Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Kelly's Finance Cheat Sheet V6
Caricato da
Kelly KohDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Kelly's Finance Cheat Sheet V6
Caricato da
Kelly KohCopyright:
Formati disponibili
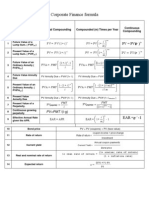
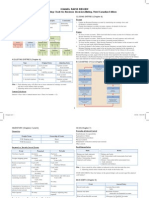
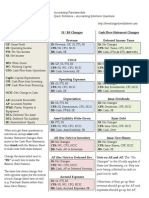
Chapter 2: Financial Statements, Taxes & Cash Flow o Affected by i/r, default, inflation, taxability, liquidity Variance of N-stock
k portfolio, premiums / bond values move inversely with interest r Income = Revenue Expenses Interest payments are tax deductible (1 - tax rate) x payment Earnings per share = NI/total shares outstanding Variance of equally-weighted N-stock portfolio, Current yield = (Coupon/current price) YTM Dividend/Share = Total dividends/total shares o. Capital gain yield = (New price original price)/original price Cash flow from assets = OCF - NCS - NWC Security i s contributi on to the = Cash flow to creditors + CF to stockholders Effective current yield = EAR volatility of the portfolio CF to creditors = Interest net new borrowings SD ( R P ) x i SD ( R i ) Corr ( R i , R p ) i CF to stockholders = Dividends net new equity Bond value (pv) = OCF = EBIT + Depreciation Taxes Amount Total Fraction of i s of i held Risk of i risk that is o = PV of coupons + PV of face amount Bottom-up = Net Income + Depreciation + Interest common to P Bonds of similar risk will be priced to yield a similar return Top-down = Sales Cost - Taxes Unless all stocks in portfolio hv perfect positive correlation of regardless of coupon rate / interest rate decline buy zero, LT Tax Shield = (Sales cost)(1 T) + (Depr x T) + (Interest + T) +1, risk of portfolio < weighted avg volatility of individual stocks Bonds selling at par can have any length of maturity NCS = End net fixed assets Begin NFA + Depre Diversification unsystematic risks for each stock avged out Longer time to mature greater interest rate risk NWC = Ending NWC Beginning NWC Portfolio with Rf asset, E[Rxp] = (1 x)rf + xE[Rp] Lower coupon rate greater interest rate risk = End (CA CL) Begin (CA-CL) = rf + x(E[Rp] rf) Zero coupon bonds need to sell more bonds and incur Avg tax rate = Tax/taxable income greater repayment but has yearly cash inflow(in the form of Marginal tax rate = Tax payable on next dollar earned SD[Rxp] = interest tax shield of debt) instead of outflow Chapter 3: Ratios Interest payt of zero P1 P0 , CF (in) No. of bonds sold x tax = ST Solvency rate x interest payment of zero bond Current ratio = Current assets/Current liabilities Efficient portfolio: no way to reduce portfolio volatility w/o CF (out) of cupn bds: No. of bonds x coupon payt x (1 tax rate) o To creditor high ratio better, but maybe inefficient cash use lowering expected return; inefficient: possible find another way Holding Period Yield: r of new FV (sale price) & N (holding time) Low ratio - not a bad sign for company with large reserve of Efficient frontier: set of efficient portfolios, those offering Inflation Fisher Effect (1 + Nominal rate) = (1 + real rate) x (1 + untapped borrowing power highest possible E(R) for given volatility, northwest edge of curve expected inflation rate) Quick ratio = (CA-Inventory) CL Cash ratio = Cash/CL Long: positive investment Short: negative investment Know Pa, estimate YTMa use it to find Pb o Large, slow-moving inventory ST trouble Short sale: sell a stock tt not owned then buy tt stock back later o Dirty price price actually paid to buy NWC to total assets = NWC/TA Short sales volatility of portfolio > volatility of stocks within o Clean price price quoted in mkt Interval measure = CA/Avg