Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Principles of Islamic Economics (Ahm) 21.02.2012
Caricato da
Abdullahil MamunDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Principles of Islamic Economics (Ahm) 21.02.2012
Caricato da
Abdullahil MamunCopyright:
Formati disponibili
INTERNATIONAL ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY CHITTAGONG
Department of Business Administration Course Title : Principles of Islamic Economics Course Code : ECON-2403
Objective of the Course The aim of the course is to provide a conceptual framework of Islamic Economics. The course is designed to enable students to understand how Islam and Islamic worldview permeate all aspects of life including economics. The basic premise of this course is that the study of Islamic economics proceeds from the Islamic worldview and has to be developed according to a methodology that is founded upon this worldview. Since economics deals with various aspects such as production, consumption, distribution, factors of production, pricing of factors, market strategies etc., all these areas will be dealt within the course in Islamic perspective. Moreover, the Islamic public finance i,e zakat and Islamic banking system will also be covered in the course with due emphasis . Furthermore, a comparative analysis of different economic systems will also be made in the course so as to enable the students to formulate ideas regarding Islamic economics in its truest perspective.
COURSE OUTLINE
Mid Term Examination 1. Introduction: Definitions , development of Islamic economic thought, Islamic Economic Worldview, Basis of Islamic economics, goals or objectives of Islamic economics, assumptions of Islamic economics, main sources of knowledge of Islamic economic study, importance of Islamic economics. Comparative Economic System: Laissez faire economy, market economy, command economy, mixed economy, differences between Islamic economy and capitalist economy. 2. An overview of microeconomics in an Islamic frame work i) Consumer Behavior in Islam: Some basic concepts: need vs demand, Islamic concept of need, want-utility vs need-maslahah, Characteristics of consumer in an Islamic economy, differences between capitalist and Islamic consumer's behavior, Objectives of consumption in Islam, Theory of consumer behavior in Islamic economics: Monzer Kahf Model and its differences with conventional theory of consumer behaviour. Derivation of Final Spending Function, Shifts in the Final Spending Function. ii) Market Mechanism from Islamic Perspective: Islamic theory of effective needbased demand and potential capacity- based supply, Market Mechanism: Determination of Price and Quantity, Islamic Approach to Market Prices- Islamic pricing policy- Three policy options: Desirable policy option in Islam. iii) The Theory of Production in Islam: Objectives of Production, the goals of the firm- Profit Maximization VS Sales Maximization, Factors of Production and Their Pricing: Islamic Perspective. Characteristics of an Islamic Firm, Theory of Islamic Firm: Metwally Model, Differences between firms in an Islamic society and in a non-islamic society, understanding of the concept of profit and profit share in Islam. Satisfying behaviour, Advertising in Islam. Final Examination iv) Market structure in Islam: Monopoly market and Islam characteristics of a monopolist in Islam, price-quantity relationship of a monopoly market in an Islamic perspective, price discrimination and Islam, Covering Loss through price discrimination, Oligopoly market and Islam definition of oligopoly market and its characteristics, kink demand curve in an oligopoly market and Islamic perspective.
3. An overview of macroeconomics in an Islamic frame work: i) Consumption function in Islam: Concept of Consumption in Islam, Consumption Function in Islam, Determinants of Islamic Consumption Function, Debates regarding APC and MPC- Model of M. A. MANNAN, Expected Desirable income hypothesis and Consumption, Aggregate Consumption Function. ii) Riba or Interest and Profit Loss Sharing System: Definition of riba, different concepts about riba, characteristics of riba, types of riba, Arguments for Riba or Interest in Conventional Economy, Reasons behind Prohibition of Riba in an Islamic Economy, Profit: How is it different from Riba? Saving and Investment Behaviour in Islam: Saving and Investment Decisions, Profit-Loss Sharing System- Its superiority over interest based system. iii) Islamic banking system: Problems of Traditional Banking System, Concept of Islamic banking, emergence of Islamic banking system, features of Islamic banking, Functions of Islamic banks, objectives of Islamic banking, Contributions of Islamic Banks towards Socio-economic development. differences between traditional banking and Islamic banking, sources and uses of funds of Islamic bank, financing systems of Islamic bank. iv) Public finance in Islam Zakat : Zakat and Islam What is zakat and why is zakat? Principles of Zakat. Differences between Zakat and capitalist tax system, Basis of Zakat: Nisab and the rate of Zakat, Inflation and Zakat objectives of Zakat moral, religious and socio-economic objectives, Zakat recipients, the role of state in Zakat collection and distribution. v) Law of inheritance in Islam and its significance. C.RECOMMENDED BOOKS: Sayyid Tahir, Aidit Ghazali, Syed Omar Syed Agil M. A. Hamid Texts Readings on Microeconomics: An Islamic Perspective Islamic Economics An Introductory Analysis
