Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Crude Oil: TABLE 8-Degumming Processes
Caricato da
Gageanu PaulDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Crude Oil: TABLE 8-Degumming Processes
Caricato da
Gageanu PaulCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Rening Introduction to the Processing of Fats and Oils
TABLE 8Degumming Processes
Water degumming Acidwater degumming Acidbase degumming Enzymatic degumming Chelate/detergent degumming The following degumming method is used with oils that will be caustic refined (Table 8). In the water degumming process (Figs. 2 and 3) crude oil is mixed with 12% water, mechanically agitated at 70C to hydrate the phospholipids and colloidal impurities. Water quality is important; water with high levels of dissolved minerals could interfere with proper degumming. The water and oil mixture is then mildly agitated
Crude oil
Heater
Mixer
Hydrat./ agglom Centrifuge
FIGURE 2. Water degumming scheme.
III-16
Rening Introduction to the Processing of Fats and Oils
FIGURE 3. Water degumming diagram. for 1530 minutes. The water soluble phospholipids and hydrophilic components are then separated from the oil by centrifugation, and the oil further dried by vacuum. The following degumming steps are used with oils that are physically rened (Figs. 4 and 5). In the acidwater degumming process crude oil is mixed with 0.0050.1% citric acid and 12% water at 70C. The acid-water-oil mixture is then mixed for seconds only. The mixture is then cooled to 45C and allowed to hydrate for 60 minutes. The water-soluble substances are then separated from the oil. Degummed oil goes to the bleaching process. In the acidcaustic degumming process (Fig. 6) crude oil is heated to 90C, mixed with 0.1% concentrated phosphoric acid, and mixed at a high intensity for seconds. The mixture is allowed to rest for 15 minutes. Then 0.1% NaOH (to neutralize phosphoric acid) is added and the solution is mixed at a low intensity for seconds. The low oil content gums are collected as meal. Water is then added to the mixture, and the degummed oil then goes to bleaching. The high oil gums are then recycled back into the mixture. This process is not suitable if making lecithin. A comparison of the nontriglyceride components in an oil (Table 9), after the degumming process, to the crude canola oil, shows that degumming affects only the phosphorus content of the oil. Chemical degumming reduces iron content. Neither rening process reduces chlorophyll content.
III-17
Rening Introduction to the Processing of Fats and Oils
Crude oil
Heat/cool Mixer Mixer Cooler Hydrat./ agglom Heater Centrifuge (selfdesl.)
FIGURE 4. Acidwater degumming scheme.
FIGURE 5. Acidwater degumming diagram.
III-18
Rening Introduction to the Processing of Fats and Oils
Crude or water degummed oil
FIGURE 6. Acidcaustic degumming.
TABLE 9Nontriglyceride Components of Crude, Water-Degummed, and Chemically Degummed Canola Oil
Crude oil Free fatty acids, % Phosphorus, mg/kga Sulfur, mg/kgb Chlorophyll, mg/kgc Fe, mg/kgd
a b
Water degummed 0.41.2 100250 315 535 25
Chemically (acid) degummed 0.41.2 550 315 535 < 0.5
0.41.2 300500 315 535 25
Degumming affects only the phosphorus content of the oil. Sulfur, if present, is not decreased, as in rapeseed. c Chlorophyll content is not decreased. d Iron content is usually removed to only a minor extent, except in chemical degumming. III-19
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Trait-Modified Oils in FoodsDa EverandTrait-Modified Oils in FoodsFrank T. OrthoeferNessuna valutazione finora
- Crystallization of Lipids: Fundamentals and Applications in Food, Cosmetics, and PharmaceuticalsDa EverandCrystallization of Lipids: Fundamentals and Applications in Food, Cosmetics, and PharmaceuticalsKiyotaka SatoNessuna valutazione finora
- Degumming of OilDocumento31 pagineDegumming of OilGOVIND KUMAR100% (2)
