Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Douglas-Fir: Pseudotsuga Menziesii (Mirb.) Franco
Caricato da
Robert AmorusoDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Douglas-Fir: Pseudotsuga Menziesii (Mirb.) Franco
Caricato da
Robert AmorusoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Botanical Name: Pseudotsuga menziesii (Mirb.
) Franco
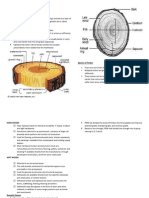
Douglas-fir is one of the best known wood species in the world. In British Columbia there are two varieties of Douglas-fir, Coastal and Interior. The Coastal variety occurs along the southern mainland Coast and across Vancouver Island, except for the very northern tip. The Interior variety is found throughout southern British Columbia, and as far north as the centre of the province. Douglas-fir is a large tree reaching heights of 85 metres on the Coast, and 42 metres in the Interior. Douglas-fir makes up 8.8% of the provincial growing stock.
CoaSTal DoUglaS-FIr
Common Uses
Douglas-fir is primarily used for building and construction purposes due to its strength advantages and availability of large dimensions from old-growth trees. It is one of the finest timbers for heavy structural purposes, including laminated arches and roof trusses. Structurally, it is used in the form of lumber, timbers, pilings and plywood. Douglas-fir is seen as a first class wood for the manufacturing of sashes, doors and windows. The wood is also used to produce a wide variety of products including general millwork, flooring, furniture, cabinets, veneer, vats, ship and boat construction, transmission poles, and marine pilings.
INTerIor DoUglaS-FIr
DOUGLAS-FIR
DOUGLAS-FIR
DOUGLAS-FIR
What is the difference between Coastal and Interior Douglas-fir?
Coastal Douglas-fir is a much bigger tree than Interior Douglas-fir. The timber from the Coastal trees is generally lighter in colour, and more uniform in texture than that of Interior trees. Both have the same wood properties, however, one main difference is that Interior Douglas-fir is less permeable to preservative treatments. Douglas-fir lumber is dried according to end-use and customer specifications. Kiln drying inhibits natural staining of the wood, improves its strength and stiffness, enhances its appearance, and increases its resistance to decay and attack by insects.
pHySIcAL pROpeRtIeS
DenSIty (kg/m3)
green air Dry Standard Side end green air Dry green air Dry air Dry air Dry air Dry air Dry radial (oD) Tangential (oD) Volumetric (oD) Volumetric (air) Tang / rad ratio
450 487 0.45 2990 4020 11100 13500 52.0 88.6 50.1 6.01 9.53 38.9 4.8% 7.4% 11.9% 7.0% 1.5
SpecIFIc GRAvIty (12% m.c.) HARDneSS (n)
mOe (mpa)
mOR (mpa)
cOmpReSSIOn pARALLeL (mpa) cOmpReSSIOn peRpenDIcULAR (mpa) SHeAR (mpa) cLeAvAGe (n/mm Width) SHRInkAGe OD = oven dry air = air dry 12%
vISUAL pROpeRtIeS
cOLOUR
Heartwood Sapwood Heartwood / Sapwood Contrast latewood / earlywood Contrast
GRAIn
orange red to reddish-brown. Yellowish-white (light in colour). Sapwood is well defined and narrow in old-growth and up to 7 cm wide in second-growth. Pronounced difference in colour between earlywood and latewood zones.
Wood is generally straight-grained, although there is sometimes a tendency for wavy or spiral grain to be present.
FIGURe
Plainsawn lumber or rotary-cut veneer: Conspicuous growth ring pattern. Quartersawn lumber or quarter-sliced veneer: Distinct, conspicuous latewood stripes.
knOtS
large knots with large areas of clear material in between.
OtHeR
Wood is resinous, pitch pockets may be present.
