Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Lab 3
Caricato da
Sam AngDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Lab 3
Caricato da
Sam AngCopyright:
Formati disponibili
ELEC3540
Laboratory Notes
2012 S1
The University of Newcastle School of Electrical Engineering & Computer Science
ELEC3540 Analog and Digital Communications
Laboratory 3: Frequency Modulation
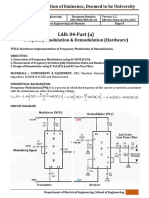
1. Equipment TIMS-301 with basic modules + microphone module; Digital Oscilloscope with FFT capability; Your own USB flash drive to save waveforms (Note: the oscilloscope cannot handle flash drivers greater than 2GB); Your own headphones. 2. Questions (to be completed before the Lab) 1. Sketch the block diagram for a wideband FM modulator. 2. Sketch the Fourier transform of an FM modulated signal with = 2.405 . 3. Sketch the Fourier transform of an FM modulated signal with = 1.44 . 4. Sketch the block diagram for an FM demodulator using zero-cross detection. 3. Procedures Part 1 Modulation T1 Make sure the onboard switch SW2 on the VCO module is on the VCO position; T2 Patch up the model on figure 1;
Figure 1. FM generator. T3 Set the VCO frequency to 10kHz using the knob labelled fo and set the VCO gain cpmpletely anti-clockwise. Use the FREQUENCY COUNTER to measure the frequency; T4 Use the Variable DC and the Buffer Amplifier knobs to set the voltage at the input of the VCO to -1V; T5 Adjust the VCO gain to have 1kHz frequency deviation. This will set the VCO module to give a deviation of 1kHz per volt; T6 Apply a range of input voltages at the input of the VCO module. Start with 0V and increase in 0.4V intervals until the relation in clearly non-linear. After 4V you can use 1V increments. Complete a table with input voltages and output frequencies; T7 Repeat the above for negative frequencies, i.e., start with 0V and decrease the input voltage in 0.4V steps; T8 Present the information obtained in T6, T7 as a plot of Vin vs Fout;
ELEC3540
Laboratory Notes
2012 S1
T9 Replace the DC voltage for the audio oscilator tunned at 600Hz; T10 Adjust the amplitude on the input of the VCO module to have = 2.405 . Recall that = f . f m , where f is the maximum frequency deviation and f m is the message frequency. Note the amplitude used and save the FFT of the modulated signal; T11 Fine adjust the amplitude on the input of the VCO module in order to achieve the best match between the observed and the expected FFT. Note the amplitude used; T12 Repeat the steps T10 and T11 for = 1.44 ; Part 2 Demodulation (keep your modulator connections) T 13 Make sure the onboard switch SW1 is at the SINGLE position on the TWIN PULSE GENERATOR module. Patch up the demodulator in figure 2.
1
Figure 2. FM demodulator. T14 Set the width of the pulse in the Twin Pulse Generator module to its maximum; T15 Using the audio oscillator as the message source, observe the demodulated signal and answer to the following quastions: a) Does the amplitude of the demodulated signal vary according to the amplitude of the message? b) Does the frequency of the demodulated signal vary according to the frequency of the message? c) Does the frequency of the demodulated signal vary according to the frequency of the carrier? T16 Return the carrier frequency to 10kHz and the VCO gain to 1kHz/volt. T17 Replace the audio oscillator by the microphone module. Use a speech signal (the pitch MUST vary) as message. Save the FFT of the modulated signal; T18 Plug your headphones into the headphone amplifier output. Adjust the Buffer Amplifier and Headphone Amplifier gains to obtain a good message reconstruction. Save the original and reconstitued message waveforms. 4. Report Structure Each group is required to hand in one report. The report must contain the following items: a) Individual answers for the pre-lab questions (25%); b) Plot and waveforms asked on steps T8, T10, T12, T17 and T18 (40%); c) Answers for the questions below (35%). 1. What were the amplitudes used on steps T10, T11 and T12? 2. Answers for the questions on the step T15. 3. What was the bandwidth observed on step T17?
