Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Gateways
Caricato da
Abhinav MalviyaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Gateways
Caricato da
Abhinav MalviyaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
GATEWAYS
Gateways are devices which connect two are more networks that use different protocols. They are similar in function to routes but they are more powerful and intelligent devices. A gateway can actually convert data so that network with an application on a computers on the other side of the gateway e.g a get way can receive email messages in one format in convert them into another format. Gateway can operate at all seven layer of OSI model. Since Gateway perform data conversion so they are slower in speed and very expensive devices.
a gateway can translate information between different networks data formats or network architecture. most gateways operate at the application layer. it can also be operated on network or session layer.
Application gateway is one of the firewall systems. A service is provided by different processes which maintain complete TCP connection state and sequencing. Re-addressing of traffic for outgoing traffic appears to have originated from the firewall, is performed often. The following are the advantages of Application Level Gateways: - Direct connections between internal and external hosts are disallowed. - User-level authentication is supported. - The application commands are analyzed inside the payload portion of the data packets. The following are the disadvantages of Application Level Gateways: - Slower than packet filters - Needs the internal client to know about them. - Every possible type of connection can not be supported
REPEATERS
Repeaters are used within network to extend the length of communication. Data process through transmission media in the farm of waves or signals. The transmission media weaken signals that move through it. The weakening of signal is called attenuation. If the data is to be transmitted beyond the maximum length of a communication media, signals have amplified. The devices that are used to amplify the signals are called repeaters. Repeaters work at the physical layer of OSI model. Repeaters are normally two ports boxes that connect two segments. As a signal comes in one port , it is Regenerated and send out to the other port. The signal is read as 1s and 0s. As 1s and 0s are transmitted, the noise can be cleaned out. A repeater is the simplest facility used for network interconnection, whose major function is to receive a network signal from one LAN terminal cable segment and to regenerate and retransmit the signal as it is in its original strength over a one or more other cable segment. Basically repeater regenerates the strength of the signal before transmitting it Repeaters operate in the OSI modelPhysical layer and are transparent to all the protocols operating in the layers above the Physical layer. A specific LAN implementation usually places a limit on the physical size of a single cable segment. The limit is based on the physical medium and transmission techniques used
Repeaters allow a network to be constructed to exceed the size limit of a single, physical, cable segment. The number of repeaters that can be used intandem is generally limited by a particular LAN implementation. Using a repeater between two or more LAN cables segment requires that the same physical layer protocol be used to send signal over all the cable segments Advantages of a repeater Simple to connect Cost effective Ability to strengthen signal
Repeaters easily extend the length of network. They require no processing over head, so very little if any performance degradation occurs. It can connect signals from the same network type that use different types of cables.
Disadvantages of a repeater Repeaters provide no method for isolating traffic generated on one cable segment from traffic generated by the other cable segment When network uses a repeater to connect cable segment A to segment B whether or not there is a station in segment B that is the destination of the signal
Repeaters can not be used to connect segments of different network types. They cannot be used to segment traffic on a network to reduce congestion . Many types of network have a limit on the number of network s that can be used at once .
BRIDGES
Bridges are used to connect similar network segments. A bridge does not pass or signals it receives. When a bridge receive a signal , it determines its destination by looking at its destination and it sends the signals towards it. For example in a above figure a bridge has been used to join two network segments A AND B. When the bridge receives the signals it read address of both sender and receiver. If the sender is a computer in segment A and the receiver is also segment A, it would not pass the signals to the segments B. It will however pass signals if the sender is in one segment and the receiver in other segment. Bridge works at the data link layer of O.S.I model. A network bridge, or a layer 2 switch, connects two different local area networks (LAN) or segments of
the same LAN. A bridge is used to segregate data by dividing it into two streams. This way it effectively reduces the traffic flow over a LAN. A bridge operates by determining whether incoming data (or traffic) is to be routed to a forwarding address or discarded. Packets of data received by the bridge carry the destination address, which is read by the bridge and deciphered accordingly. The three major types of network bridges include local bridges (to connect LANs), remote bridges (to connect LANs with a wide area network or a WAN) and wireless bridges (to connect remote networks with LANs)
Advantages of Bridges
Bridge extends network segments by connecting them together to make one logical network. They can affect the segment traffic between networks by filtering data if it does not need to pass. Like repeaters they can connect similar network types with different cabling.
Disadvantages of Bridges
Bridge possess information about the data they receive with can slow performance.
Does not limit the scope of broadcasts Does not scale to extremely large networks Buffering and processing introduces delays A complex network topology can pose a problem for transparent bridges. For example, multiple paths between transparent bridges and LANs can result in bridge loops. The spanning tree protocolhelps to reduce problems with complex topologies.
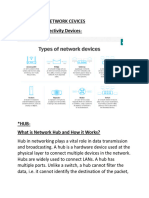
HUB
Hubs are basically multi ports repeaters for U.T.P cables. Some hubs have ports for other type of cable such as coaxial cable. Hubs range in size from four ports up to and for specific to the network types. These are some hubs which are I. Passive Hub II. Active Hub III. Switch/ Intelligent Hub
Passive Hub
It provides no signal regeneration. They are simply cables connected together so that the signal is broken out to other nodes with out regeneration. These are not used often today because of loss of cable length that is allowed.
