Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Must
Caricato da
vinodh76Descrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Must
Caricato da
vinodh76Copyright:
Formati disponibili
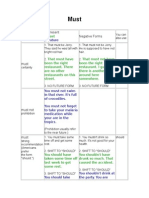
Must
"Must" is most commonly used to express certainty. It can also be used to express necessity or strong recommendation, although native speakers prefer the more flexible form "have to." "Must not" can be used to prohibit actions, but this sounds very severe; speakers prefer to use softer modal verbs such as "should not" or "ought not" to dissuade rather than prohibit. Examples:
This must be the right address! certainty Students must pass an entrance examination to study at this school. necessity You must take some medicine for that cough. strong recommendation Jenny, you must not play in the street! prohibition
Using "Must" in Present, Past, and Future
Most modal verbs behave quite irregularly in the past and the future. Study the chart below to learn how "must" behaves in different contexts. Positive Forms 1. = Present 2. = Past 3. = Future 1. That must be Jerry. They said he was tall with bright red hair. must certainty 2. That must have been the right restaurant. There are no other restaurants on this street. 3. NO FUTURE FORM Negative Forms 1. = Present 2. = Past 3. = Future 1. That must not be Jerry. He is supposed to have red hair. 2. That must not have been the right restaurant. I guess there is another one around here somewhere. 3. NO FUTURE FORM You must not swim in that river. It's full of crocodiles. must not prohibition You must not forget to take your malaria medication while your are in the tropics. Prohibition usually refer to the near future. must strong 1. You must take some time off and get some rest. 1. You mustn't drink so much. It's not good for your health. should have to
Modal Use
You can also use:
recommendation (Americans prefer the form "should.")
2. SHIFT TO "SHOULD" You should have taken some time off last week to get some rest. 3. SHIFT TO "SHOULD" You should take some time off next week to get some rest. 1. You must have a permit to enter the national park. 2. SHIFT TO "HAVE TO" We had to have a permit to enter the park. 3. We must get a permit to enter the park next week.
2. SHIFT TO "SHOULD" You shouldn't have drunk so much. That caused the accident. 3. SHIFT TO "SHOULD" You shouldn't drink at the party. You are going to be the designated driver. 1. SHIFT TO "HAVE TO" We don't have to get a permit to enter the national park. 2. SHIFT TO "HAVE TO" We didn't have to get a permit to enter the national park. 3. SHIFT TO "HAVE TO" We won't have to get a permit to enter the national park. have to
must necessity (Americans prefer the form "have to.")
REMEMBER: "Must not" vs. "Do not have to" "Must not" suggests that you are prohibited from doing something. "Do not have to" suggests that someone is not required to do something. Examples:
You must not eat that. It is forbidden, it is not allowed. You don't have to eat that. You can if you want to, but it is not necessary.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Russian Beginners - 2019Documento123 pagineRussian Beginners - 2019Roman Kim100% (6)
- English Level 3 Lesson 4 Activity Final: Portafolio Integrador Del NIVEL TRESDocumento28 pagineEnglish Level 3 Lesson 4 Activity Final: Portafolio Integrador Del NIVEL TRESCarlos Alberto Damas Lazaro100% (1)
- Modal VerbsDocumento21 pagineModal VerbsIoana Margineanu100% (1)
- Ought ToDocumento2 pagineOught Tojawad khanNessuna valutazione finora
- MarekHlavac SlovakLanguageLessonsforBeginnersDocumento121 pagineMarekHlavac SlovakLanguageLessonsforBeginnersLupus Astaroth100% (1)
- What Is The D Ragon Language? What Is The D Ragon Language?: Section I: GrammarDocumento55 pagineWhat Is The D Ragon Language? What Is The D Ragon Language?: Section I: GrammarDovahkiinNessuna valutazione finora
- Adjective-Clauses With ExerciseDocumento2 pagineAdjective-Clauses With ExerciseMuhammad muslehNessuna valutazione finora