WORkInG pROpeRtIeS
Douglas-fir has excellent strength properties and is well known for its workability. The wood dries rapidly with small dimensional movement and little tendency to check. It is relatively easy to work, with good machining qualities. It turns, planes and shapes well and can be sanded to a smooth finish. The wood glues moderately easily, has moderate nail and good screw holding ability, and takes a good finish.
pROceSS
mAcHInInG
p eR FO R m A nc e
c O m m entS
Planing Turning Sawing
good planing quality High surface quality easy to work with tools good excellent excellent shaping quality excellent good good good good good to moderate
good surface quality. Typical defects are raised grain and fuzzy grain. Very good surface quality. easy to work with both hand and power tools. Moderate to severe blunting effect. resin build up on cutters may cause problems. Very good boring quality. excellent mortising quality with both chain mortise and hollow chisel mortise. Important plywood species. Very good sanding properties. Very good holding. excellent resistance to splitting. average screw retention: 494 lb. good holding. excellent resistance to splitting.
Boring Mortising Shaping Veneering Sanding
FAStenInG
Screwing lateral Nail Holding Nail retention gluing
Bonds well with a fairly wide range of adhesives under a moderately wide range of bonding conditions. old-growth: Smooth finish. grain becomes wild and pronounced with dark stain. a clear coating works the best. Second-growth: Stainability is average for light colours, poor for dark ones. good results with light stain or clear finish followed by nitrocellulose alkyd clear sealer and finish. rotary cut veneers are reported to display such strong natural color that staining is sometimes unnecessary. Satisfactory to good results.
FInISHInG
Staining
easy
Painting lacquering Waxing
average to good paint holding ability excellent results good
Very good results are obtained when using light- to medium-coloured waxes, such as Mellow Pine and Chestnut.
DRyInG
ease of Drying
DURAbILIty
easy to moderately easy a relatively easy wood to dry with little trouble occurring from checking, warping and splitting. lower grades require more care. Should not be used in applications with prolonged ground contact without treatment. Can be improved by incising.
Natural Decay Moderately durable resistance Treatability Impermeable to extremely impermeable
DOUGLAS-FIR
DOUGLAS-FIR
Commercial availability
Douglas-fir is marketed predominantly as Douglas-fir larch in structural grades according to National lumber grades authority (Nlga) rules for dimension lumber. Select Structural, #2 and better and stud grades are the most common grades produced. Specialty in-house grades, and export grades are also available. appearance grades are also produced according to Nlga rules. Clears, shop lumber and moulding stock are most common, though there are many potential appearance grades that can be produced.
* Marketed as structural lumber in the D Fir-L (N) (Douglas-fir Larch) species mix.
Data for this factsheet has been compiled by Forintek Canada Corp. from internal and external scientific sources. Forintek is a not-for-profit technical research institute serving the Canadian forest sector.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Method Statement - Roof VentilatorDocumento7 pagineMethod Statement - Roof VentilatorJuwe Pkdo100% (1)
- Construction Materials and Testing: "WOOD"Documento31 pagineConstruction Materials and Testing: "WOOD"Aira Joy AnyayahanNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 5 Compressive and Flexural Strength of Wood NewDocumento31 pagineModule 5 Compressive and Flexural Strength of Wood NewEUREKA JANAH MENDOZANessuna valutazione finora
