Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Experiment 2 Half-Wave & Full-Wave Rectification: Eastern Mediterranean University
Caricato da
Chalez ZengeretsiDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Experiment 2 Half-Wave & Full-Wave Rectification: Eastern Mediterranean University
Caricato da
Chalez ZengeretsiCopyright:
Formati disponibili
EASTERN MEDITERRANEAN UNIVERSITY
DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRICAL & ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING
EENG341 LAB EEE 341 LAB ELECTRONIC ELECTRONICS II
EXPERIMENT 2 HALF-WAVE & FULLWAVE RECTIFICATION
Std. No. Name &Surname: 1________ _______________ 2________ _______________ 3________ _______________ Group No :_____________ Submitted to:_____________ Date :_____________
Suat SELIM
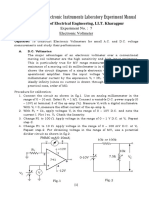
Objectives: To recognize a half-wave rectified sinusoidal voltage. To understand the term mean value as applied to a rectified waveform. To understand the effect of a reservoir capacitor upon the rectified waveform and its mean value. Simple Half-Wave Rectification Construct the circuit of Fig. 2.1 where V is the voltmeter. Note that the resistor limits the current to a safe value.
Oscilloscope Y input a.c. supply 20V rms SY625/1.5 10k Load Resistor 50V d.c. Oscilloscope common
Fig. 2.1. Half-Wave Rectification
Switch on the oscilloscope and the sinusoidal supply. With the oscilloscope d.c. coupled adjust the time-base and the Y amplifier sensitivity to obtain a steady trace of about 4cm vertical and 5ms/cm horizontal. Measure and record time T and peak voltage Vpk:
Sketch the waveform and label it to show the periods when the diode is conducting and those when it is not. Time T depends upon the frequency of your power supply.
Confirm this. Vpk should be very nearly equal to the peak voltage of the alternating supply.
Suat SELIM
Questions 1. Why will Vpk not be exactly equal to the peak value of the supply?
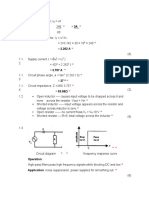
2. How much is the difference between the measured and theoretical mean voltage? V pk . (Hint: The mean value of a half-sinusoid can be shown by geometry to be : 2 But at every half-cycle the voltage is zero. The mean value of the waveform, therefore is:
V pk 2 2
. Note the mean voltage indicated by the voltmeter, and compare it with 0.35Vpk.)
3. The mean voltage you obtain is positive relative to zero. How could you obtain a negative voltage? (Hint: Verify your answer by experiment and sketch the waveform.)
Fig. 2.2. The Effect of a Reservoir Capacitor Very often when rectifying an alternating voltage, we wish to produce a steady direct voltage free from variations of the sort observed in Fig. 2.2. One way of doing this is to connect a capacitor in parallel with the load resistor as in Fig. 2.3.
Suat SELIM
Oscilloscope Y input a.c. supply 20V rms SY625/1.5 R Load Resistor C V 50V d.c. Oscilloscope common
Fig. 2.3. Half-Wave Rectifier with Reservoir Capacitor
Set C=1F and R=10k. Observe the output waveform on the oscilloscope and note the value of the peak-topeak variations in voltage. Note also the new mean voltage on the voltmeter.
4. Is the new mean voltage greater or less than it was before?
Now replace the 1F capacitor by a much larger value of 22F, and answer the following questions.
5. The variations on the rectified waveform are called RIPPLE. Is the ripple now less than it was with the lower value capacitor?
6. Is the mean rectified voltage now greater or less?
Suat SELIM
A Bridge Rectifier with Resistive Load Construct the circuit of Fig. 2.4. Note that the resistor limits the current to a safe value.
a.c. supply 20V rms
10k Load Resistor
50V d.c. Oscilloscope common
Fig. 2.4. Full-Wave Rectification
Switch on the sinusoidal supply. Measure and record time mean value of output voltage indicated on the voltmeter Vm.
