Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Kidney
Caricato da
María Afanador RodríguezDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Kidney
Caricato da
María Afanador RodríguezCopyright:
Formati disponibili
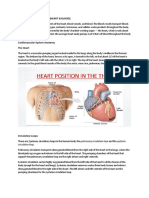
KIDNEY: RION -HEART: CORAZN -BLADDER: VEJIGA -PULMN: LUNG -CEREBRO: CEREBRUM Estomach: It pummels the food with
its muscular walls. Salivary glands: these produce saliva Liver (higado): Where bile is produced Large intestine: Porduce pancrease, amylase and lipase enzymes Rectum: Where the faeces are stored Small intestine: produces protease, amylase and lipase enzymes Gullet: Another name for aesophagus Vena Cava: It carries oxygen-poor blood to the heart Right Atrium: It receives the oxygenated bloof from the body Right Ventricle: This pumps the desocygenated blood to the lungs via the pulmonary artery Left Atrium: Its receives oxygenated blood from the lungs Valves. These prevent the backflow of blood Neurotrasmitter: ChemIcal released in the synaptic gap Axon: Lon extension of the neurone Urea: Its a toxic chemical found in urine Lymphatic system: It produces linfocites Urethra: Tube that connects the urinary bladder to the genitals Sweat: A fluid excreted by sweat glands Urinary bladder (vejiga urinaria): its collects urine excreted by the kidneys Excretion: Elimination of toxic substances Kidney: Excretory organ of vertebrates CNS: Brain and spinal cord are its components Dendritis: Branching threads of neurons Lungs: They take oxygen from air Systole: Contraction movement of the heart Pulmonary Arterie: it carries oxygen rich blood to the heart Digestion: the mechanical and chemical breakdown of foods for use by the body's cell Absorption: the passage of digested food from the digestive tract into the circulatory system Elimination: the expulsion of undigested food or body wastes Peristalsis: a series of involuntary musclar contractions-moves food through esophagus. Bile: a series of involuntary musclar contractions-moves food through esophagus Urine: liquid waste material Nephrons: the functional units of the kidneys woth the bladder Ureters: tubes that connect the kidneys with the bladder Bladder: a hollow hueco- , muscular organ that acts as a reservoir for urine Urethra. the tube that leads from the bladder to the outside of the body Stimulus: A change either inside or outside the body. Response: The effector cells make a _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _. Effector: These can be a muscle or a gland.
Sensor: These cells detect a stimulus. Neuron: A nerve cell. Brain: The _ _ _ _ _ and the spinal cord make up the central nervous system. Electrical: The nervous system uses _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ impulses to transmit messages. Coordinates: The brain _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ the response to the stimulus. Receptor: Another name for sensor cells Septum (tabique): it divides the heart into two sides Atrium: an upper chamber of the heart. Ventricle: an lower chamber of the heart AV: a one-way valve sepperating each atrium from the ventricle beneath it Tricuspid valve: the atrioventricular valve on the right side Mitral valve: also called the tricuspid valve is on the left Aorta: a large blood vessel Pacemaker: the sinoatrial node is also called this because it regulates the heart beat Systole: the first phase of the heart beat Diastole: the second phase of the heart beat Pulmonary veins: the only veins that carry oxygenated blood Pulmonary: movement of blood from the heart to the lungs Valve: device that regulates the flow of substances Hemoglobin: pigment containing iron and found in the red blood cells Hormones: produced by glands and carried to other organs in the blood Heart: supplies blood and oxygen to all parts of the blood Calcium: a substance required for the clotting of blood Alveoli: final branching of the respiratory system and performs gas exchange for the lung Tricuspid: guards the junction between the right atrium and right ventricle Oxygenated: blood on the left side of the heart Desoxygenated: blood on the right side of the heart Diastole: pressure created when the ventricles are filling with blood Arteries: vessels which carry blood away from the heart Aorta: largest artery in the human body Plasma: the liquid part of blood Antibody: muscular blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart Fibrinogen: protein involved in the clotting of the blood Platelet: Responsible for blood clotting Aorta: Largest artery in the heart Arteries: Takes blood away from the heart Antigens: Each body cell has a particular chemical structure on its surface, called ______________ Vena cava: Major vessel Erythrocytes: Red blood cells Bacteria: Causes infections Ventricle: Chamber of the heart Plasma: Straw colored fluid Veins: Carries blood to the heart
