Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
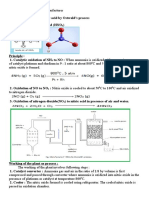
GO 4 Preparation of Carboxylic Acid
Caricato da
cikaifaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
GO 4 Preparation of Carboxylic Acid
Caricato da
cikaifaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
CARBOXYLIC ACID
Carboxylic Acid
Carboxylic acids are organic acids characterized by the presence of at least one carboxyl group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R-COOH, where R is some monovalent functional group. Carboxylic acids are Brnsted-Lowry acids because they are proton donors. They are the most common type of organic acid. Among the simplest examples are formic acid H-COOH, that occurs in ants, and acetic acid CH3-COOH, that gives vinegar its sour taste. Acids with two or more carboxyl groups are called dicarboxylic,tricarboxylic, etc.
Preparation Properties
Uses
compounds which contain a -COOH group that is attached either to a hydrogen atom or to an alkyl group.
Oxidation of alkenes
The oxidation of primary alcohols and aldehydes
Preparation
The oxidation of alkyl benzenes
Hydrolysis of nitriles
Carboxylic acid
The carbonation of Grignard reagents
Solubility in Water
Boiling point
Properties
Melting point
Uses
Acidity
Odour
Preparation of Carboxylic acid
Oxidation of alkenes Alkenes are oxidized to acids by heating them with solutions of potassium permanganate (KMnO4) or potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7).
Oxidation of alkenes The ozonolysis of alkenes produces aldehydes that can easily be further oxidized to acids.
The oxidation of primary alcohols and aldehydes The oxidation of primary alcohols leads to the formation of alde-hydes that undergo further oxidation to yield acids. All strong oxidizing agents (potassium permanganate, potassium dichromate, and chromium trioxide) can easily oxidize the aldehydes that are formed
The oxidation of alkyl benzenes Alkyl groups that contain benzylic hydrogenshydrogen(s) on a carbon to a benzene ringundergo oxidation to acids with strong oxidizing agents.
In the above example, t-butylbenzene does not contain a benzylic hydrogen and therefore doesn't undergo oxidation
The carbonation of Grignard reagents Grignard reagents react with carbon dioxide to yield acid salts, which, upon acidification, produce carboxylic acids.
Hydrolysis of nitriles
The hydrolysis of nitriles containing a cyano group, leads to carboxylic acid formation. It can take place in either acidic or basic solutions.
The mechanism follows these steps:
The nitrogen atom of the nitrile group is protonated.
The carbocation generated in Step 1 attracts a water molecule.
The oxonium ion loses a proton to the nitrogen atom, forming an enol.
The enol tautomerizes to the more stable keto form.
The amide is protonated by the acid, forming a carbocation.
A water molecule is attracted to the carbocation.
The oxonium ion loses a proton.
The amine group is protonated.
An electron pair on one of the oxygens displaces the ammonium group from the molecule.
Higher fatty acids
manufacture of soaps. Soaps are sodium potassium salts of higher fatty acids such as stearic acid.
used in foods, cold drinks
Organic acids Uses Organic acids
used as preservatives.
used for the preparation of many drugs such as aspirin, phenacetin etc.
coagulant in the manufacture of rubber.
Acetic acid
manufacture of various dye stuffs, perfumes and rayon.
Ester
Esters are chemical
compounds derived
by
reacting
an oxoacid with
a hydroxyl compound such as an alcohol or phenol. Esters are usually derived from an inorganic acid or organic acid in which at least one -OH (hydroxyl) group is replaced by an -O- alkyl (alkoxy) group, and most commonly from carboxylic acids and alcohols. That is, esters are formed by condensing an acid with an alcohol.
Preparation
Uses
Properties
Carboxylic acids + alcohols
Heat
ester + water
Catalyst (concentrated H2SO4)
Preparation
The equation for the reaction between an acid RCOOH and an alcohol R'OH (where R and R' can be the same or different) is:
Example: ethanoic acid + ethanol
ethyl ethanoate + water
Step in producing ester
Reflux
Separation
Purification
The reaction mixture consisting of the alkanol, the alkanoic acid and a small amount of concentrated sulfuric acid is heated in a vessel with a watercooled condenser (Liebig condenser) to prevent loss of volatile material.
