Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Multiple Choice: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The Question
Caricato da
Faysal RifaiDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Multiple Choice: Identify The Choice That Best Completes The Statement or Answers The Question
Caricato da
Faysal RifaiCopyright:
Formati disponibili
PT1
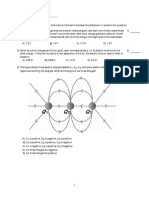
Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. Two point charges, separated by 1.5 cm, have charge values of +2.0 and 4.0 C, respectively. What is the value of the mutual force between them? (ke = 8.99 109 Nm2/C2) a. 320 N b. 3.6 108 N c. 8.0 1012 N d. 3.1 103 N 2. Charge A and charge B are 3.00 m apart, and charge A is +2.00 C and charge B is +3.00 C. Charge C is located between them at a certain point and the force on charge C is zero. How far from charge A is charge C? a. 0.555 m b. 0.667 m c. 1.35 m d. 1.50 m 3. A 6.00 C charge is placed at the origin and a second charge is placed on the x-axis at x = 0.300 m. If the resulting force on the second charge is 6.40 N in the positive x-direction, what is the force on the charge at the origin? a. 6.40 N in the positive x-direction b. 6.40 N in the negative x-direction c. 0 N d. not able to be determined until the second charge is known 4. The average distance of the electron from the proton in the hydrogen atom is 0.51 1010 m. What is the electric field from the protons charge at the location of the electron? (ke = 8.99 109 Nm2/C2, e = 1.6 1019 C) a. 5.5 1011 N/C b. 1.0 106 N/C c. 3.2 102 N/C d. 8.8 108 N/C 5. A proton initially moves left to right long the x axis at a speed of 2.00 103 m/s. It moves into an electric field, which points in the negative x direction, and travels a distance of 0.200 m before coming to rest. If the proton's mass and charge are 1.67 1027 kg and 1.60 1019 C respectively, what is the magnitude of the electric field? a. 28.3 N/C b. 13.9 N/C c. 0.104 N/C d. 0.038 N/C 6. Two charges, +Q and Q, are located two meters apart and there is a point along the line that is equidistant from the two charges as indicated. Which vector best represents the direction of the electric field at that point?
____
____
____
____
____
a. b. c. d. ____
Vector EA Vector EB Vector EC The electric field at that point is zero.
7. The electric field in a cathode ray tube is supposed to accelerate electrons from 0 to 1.60 107 m/s in a distance of 2.00 cm. What electric field is required? (me = 9.11 1031 kg and e = 1.60 1019 C) a. 9 110 N/C b. 18 200 N/C c. 36 400 N/C d. 72 800 N/C 8. Q1 has 50 electric field lines radiating outward and Q2 has 100 field lines converging inward. What is the ratio Q1/Q2? a. 2 b. 2 c. 1/2 d. 1/2 9. If an electron is accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 1 200 V, find its approximate velocity at the end of this process. (e = 1.6 1019 C; me = 9.1 1031 kg) a. 1.0 107 m/s b. 1.4 107 m/s c. 2.1 107 m/s d. 2.5 107 m/s
____
____
____ 10. A uniform electric field, with a magnitude of 600 N/C, is directed parallel to the positive x-axis. If the potential at x = 3.0 m is 1 000 V, what is the potential at x = 1.0 m? a. 400 V b. 1 600 V c. 2 200 V d. 2 500 V ____ 11. An electron in a cathode ray tube is accelerated through a potential difference of 5.0 kV. What kinetic energy does the electron gain in the process? (e = 1.6 1019 C) a. 1.6 1016 J b. 8.0 1016 J c. 1.6 1022 J d. 8.0 1022 J
____ 12. An electron with velocity v = 1.0 106 m/s is sent between the plates of a capacitor where the electric field is E = 500 V/m. If the distance the electron travels through the field is 1.0 cm, how far is it deviated (Y) in its path when it emerges from the electric field? (me = 9.1 1031 kg, e = 1.6 1019 C)
a. b. c. d.
