Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Mercury-in-glass thermometer principles
Caricato da
Jay KimDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Mercury-in-glass thermometer principles
Caricato da
Jay KimCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Thermometer assignment
Abstract This paper will briefly cover the principles and describe the practice of the Mercury-in-glass thermometer Overview of the thermometer A mercury thermometer also known as a mercury-in-glass thermometer was the invention by German physicist Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit in 1714 and is a thermometer that consists of mercury in a glass tube. Calibrated marks on the tube allow the temperature to be read by the length of the mercury within the tube, which varies (nearly linearly) according to the temperature of the mercury. There is usually a mercury filled bulb at the end of the thermometer, to increase the sensitivity. The expansion and contraction of this mercury is then increased in the narrower part of the tube. The space above the mercury may be filled with nitrogen or it may be less than atmospheric pressure, which is normally known as a vacuum.
Principle of operation Mercury will solidify (freeze) at -38.83 C (-37.89 F) and so may only be used at higher temperatures. Mercury does not expand upon solidification and will not break the glass tube. If the thermometer contains nitrogen, the gas may flow down into the column and be trapped there when the temperature rises. If this happens, the thermometer will be unusable until returned to the factory for reconditioning. To avoid this, some weather services require that all mercury-in-glass thermometers be brought indoors when the temperature falls to -37 C (34.6 F). In areas where the maximum temperature is not expected to rise above -38.83 C (37.89 F), a thermometer containing a mercury-thallium alloy may be used. This has a solidification (freezing) point of -61.1 C (-78 F). Comparison of performance of the thermometer against at least one other type of thermometer The Alcohol thermometer or spirit thermometer is an alternative to the mercury-in-glass thermometer, and functions in a similar way. The contents of the mercury-in-glass thermometer are highly toxic but the alcohol thermometer is less harmful and its contents will evaporate away fairly quickly. An organic liquid is contained in a glass bulb which is connected to a capillary of the same glass and the end is sealed with an expansion bulb. The space above the liquid is a mixture of nitrogen and the vapor of the liquid. For the working temperature range, the meniscus or interface between the liquid is within the capillary. With increasing
temperature, the volume of liquid expands and the meniscus moves up the capillary. The position of the meniscus shows the temperature against an inscribed scale. The liquid used can be pure ethanol, toluene, kerosene or Is amyl acetate, depending on manufacturer and working temperature range. Since these are transparent, the liquid is made more visible by the addition of a red or blue dye. One half of the glass containing the capillary is usually enameled white or yellow to give a background for reading the scale. The ethanol version is the most widely used due to the low cost and relatively low hazard posed by the liquid in case of breakage. Limitations of the thermometer including sources of error The Mercury in glass thermometers main problem is health issues. Mercury is poisonous and when the thermometer is broken can cause damage. Its expansively is fairly low. It is expensive and it has a high freezing point therefore it cannot be used in places where the temperature gets very low. Where this type of thermometer is used Thermometers have been built which utilize a range of physical effects to measure temperature. Temperature sensors are used in a wide variety of scientific and engineering applications, especially measurement systems. Temperature systems are primarily either electrical or mechanical, occasionally inseparable from the system which they control (as in the case of a mercury-in-glass thermometer). Thermometers are used within roadways in cold weather climates to help determine if icing conditions exist. Indoors, thermistors are used in climate control systems such as air conditioners, freezers, heaters, refrigerators, and water heaters. Galileo thermometers are used to measure indoor air temperature, due to their limited measurement range. Alcohol thermometers and mercury-in-glass are used outside in areas which are well-exposed to the elements at various levels of the Earth's atmosphere and within the Earth's oceans is necessary within the fields of meteorology and climatology. Aircraft use thermometers and hygrometers to determine if there are atmospheric icing conditions in their flight path, and these measurements are used to initialize weather forecast models. Thermometers are used within roadways in cold weather climates to help determine if icing conditions exist and indoors within climate control systems.