After heating, the reaction mixture is then poured into a separating funnel. Calcium carbonate (CaCO3), or a similar neutralizing agent, is added to the mixture to react with any unreacted acid present in the mixture.
The organic layer separated in the separating funnel above contains the ester. This organic layer is distilled to obtain the pure ester. A sharp boiling point is an indication of the purity of the ester.
Properties
more volatile than carboxylic acids
colourless and exist in liquid state at room temperature.
polar due to the presence of carbonyl (=C=O)group and act as hydrogen bond acceptors not as donors.
Properties
have low boiling and melting points
highly soluble in organic solvents and partly soluble in water.
sweet odour
Uses
Use of ester
To make a substance less water soluble meaning the carboxylic acid is more soluble then its ester.
To combine two substances together Eg. Procaine with Penicillin so 1 drug 2 effects
To create surfactants Eg. Soap
used in flavouring and perfumes
Amides
Amides are derived from carboxylic acids. A carboxylic acid contain the COOH group and in an amide the OH part of that group is replaced by an NH2 group. Soamides contain the CONH2 group.
Three simplest amides are: HCONH2 CH3CONH2 CH3CH2CONH2 methanamide ethanamide propanamide
Notice that, the name derived from the acid by replacing the oic acid ending by amide
Preparation Properties
Uses
Preparation
The ammonium salt is formed by adding solid ammonium carbonate to an excess of the acid.
When the reaction is complete, the mixture is heated and the ammonium salt dehydrates producing ethanamide.
The carboxylic acid is first converted into an ammonium salt which then produces an amide on heating.
The excess of ethanoic acid is there to prevent dissociation of the ammonium salt before it dehydrates. The dissociation is reversible: The presence of the excess ethanoic acid helps to prevent this from happening by moving the position of equilibrium to the left.
Ammonium salts tend to split into ammonia and the parent acid on heating, recombining on cooling.
The melting points of the amides are high
much stronger bases than carboxy lic acids, esters, aldehydes, and ketones
Properties of Amides
The small amides are soluble in water because they have the ability to hydrogen bond with the water molecules.
weak bases
Uses of Amides color, in crayons, pencils and inks, paper industry , plastic and rubber industry, and water and sewage treatment.
Amides use as
used in the treatment of drinking water and sewage. In paper industry polyacrylamide is used as a binder and for retention for fibres. It is also used to retain the color pigments on the paper. Polyacryla as a coating on many household appliances and car parts with thermosetting mide acrylics. used to make tyre cords (the inner structure of a vehicle tyre which is underneath the rubber) Nylons are to make ropes and nylon can be cast easily into solid shapes and used for cogs polyamides and bearings in machines.
used in the cosmetic industry to prepare hair products, soaps, and pre-shave lotions. Acrylamide printing inks, explosives, latex thickeners, adhesives and emulsion stabilizers. s
Kevlar
a form of polyamide. Is a very strong material which is about five times as strong as steel, weight for weight. It is used in composites for boat construction, in manufacture of bulletproof vests, and in lightweight mountaineering ropes and skis and racquets.
used as asanalgesic (pain-killer) used as active ingredient in products such as Amadil, Datril, Cetadol, Naprinol, Acetamino Tylenol, and Panadol. Another amide analgesic is phenacetin, used in products phen an such as Empirin and APC (aspirin, phenacetin, and caffeine) tablets. amide N,N-dimethyl-m-toluamide, used as insect repellant) lidocaine (Xylocaine) and dibucaine (Nupercaine), used as the local anesthetics Other the tranquilizer meprobromate (Equaine, Miltown), and Sevin and Mipcin used commercial as insecticides. ly used
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Chapter - 13 Hydro CarbonDocumento22 pagineChapter - 13 Hydro CarbonManan TyagiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chlor Akali IndustryDocumento26 pagineChlor Akali Industryshenellekhan107Nessuna valutazione finora