Compare the mean value of output voltage indicated on the voltmeter those obtained in the Half-Wave rectification.
Questions 7. The mean value of output voltage indicated on the voltmeter is it the same as it was for half-wave rectifier? If there is any difference explain why?
8. How does the mean value compare with that found for half-wave rectification? (Hint: the mean value of a half-sinusoid can be shown by geometry to be:
V pk 2
and
Vpk=10V. Then every half-cycle is present, this should be the mean value measured. Confirm this from your readings.
Suat SELIM
The Effect of a Reservoir Capacitor in the Bridge Rectifier Add a 1F capacitor in parallel with the load resistor and note the new mean value of the rectified waveform. Compare this values with those obtain in the Simple HalfWave rectification for the same load and capacitor values.
CONCLUSIONS:
Suat SELIM
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- UntitledDocumento3 pagineUntitledsajjaddrNessuna valutazione finora
- BasicElecLab Expt5 Individual-ReportDocumento8 pagineBasicElecLab Expt5 Individual-ReportDANRHEY BALUSDANNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Manual 3 Semester Basic Electronics - I: Lab Engineerer: Subject TeacherDocumento21 pagineLab Manual 3 Semester Basic Electronics - I: Lab Engineerer: Subject TeacherOmer Sheikh100% (1)
- Lab 3 (To Analyze The Working of Diode in Half and Full Wave Rectification)Documento6 pagineLab 3 (To Analyze The Working of Diode in Half and Full Wave Rectification)afaq ahmad khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Uncontrolled Half-Wave Rectifier: ObjectivesDocumento5 pagineUncontrolled Half-Wave Rectifier: ObjectivesKamil Rasheed SiddiquiNessuna valutazione finora
- Student Workbook PDFDocumento103 pagineStudent Workbook PDFCarbon Nano TubeNessuna valutazione finora
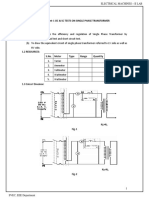
- 1.O.C. & S.C. Tests On Single Phase TransformerDocumento6 pagine1.O.C. & S.C. Tests On Single Phase Transformerchandrakanth100% (3)
- Workshop 02Documento5 pagineWorkshop 02Damith ErangaNessuna valutazione finora
- Course - Section: - ECE20L-2 - E06 Group Number: Group MembersDocumento11 pagineCourse - Section: - ECE20L-2 - E06 Group Number: Group MembersLuch ÜNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 2 ElectronicsDocumento6 pagineExperiment 2 ElectronicsRhea Daluddung SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Wave RectificationDocumento6 pagineFull Wave RectificationDavid OkoyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 3Documento11 pagineLab 3Praharsh VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 1 - AC MeasurementDocumento7 pagineExperiment 1 - AC MeasurementmixchescakeNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Experiment No. 2Documento16 pagineLaboratory Experiment No. 2johnpaul varonaNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment ManualDocumento17 pagineExperiment ManualKavita BishtNessuna valutazione finora
- (ALCANTARA - BSEE-2D) Experiment 2 Final ReportDocumento11 pagine(ALCANTARA - BSEE-2D) Experiment 2 Final ReportLawrence Abram AlcantaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Device Exp 2 Student ManualDocumento4 pagineDevice Exp 2 Student Manualgg ezNessuna valutazione finora
- 3a PowerSupplyDocumento25 pagine3a PowerSupplymirulazwanNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Exercise 3Documento7 pagineLaboratory Exercise 3BenedictNessuna valutazione finora
- Electrical Workshop Practice: Laboratory ManualDocumento30 pagineElectrical Workshop Practice: Laboratory ManualJigar SoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electronics Lab (Experiment 2 Report) : Submitted By: Group: G7 Ashutosh Garg (2018MEB1213) Ashwin Goyal (2018MEB1214)Documento8 pagineBasic Electronics Lab (Experiment 2 Report) : Submitted By: Group: G7 Ashutosh Garg (2018MEB1213) Ashwin Goyal (2018MEB1214)Ashutosh GargNessuna valutazione finora