Leukocytes: White blood cells Red blood cells: blood cells with no nuclei Phagocytes: type of white blood cell that engulfs a bacterium Inferior vena cava: brings blood from truck and legs to right atrium Blood: what carries oxygen, nutrients, digested foods, and water to all cells of the body Lymphocyte: example of a phagocyte Capillaries: blood vessels where the exchange materials take place Lymph: a fluid similar to plasma that contains white blood cells Antigen: any substance capable of exciting our immune system Plasma cell: release antibodies Follicles: collections of lymphocytes Lymphocytes: a type of white blood cell located in the lymph nodes Macrophage: destroy bacteria, viruses, and other foreign substances Lymph: meaning clear water
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- Manual of Pediatric Cardiac Intensive CareDocumento326 pagineManual of Pediatric Cardiac Intensive CareLeydi Baltazar T100% (4)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Medical Surgical QandADocumento63 pagineMedical Surgical QandAAlona Lumidao100% (8)
- Chapter 8 Transport in Mammals - WorksheetDocumento5 pagineChapter 8 Transport in Mammals - Worksheetapi-3728508100% (2)
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory System TESTDocumento9 pagineCardiovascular and Respiratory System TESTHappy Happy Life100% (1)
- StemphylumDocumento5 pagineStemphylumapi-276652085Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/22Documento16 pagineCambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/22walsha khanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lorma Colleges College of Physical and Respiratory TherapyDocumento33 pagineLorma Colleges College of Physical and Respiratory TherapyAnab Mohamed Elhassan Abbas AlnowNessuna valutazione finora
- Permanent Pacemaker Implantation Technique Part IIDocumento10 paginePermanent Pacemaker Implantation Technique Part IIRaul OrtegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Subject Enrichment Material English Core Class XII 2019-20-0Documento304 pagineSubject Enrichment Material English Core Class XII 2019-20-0Abirami Anbalagan100% (1)
- Cardiovascular SystemDocumento17 pagineCardiovascular SystemPoojaNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTER - 6 LIFE PROCESSES CLASS XTH 2020-2021Documento20 pagineCHAPTER - 6 LIFE PROCESSES CLASS XTH 2020-2021FACTOPEDIANessuna valutazione finora
- Biology SSC I SolutionDocumento11 pagineBiology SSC I SolutionFaisal SamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Basicpacingconceptsppt2017-171221084227 2Documento101 pagineBasicpacingconceptsppt2017-171221084227 2Bob RiouxNessuna valutazione finora
- Q1W2-Lesson 1-2 CIRCULATION OF BLOODDocumento40 pagineQ1W2-Lesson 1-2 CIRCULATION OF BLOODKRISTA MAE BALANAYNessuna valutazione finora
- EmbryologyDocumento26 pagineEmbryologyMeer BabanNessuna valutazione finora
- SeminorDocumento6 pagineSeminorsherjin tintuNessuna valutazione finora
- AAPC 2012 Midterm and AnswersDocumento18 pagineAAPC 2012 Midterm and AnswersKuro100% (2)
- @medical - MCQ Chest Radiology MCQsDocumento20 pagine@medical - MCQ Chest Radiology MCQsKhalid Refaey100% (1)
- Chapter 6 Q. P.1Documento28 pagineChapter 6 Q. P.1RawanMazen SharifNessuna valutazione finora
- 100 Questions Micro-Gross HSBDocumento9 pagine100 Questions Micro-Gross HSBfilchibuffNessuna valutazione finora
- SWC12Documento11 pagineSWC12vikkasNessuna valutazione finora
- Chest X-Ray AnnaDocumento51 pagineChest X-Ray Annaapi-26159412100% (1)
- Science PT3 2019Documento15 pagineScience PT3 2019Roseanne ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Echo and ECG ReportDocumento3 pagineEcho and ECG Reportpsahu74Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy - Physiology (Chapter 12 - Heart)Documento20 pagineAnatomy - Physiology (Chapter 12 - Heart)Avi ZychNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac MRI Made Easy 2008Documento164 pagineCardiac MRI Made Easy 2008Benjamin Gonzalez100% (1)
- NEET Question Paper Code G1 ResonanceDocumento27 pagineNEET Question Paper Code G1 ResonanceTaher MohdNessuna valutazione finora
- P1 Medworld Academy: Respiratory SystemDocumento123 pagineP1 Medworld Academy: Respiratory SystemThenunda തേനുണ്ടNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP-congenital Heat DefectDocumento5 pagineNCP-congenital Heat DefectFavor ColaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Cycle (Page Print 1-2)Documento2 pagineCardiac Cycle (Page Print 1-2)hihariv794Nessuna valutazione finora