daily operating cost Sharpe ratio = / Reward-to-volatility ratio = Dirty price accrued interest (of coupon) LT Solvency Chapter 8: Stock Valuation Total debt ratio = (TA TE)/TA Optimal portfolio: Tangent to efficient frontier of risky invest. Stock price = PV of future dividends, R = required return o x% of assets financed by debt, rest by equity Investor will determine how much to invest along the tangent or o Debt-equity ratio = TD/TE = TD ratio/(1- TD ratio) Dividend growth model, the capital market line depending on taste of risk o Equity Multiplier = TA/TE = (TE + TD)/TE = 1 + D/E CAPM = Cost of preferred stock = dividend yield = D1/P0 LT Debt ratio = LT Debt/(LT Debt + TE) - measure Pt = D0 x (1 + g)t+1 / ( R g ) = P0 x (1 + g)t Coverage Ratio (likelihood of default) Required return, R =capital gains yield + dividend yield systematic risk. Beta of a portfolio, Times Interest Earned ratio = EBIT/Interest Capital gains yield = g Dividend yield = D1/P0 Assumptions: buy&sell at competitive mkt prices + borrow/lend Cash coverage = (EBIT + Depre)/Interest Supernormal, Dividend grows steadily aft t periods, at risk-free interest rate; only efficient portfolios are held for a Turnover Ratios given volatility; homogeneous expectations regarding future Inventory turnover = COGS/Inventory demand same efficient portfolio (not possible in real life) Receivables turnover = Credit sales/Acct receiv SML linear r/s between a stocks beta and its expected return Payable turnover = COGS/Acct payable Chapter 15: Cost of Capital = cost of (equity + debt + pref stock) Days sales in ___ = 365 days/___ turnov. Chapter 9: Investment Decisions Cost of equity, Dividend Approach, RE = (D1/P0 ) +g Asset Turnover Ratios Payback period / Discounted payback period NWC turnover = Sales/NWC SML Approach, E(RE) = Rf + E x [E(RM) Rf] o (+)tmv, easy to understand, reject (-) NPV Fixed asset turnover= Sales/Net fixed asset Use average of SML and Dividend approach if cannot decide o (-) arb pt, ignore CF aft, +NPV rej. cos too long Total asset turnover = Sales/TA Cost of debt, YTM on bonds / Cost of Pref Stock, RP = D/P0 Avg Accounting Return (Avg NI/Avg Book Value) o Every $1 in TA generate $x in sales WACC = (E/V)(RE) + (D/V)(RD)(1 TC) + (P/V)(RP) o (+) easy to calculate, info available Profitability Ratios Tend to accept unprofitable investments w/ risk > than firm o (-) no tmv, bk value, not mkt or cashflow Profit margin = Net income/Sales Reject some +NPV & accept some NPV projects o Avg bk value = (initial + end)/2 ROA = Net income/TA ROE = NI/TE = ROA x EM Pure play approach use of WACC tt unique to particular prj IRR (acpt if > required return or WACC) , NPV=0 Market Value Ratios o (-) Nonconventional cash flow & Mutually exclusive projects Avg floatation cost, fA = (E/V) x fE + (D/V) X fD Market-to-book ratio = Mkt value per share bk value per share o Crossover rate = IRR of NPV (B-A) True cost = Amount needed / (1 floatation cost%) Price-sales ratio = Price per share/Sales per share o (+) related to NPV, easy to understand Chapter 17: Financial Leverage & Capital Structure Policy PEG ratio = Price-earnings ratio/earnings growth rate Profitability Index (NPV/Initial investment) M&M I: Value of levered firm is equal to unlevered firm Price-earnings ratio = Price/share earnings/share o > 1 for +NPV, < 1 for NPV VL = VU > 1.firms capt. struct. irrelevant 2.firm WACC is same Du Pont Identity Chapter 10: Capital Budgeting (Investment decisions) M&M I - Homemade leverage: borrow & lend on their own ROE = Profit Margin (operating efficiency) x TAT (asset use Pro forma (Sales, VC, FC, Depre, EBIT, T, NI) Since RD < RE, as D/V , WACC, V Equity = EBIT/Ru efficiency) x