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Build Your Own Low-Power Transmitters: Projects for the Electronics ExperimenterDa EverandBuild Your Own Low-Power Transmitters: Projects for the Electronics ExperimenterValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (4)
- Experiment 1Documento3 pagineExperiment 1mursyidahnrlNessuna valutazione finora
- Learn Amateur Radio Electronics on Your SmartphoneDa EverandLearn Amateur Radio Electronics on Your SmartphoneNessuna valutazione finora
- 3ECE-AC Lab ManualDocumento62 pagine3ECE-AC Lab ManualShannon DunnNessuna valutazione finora
- EECB351 - Exp 4Documento8 pagineEECB351 - Exp 4yip_wengNessuna valutazione finora
- Study Selectivity Characteristics of AM Radio ReceiverDocumento26 pagineStudy Selectivity Characteristics of AM Radio ReceiverKhan Shahrukh AshrafNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication Lab Manual GitamDocumento35 pagineCommunication Lab Manual Gitamଦେବୀ ପ୍ରସାଦ ପଟନାୟକNessuna valutazione finora
- TSEK02 - Radio Electronics: L 1: R R MDocumento14 pagineTSEK02 - Radio Electronics: L 1: R R MTessa AlgarraNessuna valutazione finora
- Kenwood TM-D700Documento68 pagineKenwood TM-D700Theodoros Kalom100% (1)
- Frequency Modulation and demodulation using optical linkDocumento11 pagineFrequency Modulation and demodulation using optical linkPriyansh RupaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Report#9Documento6 pagineReport#9tahaalshawesh3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Experiment 3 TE2016 V.em13Documento6 pagineLab Experiment 3 TE2016 V.em13mstgofcoNessuna valutazione finora
- TMR If5Documento20 pagineTMR If5Alvaro AzevedoNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 Stage FM TransmitterDocumento1 pagina4 Stage FM TransmitterNikhil R. LalwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- FM Modulation & Demodulation LabDocumento2 pagineFM Modulation & Demodulation LabAhmed MashhoorNessuna valutazione finora
- Sy, Francis Oliver F.-402a-Com01lab-Experiment No. 8Documento18 pagineSy, Francis Oliver F.-402a-Com01lab-Experiment No. 8SY, FRANCIS OLIVER F.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Amplitude Modulation: Name: Branch: Lab Section: ID NoDocumento10 pagineAmplitude Modulation: Name: Branch: Lab Section: ID NoSatya GopalNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical 2: Study of Telephone SectionsDocumento3 paginePractical 2: Study of Telephone SectionsYogesh PalkarNessuna valutazione finora
- ObjectivesDocumento22 pagineObjectivesMohd YasirNessuna valutazione finora
- EE370 Lab Experiment 04Documento4 pagineEE370 Lab Experiment 04Gellie Anne MercadoNessuna valutazione finora
- 2-FM MOD demodDocumento8 pagine2-FM MOD demodsmilyboy2904Nessuna valutazione finora
- Expt#5 Phase Modulation (PM) Generation and DemodulationDocumento5 pagineExpt#5 Phase Modulation (PM) Generation and DemodulationM AlzNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Report Cover SheetDocumento12 pagineLaboratory Report Cover Sheetswagata mandalNessuna valutazione finora
- Communication LabDocumento34 pagineCommunication LabSingam DonNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 11castroDocumento13 pagineExperiment 11castroHarry FabrosNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE 401L Lab5Documento10 pagineECE 401L Lab5mrpatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab - 2 Frequency Modulation: 2.1 ObjectiveDocumento4 pagineLab - 2 Frequency Modulation: 2.1 ObjectiveJoshua DuffyNessuna valutazione finora
- Stereo FM Transmitter (TEL049E)Documento10 pagineStereo FM Transmitter (TEL049E)ERNANIPARNOWNessuna valutazione finora
