Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Module Chapter 3 f55
Caricato da
Herdawati HamdanCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Module Chapter 3 f55
Caricato da
Herdawati HamdanCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Chapter 3 : Coordination and Response
SMK SEKSYEN 4 KOTA DAMANSARA BIOLOGY FORM 5 LEARNING MODULE Chapter 3: Coordination and Response
NAME: CLASS:
HERDAWATI HAMDAN BIOBEST
Chapter 3 : Coordination and Response
1. What types of stimuli ???????????? Sensing danger from a predatorGlucose level in bloodGravityTaste Blood pHSmellTemperatureTouch-
2. State the necessity for living organisms to respond to external and internal stimuli. (to enable the organisms to : Adjust to environmental ____________________ Protect the organism from ___________________ Ensure the ______________ of the organism.
3. Tropism response in plants. a. Phototropism response The stimulus for this type of response is ____________________. b. Geotropism response ___________________ force is the stimuli for this type of response. c. Hydrotropism response A type of plant growth response towards __________________ stimuli. d. Thigmotropism This response can be observed on plants with soft stems, which respond towards ______________ stimuli.
Chapter 3 : Coordination and Response
Coordination-Process involved the detection of stimulus and the subsequent response of
the organism towards the stimulus which involved both the n____ s and e____________n system. 1. Nervous system Functions of nervous system in human a) Receives information from r__________________ b) Transmit and i______________ the information c) Formulates appropriate responses to be sent to the e_____________ organs d) Controls and coordinates functions throughout the body e) Helps to maintain h__________________________ What are the main components of nervous system? i. Central nervous system - b________ and s_________ c______
ii.
Peripheral nervous system- the nerves and nervous tissue outside the brain and the spinal cord
Chapter 3 : Coordination and Response
Central Nervous System (CNS) a. Refer text book..page 79
The Brain
Parts Cerebrum
Structure
Function
Cerebellum
Brain Stem Medulla oblongata Pons Thalamus
Hypothalamus
Chapter 3 : Coordination and Response
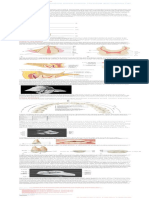
1. Diagram below shows a cross section of the spinal cord. Name the parts of the spinal cord labelled as P, Q, R and S.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Structures of the PNS 1) Cranial nerves: (12 pairs) 2) Spinal nerves: (31 pairs) - Carry nerve impulses to and from the spinal cord to body parts not served by the cranial nerves. 3) Somatic nervous system -Carries nerve impulses to the skeletal muscles, joints and skin 4) Autonomic nervous system (ANS) -Carries nerve impulses to the smooth muscles of internal organs and to glands without conscious thought Two subdivisions of autonomic nervous system : a) Sympathetic system - Controls "fight or flight" responses b) Parasympathetic system - Controls those responses associated with a relaxed state.
Chapter 3 : Coordination and Response
Cells of the Nervous System Neurons -They are the basic structural and functional unit of the nervous system. - They conduct nerve impulses.
Chapter 3 : Coordination and Response
Composed of: a. Cell Body - Part that contains the nucleus b. Dendrite(s) -Carries a nerve impulse towards the cell body c. Axon(s) -Carries a nerve impulse away from the cell body (and towards the dendrite of the next neuron).Axons are also called nerve fibers. d. Myelin:- Provides insulation forms myelin sheath around axons e. Nodes of Ranvier - gaps on axons f. Note: Definition of a nerve impulse : A self-propagating wave of electrical disturbance that travels along the surface of a neuron's plasma membrane. Three types of neurons (by functional classification):
Afferent neurone
Efferent neurone
Interneurone
Function: Transmit nerve impulses to the _____________ and ___________ from all over the body.
Function: Carries impulses away from the spinal cord and brain to ________/muscle / glands
Function: Transmits nerve impulses from one neuronal dendrite to the axion of another neuron. All are found only in the gray matter of the brain or spinal cord.
Chapter 3 : Coordination and Response
1. Define a synapse.
A narrow gap located at the junction between the axon terminal of one neurone and the dendrite of an adjacent neurone
2. A synapses may be found between a) A neurone and a _________________ b) A neurone and a _________________ c) A neurone and a _________________
3. Describe briefly the transmission of impulses across a synapse. [7m]
4. Give 2 examples of neurotransmitters (a)_________________________ (b) __________________________
Chapter 3 : Coordination and Response
What is voluntary action? Answer: It is defined as the action that is controlled by the conscious will of a person. It involves the integration and interpretation of information in the cerebrum. Example: Raising your hand to answer a question.
What is an involuntary action? An action not bound by the will of a person. Occurs automatically in the body without any conscious control.
Involves receptors to detect the stimulus, medulla oblongata to interpret the information and effectors to carry out the response automatically. Example: Involving skeletal muscles such as knee jerk, and smooth muscles (cardiac muscles or glands) such as normal blood pressure
Chapter 3 : Coordination and Response
Define reflex action. Reflex is an automatic, innate response to a particular stimulus. It involves the contraction of skeletal muscles and the spinal cord only. What is a reflex arc? The pathway along which an impulse travels from the receptor to the effector
Using two examples each,explain the difference between (a) Voluntary actions (b) involuntary action
10
Chapter 3 : Coordination and Response
GLAND
HORMONE
FUNCTION
TARGET
11
Chapter 3 : Coordination and Response
12
Chapter 3 : Coordination and Response
Differences between nervous system and endocrine system.