- BJT AC DC & MultistageDocumento42 pagineBJT AC DC & MultistageJose EspinoNessuna valutazione finora
- EEE 124 Exp5Documento4 pagineEEE 124 Exp5Rakibul Hassan SajonNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electrical Engineering Laboratory Exp 3Documento5 pagineBasic Electrical Engineering Laboratory Exp 3Afiq BahaNessuna valutazione finora
- ECE20L - 2 - Expt4Documento10 pagineECE20L - 2 - Expt4Niko de LemosNessuna valutazione finora
- Experimental Method 3 PDFDocumento14 pagineExperimental Method 3 PDFtungpham2014Nessuna valutazione finora
- Power Electronics ManualDocumento42 paginePower Electronics ManualJavaria Chiragh50% (2)
- EXP2 Half Wave RectifierDocumento3 pagineEXP2 Half Wave RectifierMohammed Dyhia Ali50% (2)
- DEVICE EXP 2 Student - 2Documento4 pagineDEVICE EXP 2 Student - 2Pablo ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 2: AC Measurements-Capacitors and Inductors: Prerequisite Reference MaterialsDocumento10 pagineLab 2: AC Measurements-Capacitors and Inductors: Prerequisite Reference MaterialsLeandro ArvattiNessuna valutazione finora
- Bee Exp 3Documento11 pagineBee Exp 3Dhwani PatelNessuna valutazione finora
- EEE 54 DP2 DocumentationDocumento5 pagineEEE 54 DP2 DocumentationDarl John MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronics Laboratory DC Power Supply CircuitsDocumento10 pagineElectronics Laboratory DC Power Supply CircuitsDen CelestraNessuna valutazione finora
- BALUSDAN BasicElecLab Expt5 Individual-ReportDocumento8 pagineBALUSDAN BasicElecLab Expt5 Individual-ReportDANRHEY BALUSDANNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1c (RECTIFIER)Documento15 pagineChapter 1c (RECTIFIER)Akmal Amyrul Aizat100% (1)
- D.C. Power Supply: Experiment ADocumento5 pagineD.C. Power Supply: Experiment AReddyvari VenugopalNessuna valutazione finora
- BJT Amplifiers Frequency ResponseDocumento29 pagineBJT Amplifiers Frequency ResponseKrista JacksonNessuna valutazione finora
- Pe Unit 5 PDFDocumento8 paginePe Unit 5 PDFmjrsudhakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Department of Electrical Engineering: Faculty Member: - DatedDocumento10 pagineDepartment of Electrical Engineering: Faculty Member: - DatedWaleed BajwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 3Documento7 pagineLab 3ShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied Electronics Lab 2Documento9 pagineApplied Electronics Lab 2Rickel RoweNessuna valutazione finora
- DocumentationDocumento4 pagineDocumentationEugene Paul Brian SebiloNessuna valutazione finora
- Electronic Devices Experiment 4Documento13 pagineElectronic Devices Experiment 4ArvinALNessuna valutazione finora
- Circuit LabDocumento7 pagineCircuit LabBiftu ShibbireNessuna valutazione finora
- Eet 3251 - LabsDocumento17 pagineEet 3251 - LabsEG209/108489/21 ISAAC DUNCAN MWENDWANessuna valutazione finora
- Question of EE ProjectDocumento5 pagineQuestion of EE ProjectANJALI KUMARINessuna valutazione finora
- Appendix Chapter For Transformer StandardDocumento28 pagineAppendix Chapter For Transformer StandardHabib SimorangkirNessuna valutazione finora
- Basic Electrical Engineering Lab ManualDocumento44 pagineBasic Electrical Engineering Lab Manualdinuarslan86% (7)
- Full Wave Rectification ExperimentDocumento6 pagineFull Wave Rectification ExperimentDavid OkoyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Diode As RectifiersDocumento13 pagineDiode As RectifiersShahZaib AnwarNessuna valutazione finora
- The D.C. Power Supply: Experiment ADocumento6 pagineThe D.C. Power Supply: Experiment AArnulfo LavaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Full Wave Diode Bridge RectificationDocumento4 pagineFull Wave Diode Bridge RectificationMuhammad Riyaz AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 5Documento21 pagineExperiment 5Jervin JamillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Experiment 4Documento10 pagineExperiment 4djelbouNessuna valutazione finora