Equity Multiplier (financial leverage) X Sunk cost , Opportunity cost, Erosion Good prj, NPV > 0 M&M II: cost of equity, RE = RA + (RA RD) x (D/E), RA-WACC o (NI/sales) x (sales/assets) x (TA/TE) EAC = NPV cost on annual basis (PMT) 1.Cost of equ rises as debt use increase 2.risk of equ depends on Chapter 4: LT Financial Planning & Growth Aft tax salvage value = S x (1-T) i. Business risk (RA) ii.financial risk [(RA RD) x (D/E)] NWC returns to the firm at the end (depends on qn) Required return rate on firms asset RA, cost of debt RD and D/E Internal growth rate = Chapter 12: Some Lessons from History Solve for RE, calculate WACC -> remains same for diff D/E ratio o b = plowback (retention) ratio RE = RU + (RU RD) x (D/E), when RU = RE = WACC, interest r > RD Risk premium: excess return required from risky asset over o b = 1- dividend payout ratio M&M I w/ taxes, VL = VU + (TC x D) > 1. debt fin is v advantag, required from risk-free investment (1: Risky asset earn risk o b = addition to retained earnings/NI optimal capital structure is 100% 2.lower WACC w/ more debt premium; reward for bearing risk) (2: Greater potential reward, o Max. growth rate attain with no ext. financing PV of interest tax shield = (TC x D x RD)/RD = TC x D greater the risk Sustainable growth rate = M&M II w/ taxes, RE = RA + (RA RD) x (D/E) x (1 TC) > same Var(R) = 1/(T 1) x [(R1 Mean)2 + + (RT Mean)2] VU = (EBIT Taxes )/RU = [EBIT x (1-TC)] /RU VL = VU + TC x D Arithmetic avg return (R1 + R2 + RT)/T (>Geometric) o Max. growth rate attain with no ext. equity financing while E = VL D, find E/D, find RE using M&MII w/ taxes, find WACC Geometric avg return [(1 + R1) x (1 + R2) x x (1 + RT)]1/T 1 maintaining a constant D/E ratio Static theory: Too much debt increase prob. of fin distress due o What actually earned per year on avg, compounded annually Chapter 5/6: TVM to bankruptcy (optimal: tax benefit of debt = cost of distress) o AAR too high for longer period, GAR too low for shorter , , PV factor = 1/(1 + r)t Chapter 18: Dividends & Dividend Policy Efficient capital mkt: security prices reflect available info Declaration date: declares payment; ex-dividend date: 2 Rule of 72: Time taken to double $ = 72/r% Efficient mkts hypothesis: actual capital mkt are efficient NPV business days before date of record buy on day or after no of projects are 0 (mkt value of investment & cost = 0) dividend; date of record: holder of stock determined; Chapter 13: Return, Risk and SML Annuity, = Capital mkt imperfection: Low-payout (personal income tax + Expected return, E(R) = Weighted avg of possible returns floatation cost + dividend restrictions) High-payout (Corp tax + Annuity due = start of each period = Ordinary annuity x (1 + r) Risk premium = Expected return of stock risk-free rate (Rf) institutional investing requmt + transact. costs + current income) Growing annuity, Variance, = E[(R E[R])2] = Clientele effect Payout does not matter assuming equilibrium Perpetuity, Growing perpetuity, Standard dev, = - measures volatility or total risk Residual dividend approach: payout aftr meeting invest. needs Portfolio exp return = weighted returns from each stock and maintain desired D/E ratio (Dividend stability consideration) EAR = APR = Compromise dividend approach: APR/quoted rate = period rate x no. of periods/year Portfolio weights, Stock repurchase: prefer repurchase (akin a cash dividend Continuous compoundg, Variance of 2-stock portfolio, program provided no taxes or other imperf.) homemade divide. Partial Amortization Balloon payment (PV of remaining) Stock dividend/stock split: no change in equity (trading range) Chapter 8: Interest Rates & Bonds Dividend policy does not matter firm reinvest capital > pay Covar. btw returns R1 and R2, Coupon rate (pmt) = Annual coupon/Face value ($1000) higher dividends in the future bt offset of lower PV factor Cov(Rx,Ry) = E[ (Rx E[Rx]) (Ry E[Ry]) ] = YTM (r) = Rate required in mkt for bond (find r on fin cal.) associated w/ CF Homemade dividends policy w/ perfect mkt o Current Yield + Capital Gains Yield Correl. btw returns R & R ,