2.2 mm 4.4 mm 2.2 cm 4.4 cm
____ 13. Four identical 1-mF capacitors are connected together electrically. What is the greatest possible capacitance of the combination? a. 8 mF b. 4 mF c. 1 mF d. 1/4 mF ____ 14. A 10.0-F capacitor is attached to a 20-V power supply. How much energy is stored in the capacitor? a. 2.0 103 J b. 1.2 103 J c. 2.0 104 J d. 5.2 104 J ____ 15. The current in an electron beam in a cathode-ray tube is measured to be 70 A. How many electrons hit the screen in 5.0 s? (e = 1.6 1019 C) a. 2.2 1011 electrons b. 8.8 1013 electrons c. 2.2 1015 electrons d. 8.8 1018 electrons ____ 16. A flashlight bulb operating at a voltage of 4.5 V has a resistance of 8.0 . How many electrons pass through the bulb filament per second (e = 1.6 1019 C)? a. 3.7 1016 b. 1.8 1021 c. 9.4 1017 d. 3.5 1018 ____ 17. A metallic conductor has a resistivity of 18 106 m. What is the resistance of a piece that is 30 m long and has a uniform cross sectional area of 3.0 106 m2? a. 0.056 b. 180 c. 160 d. 90 ____ 18. A Nichrome wire has a radius of 0.50 mm and a resistivity of 1.5 106 m. If the wire carries a current of 0.50 A, what is the potential difference per unit length along this wire? a. 0.003 V/m
b. 0.95 V/m c. 1.6 V/m d. 1.9 V/m ____ 19. A 60-W light bulb is in a socket supplied with 120 V. What is the current in the bulb? a. 0.50 A b. 2.0 A c. 60 A d. 7 200 A ____ 20. The two ends of a 3.0- resistor are connected to a 9.0-V battery. What is the total power delivered by the battery to the circuit? a. 3.0 W b. 27 W c. 0.33 W d. 0.11 W ____ 21. When a 24.0- resistor is connected across a 12.0-V battery, a current of 482 mA flows. What is the internal resistance of the battery? a. 0.02 b. 0.9 c. 25.0 d. 49.8 ____ 22. Three resistors connected in parallel have individual values of 4.0, 6.0 and 10.0 , respectively. If this combination is connected in series with a 12-V battery and a 2.0- resistor, what is the current in the 10- resistor?
a. b. c. d.
0.59 A 1.0 A 11 A 16 A
____ 23. Household circuits are wired in ________. a. series b. parallel c. both series and parallel d. neither series nor parallel ____ 24. Using a capacitor and two different value resistors, which of the following combinations in an RC circuit would give the greatest time constant? a. the capacitor in series with both resistors in series with each other b. the capacitor in series with both resistors in parallel with each other c. the capacitor in series with the higher value resistor d. the capacitor in series with the lower value resistor
PT1 Answer Section
MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: TOP: ANS: TOP: ANS: TOP: ANS: TOP: ANS: TOP: ANS: TOP: ANS: ANS: TOP: ANS: TOP: ANS: TOP: ANS: ANS: TOP: ANS: TOP: ANS: TOP: ANS: TOP: ANS: A PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 15.3 Coulombs Law C PTS: 1 DIF: 3 TOP: 15.3 Coulombs Law B PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 15.3 Coulombs Law A PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 15.4 The Electric Field C PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 15.4 The Electric Field A PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 15.4 The Electric Field C PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 15.4 The Electric Field D PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: 15.5 Electric Field Lines C PTS: 1 DIF: 2 16.1 Potential Difference and Electric Potential C PTS: 1 DIF: 2 16.1 Potential Difference and Electric Potential B PTS: 1 DIF: 2 16.1 Potential Difference and Electric Potential B PTS: 1 DIF: 3 16.1 Potential Difference and Electric Potential B PTS: 1 DIF: 2 16.7 The Parallel-Plate Capacitor | 16.8 Combinations of Capacitors A PTS: 1 DIF: 2 16.9 Energy Stored in a Charged Capacitor C PTS: 1 DIF: 1 TOP: 17.1 Electric Current D PTS: 1 DIF: 2 17.4 Resistance, Resistivity, and Ohms Law B PTS: 1 DIF: 2 17.4 Resistance, Resistivity, and Ohms Law B PTS: 1 DIF: 2 17.4 Resistance, Resistivity, and Ohms Law A PTS: 1 DIF: 1 TOP: 17.6 Electrical Energy and Power B PTS: 1 DIF: 1 18.1 Sources of emf | 18.2 Resistors in Series | 18.3 Resistors in Parallel B PTS: 1 DIF: 2 18.1 Sources of emf | 18.2 Resistors in Series | 18.3 Resistors in Parallel A PTS: 1 DIF: 3 18.1 Sources of emf | 18.2 Resistors in Series | 18.3 Resistors in Parallel B PTS: 1 DIF: 1 18.6 Household Circuits | 18.7 Electrical Safety A PTS: 1 DIF: 2 TOP: Conceptual Questions