- BENT 3711 Telecommunication Electronics Lab 1: RF Tuned AmplifierDocumento4 pagineBENT 3711 Telecommunication Electronics Lab 1: RF Tuned AmplifierGilew LensaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adc Lab Manual STUDENTDocumento59 pagineAdc Lab Manual STUDENTramNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp 4 - Frequency Modulation and Demodulation PDFDocumento8 pagineExp 4 - Frequency Modulation and Demodulation PDFYerneni SasankNessuna valutazione finora
- 09 Com104Documento8 pagine09 Com104CauVong JustinNessuna valutazione finora
- L170 FreqSynDocumento21 pagineL170 FreqSynSheriff LoweNessuna valutazione finora
- Amplitude ModulationDocumento72 pagineAmplitude ModulationJeel ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- COMMUNICATIONS LAB. Experiment 1: Amplitude Modulation / Demodulation ObjectivesDocumento2 pagineCOMMUNICATIONS LAB. Experiment 1: Amplitude Modulation / Demodulation ObjectivesmahinNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 5Documento8 pagineExperiment 5gofrang877Nessuna valutazione finora
- FM Using PLL CompressDocumento8 pagineFM Using PLL CompressKARKAR NORANessuna valutazione finora
- FM Modulation and Demodulation Using PLL IC CD4046Documento8 pagineFM Modulation and Demodulation Using PLL IC CD4046Mohamed Bilal50% (2)
- AM Lab - SSB Modulation ExperimentDocumento109 pagineAM Lab - SSB Modulation ExperimentMalladi Sreedevi RajithaNessuna valutazione finora
- ExP 4 Frequency Modulation Ee240Documento10 pagineExP 4 Frequency Modulation Ee240Aiman Yusof100% (1)
- Ec2307 Cs Lab ManualDocumento76 pagineEc2307 Cs Lab ManualrameshdurairajNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Specs of TV ModelDocumento41 pagineTechnical Specs of TV ModelfernandoalejandroNessuna valutazione finora
- COMMUNICATIONS LAB. Experiment #3: Frequency Modulation / DemodulationDocumento2 pagineCOMMUNICATIONS LAB. Experiment #3: Frequency Modulation / DemodulationaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Frequency Modulation/ Demodulation System Trainer: MODEL-COM104Documento8 pagineFrequency Modulation/ Demodulation System Trainer: MODEL-COM104Lê Xuân HiếuNessuna valutazione finora
- Frequency Modulation/ Demodulation System Trainer: MODEL-COM104Documento8 pagineFrequency Modulation/ Demodulation System Trainer: MODEL-COM104Lê Xuân HiếuNessuna valutazione finora
- FM Trainer Model-COM104Documento8 pagineFM Trainer Model-COM104Thành VỹNessuna valutazione finora
- Comm2 Lab Activities CompleteDocumento36 pagineComm2 Lab Activities CompletecaptainjackrNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Watt AM_CW Transmitter CircuitDocumento6 pagine1 Watt AM_CW Transmitter CircuitGaryNessuna valutazione finora
- Bangladesh University of Professionals Department of Information and Communication Technology Course No.: Communication Theory Laboratory (ICT 2208)Documento2 pagineBangladesh University of Professionals Department of Information and Communication Technology Course No.: Communication Theory Laboratory (ICT 2208)Sadia AfreenNessuna valutazione finora
- Frequency Modulator Experiment ReportDocumento7 pagineFrequency Modulator Experiment ReportreganoctNessuna valutazione finora
- TBS1000B-EDU Courseware Lab Sampler: Selection GuideDocumento50 pagineTBS1000B-EDU Courseware Lab Sampler: Selection GuideAnonymous uiqGXPYbNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical ManualDocumento68 pagineTechnical Manualjadi purwonoNessuna valutazione finora
- EC6512 Communication System Lab ManualDocumento52 pagineEC6512 Communication System Lab ManualSalai Kishwar JahanNessuna valutazione finora
- Mini FM Station - 1Documento39 pagineMini FM Station - 1electronicsmadeeasy_emeNessuna valutazione finora
- Rmohn ELEN4314 Project ReportDocumento10 pagineRmohn ELEN4314 Project Reportjackal1710Nessuna valutazione finora