1 2
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- CorpFinance Cheat Sheet v2.2Documento2 pagineCorpFinance Cheat Sheet v2.2subtle69100% (4)
- CheatSheet (Finance)Documento1 paginaCheatSheet (Finance)Guan Yu Lim100% (3)
- Fnce 100 Final Cheat SheetDocumento2 pagineFnce 100 Final Cheat SheetToby Arriaga100% (2)
- Corporate Finance Formula SheetDocumento4 pagineCorporate Finance Formula Sheetogsunny100% (3)
- CFA Formula Cheat SheetDocumento9 pagineCFA Formula Cheat SheetChingWa ChanNessuna valutazione finora
- Corporate Finance Math SheetDocumento19 pagineCorporate Finance Math Sheetmweaveruga100% (3)
- Cheat Sheet Corporate - FinanceDocumento2 pagineCheat Sheet Corporate - FinanceAnna BudaevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cheat Sheet Final - FMVDocumento3 pagineCheat Sheet Final - FMVhanifakih100% (2)
- Corporate Finance - FormulasDocumento3 pagineCorporate Finance - FormulasAbhijit Pandit100% (1)
- BF2201 Cheat Sheet FinalsDocumento2 pagineBF2201 Cheat Sheet Finalssiewhong93100% (1)
- FIN6215-Cheat Sheet BigDocumento3 pagineFIN6215-Cheat Sheet BigJojo Kittiya100% (1)
- Corporate Finance FormulasDocumento3 pagineCorporate Finance FormulasMustafa Yavuzcan83% (12)
- Cheat Sheet For Financial AccountingDocumento1 paginaCheat Sheet For Financial Accountingmikewu101Nessuna valutazione finora
- Equity Valuation DCF, WACC and APVDocumento64 pagineEquity Valuation DCF, WACC and APVstf2xNessuna valutazione finora
- CheatDocumento1 paginaCheatIshmo KueedNessuna valutazione finora
- Finance Cheat SheetDocumento4 pagineFinance Cheat SheetRudolf Jansen van RensburgNessuna valutazione finora
- ACC1002X Cheat Sheet 2Documento1 paginaACC1002X Cheat Sheet 2jieboNessuna valutazione finora
- Accounting Cheat SheetsDocumento4 pagineAccounting Cheat SheetsGreg BealNessuna valutazione finora
- Finance Cheat SheetDocumento2 pagineFinance Cheat SheetMarc MNessuna valutazione finora
- Accounting Cheat SheetDocumento2 pagineAccounting Cheat Sheetanoushes1100% (2)
- General Accounting Cheat SheetDocumento35 pagineGeneral Accounting Cheat SheetZee Drake100% (5)
- Management Cheat SheetDocumento2 pagineManagement Cheat Sheetnightmonkey215100% (2)
- Corporate FinanceDocumento19 pagineCorporate FinanceBilal Shahid100% (4)
- Valuation Spreadsheet DCFDocumento8 pagineValuation Spreadsheet DCFHilal MilmoNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial Accounting: Tools For Business Decision-Making, Third Canadian EditionDocumento6 pagineFinancial Accounting: Tools For Business Decision-Making, Third Canadian Editionapi-19743565100% (1)
- Cheat Sheet For AccountingDocumento4 pagineCheat Sheet For AccountingshihuiNessuna valutazione finora
- Corporate Finance OutlineDocumento45 pagineCorporate Finance Outlinemweaveruga100% (5)
- Finance Interview PracticeDocumento126 pagineFinance Interview PracticeChetankabra100% (1)
- CFA Level 1 Corporate Finance - Our Cheat Sheet - 300hoursDocumento14 pagineCFA Level 1 Corporate Finance - Our Cheat Sheet - 300hoursMichNessuna valutazione finora
- 01 BIWS Accounting Interview ReferenceDocumento1 pagina01 BIWS Accounting Interview ReferenceSvinoPukasNessuna valutazione finora
- CFI AccountingfactsheetDocumento1 paginaCFI AccountingfactsheetHue PhamNessuna valutazione finora