Active Hub
It acts as repeaters and regenerates the data signals to all ports. They have no real intelligence to tell weather the signal needs to go to all ports that is blindly repeated.
Switch Hub
Switches are multi ports bridges. They filter traffic between the ports on the switch by using the address of computers transmitting to them. Switches can be used when data performance is needed or when collision need to be reduce.
Advantages of Hub
Hubs need almost no configuration. Active hub can extend maximum network media distance.
Hub is less expensive product.
No processing is done at the hub to slow down performance
Disadvantages of Hub
Passive hubs can greatly limit maximum media distance. Hubs have no intelligence to filter traffic so all data is send out on all ports whether it is need or not.
Since hubs can act as repeaters the network using them must follow the same rules as repeaters
It will broadcast to all the ports It runs half duplex If 10 Ports in a hub it will share bandwidth of 100 MbPs. So each port share 10 Mbps
MODEM
The device that converts digital signals into analog signals and analog signals to digital signals is called Modem. The word modem stands for modulation and demodulation. The process of converting digital signals to analog signals is called modulation. The process of converting analog signals to digital signals is called demodulation. Modems are used with computers to transfer data from one computer to another computer through telephone lines. Modems have two connections these are.
Analog connection Digital connection
Analog connection.
The connection between the modem and the telephone line is called analog connection.
Types of Modem
THERE ARE TWO TYPES OF MODEMS
Internal modem External modem
Digital connection.
The connection of modem to computer is called digital connection
INTERNAL MODEM
It fits into expansion slots inside the computer. It is directly linked to the telephone lines through the telephone jack. It is normally less inexpensive than external modem. Its transmission speed is also less external modem.
EXTERNAL MODEM
It is the external unit of computer and is connected to the computer through serial port. It is also linked to the telephone line through a telephone jack. External modems are expensive and have more operation features and high transmission speed.
Advantages of Modem
i. Inexpensive hardware and telephone lines. ii. Easy to setup and maintain.
Disadvantages of Modem
i. Very slow performance.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Network Devices - PPSXDocumento37 pagineNetwork Devices - PPSXMaricris Bejer LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Types DevicesDocumento4 pagineNetwork Types DevicesM.n KNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Network Lec 8Documento9 pagineComputer Network Lec 8Numan arshadNessuna valutazione finora
- EP 301 - Computer Networking FundamentalsDocumento18 pagineEP 301 - Computer Networking FundamentalsShazul Afizi Zulkiflee100% (1)
- Network Devices and Their FunctionsDocumento7 pagineNetwork Devices and Their Functionsbekalu amenuNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer NetworksDocumento30 pagineComputer NetworksratnadeepNessuna valutazione finora
- CN Unit 2Documento8 pagineCN Unit 2igor iljinNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer NetworkDocumento10 pagineComputer NetworkTrushi BhensdadiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hardware Elements of Network Design: Repeater FunctionDocumento13 pagineHardware Elements of Network Design: Repeater Functionsuleman idrisNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework TCILDocumento18 pagineHomework TCILChirag GoyalNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router and Gateways)Documento35 pagineNetwork Devices (Hub, Repeater, Bridge, Switch, Router and Gateways)Aaizah WaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Devices, or in Other Words Network Hardware, Are Physical Devices Intended To ProvideDocumento6 pagineNetwork Devices, or in Other Words Network Hardware, Are Physical Devices Intended To ProvideUterus Xbox er f u. RNessuna valutazione finora
- Connecting Devices: 1. RepeaterDocumento5 pagineConnecting Devices: 1. RepeaterAadhya JyothiradityaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hubs Are Used To Build A LAN by Connecting Different Computers in A Star/hierarchal NetworkDocumento4 pagineHubs Are Used To Build A LAN by Connecting Different Computers in A Star/hierarchal NetworkVKNCKBGNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-I PPT2 BasicsDocumento34 pagineUnit-I PPT2 BasicsTejas MahadikNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept of InternetDocumento12 pagineConcept of InternetMeghant ModiNessuna valutazione finora
- Hardware & Network Servicing Level III: UC2: Determine Best Fit TopologyDocumento80 pagineHardware & Network Servicing Level III: UC2: Determine Best Fit TopologyKinfe BeregaNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit VDocumento34 pagineUnit Vsaurav shekharNessuna valutazione finora
- Hub Bridge Switch Router Assignment - Computer NetworkDocumento12 pagineHub Bridge Switch Router Assignment - Computer Networkyabaidullah100% (1)
