethers Using Calcium HypochloriteDocumento3 pagineThe Oxidation of Alcohols and Ethers Using Calcium HypochloriteVictor VikeneNessuna valutazione finora
- I. Experiment Title: Aldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic AcidDocumento10 pagineI. Experiment Title: Aldehyde, Ketone and Carboxylic AcidLaily SafitriNessuna valutazione finora
- Fatty Acid Derivatives of DiethanolamineDocumento6 pagineFatty Acid Derivatives of DiethanolamineLeek AgoessNessuna valutazione finora
- Non Aqueous AcidDocumento10 pagineNon Aqueous Acidcyper zoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp 3-Reduction of Cyclohexanone With Sodium BorohydrideDocumento11 pagineExp 3-Reduction of Cyclohexanone With Sodium Borohydrideakuserai100% (3)
- JPPS 0209 Zhen GalleyDocumento8 pagineJPPS 0209 Zhen GalleyGregorio ValeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydroformylation Reaction ProcessDocumento5 pagineHydroformylation Reaction ProcessJohann ChorenNessuna valutazione finora
- Reppe Chemistry, Result in A Class of Materials Fond Commonly in Persdnal CareDocumento7 pagineReppe Chemistry, Result in A Class of Materials Fond Commonly in Persdnal Careadamsamodra0% (1)
- Formal Report Chem 31.1Documento6 pagineFormal Report Chem 31.1Elah PalaganasNessuna valutazione finora
- REDUCTION OF CAMPHOR TO ISOBORNEOL and OXIDATION OF ISOBORNEOL TO CAMPHORDocumento3 pagineREDUCTION OF CAMPHOR TO ISOBORNEOL and OXIDATION OF ISOBORNEOL TO CAMPHORPaul ColoyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Swimming Pool Water TreatmentDocumento7 pagineSwimming Pool Water TreatmentTejinder SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Titrasi Karl Fischer Metode Penentuan Kadar AirDocumento13 pagineTitrasi Karl Fischer Metode Penentuan Kadar AirNovia Tri AstutiNessuna valutazione finora
- Formal Report For Synthesis of An Alkyl HalideDocumento5 pagineFormal Report For Synthesis of An Alkyl HalideLovelyn Marie Morada Nievales80% (5)
- A Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidDa EverandA Further Investigation of the Symmetrical Chloride of Paranitroorthosulphobenzoic AcidNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry of Hydrocarbon Experiment 16: ObjectiveDocumento10 pagineChemistry of Hydrocarbon Experiment 16: ObjectiveWena Sta Maria100% (1)
- Cyanex 272Documento37 pagineCyanex 272partyweirdo100% (2)
- Exp 10 EsterDocumento14 pagineExp 10 EsterLaris J. Garcia100% (1)
- Formal Report, Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocumento4 pagineFormal Report, Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesVicente Romeo M Macatangay88% (8)
- Synthesis of 1,4-Dihydropyridine Derivatives via Hantzsch ReactionDocumento10 pagineSynthesis of 1,4-Dihydropyridine Derivatives via Hantzsch Reactionkavi_prakash6992Nessuna valutazione finora
- Biokim I (3) 2Documento14 pagineBiokim I (3) 2Aisyah LarasatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Synthetic Tannins, Their Synthesis, Industrial Production and ApplicationDa EverandSynthetic Tannins, Their Synthesis, Industrial Production and ApplicationNessuna valutazione finora
- 20.6 Per Cent During: (Contribution Research Department H - D. Justi INC.)Documento4 pagine20.6 Per Cent During: (Contribution Research Department H - D. Justi INC.)Ahmed SoltanNessuna valutazione finora
- Group journal on classification testsDocumento6 pagineGroup journal on classification testsErica OcheaNessuna valutazione finora
- AquametryDocumento36 pagineAquametryFoyz Ahmed Shohel75% (4)
- Transition Metal Catalyzed Furans Synthesis: Transition Metal Catalyzed Heterocycle Synthesis SeriesDa EverandTransition Metal Catalyzed Furans Synthesis: Transition Metal Catalyzed Heterocycle Synthesis SeriesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 31.1 Formal Report 1Documento3 pagineChem 31.1 Formal Report 1chewazableNessuna valutazione finora
- Alcohols2halides hcl-zncl2Documento5 pagineAlcohols2halides hcl-zncl2mancivalNessuna valutazione finora
- A Convenient Preparation of Volatile Acid ChloridesDocumento4 pagineA Convenient Preparation of Volatile Acid ChloridesScott SwartzNessuna valutazione finora
- Carbonyl GroupDocumento32 pagineCarbonyl GroupYan Xin LuNessuna valutazione finora
- Aldehydes and Ketones ReactionsDocumento9 pagineAldehydes and Ketones ReactionsKudzayi Tusaumwe100% (1)
- Lab Number 10: Green Oxidation of Alcohols Synthesis of CamphorDocumento1 paginaLab Number 10: Green Oxidation of Alcohols Synthesis of CamphorAbdulNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacture of Formaldehyde from Methanol Plant DesignDocumento51 pagineManufacture of Formaldehyde from Methanol Plant DesignHamdan YusoffNessuna valutazione finora