- Cheat Sheet Exam 1Documento1 paginaCheat Sheet Exam 1Shashi Gavini Keil100% (2)
- Cfa Level I - Us Gaap Vs IfrsDocumento4 pagineCfa Level I - Us Gaap Vs IfrsSanjay RathiNessuna valutazione finora
- Private Equity Case StudyDocumento11 paginePrivate Equity Case StudyAmineBekkalNessuna valutazione finora
- Corporate Finance Outline, Spring 2013Documento60 pagineCorporate Finance Outline, Spring 2013Kasem Ahmed100% (1)
- Corporate Finance Cheat SheetDocumento3 pagineCorporate Finance Cheat Sheetdiscreetmike50Nessuna valutazione finora
- M&I Merger-Model-GuideDocumento66 pagineM&I Merger-Model-GuideSai Allu100% (1)
- Accounting Cheat Sheet FinalsDocumento5 pagineAccounting Cheat Sheet FinalsRahel CharikarNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 BIWS Valuation Metrics MultiplesDocumento2 pagine03 BIWS Valuation Metrics Multiplescarminat100% (1)
- Corporate Finance CheatsheetDocumento4 pagineCorporate Finance CheatsheetLynetteNessuna valutazione finora
- Business Valuation PresentationDocumento43 pagineBusiness Valuation PresentationAngus Sadpet100% (1)
- LBO In-Depth AnalysisDocumento12 pagineLBO In-Depth Analysisricoman19890% (1)
- LBO Valuation Model PDFDocumento101 pagineLBO Valuation Model PDFAbhishek Singh100% (3)
- Formulas and ConceptsDocumento7 pagineFormulas and Conceptscolen.anneNessuna valutazione finora
- Cheat SheetDocumento4 pagineCheat Sheetppxxdd666Nessuna valutazione finora
- R M R M R M R M: Time Value of MoneyDocumento8 pagineR M R M R M R M: Time Value of MoneyHenry JiangNessuna valutazione finora
- Midsem Cheat Sheet (Finance)Documento2 pagineMidsem Cheat Sheet (Finance)lalaran123Nessuna valutazione finora
- 12 & 13. Cost of CapitalDocumento5 pagine12 & 13. Cost of CapitalSatyam RahateNessuna valutazione finora
- Fin 3101Documento5 pagineFin 3101Park JiyeonNessuna valutazione finora
- CiiiDocumento19 pagineCiiimikelNessuna valutazione finora
- Finance NoteDocumento19 pagineFinance NoteHui YiNessuna valutazione finora
- FM NotesDocumento2 pagineFM NotesPhotos Back up 2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Formula Sheet-2nd QuizDocumento6 pagineFormula Sheet-2nd QuizEge MelihNessuna valutazione finora
- Corporate FinanceDocumento2 pagineCorporate Financeapi-294072125Nessuna valutazione finora
- O o o o o Total Costs Q X V + FC o Accounting Break-Even: Q (FC + D) / (P-V)Documento3 pagineO o o o o Total Costs Q X V + FC o Accounting Break-Even: Q (FC + D) / (P-V)Ana C. RichiezNessuna valutazione finora
- Corporate FinanceDocumento96 pagineCorporate FinanceRohit Kumar80% (5)
- Corporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionDa EverandCorporate Finance Formulas: A Simple IntroductionValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (8)
- FIN3101 Corporate Finance Practice Questions Topic: Capital BudgetingDocumento3 pagineFIN3101 Corporate Finance Practice Questions Topic: Capital BudgetingKelly KohNessuna valutazione finora
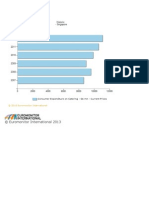
- Select A Chart Style Go : © Euromonitor International 2013Documento1 paginaSelect A Chart Style Go : © Euromonitor International 2013Kelly KohNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 4 Bodie 9eDocumento8 pagineChap 4 Bodie 9eKelly Koh100% (2)
- Case 1 TWG TeaDocumento2 pagineCase 1 TWG TeaKelly Koh33% (3)
- Nature, Scope and Importance of International OrganisationsDocumento13 pagineNature, Scope and Importance of International OrganisationsDr. Afroz Alam93% (115)
- Trading Models and ChecklistDocumento5 pagineTrading Models and Checklistthongxay thepphahuksaNessuna valutazione finora
- TD BANK-JUL-28-TD Economic-Teranet-National Bank House Price IndexDocumento1 paginaTD BANK-JUL-28-TD Economic-Teranet-National Bank House Price IndexMiir ViirNessuna valutazione finora