Bibliography Lee, C 2003, Thermostat' Scientific American, vol. 289, no. 5, p. 32. 'Thermometer' The world book encyclopedia 2004, World Book, Sydney, vol. 8, pp. 114-116. ' Mercury' Encyclopedia Britannica Online School Edition 2006, viewed 10 November 2006, <http://www.school.eb.com.au/all/comptons/article-9345009>. Oakley, V 2003, 'Mercury in devices', Australian, 15 November, p. 29. Middleton, 2006, ' A history of the thermometer, and its uses in meteorology Baltimore Chang, Hasok. Inventing Temperature. New York : Oxford University Press, c2004.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Temperature MeasurementDocumento38 pagineTemperature MeasurementTarun Singhal100% (1)
- Thermocouples: Prepared By: K Krishna Kishore 4 Year ECE 15F41A0440 Presented To: Mr. S. Nanda Kishore (PH.D.)Documento17 pagineThermocouples: Prepared By: K Krishna Kishore 4 Year ECE 15F41A0440 Presented To: Mr. S. Nanda Kishore (PH.D.)k kNessuna valutazione finora
- ECG Measurement SystemDocumento10 pagineECG Measurement SystemMary HelenNessuna valutazione finora
- Survey of Temperature Sensors Used in Various Thermal SystemsDocumento3 pagineSurvey of Temperature Sensors Used in Various Thermal SystemsRavi PatilNessuna valutazione finora
- Temperature, Light & Pressure SensorsDocumento60 pagineTemperature, Light & Pressure SensorsHaider-e-KararNessuna valutazione finora
- TransducersDocumento24 pagineTransducersChandra Sekher Reddy BhimiReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermistor:: PTC ThermistorsDocumento6 pagineThermistor:: PTC ThermistorsTanveer AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Bactron Anaerobic ChamberDocumento8 pagineBactron Anaerobic ChamberAsvene SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Resistive TransducerDocumento75 pagineResistive TransducerDhineshSKNessuna valutazione finora
- Working Principle of Thermocouple.Documento9 pagineWorking Principle of Thermocouple.Akshat ChitnisNessuna valutazione finora
- Factors Affecting Temperature Measurement AccuracyDocumento2 pagineFactors Affecting Temperature Measurement AccuracyMarvZz VillasisNessuna valutazione finora
- Carnot CycleDocumento3 pagineCarnot CyclealexontingNessuna valutazione finora
- TN 324: Intelligent InstrumentationDocumento43 pagineTN 324: Intelligent InstrumentationAlango Jr Tz100% (1)
- Test de RadiadorDocumento10 pagineTest de RadiadorOmar Reinoso TigreNessuna valutazione finora
- Physics ProjectDocumento5 paginePhysics ProjectSAAD SHAIKH100% (1)
- Group 1 Experimental and MeasurementDocumento46 pagineGroup 1 Experimental and MeasurementAmir O. OshoNessuna valutazione finora
- Instrumentation Lab.: RTD Thermistors Thermocoupl eDocumento31 pagineInstrumentation Lab.: RTD Thermistors Thermocoupl eGAURAV SINGHNessuna valutazione finora
- Vacuum GaugeDocumento4 pagineVacuum GaugeDebanjana ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- Characteristics of ThermocoupleDocumento6 pagineCharacteristics of ThermocouplekusumgdasNessuna valutazione finora
- Loading Effects and Two-Port Networks Week 5 - 6Documento31 pagineLoading Effects and Two-Port Networks Week 5 - 6منتصر الجعبريNessuna valutazione finora
- CAPE2030 Experiment 4: Thermal Conductivity and Radiation Your Name (ID No. XXXXXXXXX)Documento4 pagineCAPE2030 Experiment 4: Thermal Conductivity and Radiation Your Name (ID No. XXXXXXXXX)Sayed Abu Sufyan100% (1)
- Resistance Temperature DetectorDocumento2 pagineResistance Temperature DetectorDebanjana ChowdhuryNessuna valutazione finora
- A Study On Heat Transfer in MicroDocumento2 pagineA Study On Heat Transfer in MicroPabitraBadhukNessuna valutazione finora
- Measuring The Thermal Conductivity of CopperDocumento4 pagineMeasuring The Thermal Conductivity of CopperPiyush MoradiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Composite WallDocumento6 pagineComposite WallRushabh PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Layout and Working of A Nuclear Power PlantDocumento3 pagineBasic Layout and Working of A Nuclear Power Plantsaranya saiganeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding the Key Components of a Generalized Measurement SystemDocumento3 pagineUnderstanding the Key Components of a Generalized Measurement SystemJeba ChristoNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Temperature MeasurementDocumento20 pagineIntroduction To Temperature MeasurementjimsistiNessuna valutazione finora
