Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Trigeminal Nerve
Caricato da
AbdulAziz BaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Trigeminal Nerve
Caricato da
AbdulAziz BaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Trigeminal Nerve
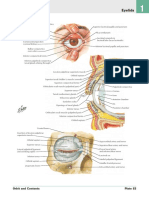
Opthalmic Nerve: Sensory Leaves cranium through superior orbital fissure Supplies eyeball, lacrimal glands, mucous membranes of nose and paranasal sinuses, skin of forehead, eyelids, nose Before it enters the fissure, it gives 3 main branches:
Maxillary Nerve
Mandibula r Nerve
.: Nasociliary N Travels along medial border of orbital roof (giving branches to nasal cavity and skin : then branches to
Frontal Nerve. Supratrochlear N. : supplies skin & conjunctiva of medial 1/3 of upper eyelid, skin over lower and mesial aspects of forehead
Lacrima l Nerve
Supraorbital N.: upper eyelid, scalp as far as parietal bone and lamboid suture
supplies lateral part of upper eyelid and adjacent skin
Anterior ethmoidal: gives internal nasal nerve that supplies m.m. of anterior part of septum and lateral wall of nasal cavity
External nasal N.: skin over tip &ala of nose
Posterior ethmoidal N.: ethmoidal and sphenoid sinuses
Infratrochlear N.: skin of lacrimal sac and lacrimal caruncle
Long ciliary N.: supplies iris and cornea
Ciliary ganglia: has sensory nerves that travel to eyeball by short ciliary N.
Trigeminal Nerve
Opthalmic :Nerve
Zygomatic Nerve: travels anteriorly, enters orbit via inferior orbital fissure
Maxillary Nerve: Arises from middle of trigeminal nerve Pure sensory Inside cranium gives branch to middle meningeal N. Exits through foramen rotundum, crosses uppermost plates of sphenoid and palatine bone, gives branches:
Mandibula r Nerve
Zygomatico - temporal N.: supplies skin on side of forehead
Zygomaticofacial N.: supplies skin on prominence of cheek
Spheno-palatine ganglia (Pterygopalatine N.): communicates with pterygopalatine ganglion, its branches:
Posterior superior Alveolar N.: travels in post. Wall of max. sinus supplies max. sinus, alveoli, PDL, pulp of max. molars
Orbital branch: supplies periosteum of orbit
Nasopalatine branch: Passes across roof of nasal cavity downward and forward, enters incisive canal then into oral cavity by incisive foramen (gives sensation to palate in premaxilla; anterior teeth)
Palatine : branch Greater palatine (anterior) branch: Supplies palatal soft tissues & bones as far anteriorly as 1st premolar (meets terminal fibers of nasoplatine)
Pharyngeal : branch
Lesser palatine (middle and posterior) branch: Middle: innervation of soft palate Posterior: tonsil region
Then the maxillary nerve angles laterally and enters through the groove on the posterior surface of the maxilla enters orbit via the inferior orbital fissure >> then it goes through the inferior orbital canal and becomes inferior orbital N., it gives branches in the canal:
Middle Superior Alveolar Nerve: MSA Supplies sensory innervation of max. premolars & maybe the mesiobuccal of the 1st molar and the periodontal tissues, buccal soft tissue and bone in premolar area
Anterior Superior Alveolar Nerve: ASA Descends within the wall of the max. sinus, provides pulpal innervation of anterior teeth and sensory innervation of surrounding periodontal tissues, buccal bone, mucous membranes
Nerves from superior Alveolar N. (anterior + middle + posterior) form a dental plexus and gives 3 N., each nerve is accompanied with an artery: Dental N.: enters tooth through apical foramen, supply pulpal innervation Interdental N.: travel through interdental septum, supply PDL then they emerge at crest of alv. Bone and supply interdental and buccal gingiva Interradicular N.: within interradicular septum, supply PDL of roots, terminate in PDL at furcation areas Then the infraorbital N. exits through the infraorbital foramen on to face & gives terminal branches:
Inferior palpebral branches: Skin of lower eyelid with sensory innervation
Exterior Nasal branches: Skin on lateral aspect of nose
Superior labial branches: Skin & mucous membranes of upper lip
Trigeminal Nerve
:Mandibular Nerve Mixed: 2 roots; large sensory root and small motor root Both roots unite outsie the skull and then divide again into a small anterior and a larger posterior division
Maxillary Nerve
Opthalmic :Nerve
Undivided Branch: Leaves foramen ovale and gives branches: Small motor branches to tensor tympani and tensor veli palatini Nervous spinosus (meningeal branch) along with middle meningeal artery
Medial ptyergoid N.: to medial ptyergoid muscle