NERVOUS SYSTEM
ASPECTS
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
COORDINATION BETWEEN THE NERVOUS SYSTEM AND THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM HOMEOSTASIS ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Examples of physical factorsExamples of chemical factor-
13
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- Ujian Penilaian KendiriDocumento12 pagineUjian Penilaian KendiriHerdawati HamdanNessuna valutazione finora
- Rajah 1 Menunjukkan Struktur Utama Membran Plasma.: Ulangkaji Topik Tingkatan 4 Biologi Pergerakan Bahan Mrentasi MembranDocumento21 pagineRajah 1 Menunjukkan Struktur Utama Membran Plasma.: Ulangkaji Topik Tingkatan 4 Biologi Pergerakan Bahan Mrentasi MembranHerdawati HamdanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bab 5F4Documento17 pagineBab 5F4Herdawati Hamdan100% (1)
- Kertas 1 PercubaanDocumento28 pagineKertas 1 PercubaanHerdawati HamdanNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Business Communication Building Critical Skills 6th Edition Locker Test BankDocumento34 pagineBusiness Communication Building Critical Skills 6th Edition Locker Test Bankrubepazuqo88% (8)
- Sculpting Tut01Documento27 pagineSculpting Tut01SliverBirth86% (14)
- Introduction To Dental Anatomy (Dental Anatomy, Physiology and Occlusion) Part 2Documento1 paginaIntroduction To Dental Anatomy (Dental Anatomy, Physiology and Occlusion) Part 2Hicham KarrouchiNessuna valutazione finora
- Pancreas: Cynthia D. Guy, MD Associate Professor of Pathology DumcDocumento56 paginePancreas: Cynthia D. Guy, MD Associate Professor of Pathology Dumcionut1ilie-1Nessuna valutazione finora
- 4LIVfunctions ElizabethDocumento23 pagine4LIVfunctions ElizabethLunaLure100% (1)
- Biology 12: Provincial ExaminationDocumento36 pagineBiology 12: Provincial ExaminationVaniseNessuna valutazione finora
- Histology of TestisDocumento2 pagineHistology of TestisyolandadwiooNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Group IncompatibilityDocumento7 pagineBlood Group IncompatibilityHendrikus Surya Adhi PutraNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood ComponentDocumento4 pagineBlood ComponentVictor GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Biology and GeneticsDocumento54 pagineCell Biology and Geneticspnguyen810Nessuna valutazione finora
- Plant StemDocumento6 paginePlant StemAndreaaAAaa TagleNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Qns v2Documento37 pagineBiology Qns v2randomvidsNessuna valutazione finora
- Boala AmnioticaDocumento53 pagineBoala AmnioticaAlex CirlanNessuna valutazione finora
- Antibody EngineeringDocumento14 pagineAntibody EngineeringJholina Aure ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- The Theater of Anatomy - The Anatomical Preparations of Honore Fragonard PDFDocumento18 pagineThe Theater of Anatomy - The Anatomical Preparations of Honore Fragonard PDFFrancisco SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- 21 Plant Structure and FunctionDocumento50 pagine21 Plant Structure and FunctionRoan James OcampoNessuna valutazione finora
- Answers To End-Of-Chapter Questions Chapter 7: Animal NutritionDocumento2 pagineAnswers To End-Of-Chapter Questions Chapter 7: Animal NutritionRNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 - Preface - Table of ContentsDocumento10 pagine01 - Preface - Table of ContentsLouise Lee0% (5)
- Work Sheet 6 Skeletal System A28 Group1Documento8 pagineWork Sheet 6 Skeletal System A28 Group1Japet Floyd AlipioNessuna valutazione finora
- Complete Denture ProsthodonticsDocumento348 pagineComplete Denture ProsthodonticsRazvan Ungureanu67% (3)
- AVP Palatine Ulcers Article PDFDocumento5 pagineAVP Palatine Ulcers Article PDFartzain1991Nessuna valutazione finora
- Check List CrossmatchDocumento2 pagineCheck List CrossmatchDwi IswantiadiatunNessuna valutazione finora
- Histological Variants:: PathogenesisDocumento2 pagineHistological Variants:: PathogenesisPravin KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Soal No 2 Bedah DigestifDocumento7 pagineSoal No 2 Bedah DigestifRaniPradnyaSwariNessuna valutazione finora
- Development Theories 1 2Documento66 pagineDevelopment Theories 1 2Aaryan GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Human Heart ScienceDocumento7 pagineHuman Heart ScienceJewel Kathryn MorenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology of The StomachDocumento7 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of The StomachEmmi Maliza HutagaolNessuna valutazione finora
- Hypersensitivity An OverviewDocumento2 pagineHypersensitivity An OverviewVaishnav SNessuna valutazione finora
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Science VIDocumento5 pagineA Detailed Lesson Plan in Science VIJose Anthony AlmoceraNessuna valutazione finora
- AUBF - Amniotic Fluid and Semen Study MaterialDocumento10 pagineAUBF - Amniotic Fluid and Semen Study MaterialVienna Jamaica Be Cari-CariNessuna valutazione finora