- Edexcel & Cambridge Syllabus: Unit 4: Carbonyl Compounds Alauddin Sir A & O Level Chemistry TeacherDocumento8 pagineEdexcel & Cambridge Syllabus: Unit 4: Carbonyl Compounds Alauddin Sir A & O Level Chemistry TeacherMaliha Ishrat JarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrogen PDFDocumento36 pagineHydrogen PDFAryaman VyasNessuna valutazione finora
- ElectrolysisDocumento25 pagineElectrolysisMuhammad UmerNessuna valutazione finora
- GRP VII Tutorial AnsDocumento9 pagineGRP VII Tutorial AnslayssourcreamNessuna valutazione finora
- Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives NewDocumento18 pagineCarboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Newxinying94Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemsheets - co.UkIron Redox QuestionsDocumento1 paginaChemsheets - co.UkIron Redox QuestionsdoggiesrcuteNessuna valutazione finora
- Hand-Out: Chemistry Chapter 4: Haloalkanes & HaloarenesDocumento11 pagineHand-Out: Chemistry Chapter 4: Haloalkanes & HaloarenesLuisgarciaBerlangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Formulae and EquationsDocumento3 pagineChemical Formulae and EquationsFatema KhatunNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial 4Documento6 pagineTutorial 4Jayakumar SankaranNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Aldehydes & Ketones Que. Final EDocumento14 pagine02 Aldehydes & Ketones Que. Final EJagdish SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- Detection of NitrogenDocumento1 paginaDetection of NitrogenFira FfirehsNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry WordDocumento19 pagineOrganic Chemistry Wordisnaini safitriNessuna valutazione finora
- CrackingDocumento5 pagineCrackingnorlin facultadNessuna valutazione finora
- 06 Chapter 1Documento63 pagine06 Chapter 1Dintakurthi PrasanthNessuna valutazione finora
- 13.phenols (915-968)Documento54 pagine13.phenols (915-968)AbhiNessuna valutazione finora
- F325 Transition ElementsDocumento18 pagineF325 Transition ElementsDoc_CrocNessuna valutazione finora
- Acid Base LectureDocumento9 pagineAcid Base LectureJulia Kropel'nytskaNessuna valutazione finora
- Choloro AlkaliDocumento5 pagineCholoro AlkaliPratik AgajNessuna valutazione finora
- Extra Combustion Analysis QuestionsDocumento2 pagineExtra Combustion Analysis QuestionsAnshu MovvaNessuna valutazione finora
- ArenesDocumento5 pagineArenes林琪Nessuna valutazione finora
- Group IV ElementsDocumento11 pagineGroup IV ElementsVince MarsNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry PracticalDocumento16 pagineChemistry PracticalmayashankarjhaNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocumento117 pagine1.aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsKRISHNARJUNA NNessuna valutazione finora
- Excel JEE Booster (3A, 3B) Chemistrty Alcohol Phenol and EtherDocumento21 pagineExcel JEE Booster (3A, 3B) Chemistrty Alcohol Phenol and Ethersourav gargNessuna valutazione finora
- Acid Base TitrationDocumento10 pagineAcid Base TitrationMalini BoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufactured Substances in Industry2Documento20 pagineManufactured Substances in Industry2Sam ZeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Modern Chemical ManufacturerDocumento8 pagineModern Chemical ManufacturerUltra Gamer (sishant)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Content: P-Block ElementsDocumento8 pagineContent: P-Block ElementssachinkurhekarNessuna valutazione finora
- 2020 YIJC Atomic Structure (Student's Copy) PDFDocumento35 pagine2020 YIJC Atomic Structure (Student's Copy) PDFLeng RyanNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrogen and Its Compounds: ST THDocumento8 pagineHydrogen and Its Compounds: ST THAravind NarasimhaluNessuna valutazione finora
- in An Experiment To Find The Enthalpy Change When Copper Is Displaced From A Solution of Copper Ions Excess ZincDocumento8 paginein An Experiment To Find The Enthalpy Change When Copper Is Displaced From A Solution of Copper Ions Excess ZincJake RobinsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Group IV Trends - Carbon To LeadDocumento76 pagineGroup IV Trends - Carbon To LeadRhondene WintNessuna valutazione finora