- Vegetable Oils and Fats For Edible Use: R. O. FeupeDocumento9 pagineVegetable Oils and Fats For Edible Use: R. O. FeupepkbiotechNessuna valutazione finora
- Oil RefiningDocumento18 pagineOil RefiningNeha ShriNessuna valutazione finora
- Biodiesel Production Techniques PDFDocumento4 pagineBiodiesel Production Techniques PDFatomixmanNessuna valutazione finora
- CIE MechanismDocumento6 pagineCIE MechanismEvan KeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Oilref-Soybean Oil RefiningDocumento37 pagineOilref-Soybean Oil RefiningirfanNessuna valutazione finora
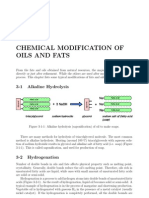
- Chap3 - Chemical Modification of Oils and FatsDocumento6 pagineChap3 - Chemical Modification of Oils and FatsidalponteNessuna valutazione finora
- Biodiesel Production Processes ExplainedDocumento22 pagineBiodiesel Production Processes ExplainedDr Churamani Dev MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrogenation Process Design and Jet Reactor DrawingDocumento31 pagineHydrogenation Process Design and Jet Reactor DrawingRishya Prava ChatterjeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Stearic 2520acid Methods 2520of 2520productionDocumento6 pagineStearic 2520acid Methods 2520of 2520productionoida_adNessuna valutazione finora
- Lipid ManualDocumento48 pagineLipid ManualRakesh K TrivediNessuna valutazione finora
- CPT4Documento5 pagineCPT4daddarioalexander01Nessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Preparation and CharactersationDocumento26 pagine3 Preparation and Charactersationsindhnayak48Nessuna valutazione finora
- US2831811Documento2 pagineUS2831811hugo vignoloNessuna valutazione finora
- PROCESSING OF EDIBLE OIL: DEGUMMING METHODSDocumento34 paginePROCESSING OF EDIBLE OIL: DEGUMMING METHODSAzhan FikriNessuna valutazione finora
- Biodiesel Production and Fuel Quality: BackgroundDocumento12 pagineBiodiesel Production and Fuel Quality: BackgroundAboo KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Edible Oil Processing - Alkali RefiningDocumento8 pagineEdible Oil Processing - Alkali RefiningKard SamndNessuna valutazione finora
- Small Scale BiodieselDocumento21 pagineSmall Scale BiodieselAdil KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Biodiesel Production Techniques: Food Technology Fact SheetDocumento4 pagineBiodiesel Production Techniques: Food Technology Fact SheetPradeep BhatiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Oxidative Desulfurization of Lube Oil Distillates: Chemistry and Technology of Fuels and Oils, Vol. 44, No. 1, 2008Documento3 pagineOxidative Desulfurization of Lube Oil Distillates: Chemistry and Technology of Fuels and Oils, Vol. 44, No. 1, 2008MohamadMostafaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Neutral Loss During Alkali RefinationDocumento3 pagineNeutral Loss During Alkali RefinationAilin SeibaneNessuna valutazione finora
- Biodiesel Seminar Report OverviewDocumento14 pagineBiodiesel Seminar Report Overviewjayanth agNessuna valutazione finora
- Characteristics of Lubricating Greases Production ProcessesDocumento21 pagineCharacteristics of Lubricating Greases Production ProcessesJorge ZegarraNessuna valutazione finora
- Asades: Crude Oil Treatment For Cotton Transesterification AlkalineDocumento4 pagineAsades: Crude Oil Treatment For Cotton Transesterification AlkalineJavier AlbaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Interesterification of Palm, Palm KernelDocumento8 pagineChemical Interesterification of Palm, Palm KernelAfsoon QNetNessuna valutazione finora
- Oil RefiningDocumento13 pagineOil RefiningRavindra AgarwalNessuna valutazione finora
- Vanduijn 2000Documento10 pagineVanduijn 2000MANUEL JULCANessuna valutazione finora