- 2.1 Introduction To Timber DesignDocumento66 pagine2.1 Introduction To Timber DesignNazihahNessuna valutazione finora
- The Complete Book of Birdhouse Construction for WoodworkersDa EverandThe Complete Book of Birdhouse Construction for WoodworkersValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (1)
- Is 9595 WPSDocumento56 pagineIs 9595 WPSSubramani ArumugamNessuna valutazione finora
- Priya Seminar ReportDocumento19 paginePriya Seminar ReportVinay Bagade50% (4)
- Compression of Wood (E45)Documento31 pagineCompression of Wood (E45)Bgee LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- PlywoodsDocumento23 paginePlywoodsNavya ShreeNessuna valutazione finora
- Plywood Is A Type of Manufactured Wood Made From Thin Sheets of WoodDocumento4 paginePlywood Is A Type of Manufactured Wood Made From Thin Sheets of WoodSarinKumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Artificial TimbersDocumento39 pagineArtificial TimbersDarshit ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- AssessmentDocumento49 pagineAssessmentAj EstradaNessuna valutazione finora
- Compression of Wood (E45)Documento31 pagineCompression of Wood (E45)Fernando LopezNessuna valutazione finora
- Ce 222 Module 9 WoodDocumento17 pagineCe 222 Module 9 WoodAnna Loraine AquinoNessuna valutazione finora
- WoodsDocumento41 pagineWoodsGrace Suzette ChiPandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Timber Ceiling Types and Materials for InsulationDocumento10 pagineTimber Ceiling Types and Materials for InsulationKruthikaNatarajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Panel Pergola Cladding Roof truss Cabinet Stairs Formwork Flooring Tree ComponentsDocumento48 paginePanel Pergola Cladding Roof truss Cabinet Stairs Formwork Flooring Tree ComponentsyosefNessuna valutazione finora
- Diy Uk 2013 14Documento60 pagineDiy Uk 2013 14Cotul Daniel MihaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lumber CMTDocumento7 pagineLumber CMTDAVE GABAYNONessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of TimberDocumento44 pagineProperties of TimberMary Joy RuilesNessuna valutazione finora
- Wood and Its DerivativesDocumento35 pagineWood and Its DerivativesA 04 Ankit SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- TIMBER CONSTRUCTION: A VERSATILE BUILDING MATERIALDocumento17 pagineTIMBER CONSTRUCTION: A VERSATILE BUILDING MATERIALyeabsira mulukenNessuna valutazione finora
- Wood ReportDocumento36 pagineWood Reportメルヴリッ クズルエタNessuna valutazione finora
- Wood: A Versatile Construction MaterialDocumento42 pagineWood: A Versatile Construction MaterialJoey Guarin100% (1)
- Types Od WoodDocumento4 pagineTypes Od Woodkath mirandaNessuna valutazione finora
- GluamDocumento13 pagineGluamMadelline Joy RitaritaNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 10 WoodDocumento9 pagineModule 10 WoodMinari ChaengNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of ReconstitutedDocumento13 pagineTypes of ReconstitutedJishnu SamadderNessuna valutazione finora
- HDF High Density Fiber BoardsDocumento75 pagineHDF High Density Fiber BoardssennimalaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Timber Lecture 2020 Modified XXDocumento47 pagineTimber Lecture 2020 Modified XXazapNessuna valutazione finora
- Front-Cover BT Group1Documento12 pagineFront-Cover BT Group1GUTIERREZ, VIANCA MARIE R.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Market Sorvey On PlywoodDocumento19 pagineMarket Sorvey On PlywoodEduardo MafraNessuna valutazione finora
- Timber Industry RatanmolDocumento25 pagineTimber Industry RatanmolMohit AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Medium-Density Fibreboard (MDF) Is AnDocumento6 pagineMedium-Density Fibreboard (MDF) Is AnAbok AduogoNessuna valutazione finora