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Electrical Energy and CapacitanceDocumento9 pagineElectrical Energy and CapacitanceReymond CañoneroNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrostatics Questions Energy and Work With AnswersDocumento14 pagineElectrostatics Questions Energy and Work With Answersmicheal_cksNessuna valutazione finora
- Ee1 Ece 500Documento7 pagineEe1 Ece 500Karen Gale A. Lodia - AlarconNessuna valutazione finora
- Mid Term Test Phy098 Feb 2021 ObjDocumento5 pagineMid Term Test Phy098 Feb 2021 ObjanisahNessuna valutazione finora
- VII Phys 205 Final Winter2012 SolutionsDocumento9 pagineVII Phys 205 Final Winter2012 SolutionsJashan ThindNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy 124Documento18 paginePhy 124hardebolzem12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Engineering Actual BoardDocumento13 pagineElectrical Engineering Actual BoardRaslany Mambuay100% (1)
- RC 1-20 ElexDocumento86 pagineRC 1-20 ElexuvubwebweNessuna valutazione finora
- Emags - Elex CKTDocumento26 pagineEmags - Elex CKTAlvin RivasNessuna valutazione finora
- Electric FieldsDocumento8 pagineElectric FieldsrealNessuna valutazione finora
- Class-Xii - Final Cbse Board Physics Sample Paper-1Documento8 pagineClass-Xii - Final Cbse Board Physics Sample Paper-1kamali.v777Nessuna valutazione finora
- MV July2018 EeDocumento13 pagineMV July2018 EeMargo Isay EriveNessuna valutazione finora
- July 2018 Pre Board Exam EeDocumento18 pagineJuly 2018 Pre Board Exam EeAshlien Valdez0% (2)
- Physics Unit 2 Test 1Documento6 paginePhysics Unit 2 Test 1ron971Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cusat 2016Documento37 pagineCusat 2016sreejitha KNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics Mastery 1 Problems:: R C C R R C R CDocumento6 pagineElectronics Mastery 1 Problems:: R C C R R C R CJonas ParreñoNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY 2054 Discussion Spring 09 Conceptual Review: Chapter 16 A - Potential Energy & PotentialDocumento2 paginePHY 2054 Discussion Spring 09 Conceptual Review: Chapter 16 A - Potential Energy & PotentialJiyuNessuna valutazione finora
- Prac FinaleDocumento14 paginePrac FinaleadadafasfasNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics and Maths 12thDocumento38 paginePhysics and Maths 12thPraveenNessuna valutazione finora
- EE Online SAEx 2 1 PDFDocumento6 pagineEE Online SAEx 2 1 PDFJunnar Jay AbañoNessuna valutazione finora
- Spty, Yr6ti7iuhliphysics2013allindia PDFDocumento14 pagineSpty, Yr6ti7iuhliphysics2013allindia PDFyeateshwarriorNessuna valutazione finora
- 29TH September 2022 Phyew601 ExerciseDocumento4 pagine29TH September 2022 Phyew601 Exercisebenimana cedricNessuna valutazione finora
- Class 12 Physics 1st Term 23 - 24Documento3 pagineClass 12 Physics 1st Term 23 - 24PrinceNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter15 Electric Forces and Electric FieldsDocumento17 pagineChapter15 Electric Forces and Electric FieldsSky SailingNessuna valutazione finora
- 3rd Quarterly Physics 2 STEM Questions and AnswersDocumento5 pagine3rd Quarterly Physics 2 STEM Questions and Answersronaldo maanoNessuna valutazione finora
- PHY126 PQ InfomasDocumento11 paginePHY126 PQ InfomascodforphilsamNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Bank For May 2017 PhysicsDocumento5 pagineQuestion Bank For May 2017 PhysicsKushagra MittalNessuna valutazione finora
