Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Sheet 1
Caricato da
Abdalla Mohamed AbdallaCopyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Sheet 1
Caricato da
Abdalla Mohamed AbdallaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
BENHA UNIVERSITY BANHA FACULTY OF ENGINEERING MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT
M471 MACHINE DESIGN 4 YEAR MECHANICAL ENGINEERING DR. AL-ASSAL | ENG. AMRO | ENG. ABDALLA
TH
SHEET1: FORCE & STRESS ANALYSIS
1.
BICYCLE BRAKE LEVER
Problem Given Assumptions Determine the forces on the elements of the bicycle brake lever assembly shown during braking. The geometry of each element is known. The average humans hand can develop a grip force of about 267 N in the lever position shown. The accelerations are negligible. All forces are coplanar and 2D. A Class1 load model is suitable and static analysis is acceptable.
2.
HAND-OPERATED CRIMPING TOOL
Determine the forces on the elements of the crimping tool shown during a crimp operation. The geometry is known and the tool develops a crimp force of 8896 N at Given closure in the position shown. The accelerations are negligible. All forces are coplanar and 2D. A Class1 load Assumptions model is suitable and static analysis is acceptable. Problem
3.
AUTOMOBILE SCISSOR-JACK
Determine the forces on the elements of the scissors jack in the position shown. The geometry is known and the jack supports a force of P = 4448 N in the Given position shown. The accelerations are negligible. The jack is on level ground. The angle of the elevated car chassis doesnt impart an overturning moment to the jack. All Assumptions forces are coplanar and 2D. A Class1 load model is suitable and static analysis is acceptable. Problem
4. Problem Put all possible reactions due to the shown load.
5.
BICYCLE BRAKE ARM
Determine the forces acting in 3D on the bicycle brake arm in its actuated Problem position as shown. This brake arm has been failing in service and may need to be redesigned. The existing brake arm geometry is known and the arm is acted on by a cable Given force of 1046 N in the position shown. The accelerations are negligible. A Class1 load model is suitable and static analysis is acceptable. The coefficient of friction between the brake pad and Assumptions wheel rim has been measured and is 0.45 at room temperature and 0.4 at 66 c.
6.
LOADED ARM
Problem Given Determine the maximum normal and shear stresses at A. F = 900 N.
7. Problem Put the stresses induced at point J and H due to load F that is shown in the fig. (No numbers are needed).
8. Problem Put all possible loads at the corresponding points along the beam that may result the shown shear force and bending moment diagrams.
9. Problem Put all possible loads at the corresponding points along the beam that may result the shown shear force and bending moment diagrams.
10.
SUPPORTED ARM
Problem Given 1. What loads act at A and B? 2. Draw a free-body diagram of the bar. A bar is supported at A by a frictionless collar guide. At B it rests against a rough surface. Known forces act at D and E, as shown in fig.
DUE DATE: NEXT WEEK | 1,2 DAYS AFTER D.D.: -5% | 3,6: -10% | 7,21: -20% | >21: 0 PLAGIARISM = 0 | A4 PAPERS | NAME SECTION & SUB.; CLEAR ON THE 1ST PAPER ONLY
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- OAFISjLOEeiP Qrke KVoA Setting A Sales Goal AOSDocumento1 paginaOAFISjLOEeiP Qrke KVoA Setting A Sales Goal AOSAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimization of UHMWPE/graphene Nanocomposite Preparation by Single Supported Ziegler Natta Catalytic System Via RSMDocumento6 pagineOptimization of UHMWPE/graphene Nanocomposite Preparation by Single Supported Ziegler Natta Catalytic System Via RSMAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Investigation On Tensile Properties of Epoxy/graphene Nano-Platelets/ Carboxylated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber Ternary Nanocomposites Using Response Surface MethodologyDocumento12 pagineInvestigation On Tensile Properties of Epoxy/graphene Nano-Platelets/ Carboxylated Nitrile