- Me 7Documento3 pagineMe 7first lastNessuna valutazione finora
- LAB LEDs and ZenerDocumento12 pagineLAB LEDs and ZenerjosembosemNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 2 - Diode CharacteristicsDocumento7 pagineLab 2 - Diode CharacteristicsFasil EndalamawNessuna valutazione finora
- Exp. 1 ManualDocumento4 pagineExp. 1 Manualf20212001Nessuna valutazione finora
- As A Highly Skilled Electronics TechnicianDocumento2 pagineAs A Highly Skilled Electronics TechnicianChalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- RAM Clear Casino Tech GeminiDocumento4 pagineRAM Clear Casino Tech GeminiChalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Slot TrainingDocumento17 pagineSlot TrainingChalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- MK7 - Common Faults1Documento2 pagineMK7 - Common Faults1Chalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Slot TrainingDocumento17 pagineSlot TrainingChalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A Slot TechnicianDocumento4 pagineWhat Is A Slot TechnicianChalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- NR - Part Details QuantityDocumento1 paginaNR - Part Details QuantityChalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- August Tech FestDocumento20 pagineAugust Tech FestChalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Astable Multivibrator Using TransistorsDocumento24 pagineAstable Multivibrator Using TransistorsChalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- MemoDocumento6 pagineMemoChalez Zengeretsi100% (1)
- MT7 Software Suite: March 07Documento14 pagineMT7 Software Suite: March 07Chalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- L4 LESSON PLAN PLCDocumento2 pagineL4 LESSON PLAN PLCChalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- TechFest 18 Technical TrainingDocumento3 pagineTechFest 18 Technical TrainingChalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- L4 Ecde QPDocumento4 pagineL4 Ecde QPChalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Markers Report For TestsDocumento5 pagineMarkers Report For TestsChalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Test 2Documento3 pagineTest 2Chalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning Objectives:: Topic 1.2.2 - System Simplification Using Boolean AlgebraDocumento52 pagineLearning Objectives:: Topic 1.2.2 - System Simplification Using Boolean AlgebraChalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- 2016 EBEIT Prospectus PDFDocumento171 pagine2016 EBEIT Prospectus PDFChalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Supervisory Management N4 - Module 1Documento8 pagineSupervisory Management N4 - Module 1Chalez Zengeretsi100% (7)
- Cap PDFDocumento82 pagineCap PDFChalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- EIC L4 ISAT Electronic ComponentsDocumento4 pagineEIC L4 ISAT Electronic ComponentsChalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Year Planner 2016 NCVDocumento3 pagineYear Planner 2016 NCVChalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Eic Icass Materila - RFQDocumento10 pagineEic Icass Materila - RFQChalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Report 191: Eastcape Midlands CollegeDocumento2 pagineReport 191: Eastcape Midlands CollegeChalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Motor Forward and Reverse Direction Control Using A PLCDocumento5 pagineMotor Forward and Reverse Direction Control Using A PLCChalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- L4 Test 1 2015Documento4 pagineL4 Test 1 2015Chalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- Binary Codes: Advantag Es of Binary CodeDocumento3 pagineBinary Codes: Advantag Es of Binary CodeKamalendu Kumar DasNessuna valutazione finora
- Flowchart, Algoruthm and Pseudo Codes in C++Documento6 pagineFlowchart, Algoruthm and Pseudo Codes in C++MAveRicK135100% (4)