- Build A FM TransmitterDocumento4 pagineBuild A FM TransmitterrastamonnNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment One - Generating FM Using VCO - 2016Documento6 pagineExperiment One - Generating FM Using VCO - 2016Niklas LuwamNessuna valutazione finora
- COM02 Activity 1Documento15 pagineCOM02 Activity 1Claire AragoncilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Testing, Maintenance & Protection of Distribution TransformersDocumento47 pagineTesting, Maintenance & Protection of Distribution TransformersHarikrishnan Natarajan92% (25)
- Competence Profiles - Guidance For Applicants and AssessorsDocumento6 pagineCompetence Profiles - Guidance For Applicants and AssessorsSam AngNessuna valutazione finora
- Chartered Engineer Application FINAL 2016Documento17 pagineChartered Engineer Application FINAL 2016Sam AngNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering Ethics and Technology CourseDocumento40 pagineEngineering Ethics and Technology CourseSam AngNessuna valutazione finora
- Ang Kuan Jian: CAR VS BicycleDocumento5 pagineAng Kuan Jian: CAR VS BicycleSam AngNessuna valutazione finora
- TestDocumento53 pagineTestReji KurianNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 - IEM EC - Electrical Safety Seminar PDFDocumento91 pagine02 - IEM EC - Electrical Safety Seminar PDFredisme09Nessuna valutazione finora
- TestDocumento53 pagineTestReji KurianNessuna valutazione finora
- C715 ScheduleDocumento1 paginaC715 ScheduleSam AngNessuna valutazione finora
- TBM 1 Turn On ProceduresDocumento2 pagineTBM 1 Turn On ProceduresSam AngNessuna valutazione finora
- 170128122637Documento45 pagine170128122637Sam AngNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 - IEM EC - Electrical Safety Seminar PDFDocumento91 pagine02 - IEM EC - Electrical Safety Seminar PDFredisme09Nessuna valutazione finora
- B81PI Assignment B SamplesDocumento6 pagineB81PI Assignment B SamplesliamlimNessuna valutazione finora
- Self-Powered Feeder Protection REJ603: Application ManualDocumento56 pagineSelf-Powered Feeder Protection REJ603: Application ManualUsman HaroonNessuna valutazione finora
- A15 - Appendix E - No LouverDocumento1 paginaA15 - Appendix E - No LouverSam AngNessuna valutazione finora
- Get Started With Dropbox PDFDocumento10 pagineGet Started With Dropbox PDFReka ErdantoNessuna valutazione finora
- ELEC4160 Advanced Drives and Power ElectronicsDocumento1 paginaELEC4160 Advanced Drives and Power ElectronicsSam AngNessuna valutazione finora
- Transfomer Protection Device and Terminal Diagrams For 4 TXDocumento8 pagineTransfomer Protection Device and Terminal Diagrams For 4 TXSam AngNessuna valutazione finora
- ELEC4100 Electrical SystemsDocumento1 paginaELEC4100 Electrical SystemsSam AngNessuna valutazione finora
- Elec 3850Documento3 pagineElec 3850Sam AngNessuna valutazione finora
- 500A PanelDocumento1 pagina500A PanelSam AngNessuna valutazione finora
- ManholeCatalog PDFDocumento8 pagineManholeCatalog PDFSam AngNessuna valutazione finora
- Form H 2016Documento3 pagineForm H 2016Sam AngNessuna valutazione finora
- Walkie TalkieDocumento2 pagineWalkie TalkieSam AngNessuna valutazione finora
- 300A Panel PDFDocumento1 pagina300A Panel PDFSam AngNessuna valutazione finora
- Dse8 Electrical Machines I - MQPDocumento2 pagineDse8 Electrical Machines I - MQPSam AngNessuna valutazione finora
- MT 2Documento6 pagineMT 2Sam AngNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 in 1 Out PanelDocumento1 pagina1 in 1 Out PanelSam AngNessuna valutazione finora
- Internship Program ReportDocumento1 paginaInternship Program ReportSam AngNessuna valutazione finora
- Design of Electrical Apparatus Solved ProblemsDocumento14 pagineDesign of Electrical Apparatus Solved ProblemsRichard RegidorNessuna valutazione finora
- CAP Regulation 20-1 - 05/29/2000Documento47 pagineCAP Regulation 20-1 - 05/29/2000CAP History LibraryNessuna valutazione finora