Butadiene Rubber Ternary Nanocomposites Using Response Surface MethodologyAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Engineering From Home: White PaperDocumento7 pagineEngineering From Home: White PaperAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Optimization of Polysulfone / Graphene Oxide / Polyethylene Glycol / Triaminopyrimidine by Using Response Surface MethodologyDocumento8 pagineOptimization of Polysulfone / Graphene Oxide / Polyethylene Glycol / Triaminopyrimidine by Using Response Surface MethodologyAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dd422i Specification Sheet EnglishDocumento4 pagineDd422i Specification Sheet EnglishAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydraulics and Conveyor Systems: TrainingDocumento3 pagineHydraulics and Conveyor Systems: TrainingAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Scrap Specification PDFDocumento62 pagineScrap Specification PDFr mohadiker0% (1)
- Research Grant Donors: ItidaDocumento5 pagineResearch Grant Donors: ItidaAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Industrial Hydraulic CircuitsDocumento16 pagineIndustrial Hydraulic CircuitskingkakingNessuna valutazione finora
- Trade MapDocumento1 paginaTrade MapAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- PublicationDocumento1 paginaPublicationAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- #Aimenjobs: R&D Senior Researcher in Advanced Materials: Polymer and CompositesDocumento2 pagine#Aimenjobs: R&D Senior Researcher in Advanced Materials: Polymer and CompositesAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- RSC Advances: PaperDocumento5 pagineRSC Advances: PaperAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Course SpecificationDocumento93 pagineCourse SpecificationAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- TKT 2003Documento2 pagineTKT 2003Abdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- W 4 Yte 54 SyDocumento2 pagineW 4 Yte 54 SyAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- مركز لخدمات الكمبيوترDocumento11 pagineمركز لخدمات الكمبيوترmax_slamNessuna valutazione finora
- JHVJHVDocumento5 pagineJHVJHVAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- ErwgrwgwDocumento5 pagineErwgrwgwAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching Statement: Roberto Silveira Silva FilhoDocumento2 pagineTeaching Statement: Roberto Silveira Silva FilhoAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Baba Yevsky 1973Documento22 pagineBaba Yevsky 1973Abdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- ﻝﺎﻤﻟﺍ ﺓﺪﻳﺮﺟ ﺭﺎﺒﺧﺃ ﻢﻫﺃ (Alltopstories - 1.Aspx/) : ﻙﻮـــﻨﺑ (Section/12/1/بنـــوك/)Documento9 pagineﻝﺎﻤﻟﺍ ﺓﺪﻳﺮﺟ ﺭﺎﺒﺧﺃ ﻢﻫﺃ (Alltopstories - 1.Aspx/) : ﻙﻮـــﻨﺑ (Section/12/1/بنـــوك/)Abdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Creating Effective Scientific Figures For PublicationDocumento24 pagineCreating Effective Scientific Figures For PublicationAbdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Jin 2013Documento9 pagineJin 2013Abdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Kurapati 2012Documento3 pagineKurapati 2012Abdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Rwgtrygr 5Documento5 pagineRwgtrygr 5Abdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Schedule of Student Affairs Required Documents - Minutes #1Documento2 pagineSchedule of Student Affairs Required Documents - Minutes #1Abdalla Mohamed AbdallaNessuna valutazione finora
- Uspesna PrezentacijaDocumento13 pagineUspesna Prezentacijaboban72Nessuna valutazione finora
- Japan VIsa Application SampleDocumento2 pagineJapan VIsa Application SampleBudi Utami Wibawani80% (5)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Door and Window Seal Impact On Acoustic and Vi-Brational Behavior of Aerodynamic NoiseDocumento8 pagineDoor and Window Seal Impact On Acoustic and Vi-Brational Behavior of Aerodynamic NoiseNivedita SahooNessuna valutazione finora