- Using "Must" in Present, Past, and Future: CertaintyDocumento2 pagineUsing "Must" in Present, Past, and Future: CertaintyGeangu GabrielNessuna valutazione finora
- Using "Must" in Present, Past, and FutureDocumento2 pagineUsing "Must" in Present, Past, and FutureAngélica BenevidesNessuna valutazione finora
- MUSTDocumento2 pagineMUSTleni tiwiyantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Modal Use 1. Present Negative Forms: 3. FutureDocumento2 pagineModal Use 1. Present Negative Forms: 3. FuturePaul HughesNessuna valutazione finora
- Modal VerbDocumento12 pagineModal VerbAry BintariNessuna valutazione finora
- Can You Hand Me The Stapler?Documento19 pagineCan You Hand Me The Stapler?usefuldoNessuna valutazione finora
- Modal VerbDocumento4 pagineModal VerbVanesa AtalayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Have ToDocumento2 pagineHave ToIsma-MANessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Modal Verbs: CharacteristicsDocumento12 pagineUnit 1 Modal Verbs: CharacteristicsMiguelin AlbánNessuna valutazione finora
- MOdals AuxilaryDocumento25 pagineMOdals Auxilarymeymirah100% (1)
- What Are Modal VerbsDocumento18 pagineWhat Are Modal VerbsSafwanAhsanSwad100% (1)
- Uses of LikeDocumento14 pagineUses of LikeadauNessuna valutazione finora
- Modal Verbs - in Theory and PracticeDocumento58 pagineModal Verbs - in Theory and Practicecristina_coteaNessuna valutazione finora
- Using "Must" in Present, Past, and Future: CertaintyDocumento2 pagineUsing "Must" in Present, Past, and Future: CertaintyAnonymous OQmcDMgNessuna valutazione finora
- EDU323 Chapter 3Documento6 pagineEDU323 Chapter 3zefanya tesaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grammar Giving AdviceDocumento10 pagineGrammar Giving AdviceTofik MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- Clase 6 Should y Ought ToDocumento16 pagineClase 6 Should y Ought ToSaray JohnsonNessuna valutazione finora
- ASTR325 Lab 10Documento8 pagineASTR325 Lab 10Marvin EduarteNessuna valutazione finora
- ModalsDocumento17 pagineModalsSatish GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- MODALSDocumento3 pagineMODALSMiroslava MassielNessuna valutazione finora
- Shall Will: VI Functional EnglishDocumento6 pagineShall Will: VI Functional EnglishBandi RamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ought To Ought To Have: Giving Advice or Suggestions in EnglishDocumento16 pagineOught To Ought To Have: Giving Advice or Suggestions in EnglishCarlos Del CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Modal Verbs: English Level 2Documento16 pagineModal Verbs: English Level 2jorge913Nessuna valutazione finora
- ModalsDocumento15 pagineModalsEsty HelkyNessuna valutazione finora
- English LessonDocumento21 pagineEnglish LessonackimNessuna valutazione finora
- General Understanding of Auxiliaries VerbDocumento4 pagineGeneral Understanding of Auxiliaries VerbMuhammad Ali HashmiNessuna valutazione finora
- English Modal VerbsDocumento10 pagineEnglish Modal VerbsOsama AliNessuna valutazione finora
- ObligationDocumento40 pagineObligationRosalie LuciniadaNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 5: Febrianto Fellya Safitri Ferin Amalia Fitri Karmeliani Fitri KurbainiDocumento19 pagineGroup 5: Febrianto Fellya Safitri Ferin Amalia Fitri Karmeliani Fitri KurbainiRospinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Logical FallaciesDocumento72 pagineLogical FallaciesKellie Clark100% (1)
- Queen Sala Celinda Del Rosario Actividad de Produccion Final Del Curso 4.2Documento30 pagineQueen Sala Celinda Del Rosario Actividad de Produccion Final Del Curso 4.2Salustino AbreuNessuna valutazione finora
- Should-Ought ToDocumento4 pagineShould-Ought ToDayana RodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Modals in English GrammarDocumento12 pagineModals in English GrammarUmmahUnity100% (1)
- Unit 4, Inter, Modal VerbsDocumento14 pagineUnit 4, Inter, Modal VerbsVong Sam Oun100% (1)
- Should, Would and CouldDocumento10 pagineShould, Would and CouldEnrique RomeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Use of Modals and ExercisesDocumento39 pagineUse of Modals and ExercisessdfsdfsdfNessuna valutazione finora