References Longman , Kuala Lumpur , Malaysia Readings in microeconomics M.A. Mannan Islamic Economics Theory and Practice Reference Journals Thoughts on Islamic Economics Islamic economics research bureau The journal of Islamic Economics International Islamic University , Malaysia D. Marks Distribution : Class test , assignment and attendance 20% Mid Term Examination (duration 90 minutes) 30% Final Examination (duration 2 hours and 30 minutes) 50% Total 100% Course Instructor: ABDULLAHIL MAMUN, Assistant Professor, DBA, IIUC. Cell: 01712138373 e-mail: ahm_economics@yahoo.com
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Remittance-Induced Output Growth in BangladeshDocumento16 pagineRemittance-Induced Output Growth in BangladeshAbdullahil MamunNessuna valutazione finora
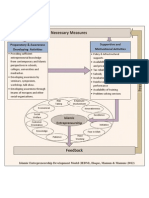
- Islamic Entrepreneurship Development ModelDocumento1 paginaIslamic Entrepreneurship Development ModelAbdullahil MamunNessuna valutazione finora
- Islamic Economics and Banking (Ahm) 21.04.2012Documento2 pagineIslamic Economics and Banking (Ahm) 21.04.2012Abdullahil MamunNessuna valutazione finora
- Working Paper 1-05 Public Expenditure in Primary Education in Ban Glades Ah - An AnalysisDocumento18 pagineWorking Paper 1-05 Public Expenditure in Primary Education in Ban Glades Ah - An AnalysisAbdullahil MamunNessuna valutazione finora
- ICMA Journal September October 2010Documento44 pagineICMA Journal September October 2010Abdullahil MamunNessuna valutazione finora
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Fact Pack Financial Services KenyaDocumento12 pagineFact Pack Financial Services KenyaCatherineNessuna valutazione finora
- Catalogue of The Herbert Allen Collection of English PorcelainDocumento298 pagineCatalogue of The Herbert Allen Collection of English PorcelainPuiu Vasile ChiojdoiuNessuna valutazione finora
- Jainithesh - Docx CorrectedDocumento54 pagineJainithesh - Docx CorrectedBala MuruganNessuna valutazione finora
- RFM How To Automatically Segment Customers Using Purchase Data and A Few Lines of PythonDocumento8 pagineRFM How To Automatically Segment Customers Using Purchase Data and A Few Lines of PythonSteven MoietNessuna valutazione finora
- Payment Plan 3-C-3Documento2 paginePayment Plan 3-C-3Zeeshan RasoolNessuna valutazione finora
- Fortigate Fortiwifi 40F Series: Data SheetDocumento6 pagineFortigate Fortiwifi 40F Series: Data SheetDiego Carrasco DíazNessuna valutazione finora
- Ting Vs Heirs of Lirio - Case DigestDocumento2 pagineTing Vs Heirs of Lirio - Case DigestJalieca Lumbria GadongNessuna valutazione finora
- Opel GT Wiring DiagramDocumento30 pagineOpel GT Wiring DiagramMassimiliano MarchiNessuna valutazione finora
- Nguyen Dang Bao Tran - s3801633 - Assignment 1 Business Report - BAFI3184 Business FinanceDocumento14 pagineNguyen Dang Bao Tran - s3801633 - Assignment 1 Business Report - BAFI3184 Business FinanceNgọc MaiNessuna valutazione finora
- 11 TR DSU - CarrierDocumento1 pagina11 TR DSU - Carriercalvin.bloodaxe4478100% (1)
- DevelopmentPermission Handbook T&CPDocumento43 pagineDevelopmentPermission Handbook T&CPShanmukha KattaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sena BrochureDocumento5 pagineSena BrochureNICOLAS GUERRERO ARANGONessuna valutazione finora
- Aisc Research On Structural Steel To Resist Blast and Progressive CollapseDocumento20 pagineAisc Research On Structural Steel To Resist Blast and Progressive CollapseFourHorsemenNessuna valutazione finora
- Divider Block Accessory LTR HowdenDocumento4 pagineDivider Block Accessory LTR HowdenjasonNessuna valutazione finora
- Cinnamon Peelers in Sri Lanka: Shifting Labour Process and Reformation of Identity Post-1977Documento8 pagineCinnamon Peelers in Sri Lanka: Shifting Labour Process and Reformation of Identity Post-1977Social Scientists' AssociationNessuna valutazione finora
- Finaniial AsceptsDocumento280 pagineFinaniial AsceptsKshipra PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- DFUN Battery Monitoring Solution Project Reference 2022 V5.0Documento50 pagineDFUN Battery Monitoring Solution Project Reference 2022 V5.0A Leon RNessuna valutazione finora
- SKF LGMT-2 Data SheetDocumento2 pagineSKF LGMT-2 Data SheetRahul SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Atom Medical Usa Model 103 Infa Warmer I - 2 PDFDocumento7 pagineAtom Medical Usa Model 103 Infa Warmer I - 2 PDFLuqman BhanuNessuna valutazione finora
- Sun Hung Kai 2007Documento176 pagineSun Hung Kai 2007Setianingsih SENessuna valutazione finora
- ADS Chapter 303 Grants and Cooperative Agreements Non USDocumento81 pagineADS Chapter 303 Grants and Cooperative Agreements Non USMartin JcNessuna valutazione finora
- Deshidratador Serie MDQDocumento4 pagineDeshidratador Serie MDQDAIRONessuna valutazione finora
- Immovable Sale-Purchase (Land) ContractDocumento6 pagineImmovable Sale-Purchase (Land) ContractMeta GoNessuna valutazione finora
- CC Anbcc FD 002 Enr0Documento5 pagineCC Anbcc FD 002 Enr0ssierroNessuna valutazione finora
- h6811 Datadomain DsDocumento5 pagineh6811 Datadomain DsChristian EstebanNessuna valutazione finora
- T&B Detailed Plan: Ceiling LineDocumento1 paginaT&B Detailed Plan: Ceiling LineKuthbert NoceteNessuna valutazione finora
- Ahakuelo IndictmentDocumento24 pagineAhakuelo IndictmentHNNNessuna valutazione finora
- Tech Mahindra Sample Verbal Ability Placement Paper Level1Documento11 pagineTech Mahindra Sample Verbal Ability Placement Paper Level1Madhav MaddyNessuna valutazione finora
- ESK-Balcony Air-ADocumento2 pagineESK-Balcony Air-AJUANKI PNessuna valutazione finora
- Standard Cost EstimatesDocumento12 pagineStandard Cost EstimatesMasroon ẨśầŕNessuna valutazione finora