- National University of Singapore: PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics IIDocumento10 pagineNational University of Singapore: PC1222 Fundamentals of Physics IIYuhua SunNessuna valutazione finora
- Sp2014 Exam1Documento4 pagineSp2014 Exam1dreamachiever12Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2021 PHY2 CLC Problems BaitapDocumento13 pagine2021 PHY2 CLC Problems BaitapThinh Nguyen100% (1)
- Tutorial QuestionsDocumento20 pagineTutorial Questionsharshiika kathiravanNessuna valutazione finora
- MV March2018 EsasDocumento9 pagineMV March2018 EsasMargo Isay EriveNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy152 CBT Exam Practice Questions (2019/20)Documento25 paginePhy152 CBT Exam Practice Questions (2019/20)SHERIFF BAKARENessuna valutazione finora
- Test1 16FDocumento8 pagineTest1 16FJasper LuNessuna valutazione finora
- WBJEEM 2014 Question Bank 5Documento18 pagineWBJEEM 2014 Question Bank 5Hussain AbbasNessuna valutazione finora
- Angel Education Society: HALFYEARLY EXAMINATION (2017-20018) Subject: Physics Class - 12 F.M - 70 Time-3 HrsDocumento3 pagineAngel Education Society: HALFYEARLY EXAMINATION (2017-20018) Subject: Physics Class - 12 F.M - 70 Time-3 HrsAtul Verma0% (1)
- Topper Sample Paper 3 Class XII-Physics Solutions: Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 70Documento14 pagineTopper Sample Paper 3 Class XII-Physics Solutions: Time: Three Hours Maximum Marks: 70coolspanky_227053Nessuna valutazione finora
- Electricity Book QuestionsDocumento6 pagineElectricity Book QuestionsshellyNessuna valutazione finora
- Acces Point - Ee Refresher 2Documento12 pagineAcces Point - Ee Refresher 2christinesarah0925100% (1)
- 12 Phy HY 21-22Documento9 pagine12 Phy HY 21-22Funky boyzzzNessuna valutazione finora
- Bài tập VL2 CLCDocumento12 pagineBài tập VL2 CLCbnthanh2209Nessuna valutazione finora
- ElectrostaticsDocumento4 pagineElectrostaticsSharan RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet No. 1 - Module 1Documento4 pagineWorksheet No. 1 - Module 1Richel Ann CapacilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12Documento19 pagineChapter 12hakitNessuna valutazione finora
- Phy 2015Documento5 paginePhy 2015ANASNessuna valutazione finora
- XII-Physics SQP 2018-19 PDFDocumento8 pagineXII-Physics SQP 2018-19 PDFNikhil singhNessuna valutazione finora
- G-Cakna Kelantan 2015 - Physics Term 2 - Module 2Documento12 pagineG-Cakna Kelantan 2015 - Physics Term 2 - Module 2annahiazNessuna valutazione finora
- Question Bank Unit I: Electrostatics.: Very Short Answer Type Questions (1, 2, 3 Marks)Documento7 pagineQuestion Bank Unit I: Electrostatics.: Very Short Answer Type Questions (1, 2, 3 Marks)NathanianNessuna valutazione finora
- Final ExamA1-2019-1Documento4 pagineFinal ExamA1-2019-1trinh.lenukieuNessuna valutazione finora
- Model QP PHY HY 12Documento6 pagineModel QP PHY HY 12Soumya KhatriNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrostaitics Class 12thDocumento3 pagineElectrostaitics Class 12thvishnuyterNessuna valutazione finora
- Legit Multivector Review and Training Center Online Self-Assessment ExaminationDocumento6 pagineLegit Multivector Review and Training Center Online Self-Assessment ExaminationJunnar Jay AbañoNessuna valutazione finora
- ElectrostaticDocumento2 pagineElectrostaticAlyssa ColeNessuna valutazione finora
- STD Xii Physics Bookback Objective Revised With KeyDocumento33 pagineSTD Xii Physics Bookback Objective Revised With KeyOM KAILASHNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ For XIIDocumento23 pagineMCQ For XIIJaya MaharjanNessuna valutazione finora
- Fizik 2 Çalışma SorularıDocumento6 pagineFizik 2 Çalışma SorularıhavvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Certc Refresher Exam EeDocumento8 pagineCertc Refresher Exam Eealbert elardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Problems 3Documento11 pagineProblems 3ansat5.ansatNessuna valutazione finora
- Homework GP 2011 2 09Documento7 pagineHomework GP 2011 2 09choiyunjungNessuna valutazione finora