- Desmet Purifine1Documento3 pagineDesmet Purifine1ricm152Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lab BiodieselDocumento7 pagineLab Biodieselskb89Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio-Diesel Production & Its Characterization: Vivek Bhaskar & Yashi AgrawalDocumento1 paginaBio-Diesel Production & Its Characterization: Vivek Bhaskar & Yashi AgrawalArpit_JaNessuna valutazione finora
- Iutt-Ppeii 9Documento24 pagineIutt-Ppeii 9Mohammed Khaled Al-ThobhaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Steam Distillation Essential OilsDocumento7 pagineSteam Distillation Essential OilsRade NovakovicNessuna valutazione finora
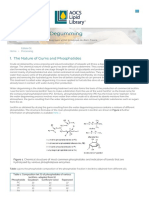
- Introduction To Degumming: 1. The Nature of Gums and PhosphatidesDocumento5 pagineIntroduction To Degumming: 1. The Nature of Gums and PhosphatidesBella Nurul Lita AlfatNessuna valutazione finora
- Oilandfat IVDocumento28 pagineOilandfat IVARATHI PMPMNessuna valutazione finora
- Biodiesel Production From Mahua (Madhuca Indica) Oil HavingDocumento5 pagineBiodiesel Production From Mahua (Madhuca Indica) Oil HavingEng Kombe ChemicalNessuna valutazione finora
- Desalting of Crude Oil: Table 1. Table 2Documento15 pagineDesalting of Crude Oil: Table 1. Table 2Mattew1712Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tahap Pembuatan MargarineDocumento3 pagineTahap Pembuatan MargarineHisam mansurNessuna valutazione finora
- Refining of OilsDocumento9 pagineRefining of OilsSherilyn Cercado EmanilNessuna valutazione finora
- BiodieselDocumento3 pagineBiodieselSavita ChemistryNessuna valutazione finora
- Purifine 1Documento3 paginePurifine 1ricm152Nessuna valutazione finora
- Degumming of Vegi Oilacs - 0028Documento8 pagineDegumming of Vegi Oilacs - 0028Xiang GaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis of Fats and OilsDocumento19 pagineAnalysis of Fats and Oilsvishnoi1988% (8)
- Yunn BuatDocumento11 pagineYunn BuatAina ShazwanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ferrocare LVDH Oil Cleaning MachineDocumento2 pagineFerrocare LVDH Oil Cleaning Machinessheart_mindNessuna valutazione finora
- Fat Splitting: Fatty Acid Isolation and Glycerine RecoveryDocumento41 pagineFat Splitting: Fatty Acid Isolation and Glycerine RecoveryAzhan FikriNessuna valutazione finora
- Universiti Teknologi Mara Fakulti Kejuruteraan Kimia Petroleum Refining Engineering (Cge 656) Group AssignmentDocumento51 pagineUniversiti Teknologi Mara Fakulti Kejuruteraan Kimia Petroleum Refining Engineering (Cge 656) Group Assignmentanip zahariNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Fat & OilDocumento59 pagine5 Fat & OilRebkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Top Edible Oil Production (Autosaved) (3)Documento16 pagineTop Edible Oil Production (Autosaved) (3)abelteshale2244Nessuna valutazione finora
- Roese-Gottlieb method determines crude fat in extruded feedDocumento2 pagineRoese-Gottlieb method determines crude fat in extruded feedHocPoLab TechNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydrogenation: Processing Technologies: Walter E. Farr & Associates Olive Branch, MississippiDocumento12 pagineHydrogenation: Processing Technologies: Walter E. Farr & Associates Olive Branch, MississippiHamid Vahedi LarijaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Oils and Fats Glossary TermsDocumento19 pagineOils and Fats Glossary TermsThais Soraluz HidalgoNessuna valutazione finora
- UPCTDocumento18 pagineUPCTXesoNessuna valutazione finora
- Transesterification For The Preparation of Biodies PDFDocumento6 pagineTransesterification For The Preparation of Biodies PDFmelvin ekboteNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit Processing MethodsDocumento12 pagineUnit Processing MethodsIsabella DonatoNessuna valutazione finora
- Characteristics of Oils and Fats Used in Biodiesel ProductionDocumento7 pagineCharacteristics of Oils and Fats Used in Biodiesel Productiondesamuduru19Nessuna valutazione finora