- Problem Set A: Electrostatic FieldsDocumento2 pagineProblem Set A: Electrostatic FieldsfsfsfsNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Simulation of The Packing of Fine ParticlesDocumento9 pagineComputer Simulation of The Packing of Fine ParticlesahmedsidalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Warp Drive PaperDocumento14 pagineWarp Drive PapercarsongbakerNessuna valutazione finora
- AI MI Catalogue - A4 PDFDocumento26 pagineAI MI Catalogue - A4 PDFAbhishek SinhaNessuna valutazione finora
- CIV2263 - Water Systems - S1 2021: My UnitsDocumento9 pagineCIV2263 - Water Systems - S1 2021: My UnitsEngr.Towhidul IslamNessuna valutazione finora
- E MC2 ProofDocumento5 pagineE MC2 ProofKartikeya BagraNessuna valutazione finora
- Numerical Study of Transient and Steady State Natural Convection and Surface Thermal Radiation in A Horizontal Square Open CavityDocumento19 pagineNumerical Study of Transient and Steady State Natural Convection and Surface Thermal Radiation in A Horizontal Square Open CavitygovindNessuna valutazione finora
- EN 295 - Part 3 - 91Documento34 pagineEN 295 - Part 3 - 91龙琦Nessuna valutazione finora
- CH 05 ISM 8eDocumento38 pagineCH 05 ISM 8eevilgnsNessuna valutazione finora
- Modeling of Low Voltage Switchgear and Controlgear Assemblies Using Computational Fluid Dynamics - 465-147668798701-06Documento6 pagineModeling of Low Voltage Switchgear and Controlgear Assemblies Using Computational Fluid Dynamics - 465-147668798701-06Bao LamNessuna valutazione finora
- A New Deformable Catenary Element For The Analysis of Cable Net Structures - 2006Documento9 pagineA New Deformable Catenary Element For The Analysis of Cable Net Structures - 2006Truong Viet HungNessuna valutazione finora
- Solution To Problem 555 - Unsymmetrical Beams - Strength of Materials ReviewDocumento5 pagineSolution To Problem 555 - Unsymmetrical Beams - Strength of Materials ReviewRehan Hakro100% (1)
- Seismic Design of Steel StructuresDocumento55 pagineSeismic Design of Steel StructuresAndrea LitzNessuna valutazione finora
- Transient Heat ConductionDocumento21 pagineTransient Heat Conductionaranna lalNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 Physics Notes Ch02 Electrostatic Potential and CapacitanceDocumento2 pagine12 Physics Notes Ch02 Electrostatic Potential and CapacitanceKOMAL NAVARIYANessuna valutazione finora
- Liquefaction Analysis - PM4sand - 025936Documento8 pagineLiquefaction Analysis - PM4sand - 025936Krlo AguindaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fresnel BiprismDocumento6 pagineFresnel BiprismRahul SrivastavaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1.docx (ME-102)Documento13 pagineAssignment 1.docx (ME-102)umair rasheedNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Mechanics-1Documento6 pagineFluid Mechanics-1Athar SajjadNessuna valutazione finora
- Roark's Formulas For Stress and Strain - REF.09Documento64 pagineRoark's Formulas For Stress and Strain - REF.09tylerstearnsNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnostic Geas 2016 2ndsemDocumento4 pagineDiagnostic Geas 2016 2ndsemjj012586Nessuna valutazione finora
- Notes On Q M C Delta TDocumento2 pagineNotes On Q M C Delta TDing30180Nessuna valutazione finora
- P11 Practice 7 SolnsDocumento7 pagineP11 Practice 7 SolnsajjagottuNessuna valutazione finora
- General Description of FEM and Its Engineering Applications: BY Dr. Srinivasa C.VDocumento29 pagineGeneral Description of FEM and Its Engineering Applications: BY Dr. Srinivasa C.VDr. Srinivas Chikkol VenkateshappaNessuna valutazione finora
- Course Title: Mechanics of Materials Course Code: MM-205 Year: S.EDocumento13 pagineCourse Title: Mechanics of Materials Course Code: MM-205 Year: S.ESahar Batool QaziNessuna valutazione finora
- Inductance - Inductors - Energy StoredDocumento2 pagineInductance - Inductors - Energy Storedsteve_yNessuna valutazione finora
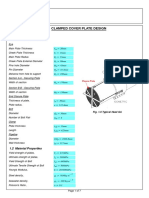
- Clamped Cover Plate DesignDocumento7 pagineClamped Cover Plate DesignChiedu OkonduNessuna valutazione finora
- The High Strength Friction GripDocumento10 pagineThe High Strength Friction GripfiarNessuna valutazione finora
- QNM V 2018Documento8 pagineQNM V 2018MatejaBoskovicNessuna valutazione finora