- On Measurement of Non-Electrical QuantitiesDocumento39 pagineOn Measurement of Non-Electrical Quantitiesrao asadNessuna valutazione finora
- Ideal Gas Lecture NotesDocumento20 pagineIdeal Gas Lecture NotesFlowerNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermo Chapter 3Documento27 pagineThermo Chapter 3Mohd AziziNessuna valutazione finora
- Expt No 1 Band Gap of A SemiconductorDocumento8 pagineExpt No 1 Band Gap of A SemiconductorNayan ChandakNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 2 Resistance Thermo PDFDocumento31 pagineUnit 2 Resistance Thermo PDFUv sai likithNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermistor: Uses of ThermistorsDocumento5 pagineThermistor: Uses of ThermistorsBisma khanNessuna valutazione finora
- A Discussion About Maximum Power TransferDocumento8 pagineA Discussion About Maximum Power TransferRebwar Osman100% (1)
- RC Dan FLIP FLOP IC 555Documento24 pagineRC Dan FLIP FLOP IC 555assaNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermal Expansion of Metals Measured by Dilatometer LabDocumento7 pagineThermal Expansion of Metals Measured by Dilatometer LabTaqqi HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermistors (Sensors)Documento27 pagineThermistors (Sensors)Saptarshi PandaNessuna valutazione finora
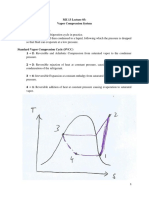
- Vapour Compression Refrigeration System Generating Fresh Water From Humidity in The AirDocumento5 pagineVapour Compression Refrigeration System Generating Fresh Water From Humidity in The AirRimsha Maryam100% (1)
- Metrology Unit 3 PPT 3Documento34 pagineMetrology Unit 3 PPT 3Punith RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Nano Fluid Volume PercentageDocumento35 pagineNano Fluid Volume PercentageMuthiah Chidambaram Muthiah100% (1)
- How Electric Irons WorkDocumento6 pagineHow Electric Irons WorkSwagat Pradhan100% (1)
- Group Assignment # 1 Measurements and Instrumentations Assignment TopicDocumento10 pagineGroup Assignment # 1 Measurements and Instrumentations Assignment TopicArsam NasimNessuna valutazione finora
- Multistage Impulse GeneratorDocumento2 pagineMultistage Impulse Generatorsurekawithana75% (4)
- Electro Cardiograph y Circuit DesignDocumento10 pagineElectro Cardiograph y Circuit DesignSaad Al HelyNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrodynamometer Type InstrumentsDocumento12 pagineElectrodynamometer Type InstrumentsmjmanishNessuna valutazione finora
- Keamanan Listrik dalam Praktik MedisDocumento14 pagineKeamanan Listrik dalam Praktik Medisnhia ulyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 12 - ThermodynamicsDocumento69 pagineChapter 12 - Thermodynamicszahid_polyNessuna valutazione finora
- Tutorial2 DisplacementDocumento4 pagineTutorial2 DisplacementOjaswa AnandNessuna valutazione finora
- Fundamentals of Electronics and Power ElectronicsDocumento2 pagineFundamentals of Electronics and Power ElectronicsTun Lin NaingNessuna valutazione finora
- 113 Using Steam in The Power Plant Course PreviewDocumento19 pagine113 Using Steam in The Power Plant Course PreviewAnonymous q9eCZHMuS100% (1)
- حل واجب عناصر 2Documento5 pagineحل واجب عناصر 2جبر احمدNessuna valutazione finora
- The Zeroth and First Law of ThermodynamicsDocumento7 pagineThe Zeroth and First Law of Thermodynamicsdennie85Nessuna valutazione finora
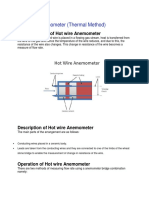
- Hot Wire AnemometerDocumento3 pagineHot Wire Anemometerneha yarrapothuNessuna valutazione finora
- DC-DC Choppers Explained for Power Electronics ApplicationsDocumento24 pagineDC-DC Choppers Explained for Power Electronics ApplicationsAbdullah NasirNessuna valutazione finora
- Heat Exchanger Presentation by Muhammad AwaisDocumento51 pagineHeat Exchanger Presentation by Muhammad AwaisBaqirMuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Pressure and Tempreture MeasurementDocumento61 paginePressure and Tempreture MeasurementVarad DateNessuna valutazione finora
- Vital Signs Monitoring System For Patients.: Universidad Politécnica Salesiana Cuenca - Ecuador AbstractDocumento12 pagineVital Signs Monitoring System For Patients.: Universidad Politécnica Salesiana Cuenca - Ecuador AbstractFreddy Valdez GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture On Thermoelectric EffectDocumento16 pagineLecture On Thermoelectric EffectjacobNessuna valutazione finora