- Soap-Making Manual: A Practical Handbook on the Raw Materials, Their Manipulation, Analysis and Control in the Modern Soap PlantDa EverandSoap-Making Manual: A Practical Handbook on the Raw Materials, Their Manipulation, Analysis and Control in the Modern Soap PlantNessuna valutazione finora
- Soap-Making Manual. A practical Handbook on the RControl in the modern Soap PlantDa EverandSoap-Making Manual. A practical Handbook on the RControl in the modern Soap PlantValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (2)
- GTT Module 5Documento156 pagineGTT Module 5ABDULRAHIMAN RAJEKHANNessuna valutazione finora
- NFPA 72 Fire Alarm TrainingDocumento376 pagineNFPA 72 Fire Alarm TrainingFavori gcbNessuna valutazione finora
- Model Fs CatalogDocumento4 pagineModel Fs CatalogThomas StempienNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Practice Self Care - WikiHowDocumento7 pagineHow To Practice Self Care - WikiHowВасе АнѓелескиNessuna valutazione finora
- Job Satisfaction RRLDocumento39 pagineJob Satisfaction RRLMarie Tiffany100% (1)
- SVIMS-No Que-2Documento1 paginaSVIMS-No Que-2LikhithaReddy100% (1)
- Universal Basic IncomeDocumento31 pagineUniversal Basic IncomeumairahmedbaigNessuna valutazione finora
- Micdak BackgroundDocumento3 pagineMicdak Backgroundappiah ernestNessuna valutazione finora
- 07 Chapter2Documento16 pagine07 Chapter2Jigar JaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Li Ching Wing V Xuan Yi Xiong (2004) 1 HKC 353Documento11 pagineLi Ching Wing V Xuan Yi Xiong (2004) 1 HKC 353hNessuna valutazione finora
- ABSCESSDocumento35 pagineABSCESSlax prajapatiNessuna valutazione finora
- EcR - 1 Leading and Lagging IndicatorsDocumento10 pagineEcR - 1 Leading and Lagging IndicatorsMiloš ĐukićNessuna valutazione finora
- RUKUS March 2010Documento32 pagineRUKUS March 2010RUKUS Magazine29% (14)
- IMCI Chart 2014 EditionDocumento80 pagineIMCI Chart 2014 EditionHarold DiasanaNessuna valutazione finora
- New930e-4se Ceam031503 930e4se Omm A31937 Up PDFDocumento273 pagineNew930e-4se Ceam031503 930e4se Omm A31937 Up PDFSergelen SakhyabazarNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Plan of Care Concept Map - Immobility - Hip FractureDocumento2 pagineNursing Plan of Care Concept Map - Immobility - Hip Fracturedarhuynh67% (6)
- Hypertension Protocol Mukta VatiDocumento18 pagineHypertension Protocol Mukta VatiDr. Avnish UpadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- Formularium ApotekDocumento12 pagineFormularium ApotekNurul Evi kurniatiNessuna valutazione finora
- FINALS REVIEWER ENVI ENGG Topic 1Documento8 pagineFINALS REVIEWER ENVI ENGG Topic 1As ReNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics ProblemsDocumento50 pagineGenetics ProblemsTasneem SweedanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Diagnosis TemplateDocumento6 pagineNursing Diagnosis Templatesdk6972Nessuna valutazione finora
- 9 To 5 Props PresetsDocumento4 pagine9 To 5 Props Presetsapi-300450266100% (1)
- Đề cương ôn tập tiếng anh 9Documento28 pagineĐề cương ôn tập tiếng anh 9Nguyễn HoaNessuna valutazione finora
- NLOG GS PUB 1580 VGEXP-INT3-GG-RPT-0001.00 P11-06 Geological FWRDocumento296 pagineNLOG GS PUB 1580 VGEXP-INT3-GG-RPT-0001.00 P11-06 Geological FWRAhmed GharbiNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 Colmac DX Ammonia Piping Handbook 4th EdDocumento64 pagine1 Colmac DX Ammonia Piping Handbook 4th EdAlbertoNessuna valutazione finora
- TS4-F - Fire SafetyDocumento2 pagineTS4-F - Fire SafetyDominic SantiagoNessuna valutazione finora
- RHS NCRPO COVID FormDocumento1 paginaRHS NCRPO COVID Formspd pgsNessuna valutazione finora
- Pulsar2 User Manual - ENDocumento83 paginePulsar2 User Manual - ENJanette SouzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Spec BoilerDocumento9 pagineSpec BoilerAchmad MakmuriNessuna valutazione finora
- Disinfecting Water Wells Shock ChlorinationDocumento3 pagineDisinfecting Water Wells Shock ChlorinationmayaNessuna valutazione finora