- Timber A Wood Prepared For The Engineering Purpose Is A TimberDocumento21 pagineTimber A Wood Prepared For The Engineering Purpose Is A TimberMohit VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Nur Isfarina Binti Ismail Muhamad Basri Bin MD Daud Mohd Fazli Bin Abu Hasan Sadam Bin Kahar Muhamad Hafiz Bin MD SaadDocumento24 pagineNur Isfarina Binti Ismail Muhamad Basri Bin MD Daud Mohd Fazli Bin Abu Hasan Sadam Bin Kahar Muhamad Hafiz Bin MD Saadjassi nishadNessuna valutazione finora
- ECM 206 CHAPTER 4 TimberDocumento8 pagineECM 206 CHAPTER 4 TimberAZUAN BIN AHMAD FAUZI100% (1)
- INTD402 Furniture, Fittings, Textile & AcessoriesDocumento38 pagineINTD402 Furniture, Fittings, Textile & AcessoriesAmr MohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- TimberDocumento55 pagineTimberAra Abdullah100% (1)
- WS PresentationDocumento60 pagineWS PresentationtechnologicaluniversityyangonNessuna valutazione finora
- MM1 - Building BoardsDocumento18 pagineMM1 - Building BoardsJoan Sy TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Plywood PDFDocumento4 paginePlywood PDFaulad999Nessuna valutazione finora
- Timber Properties and Conversion TechniquesDocumento24 pagineTimber Properties and Conversion TechniquesTerkuma IorpendaNessuna valutazione finora
- Timber 1Documento36 pagineTimber 1CHIRAG SNessuna valutazione finora
- Timber Lesson 1Documento36 pagineTimber Lesson 1Henry DiyokeNessuna valutazione finora
- Wood Composites: By: John Ralph A. MagbanuaDocumento13 pagineWood Composites: By: John Ralph A. MagbanuaJohn Ralph A. MagbanuaNessuna valutazione finora
- Construction - Week 12Documento43 pagineConstruction - Week 12Sarah HaiderNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufactured Boards: Modern TechniquesDocumento29 pagineManufactured Boards: Modern Techniquesgary.nolan100% (1)
- BMC Assignment S5 (HARDBOARD&GLULAM)Documento19 pagineBMC Assignment S5 (HARDBOARD&GLULAM)Ebin JoyNessuna valutazione finora
- Veneer, Particle Board, Plywood, Fiber BoardDocumento23 pagineVeneer, Particle Board, Plywood, Fiber BoardRatnesh PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT-I (B)Documento56 pagineUNIT-I (B)kiran raajNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineered Wood and Slate Roofing Materials StudyDocumento46 pagineEngineered Wood and Slate Roofing Materials StudySusnata ChandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 TimberDocumento44 pagineChapter 5 TimbertrfuawlachewNessuna valutazione finora
- Manufacturing Processes: Drnksingh Associate Professor (Workshop) Department of Mech Engg I S M DhanbadDocumento78 pagineManufacturing Processes: Drnksingh Associate Professor (Workshop) Department of Mech Engg I S M DhanbadAbhinavGuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- TimberDocumento68 pagineTimberBurka DinkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Building Technology Topics on Wood and Wood ProductsDocumento86 pagineBuilding Technology Topics on Wood and Wood ProductsJaypee TanNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of WOOD - Page 1 To 41Documento41 pagineProperties of WOOD - Page 1 To 41Jebone Stein Web JuarbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Timber Construction MaterialsDocumento42 pagineTimber Construction MaterialsNUR ALYA IRDINA SAZALINessuna valutazione finora
- TimberDocumento127 pagineTimberptgopoNessuna valutazione finora
- TimberDocumento26 pagineTimberPraveen Kumar R100% (1)
- Identification and study of engineered wood productsDocumento7 pagineIdentification and study of engineered wood productsAISHWARYA SAMPATHNessuna valutazione finora
- Practical Woodwork for Laboratory Technicians: Pergamon Series of Monographs in Laboratory TechniquesDa EverandPractical Woodwork for Laboratory Technicians: Pergamon Series of Monographs in Laboratory TechniquesNessuna valutazione finora