- Dairy Products Theory XIIDocumento152 pagineDairy Products Theory XIIDskNessuna valutazione finora
- FebvreDocumento449 pagineFebvreIan Pereira AlvesNessuna valutazione finora
- Flusser-The FactoryDocumento2 pagineFlusser-The FactoryAlberto SerranoNessuna valutazione finora
- Discrete Wavelet TransformDocumento10 pagineDiscrete Wavelet TransformVigneshInfotechNessuna valutazione finora
- Vanish Magic Magazine VANISH MAGIC MAGAZINE 58 May 2019Documento118 pagineVanish Magic Magazine VANISH MAGIC MAGAZINE 58 May 2019mick byrnes100% (1)
- Metaphysics of LucretiusDocumento6 pagineMetaphysics of LucretiusChristopher BennettNessuna valutazione finora
- ETR Series: A Full Spectrum of Products To Solve Your Application NeedsDocumento106 pagineETR Series: A Full Spectrum of Products To Solve Your Application Needs周小安Nessuna valutazione finora
- Harmonic Analysis of Separately Excited DC Motor Drives Fed by Single Phase Controlled Rectifier and PWM RectifierDocumento112 pagineHarmonic Analysis of Separately Excited DC Motor Drives Fed by Single Phase Controlled Rectifier and PWM RectifierGautam Umapathy0% (1)
- Reynold A. Nicholson - The Mystics of IslamDocumento65 pagineReynold A. Nicholson - The Mystics of IslamLuminon SamanNessuna valutazione finora
- 08 - 2061 USTR 2222a (1) Supor EKVDocumento24 pagine08 - 2061 USTR 2222a (1) Supor EKVHassan Houdoud0% (1)
- Tokyo Guidelines 2018Documento115 pagineTokyo Guidelines 2018Alik Razi100% (1)
- Danika Cristoal 18aDocumento4 pagineDanika Cristoal 18aapi-462148990Nessuna valutazione finora
- 23001864Documento15 pagine23001864vinodsrawat33.asiNessuna valutazione finora
- AIR Conditioner: Owner'S ManualDocumento52 pagineAIR Conditioner: Owner'S Manualashley diazNessuna valutazione finora
- CCNA Training New CCNA - RSTPDocumento7 pagineCCNA Training New CCNA - RSTPokotete evidenceNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment of Diabetic FootDocumento7 pagineAssessment of Diabetic FootChathiya Banu KrishenanNessuna valutazione finora
- Bulk Material/Part Ppap Process Checklist / Approval: Required?Documento32 pagineBulk Material/Part Ppap Process Checklist / Approval: Required?krds chidNessuna valutazione finora
- Tabla de Avances de AcesoriosDocumento3 pagineTabla de Avances de AcesoriosPedro Diaz UzcateguiNessuna valutazione finora
- Notes Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocumento12 pagineNotes Transfer of Thermal Energymahrosh mamoon100% (2)
- Adaptive Reuse Architecture Documentation and Analysis 2168 9717 1000172Documento9 pagineAdaptive Reuse Architecture Documentation and Analysis 2168 9717 1000172Komal HundiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Test09 Eoc Algebra2 ReducedDocumento33 pagineTest09 Eoc Algebra2 ReducedkristymadimikeNessuna valutazione finora
- Multi Pressure Refrigeration CyclesDocumento41 pagineMulti Pressure Refrigeration CyclesSyed Wajih Ul Hassan80% (10)
- Etoricoxib - Martindale 39thDocumento2 pagineEtoricoxib - Martindale 39thCachimbo PrintNessuna valutazione finora
- List of Fatigue Standards and Fracture Standards Developed by ASTM & ISODocumento3 pagineList of Fatigue Standards and Fracture Standards Developed by ASTM & ISOSatrio Aditomo100% (1)
- F24 60manual (New)Documento14 pagineF24 60manual (New)Robert CumpaNessuna valutazione finora
- PANASONIC - WebCam-TQZJ402 - TY-CC20W PDFDocumento188 paginePANASONIC - WebCam-TQZJ402 - TY-CC20W PDF123anthonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Joby Aviation - Analyst Day PresentationDocumento100 pagineJoby Aviation - Analyst Day PresentationIan TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Psle Science Keywords !Documento12 paginePsle Science Keywords !Aftertea CarousellNessuna valutazione finora
- The Indian & The SnakeDocumento3 pagineThe Indian & The SnakeashvinNessuna valutazione finora
- Coffee Quality Manual by Abra Rand Nig Use IDocumento25 pagineCoffee Quality Manual by Abra Rand Nig Use IIpungNessuna valutazione finora