- Management Pack Guide For Print Server 2012 R2Documento42 pagineManagement Pack Guide For Print Server 2012 R2Quang VoNessuna valutazione finora
- Benzon CaseDocumento3 pagineBenzon Casejulieanne07100% (1)
- AnkitDocumento24 pagineAnkitAnkit MalhotraNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Case - Uganda Maize Export To South SudanDocumento44 pagineBusiness Case - Uganda Maize Export To South SudanInfiniteKnowledge33% (3)
- SD Electrolux LT 4 Partisi 21082023Documento3 pagineSD Electrolux LT 4 Partisi 21082023hanifahNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Intro To Ozone LaundryDocumento5 pagine3 Intro To Ozone LaundrynavnaNessuna valutazione finora
- SAP PS Step by Step OverviewDocumento11 pagineSAP PS Step by Step Overviewanand.kumarNessuna valutazione finora
- OBHR Case StudyDocumento8 pagineOBHR Case StudyYvonne TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Part E EvaluationDocumento9 paginePart E EvaluationManny VasquezNessuna valutazione finora
- Com 0991Documento362 pagineCom 0991Facer DancerNessuna valutazione finora
- ASCE - Art Competition RulesDocumento3 pagineASCE - Art Competition Rulesswarup babalsureNessuna valutazione finora
- 2006-07 (Supercupa) AC Milan-FC SevillaDocumento24 pagine2006-07 (Supercupa) AC Milan-FC SevillavasiliscNessuna valutazione finora
- GS Ep Cor 356Documento7 pagineGS Ep Cor 356SangaranNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Syllabus: Aurora Pioneers Memorial CollegeDocumento9 pagineCourse Syllabus: Aurora Pioneers Memorial CollegeLorisa CenizaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mayor Byron Brown's 2019 State of The City SpeechDocumento19 pagineMayor Byron Brown's 2019 State of The City SpeechMichael McAndrewNessuna valutazione finora
- Denial and AR Basic Manual v2Documento31 pagineDenial and AR Basic Manual v2Calvin PatrickNessuna valutazione finora
- Server LogDocumento5 pagineServer LogVlad CiubotariuNessuna valutazione finora
- KSRTC BokingDocumento2 pagineKSRTC BokingyogeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Pig PDFDocumento74 paginePig PDFNasron NasirNessuna valutazione finora
- Queries With AND and OR OperatorsDocumento29 pagineQueries With AND and OR OperatorstrivaNessuna valutazione finora
- Milton Hershey's Sweet StoryDocumento10 pagineMilton Hershey's Sweet Storysharlene sandovalNessuna valutazione finora
- Programme Report Light The SparkDocumento17 pagineProgramme Report Light The SparkAbhishek Mishra100% (1)
- MSDS Summary: Discover HerbicideDocumento6 pagineMSDS Summary: Discover HerbicideMishra KewalNessuna valutazione finora
- Take Private Profit Out of Medicine: Bethune Calls for Socialized HealthcareDocumento5 pagineTake Private Profit Out of Medicine: Bethune Calls for Socialized HealthcareDoroteo Jose Station100% (1)
- ATOMIC GAMING Technical Tutorial 1 - Drawing Game Statistics From Diversity Multigame StatisticsDocumento4 pagineATOMIC GAMING Technical Tutorial 1 - Drawing Game Statistics From Diversity Multigame StatisticsmiltoncgNessuna valutazione finora
- E-TON - Vector ST 250Documento87 pagineE-TON - Vector ST 250mariusgrosyNessuna valutazione finora
- Railway RRB Group D Book PDFDocumento368 pagineRailway RRB Group D Book PDFAshish mishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Bob Duffy's 27 Years in Database Sector and Expertise in SQL Server, SSAS, and Data Platform ConsultingDocumento26 pagineBob Duffy's 27 Years in Database Sector and Expertise in SQL Server, SSAS, and Data Platform ConsultingbrusselarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lista Precio Septiembre 0609Documento75 pagineLista Precio Septiembre 0609gNessuna valutazione finora
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionDa EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (542)