- Nism 5 A - Mutual Fund Exam - Practice Test 6 - Copy - PDF (Secured) - Adobe ReaderDocumento28 pagineNism 5 A - Mutual Fund Exam - Practice Test 6 - Copy - PDF (Secured) - Adobe ReaderNithin Varghzz100% (2)
- NISM QuestionsDocumento333 pagineNISM QuestionsAKshay100% (1)
- Securities LawDocumento5 pagineSecurities LawAnkitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Adr & GDRDocumento6 pagineAdr & GDRJaikishan BiswalNessuna valutazione finora
- Hotel Room RekapDocumento9 pagineHotel Room RekapSoehermanto DodyNessuna valutazione finora
- Daytrading 2 PDF FreeDocumento214 pagineDaytrading 2 PDF FreeMirco NardiNessuna valutazione finora
- Dow Jones Aiding Islamic InvestingDocumento3 pagineDow Jones Aiding Islamic InvestingRory CoenNessuna valutazione finora
- Sales Summary ChartDocumento18 pagineSales Summary ChartAginesh shawNessuna valutazione finora
- Rce Online TradingDocumento85 pagineRce Online TradingGangadhara Rao100% (1)
- Liam - Mescall - Mapping and PCA ProjectDocumento8 pagineLiam - Mescall - Mapping and PCA ProjectLiam MescallNessuna valutazione finora
- The Roles of Financial Market and Financial InstitutionsDocumento4 pagineThe Roles of Financial Market and Financial InstitutionstssuvroNessuna valutazione finora
- There Are Three Ways A Malaysian MNC Can Manipulate Its Global Presence To Increase ItsDocumento3 pagineThere Are Three Ways A Malaysian MNC Can Manipulate Its Global Presence To Increase ItsStudy ThingyNessuna valutazione finora
- An Introduction To Value at Risk (VAR)Documento6 pagineAn Introduction To Value at Risk (VAR)AkshatNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQ Parity KeyDocumento6 pagineMCQ Parity Key21070653Nessuna valutazione finora
- Investment and Portfolio ManagementDocumento2 pagineInvestment and Portfolio Managementadarsh1110Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kmart CaseDocumento22 pagineKmart CaseDamiano SciutoNessuna valutazione finora
- Investment Keywords July 26Documento9 pagineInvestment Keywords July 26Judy LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- Securities TradingDocumento51 pagineSecurities TradingameetavoNessuna valutazione finora
- Introducing Composite Mean Reversion and Trend Following Measures: The Aggregate "M" Indicator - CSSADocumento15 pagineIntroducing Composite Mean Reversion and Trend Following Measures: The Aggregate "M" Indicator - CSSAjacekNessuna valutazione finora
- Negotiable Debt InstrumentsDocumento5 pagineNegotiable Debt InstrumentsnewesterthNessuna valutazione finora
- The Profit and Loss Appropriation AccountDocumento4 pagineThe Profit and Loss Appropriation AccountSarthak GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- GMI Presentation July 2011Documento24 pagineGMI Presentation July 2011Jonathan NowakNessuna valutazione finora
- Parabolic SARDocumento2 pagineParabolic SARprivatelogic100% (2)
- Book of Greeks Edition 1.0 (Preview)Documento80 pagineBook of Greeks Edition 1.0 (Preview)fporwrwerNessuna valutazione finora
- BIS Report On Derivatives - Year End 2008Documento24 pagineBIS Report On Derivatives - Year End 2008Terry Tate BuffettNessuna valutazione finora
- Financial MarketsDocumento38 pagineFinancial MarketsGabbyNessuna valutazione finora
- Stocks and Their Valuation: Features of Common Stock Determining Common Stock Values Efficient Markets Preferred StockDocumento40 pagineStocks and Their Valuation: Features of Common Stock Determining Common Stock Values Efficient Markets Preferred StocksidhanthaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chap 001Documento21 pagineChap 001Ch Rajkamal100% (1)