- Woodworker's Handbook: The Beginner's Reference to Tools, Materials, and Skills, Plus Essential Projects to MakeDa EverandWoodworker's Handbook: The Beginner's Reference to Tools, Materials, and Skills, Plus Essential Projects to MakeNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is MgO PDFDocumento5 pagineWhat Is MgO PDFjmlafortezaNessuna valutazione finora
- Richardson LacyDocumento3 pagineRichardson LacyRobert AmorusoNessuna valutazione finora
- Flyer Digisix GBDocumento2 pagineFlyer Digisix GBRobert AmorusoNessuna valutazione finora
- Red Bottle BrushDocumento5 pagineRed Bottle BrushRobert AmorusoNessuna valutazione finora
- Welding Slag Cleaning MachineDocumento5 pagineWelding Slag Cleaning Machinemohammed zeeshanNessuna valutazione finora
- Course: 141 Tig Welding of Stainless SteelDocumento17 pagineCourse: 141 Tig Welding of Stainless Steelamir moniriNessuna valutazione finora
- Solving Common Coating ProblemsDocumento1 paginaSolving Common Coating ProblemsNguyên Nguyễn100% (1)
- Defects in Brick Masonry - Causes & RemediesDocumento2 pagineDefects in Brick Masonry - Causes & Remediessuryakantame100% (1)
- Klopp: AlloysDocumento10 pagineKlopp: AlloyssunsirNessuna valutazione finora
- Stainless Steel Cladding and Weld Overlays PDFDocumento13 pagineStainless Steel Cladding and Weld Overlays PDFm5416Nessuna valutazione finora
- PM p2 d7 g6 Problemas LaminadoDocumento9 paginePM p2 d7 g6 Problemas LaminadoJorgeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cutting Ductile Iron PipeDocumento12 pagineCutting Ductile Iron Pipelamis essamNessuna valutazione finora
- 09 Samss 035Documento8 pagine09 Samss 035NASIR SYEDNessuna valutazione finora
- Elements of Gating SystemDocumento21 pagineElements of Gating SystemsudhirNessuna valutazione finora
- Ex No - 1 Crosshalving JointDocumento5 pagineEx No - 1 Crosshalving JointANISH PATIL (RA2111029010064)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pipe Components PDFDocumento179 paginePipe Components PDFmatevzartacNessuna valutazione finora
- PSSC Design Tech QPDocumento55 paginePSSC Design Tech QPAndrew ArahaNessuna valutazione finora
- NSSCC SpecDocumento12 pagineNSSCC SpecganeshNessuna valutazione finora
- Benz Packaging Solutions (P) LTDDocumento21 pagineBenz Packaging Solutions (P) LTDManan ChopraNessuna valutazione finora
- Corro-Coat PE Series 50 TDSDocumento3 pagineCorro-Coat PE Series 50 TDSBiju_PottayilNessuna valutazione finora
- Wet Processing Technology LAb DocumentDocumento3 pagineWet Processing Technology LAb DocumentSanjana Islam Nilima0% (1)
- Dynamic Air ClassifiersDocumento3 pagineDynamic Air Classifierskensley oliveiraNessuna valutazione finora
- European Steel and Alloy Grades: Gx7Crnimo12-1 (1.4008)Documento2 pagineEuropean Steel and Alloy Grades: Gx7Crnimo12-1 (1.4008)farshid KarpasandNessuna valutazione finora
- OutoKumpu TR Gates ProcessDocumento5 pagineOutoKumpu TR Gates Processattiori fabriceNessuna valutazione finora
- Soldering: Figure 2 Tack Solder Figure 3 Tag SolderDocumento2 pagineSoldering: Figure 2 Tack Solder Figure 3 Tag SolderBaqer QalawiNessuna valutazione finora
- Wooden Mallet Plans - WoodArchivistDocumento4 pagineWooden Mallet Plans - WoodArchivistErics100% (1)
- Click Bond CB309Documento2 pagineClick Bond CB309echobravo1Nessuna valutazione finora
- 17-4PH Technical DataDocumento7 pagine17-4PH Technical DataKir VinNessuna valutazione finora
- ThermoformingDocumento27 pagineThermoformingkrishnaNessuna valutazione finora
- Jis-Astm SpecDocumento1 paginaJis-Astm SpecRizki AhmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Fusion Bonded Epoxy Coating: Long Term Corrosion ProtectionDocumento2 pagineFusion Bonded Epoxy Coating: Long Term Corrosion ProtectionLi KLNessuna valutazione finora