- High Performance Loudspeakers: Optimising High Fidelity Loudspeaker SystemsDa EverandHigh Performance Loudspeakers: Optimising High Fidelity Loudspeaker SystemsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Lithium-Ion Battery: The Power of Electric Vehicles with Basics, Design, Charging technology & Battery Management SystemsDa EverandLithium-Ion Battery: The Power of Electric Vehicles with Basics, Design, Charging technology & Battery Management SystemsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- The Fast Track to Your Technician Class Ham Radio License: For Exams July 1, 2022 - June 30, 2026Da EverandThe Fast Track to Your Technician Class Ham Radio License: For Exams July 1, 2022 - June 30, 2026Valutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Off-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemDa EverandOff-Grid Projects: Step-by-Step Guide to Building Your Own Off-Grid SystemNessuna valutazione finora
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionDa EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (331)
- Understanding Automotive Electronics: An Engineering PerspectiveDa EverandUnderstanding Automotive Electronics: An Engineering PerspectiveValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (16)
- Introduction to Power System ProtectionDa EverandIntroduction to Power System ProtectionNessuna valutazione finora
- 8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionDa Everand8051 Microcontroller: An Applications Based IntroductionValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (6)
- C++ Programming Language: Simple, Short, and Straightforward Way of Learning C++ ProgrammingDa EverandC++ Programming Language: Simple, Short, and Straightforward Way of Learning C++ ProgrammingValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- The Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesDa EverandThe Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Build Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionDa EverandBuild Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Ramblings of a Mad Scientist: 100 Ideas for a Stranger TomorrowDa EverandRamblings of a Mad Scientist: 100 Ideas for a Stranger TomorrowNessuna valutazione finora
- The Rare Metals War: the dark side of clean energy and digital technologiesDa EverandThe Rare Metals War: the dark side of clean energy and digital technologiesValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeDa EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (8)
- Beginner's Guide to Reading Schematics, Fourth EditionDa EverandBeginner's Guide to Reading Schematics, Fourth EditionValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (10)
- Current Interruption Transients CalculationDa EverandCurrent Interruption Transients CalculationValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Operational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignDa EverandOperational Amplifier Circuits: Analysis and DesignValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (2)
- Digital Gold: The Beginner's Guide to Digital Product Success, Learn Useful Tips and Methods on How to Create Digital Products and Earn Massive ProfitsDa EverandDigital Gold: The Beginner's Guide to Digital Product Success, Learn Useful Tips and Methods on How to Create Digital Products and Earn Massive ProfitsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- The Graphene Revolution: The Weird Science of the Ultra-thinDa EverandThe Graphene Revolution: The Weird Science of the Ultra-thinValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (4)
- Electrical Principles and Technology for EngineeringDa EverandElectrical Principles and Technology for EngineeringValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (4)