- Isomers HandoutDocumento5 pagineIsomers HandoutMohamed MeeranNessuna valutazione finora
- Che 176 Carboxylic Acids-2Documento67 pagineChe 176 Carboxylic Acids-2BalogunNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 11 Making and Identifying Salts: Summary QuestionsDocumento3 pagineUnit 11 Making and Identifying Salts: Summary QuestionsLei YinNessuna valutazione finora
- IMPORTANT Solution and OrganicDocumento121 pagineIMPORTANT Solution and OrganicShri GuhanNessuna valutazione finora
- A2 Chemistry Questions On EnergeticsDocumento15 pagineA2 Chemistry Questions On EnergeticsmasudrhussainNessuna valutazione finora
- Fajan RulesDocumento11 pagineFajan RulesSanjita mimNessuna valutazione finora
- Preparation of Alkyl Halides by Nucleophilic Aliphatic Substitution NewDocumento9 paginePreparation of Alkyl Halides by Nucleophilic Aliphatic Substitution NewMunna Patel0% (1)
- Answers To ROH Tutorial PDFDocumento12 pagineAnswers To ROH Tutorial PDFCorvo Haosen Al-Han0% (1)
- Previous HSE Questions From The Chapter "Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids"Documento3 paginePrevious HSE Questions From The Chapter "Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids"basilNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 20: Electrochemistry: Homework QuestionsDocumento2 pagineChapter 20: Electrochemistry: Homework Questionservaldi0% (1)
- Cie QDocumento17 pagineCie Qinternationalmakkhayar100% (1)
- ElectrolysisDocumento31 pagineElectrolysisteddaboyNessuna valutazione finora
- The D - Block ElementsDocumento30 pagineThe D - Block ElementsNandya AristaNessuna valutazione finora
- 7.8.1 Sulphur Chemistry NotesDocumento6 pagine7.8.1 Sulphur Chemistry NotesbhartiyaanujNessuna valutazione finora
- Cbjesccq 02Documento12 pagineCbjesccq 02Sagar MittalNessuna valutazione finora
- P BlockDocumento52 pagineP BlockYogendra GangwarNessuna valutazione finora
- D and F Block Elements-1Documento12 pagineD and F Block Elements-1ilias1973Nessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Energetics Notes PDFDocumento22 pagine1 Energetics Notes PDFnotabc gamer100% (1)
- 9.2 Volumetric Analysis PDFDocumento24 pagine9.2 Volumetric Analysis PDFJoaquinNessuna valutazione finora
- The Indian Public School, Cbe Grade-9 Worksheet-Unit-1-Electrolysis and ChemistryDocumento1 paginaThe Indian Public School, Cbe Grade-9 Worksheet-Unit-1-Electrolysis and ChemistryDhriti GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Viva QuestionsDocumento3 pagineChemistry Viva QuestionsAnonymous vNiXkNxf8Nessuna valutazione finora
- 6.hydrogen Its CompoundDocumento17 pagine6.hydrogen Its CompoundpjaindakNessuna valutazione finora
- Electron Transfer Reactions of Complex Ions in SolutionDa EverandElectron Transfer Reactions of Complex Ions in SolutionNessuna valutazione finora
- 9.1 Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesDocumento34 pagine9.1 Carboxylic Acid and DerivativesgoverotaropafadzwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursery Rhyms LyricDocumento3 pagineNursery Rhyms LyriccikaifaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nombor BekasDocumento1 paginaNombor BekascikaifaNessuna valutazione finora
- Soalan TMK 3 N 4Documento5 pagineSoalan TMK 3 N 4cikaifaNessuna valutazione finora
- Soalan Pecutan GC Set 4Documento25 pagineSoalan Pecutan GC Set 4cikaifaNessuna valutazione finora
- Go 5 Ammonia, Sulphuric Acid, Nitric AcidDocumento21 pagineGo 5 Ammonia, Sulphuric Acid, Nitric AcidcikaifaNessuna valutazione finora
- Go 3 Alcohol, Ether, AminesDocumento13 pagineGo 3 Alcohol, Ether, Aminescikaifa100% (1)
- Go 1 FuelDocumento21 pagineGo 1 FuelcikaifaNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is Science?Documento7 pagineWhat Is Science?cikaifaNessuna valutazione finora
- Program Big Semester 1 PismpDocumento20 pagineProgram Big Semester 1 PismpHady Al FarouqNessuna valutazione finora
- Histology of Plant and Animal CellsDocumento4 pagineHistology of Plant and Animal Cellscikaifa40% (5)