- ECON246 Report 9Documento6 pagineECON246 Report 9Andrew HolnessNessuna valutazione finora
- Modals, Reported Speech, Determiners and Subject Verb Concord Notes and ExercisesDocumento8 pagineModals, Reported Speech, Determiners and Subject Verb Concord Notes and ExercisesKrishna Nilesh Lodhia G 11Nessuna valutazione finora
- Jap321 HW 9Documento5 pagineJap321 HW 9BartNessuna valutazione finora
- Modal VerbsDocumento9 pagineModal Verbsnato.kharshiladze.1Nessuna valutazione finora
- Modul Chapter 3 EditDocumento4 pagineModul Chapter 3 EditHerny RahmawatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Handout 2 (Additional) XI Sas-Ing KD 3.2 4.2 Dialog Lisan & Tulis Penggunaan KeharusanDocumento3 pagineHandout 2 (Additional) XI Sas-Ing KD 3.2 4.2 Dialog Lisan & Tulis Penggunaan KeharusanHana Hanifah RaharjoNessuna valutazione finora
- A2 Online (Tuesday)Documento12 pagineA2 Online (Tuesday)Berke BulunurNessuna valutazione finora
- HotEnglish100p29mannersplease PDFDocumento1 paginaHotEnglish100p29mannersplease PDFmareirterNessuna valutazione finora
- URBN289 Lecture Notes 1Documento5 pagineURBN289 Lecture Notes 1Jazz JaneNessuna valutazione finora
- "Will" As A Modal Verb: Decide To Do Something NowDocumento6 pagine"Will" As A Modal Verb: Decide To Do Something Nowleslys solisNessuna valutazione finora
- Modal Verb1Documento38 pagineModal Verb1AliceNessuna valutazione finora
- English Modal VerbsDocumento10 pagineEnglish Modal VerbsMaría Auxiliadora Jácome OrtegaNessuna valutazione finora
- Passive Reporting VerbsDocumento3 paginePassive Reporting VerbsvietquietNessuna valutazione finora
- You Should Also Read : 1. Misplaced ApostrophesDocumento8 pagineYou Should Also Read : 1. Misplaced ApostrophesmariamcarullaNessuna valutazione finora
- ENVI126 Problem 4Documento5 pagineENVI126 Problem 4manolitoNessuna valutazione finora
- GEO123 Practice Problems 7Documento3 pagineGEO123 Practice Problems 7samNessuna valutazione finora
- (Lecture - 6) PunctuationDocumento35 pagine(Lecture - 6) PunctuationN. W. FlannelNessuna valutazione finora
- Example:: Basic RuleDocumento9 pagineExample:: Basic RuleClaris LangngagNessuna valutazione finora
- Gerund InfinitiveDocumento9 pagineGerund Infinitivefres7451Nessuna valutazione finora
- BIO166 Doc 7Documento5 pagineBIO166 Doc 7Tanjiro KamadoNessuna valutazione finora
- Twelve Articles About Learning to Speak English BetterDa EverandTwelve Articles About Learning to Speak English BetterNessuna valutazione finora
- The Goose With The Golden Eggs Golden EggsDocumento2 pagineThe Goose With The Golden Eggs Golden Eggsvinodh76Nessuna valutazione finora
- Different Types of Plants 1Documento1 paginaDifferent Types of Plants 1vinodh76Nessuna valutazione finora
- H.E.L. Chaucer Q (2 ND Time Sending)Documento5 pagineH.E.L. Chaucer Q (2 ND Time Sending)vinodh76Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 EssayDocumento1 paginaUnit 1 Essayvinodh76Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Short StoryDocumento1 paginaUnit 1 Short Storyvinodh76Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit V Sweeney Among The NightingalesDocumento3 pagineUnit V Sweeney Among The Nightingalesvinodh76Nessuna valutazione finora
- SPRING BOARD - English Language Lab: S.K.Velayutham Women'S Arts and Science CollegeDocumento3 pagineSPRING BOARD - English Language Lab: S.K.Velayutham Women'S Arts and Science Collegevinodh76Nessuna valutazione finora
- Uenm402 Post-Colonial Literature Unit - I (Poetry) Australia - Alec Derwent HopeDocumento3 pagineUenm402 Post-Colonial Literature Unit - I (Poetry) Australia - Alec Derwent Hopevinodh76Nessuna valutazione finora
- Wuthering Heights SummaryDocumento5 pagineWuthering Heights Summaryvinodh76Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 Biography and AutobiographyDocumento2 pagineUnit 1 Biography and Autobiographyvinodh76100% (1)
- Geoffrey Chaucer: John GowerDocumento19 pagineGeoffrey Chaucer: John Gowervinodh76Nessuna valutazione finora