- NetworkingDocumento9 pagineNetworkingviper hernandesNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Networking Individual Assignments: Section:-"A"Documento9 pagineComputer Networking Individual Assignments: Section:-"A"Abi DemNessuna valutazione finora
- Networking Hardware 2023Documento27 pagineNetworking Hardware 2023Gerald KapinguraNessuna valutazione finora
- LAN Devices (Repeater, Hub, Bridge and Switch)Documento33 pagineLAN Devices (Repeater, Hub, Bridge and Switch)derejbuzuNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab DA-1Documento27 pagineLab DA-1defristosNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Engineer Interview Questions-2Documento14 pagineNetwork Engineer Interview Questions-2mushahidNessuna valutazione finora
- Gujarat Technological University: Government Engineering Collage, DahodDocumento5 pagineGujarat Technological University: Government Engineering Collage, DahodSandip MouryaNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Switch: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocumento13 pagineNetwork Switch: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediarajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Networking Devices: 1. Network HubDocumento3 pagineNetworking Devices: 1. Network HubSaurav PooniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Network DevicesDocumento15 pagineNetwork DevicesShilpa PutanikarNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 Network DevicesDocumento17 pagineChapter 5 Network Devicesninjamekwan10Nessuna valutazione finora
- NetworkingDocumento8 pagineNetworkingharsh guptaNessuna valutazione finora
- 9 Reading MaterialDocumento12 pagine9 Reading MaterialpriyeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity 2 Ece 583lDocumento4 pagineActivity 2 Ece 583lMoody MindNessuna valutazione finora
- Creating Larger NetworksDocumento3 pagineCreating Larger NetworksAnurag GoelNessuna valutazione finora
- FOCUnit 4Documento50 pagineFOCUnit 4Suhirt MukherjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- DCCNDocumento8 pagineDCCNHarsh MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- CN EXP1 Network DevicesDocumento4 pagineCN EXP1 Network Devicesshweta joshiNessuna valutazione finora
- 4.0 Repeaters, Bridges, Routers, and Gateways: A Comparative Study: 4.1 RepeatersDocumento5 pagine4.0 Repeaters, Bridges, Routers, and Gateways: A Comparative Study: 4.1 Repeatersvickypatel_63873791Nessuna valutazione finora
- Network DevicesDocumento19 pagineNetwork Devicespooja dangeNessuna valutazione finora
- Network DevicesDocumento8 pagineNetwork DevicesrevathiNessuna valutazione finora
- MODULE 5 - Cabling LAN's and WAN'sDocumento2 pagineMODULE 5 - Cabling LAN's and WAN'sGrecu GianiNessuna valutazione finora
- Repeater: Physical Layer OSI ModelDocumento4 pagineRepeater: Physical Layer OSI Modeljhony jonNessuna valutazione finora
- ComputerDocumento4 pagineComputerSunsong31Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 Physical Layer and Network Media 3Documento25 pagineUnit 2 Physical Layer and Network Media 3Sagar wagleNessuna valutazione finora
- CN Practicalno4Documento9 pagineCN Practicalno4dkchauhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Net+2009CP p04Documento77 pagineNet+2009CP p04Nigel RamasawmyNessuna valutazione finora
- Connecting DevicesDocumento28 pagineConnecting DevicesNirmalNessuna valutazione finora
- DC Lab1Documento32 pagineDC Lab1Sornali PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Planning and Cabling NetworksDocumento35 paginePlanning and Cabling NetworksJohn Carmelo SaulonNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Network PR 1Documento15 pagineComputer Network PR 1Comp116DeepVariyaNessuna valutazione finora
- DCN Unit-5Documento15 pagineDCN Unit-5swanandghaskadviNessuna valutazione finora
- LO3 Develop Topology EditedDocumento38 pagineLO3 Develop Topology Editedbiruk mollaNessuna valutazione finora
- CN Connecting DevicesDocumento3 pagineCN Connecting DevicesLife SayingsNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5Documento42 pagineChapter 5Bezabh AbebawNessuna valutazione finora
- Network SwitchDocumento12 pagineNetwork SwitchLendon LomosbogNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Computer NetworksDocumento32 pagineTypes of Computer Networksfunny videos lastest songsNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter4-Elements of Network ConnectivityDocumento8 pagineChapter4-Elements of Network ConnectivitybeleteasfawmezigebuNessuna valutazione finora
- Integrating Legacy and LAN/WAN Systems: Nathan J. MullerDocumento19 pagineIntegrating Legacy and LAN/WAN Systems: Nathan J. MullerCentaur ArcherNessuna valutazione finora
- Network Engineer Interview Questions Answers PDFDocumento25 pagineNetwork Engineer Interview Questions Answers PDFmadagonerajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyDa EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- HCL Systems Placement PapersDocumento2 pagineHCL Systems Placement PapersAbhinav MalviyaNessuna valutazione finora
- RiscDocumento25 pagineRiscAbhinav MalviyaNessuna valutazione finora
- RiscDocumento25 pagineRiscAbhinav MalviyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Gateways: Osi Modelphysical LayerDocumento5 pagineGateways: Osi Modelphysical LayerAbhinav MalviyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Admission Form JAM 2011Documento10 pagineAdmission Form JAM 2011Abhinav MalviyaNessuna valutazione finora