- Thermometers: PhysicsDocumento10 pagineThermometers: PhysicsImran HozaNessuna valutazione finora
- GenChem2 Q3 Module 2.1 Phase Changes v4Documento20 pagineGenChem2 Q3 Module 2.1 Phase Changes v4Junelle Ramos Aquino100% (1)
- Hydraulics Reviewer For Civil Engineering StudentsDocumento2 pagineHydraulics Reviewer For Civil Engineering StudentsKing BangngayNessuna valutazione finora
- VCPBR 05043 en PRV OverviewDocumento24 pagineVCPBR 05043 en PRV OverviewmagveyNessuna valutazione finora
- HyResponder - D1 - 1 - H2 Systems and Safety Features - Final 21122021Documento54 pagineHyResponder - D1 - 1 - H2 Systems and Safety Features - Final 21122021Theodoor KoenenNessuna valutazione finora
- Trickle Bed by WillyDocumento8 pagineTrickle Bed by WillyDocument PTKI MedanNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Report PDFDocumento26 pagineProject Report PDFcaloycaloy2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Quality Design Fundamental in MSMADocumento14 pagineQuality Design Fundamental in MSMANur Farhana Ahmad FuadNessuna valutazione finora
- 4 KSU - FiltrationDocumento15 pagine4 KSU - FiltrationmeitaNessuna valutazione finora
- AGA HIQ Pharmacopoeias Datasheet UK - tcm615-101359Documento2 pagineAGA HIQ Pharmacopoeias Datasheet UK - tcm615-101359Vadim RiabovNessuna valutazione finora
- Lista de Instrumentos Precom-Com - PDF ParapetiDocumento3 pagineLista de Instrumentos Precom-Com - PDF ParapetiRoy RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Training Report On TubelightsDocumento29 pagineIndustrial Training Report On TubelightsRabinsa Yadav100% (1)
- Dinamis 2 Sgt-01 BeforeDocumento2 pagineDinamis 2 Sgt-01 BeforeDwi Mulyanti DwimulyantishopNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity NoDocumento8 pagineActivity NoWilbert PialaNessuna valutazione finora
- CBM SlideDocumento28 pagineCBM SlideMARSHALLNessuna valutazione finora
- Pureit Marvella Ultima RO+UV - Manual - FN PDFDocumento18 paginePureit Marvella Ultima RO+UV - Manual - FN PDFharibabu.yadlapalliNessuna valutazione finora
- How an Auto AC System Works and Potential TXV Valve IssuesDocumento4 pagineHow an Auto AC System Works and Potential TXV Valve IssuesShashank ChheniyaNessuna valutazione finora
- ME 13 Lecture 03 PDFDocumento11 pagineME 13 Lecture 03 PDFGenerale, Rey marck C.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Brinkman EquationDocumento5 pagineBrinkman EquationAdegbite Jamiu OyekanNessuna valutazione finora
- ICSE Class 8 Physics Selina Solution Chapter 6 Heat TransferDocumento6 pagineICSE Class 8 Physics Selina Solution Chapter 6 Heat Transfersavithas19794153Nessuna valutazione finora
- Watersheds and River Basin WebquestDocumento3 pagineWatersheds and River Basin Webquestapi-330464848100% (1)
- Ce3391 FMM Mech ModelDocumento5 pagineCe3391 FMM Mech ModelVivekananda SubramaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Pumps and Pumping SystemDocumento5 paginePumps and Pumping Systemlyheang100% (1)
- Nov Dec 208-6Documento4 pagineNov Dec 208-6Deshmukh DattaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5.1 Fluid Flow Through Bit NozzleDocumento9 pagineChapter 5.1 Fluid Flow Through Bit NozzleEugene TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Water A Precious Resource Revision WorksheetDocumento4 pagineWater A Precious Resource Revision WorksheetDamini PathakNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrogen: Opening Up New Possibilities With The Highest Thermal Conductivity and Pressure of All Fuel GasesDocumento2 pagineHydrogen: Opening Up New Possibilities With The Highest Thermal Conductivity and Pressure of All Fuel GasesThasarathan RavichandranNessuna valutazione finora
- Question 1. A Refrigerator Uses Refrigerant-134a As The Working Fluid and Operates On An IdealDocumento5 pagineQuestion 1. A Refrigerator Uses Refrigerant-134a As The Working Fluid and Operates On An Idealfivos_rgNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Kinetics: Bernoulli'S Equation and Its ApplicationDocumento29 pagineFluid Kinetics: Bernoulli'S Equation and Its ApplicationMalayRoutNessuna valutazione finora
- Module1 PneumaticsDocumento31 pagineModule1 PneumaticsEarl FloresNessuna valutazione finora
- Refrigeration and Airconditioning by S K Mondal T&Q .0002Documento130 pagineRefrigeration and Airconditioning by S K Mondal T&Q .0002saitejaNessuna valutazione finora