- L4 Test CatDocumento5 pagineL4 Test CatChalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- ISAT L3 - Electrical Systems & Construction 2011-13Documento13 pagineISAT L3 - Electrical Systems & Construction 2011-13Chalez ZengeretsiNessuna valutazione finora
- LEGO Mindstorms Education Kit 9797 User GuideDocumento66 pagineLEGO Mindstorms Education Kit 9797 User Guidewsecomp100% (1)
- Jawaban MID Term Exam Semester 1 Oracle Academy English Database Design 2013-2015Documento4 pagineJawaban MID Term Exam Semester 1 Oracle Academy English Database Design 2013-2015dayatNessuna valutazione finora
- SNIA S10-110 Foundations Exam DescriptionDocumento3 pagineSNIA S10-110 Foundations Exam DescriptionFarha AzadNessuna valutazione finora
- Cmos Vlsi Design 65Documento1 paginaCmos Vlsi Design 65Carlos SaavedraNessuna valutazione finora
- VisItUsersManual1 5Documento356 pagineVisItUsersManual1 5mkpradyumnaNessuna valutazione finora
- LR2000 Spanish Specsheet - CompressedDocumento2 pagineLR2000 Spanish Specsheet - CompressedYesica SantamariaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Evolution of CalculatorsDocumento21 pagineThe Evolution of CalculatorsNitya DesulNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab 2 - Muhd Haziq Sufi - F1128Documento10 pagineLab 2 - Muhd Haziq Sufi - F1128Muhamad HaziqNessuna valutazione finora
- Hologic Selenia Installation and Hardware Maintenance Manual Part Number MAN-00745 Revision 002Documento236 pagineHologic Selenia Installation and Hardware Maintenance Manual Part Number MAN-00745 Revision 002surarystan100% (6)
- RH 134Documento2 pagineRH 134satya28Nessuna valutazione finora
- Visi SoftDocumento3 pagineVisi SoftsftgjsfyjNessuna valutazione finora
- ICT - Topic 1 - LODocumento4 pagineICT - Topic 1 - LOezzeddinezahra_55049Nessuna valutazione finora
- Pricelist 2018 Pameran 23 JuniDocumento2 paginePricelist 2018 Pameran 23 JuniRaynald SumampouwNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer BasicsDocumento32 pagineComputer BasicsDaryel CastelinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Drilling TechnologyDocumento14 pagineDrilling TechnologydhorajkarNessuna valutazione finora
- Technical Manual 36522 (Revision G) : DPG-2223-00X Digital ControllersDocumento58 pagineTechnical Manual 36522 (Revision G) : DPG-2223-00X Digital Controllersincore1976Nessuna valutazione finora
- Tps 2811Documento38 pagineTps 2811mashood_kNessuna valutazione finora
- Led Driving Using Parellel Port - ColourDocumento1 paginaLed Driving Using Parellel Port - Colourapi-3744897Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mingle Common Errors and SolutionsDocumento10 pagineMingle Common Errors and SolutionsBalaji PenumalliNessuna valutazione finora
- Output LogDocumento7 pagineOutput LogGingerAleNessuna valutazione finora
- Vijjay Kumar D Ver 1.1Documento2 pagineVijjay Kumar D Ver 1.1Mahin SyedNessuna valutazione finora
- Altera Component CreationDocumento3 pagineAltera Component Creationfran0772Nessuna valutazione finora
- Training DWDM Huawei Equipment: February, 2011Documento26 pagineTraining DWDM Huawei Equipment: February, 2011M Tanvir Anwar89% (18)
- BCN b62005 702 - ADocumento20 pagineBCN b62005 702 - ARafael GagoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cad AssignmentDocumento2 pagineCad AssignmentAnonymous 5KGkE3VNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer WorksheetDocumento6 pagineComputer WorksheetKV KAPURTHALANessuna valutazione finora
- ASX-260 CatalogDocumento12 pagineASX-260 CatalogFernandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Yamaha NU1 MIDI Control CodesDocumento6 pagineYamaha NU1 MIDI Control CodesisothermNessuna valutazione finora
- Install Compiz PDFDocumento8 pagineInstall Compiz PDFbombflexNessuna valutazione finora
- 6310 Hardware Installation GuideDocumento76 pagine6310 Hardware Installation GuideHamza_yakan967100% (1)