- Prepositions Work Sheet Answer Key: Directions: Answer The Following Questions by Choosing The Correct MultipleDocumento2 paginePrepositions Work Sheet Answer Key: Directions: Answer The Following Questions by Choosing The Correct Multiplevinodh76Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A Group DiscussionDocumento10 pagineWhat Is A Group Discussionvinodh76Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Great Indian DreamDocumento10 pagineThe Great Indian Dreamvinodh76Nessuna valutazione finora
- Lecturer 2 - Geomorphology and Weathering - 14Documento21 pagineLecturer 2 - Geomorphology and Weathering - 14Joseph ZotooNessuna valutazione finora
- The Significance of Morphometric Analysis To Understand The Hydrological and Morphological Characteristics in Two Different Morpho Climatic SettingsDocumento16 pagineThe Significance of Morphometric Analysis To Understand The Hydrological and Morphological Characteristics in Two Different Morpho Climatic SettingsKhristian EnggarNessuna valutazione finora
- Transcript. Verb Tenses in Scientific Writing.Documento2 pagineTranscript. Verb Tenses in Scientific Writing.ClauLopez99Nessuna valutazione finora
- Comprehensive Grammar Grade 3Documento69 pagineComprehensive Grammar Grade 3kranu75% (4)
- TOEIC WORD LIST 4 - Elaine Givandra L - 2019130043 (1051-1100)Documento7 pagineTOEIC WORD LIST 4 - Elaine Givandra L - 2019130043 (1051-1100)sweetprivate sugarrrNessuna valutazione finora
- Infinitive and The GerundDocumento8 pagineInfinitive and The GerundSergoSanikidze100% (2)
- Grammar Books ProjectDocumento5 pagineGrammar Books Projectrita yaremenkoNessuna valutazione finora
- LESSON 1: No Place Like Home: Test Your GrammarDocumento4 pagineLESSON 1: No Place Like Home: Test Your GrammarChesska Carla MorenoNessuna valutazione finora
- An English GrammarDocumento265 pagineAn English Grammargibson150Nessuna valutazione finora
- Present Continuous AffirmativeDocumento2 paginePresent Continuous AffirmativeAlma y doni ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Should - Should NotDocumento2 pagineShould - Should NotJesebellTorresNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 NounsDocumento19 pagine1 NounsFarhatus SholihahNessuna valutazione finora
- Ir-Regular Verbs Con GerundioDocumento2 pagineIr-Regular Verbs Con GerundioTaide Alma PrietoNessuna valutazione finora
- Punctuation Marks in English Semicolon, Colon, Apostrophe, Quotation Mark, Hyphen, Ellipsis... - YouTubeDocumento6 paginePunctuation Marks in English Semicolon, Colon, Apostrophe, Quotation Mark, Hyphen, Ellipsis... - YouTubeSyed Hassan TariqNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer Key Pre-Test Grammar For TOEFL 1Documento3 pagineAnswer Key Pre-Test Grammar For TOEFL 1putri100% (1)
- Passive Voice ChartDocumento1 paginaPassive Voice ChartCruzJavier100% (1)
- Junior French Course PDFDocumento232 pagineJunior French Course PDFSashaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grammar Workshop II - Silvia SaenzDocumento18 pagineGrammar Workshop II - Silvia SaenzAlvaro LeivaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adverbs of FrequencyDocumento4 pagineAdverbs of FrequencynatalylunaNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Tests Plus KET For Schools 9781292159522 Answer KeyDocumento17 paginePractice Tests Plus KET For Schools 9781292159522 Answer KeyVanessa SalazarNessuna valutazione finora
- MLC Basic 1 Object + Infinitive - Week 1Documento4 pagineMLC Basic 1 Object + Infinitive - Week 1Loki EinsteinNessuna valutazione finora
- Passive VoiceDocumento4 paginePassive VoicePaqui Martin AcuñaNessuna valutazione finora
- Active and PassiveDocumento16 pagineActive and Passiveendawoke anmawNessuna valutazione finora
- Inggris Skill 9Documento9 pagineInggris Skill 9Wafi AhdillahNessuna valutazione finora
- Using To Be in Daily ActivityDocumento11 pagineUsing To Be in Daily ActivityAilsaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Passive.: The Pizza Is Bening Eaten by Us We Are Eating A PizzaDocumento4 pagineThe Passive.: The Pizza Is Bening Eaten by Us We Are Eating A PizzaErick AguilarNessuna valutazione finora