- Arndt-Eistert Synthesis (Wolf Rearrangement) : O CH N N RC O OH R C O CL CH N 2 - Diazoketone R C O CH NNDocumento54 pagineArndt-Eistert Synthesis (Wolf Rearrangement) : O CH N N RC O OH R C O CL CH N 2 - Diazoketone R C O CH NNJosephine TorresNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocumento1 paginaOrganic Chemistry Cheat Sheet: by ViaKunsovann KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 ClickersDocumento41 pagine12 ClickersIbrahim M100% (1)
- Amino Crosslinkers: Product Guide - Cymel Resins - WorldwideDocumento20 pagineAmino Crosslinkers: Product Guide - Cymel Resins - WorldwidejoseNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Chemistry Reacions SummaryDocumento22 pagineOrganic Chemistry Reacions SummaryvgettinfatNessuna valutazione finora
- 7 Siyanbola 70663229 3240Documento15 pagine7 Siyanbola 70663229 3240Crisnuel RamirezNessuna valutazione finora
- Bronst Acid Base QsDocumento8 pagineBronst Acid Base QsIsta EgbetoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry 240 Summer 2001Documento5 pagineChemistry 240 Summer 2001Ismi RahmawatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Review Questions and ProblemsDocumento6 pagineReview Questions and Problemsmache dumadNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic As Test P-2Documento9 pagineOrganic As Test P-2zafarchem_iqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Tong Hop NDSRDocumento18 pagineTong Hop NDSRTrần Sơn HảiNessuna valutazione finora
- Non-Nucleoside Inhibitors On NS5BDocumento14 pagineNon-Nucleoside Inhibitors On NS5BmiklwlNessuna valutazione finora
- LSM2106-SII-Amino Acid-Proteins (2023-2024-Sem I)Documento116 pagineLSM2106-SII-Amino Acid-Proteins (2023-2024-Sem I)Jojo LomoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 8 Nucleophilic Acyl SubstitutionDocumento51 pagineChapter 8 Nucleophilic Acyl SubstitutionHalimatun MustafaNessuna valutazione finora
- A02 355Documento68 pagineA02 355jaimeNessuna valutazione finora
- Ethanoyl Chloride Propanoyl Chloride: Chapter 19: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives 19.5 Acyl Chloride 1. Iupac NamingDocumento7 pagineEthanoyl Chloride Propanoyl Chloride: Chapter 19: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives 19.5 Acyl Chloride 1. Iupac NamingsumathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ch17-Pilihan Ganda Asam Karboksilat Dan TurunannyaDocumento90 pagineCh17-Pilihan Ganda Asam Karboksilat Dan TurunannyaRiyanto Widodo100% (1)
- Cytec Cymel ResinsDocumento9 pagineCytec Cymel ResinsHarshad PorwalNessuna valutazione finora
- T3P FunctionDocumento20 pagineT3P FunctionparthabakalNessuna valutazione finora
- 500 Review Questions For MCAT OC&BC PDFDocumento273 pagine500 Review Questions For MCAT OC&BC PDFGALANG ANUGERAH P. LAMATO100% (3)
- Ethanolamines: Product InformationDocumento48 pagineEthanolamines: Product InformationElias0% (1)
- 2005 T 61 10827 852 Tvorba Conh Vazby JD PDFDocumento26 pagine2005 T 61 10827 852 Tvorba Conh Vazby JD PDFVaibhav DafaleNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Databook WDocumento24 pagineChemistry Databook Wdaemperor216Nessuna valutazione finora
- FTIR Analysis of Natural and Synthetic Collagen: Applied Spectroscopy Reviews March 2018Documento46 pagineFTIR Analysis of Natural and Synthetic Collagen: Applied Spectroscopy Reviews March 2018Imelda Irma IsauraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 10 Test BankDocumento46 pagineChapter 10 Test BankAmir ali Walizadeh100% (1)
- Chemistry 162 Workbook 3Documento51 pagineChemistry 162 Workbook 3Neen NaazNessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Pathways For Unit 4Documento2 pagineOrganic Pathways For Unit 4rajhiniNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Download Ebook Ebook PDF Organic and Biological Chemistry 7th Edition by H Stephen Stoker PDFDocumento41 pagineFull Download Ebook Ebook PDF Organic and Biological Chemistry 7th Edition by H Stephen Stoker PDFjanet.martino412100% (39)
- Assignment For Final Term Alkenes and AlkynesDocumento3 pagineAssignment For Final Term Alkenes and AlkynesAliah CanalsNessuna valutazione finora
- Study of The Internal Diesel Injector Deposit PhenomenonDocumento14 pagineStudy of The Internal Diesel Injector Deposit PhenomenonNarcisDanielPetreaNessuna valutazione finora