- Esters From T H E Reactions of Alkyl Halides and Salts Carboxylic AcidsDocumento3 pagineEsters From T H E Reactions of Alkyl Halides and Salts Carboxylic AcidsSrg9 3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Optimized 2C-B Synthesis via Nitrostyrene ReductionDocumento1 paginaOptimized 2C-B Synthesis via Nitrostyrene ReductionFermin GamboaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Green Method For Synthesis of Cyclohexanone Oxidation of Cyclohexanol Using Sodium HypochloriteDocumento6 pagineA Green Method For Synthesis of Cyclohexanone Oxidation of Cyclohexanol Using Sodium Hypochloritefleetfoxes886% (7)
- Carbonyl CompoundsDocumento73 pagineCarbonyl CompoundsRamazan AshirkhanNessuna valutazione finora
- 51LB Week5 7 W13 Background 2 PDFDocumento5 pagine51LB Week5 7 W13 Background 2 PDFValine Cysteine MethionineNessuna valutazione finora
- Esterification Oil of WintergreenDocumento8 pagineEsterification Oil of WintergreenMaria MahusayNessuna valutazione finora
- Iridium Complexes in Organic SynthesisDa EverandIridium Complexes in Organic SynthesisLuis A. OroNessuna valutazione finora
- Deal-Grove Model for Thermal Oxide GrowthDocumento13 pagineDeal-Grove Model for Thermal Oxide GrowthChithraParameswaranNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Basic Clinical Genetic - ppt-1Documento24 pagine2 Basic Clinical Genetic - ppt-1Najib M. NauvalNessuna valutazione finora
- MotionDocumento6 pagineMotionRobert willaimsNessuna valutazione finora
- Flax 7Documento7 pagineFlax 7Rajyalakshmi MNessuna valutazione finora
- Land Deep Production Casings in Menengai Geothermal FieldDocumento30 pagineLand Deep Production Casings in Menengai Geothermal FieldShafeeq ChappuNessuna valutazione finora
- Nucleic Acids BrochureDocumento2 pagineNucleic Acids BrochureCring-cring NavarroNessuna valutazione finora
- Packed bed axial thermal conductivityDocumento7 paginePacked bed axial thermal conductivityAdriano HenriqueNessuna valutazione finora
- Spontaneous Combustion ConversionDocumento68 pagineSpontaneous Combustion ConversionRizwan Ullah BaigNessuna valutazione finora
- A Comprehensive Review On The Genus: Mussaenda: Astalakshmi N and Sundara Ganapathy RDocumento8 pagineA Comprehensive Review On The Genus: Mussaenda: Astalakshmi N and Sundara Ganapathy RSahabat Baljai100% (1)
- Name of Elements Properties Use/S 1. ZinkDocumento13 pagineName of Elements Properties Use/S 1. ZinkNora Alfaro BalsakiNessuna valutazione finora
- PK - FKK.PPM - Manual Makmal Che565: Chemical Engineering Laboratory IiiDocumento21 paginePK - FKK.PPM - Manual Makmal Che565: Chemical Engineering Laboratory Iiibedirtupak92% (12)
- Cniai 34686 0003Documento45 pagineCniai 34686 0003Nirosha Dilrangi PereraNessuna valutazione finora
- Liquefied Gas HandbookDocumento38 pagineLiquefied Gas HandbookAndri Suharto100% (1)
- FlexEJ Brochure Elaflex 10 2011Documento41 pagineFlexEJ Brochure Elaflex 10 2011harlyganNessuna valutazione finora
- TubingDocumento6 pagineTubingkevin wongNessuna valutazione finora
- Onions: Vegetable Crops Production Guide For The Atlantic ProvincesDocumento8 pagineOnions: Vegetable Crops Production Guide For The Atlantic ProvincesEglNessuna valutazione finora
- ASPHALT METHOD STATEMENTDocumento7 pagineASPHALT METHOD STATEMENTBasem Donia100% (1)
- Chemical, Physical, and Baking Properties of Apple FiberDocumento4 pagineChemical, Physical, and Baking Properties of Apple FiberHector FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- SeminarDocumento15 pagineSeminarAditi ChandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Groundwater ContaminationDocumento25 pagineGroundwater ContaminationjoshjethNessuna valutazione finora
- PIP PCECV001 Guidelines For Application of Control ValvesDocumento39 paginePIP PCECV001 Guidelines For Application of Control ValvesAndresNessuna valutazione finora
- დ მიქელაძის-ბიოქიმიაDocumento201 pagineდ მიქელაძის-ბიოქიმიაJuli JulianaNessuna valutazione finora
- Water WastewaterDocumento20 pagineWater WastewaterterryjoseeNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionDocumento8 pagineLesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionGreatel Elijah TorregosaNessuna valutazione finora
- Principles of Drug Administration and OrderingDocumento26 paginePrinciples of Drug Administration and OrderingManasseh Mvula33% (3)
- 2593Documento9 pagine2593Zaid AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- PVC FlamethrowerDocumento21 paginePVC FlamethrowerMike Nichlos100% (4)
- Sample IPM PlanDocumento4 pagineSample IPM PlanEricNessuna valutazione finora
- Atracurium BesylateDocumento4 pagineAtracurium BesylateStill DollNessuna valutazione finora
- 5468-Tank Cleaning ChecklistDocumento3 pagine5468-Tank Cleaning ChecklistMaaloul FakherNessuna valutazione finora