:Anterior Division Runs forward under lateral pterygoid muscle then passes between the 2 heads of the muscle, it gives branches Buccal Nerve (long buccal N.)(buccinator N.): Sensory to skin over buccinator muscle and buccal gingiva of mandibular molars and mucobuccal fold DOES NOT innervate buccinator muscle (which is supplied by )facial nerve
:Motor innervation Deep temporal N.: supplies tempoarlis muscle Masseter N.: to masseter muscle Lateral pterygoid N.: to lateral pterygoid muscle
Posterior Division: (last branch of mandibular N.) Mostly sensory with smaller motor component Descends downward and medial to lateral pterygoid muscle It gives branches:
.:Auriculotemporal N Travels along upper part of parotid then crosses posterior portion of zygomatic arch Provides sensory Communicates with facial N. supplying skin over facial N. branches Communicates with otic ganglion Supplies skin over temporal region, ear, TMJ
.:Inferior Alveolar N Descends medial to lat. Pterygoid muscle, laterposterior to lingual N. between medial surface of ramus and sphenomandibular ligament,
Lingual N.: travels medial to lateral ptyergoid then downward between ramus and medial pterygoid muscles, runs anteriorly and medial to inferior alveolar nerve (both are parallel), continues downward and forward deep to pterygomandibular raphe and below attachment of superior constrictor of pharynx to reach side of base of tongue & behind 3rd molar, goes anterior across muscles of tongue to wharton's duct and sublingual gland Supplies general &taste sensation of ant. 2/3 of tongue, sensory innervation of floor of mouth and lingual gingiva *chorda tympani of facial N. supplies taste it runs along with ling. N.
Enters mandibular canal along with inf. Alv. Artery and vein, as far as mental foramen., the artery is ant. To the nerve The dental plexus supplies mand. Posterior teeth The inf. Alv, N. terminally divides into: Incisive N.: supplies incisors, canines, 1st molar Mental N.: 3 branches; supplies skin of chin, lip and m.m. of lip
Before entering the mandibular foramen it gives mylohyoid N.: Motor to mylohyoid & anterior belly of digastric muscle Sensory to skin on mental protuberance Sensory innervation to mand. incisors
Done by: Hanan Al-Johani, if any mistakes are found kindly inform me and they will be fixed immediately
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (120)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- The Nunology of The Pineal Gland by DR - NEB HERUDocumento107 pagineThe Nunology of The Pineal Gland by DR - NEB HERUNeb Heru95% (41)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Anatomy Reda Notes PDFDocumento197 pagineAnatomy Reda Notes PDFTamjid Khan100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Face and ScalpDocumento31 pagineThe Face and ScalpRobin TolentinoNessuna valutazione finora
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The OrbitDocumento115 pagineThe OrbitPhilip McNelson100% (1)
- Cranial Nerves MCQDocumento12 pagineCranial Nerves MCQViweka Sarangi100% (8)
- Trigeminal NerveDocumento126 pagineTrigeminal NerveAsha Praveena100% (4)
- CNS Mcqs PDFDocumento12 pagineCNS Mcqs PDFSindhi Waseem BalochNessuna valutazione finora
- Nonsurgical Lip and Eye Rejuvenation Techniques: Gabriella Fabbrocini Maria Pia de Padova Antonella TostiDocumento125 pagineNonsurgical Lip and Eye Rejuvenation Techniques: Gabriella Fabbrocini Maria Pia de Padova Antonella Tostikleidi8586% (7)
- Head and NeckDocumento11 pagineHead and NeckdrsamnNessuna valutazione finora
- Nerve Supply of Head and NeckDocumento99 pagineNerve Supply of Head and NeckKishor Bhandari100% (2)
- Anatomy of Eyelid: Presenter:-Dr. Vijayalaxmi Moderator:-Dr. SanjanaDocumento49 pagineAnatomy of Eyelid: Presenter:-Dr. Vijayalaxmi Moderator:-Dr. SanjanaRidhi Bhandari100% (1)
- Trigeminal NerveDocumento62 pagineTrigeminal NervevimalspiderNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigeminal NerveDocumento131 pagineTrigeminal NerveLavanya KalapalaNessuna valutazione finora
- FaceDocumento74 pagineFacehazell_aseronNessuna valutazione finora
- Trigeminal and Facial NerveDocumento121 pagineTrigeminal and Facial NerveFadilaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cranial NervesDocumento90 pagineCranial NervesGaVee AgranNessuna valutazione finora
- Aiims May 2009Documento50 pagineAiims May 2009Gowri ShankarNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Exam in Topographical AnatomyDocumento50 pagineFinal Exam in Topographical Anatomytastyk100% (2)
- Trigeminal NerveDocumento25 pagineTrigeminal Nerveبراءة أحمد السلاماتNessuna valutazione finora
- Anastesi TopikalDocumento10 pagineAnastesi TopikallamhotfarmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomia FacialDocumento10 pagineAnatomia FacialIgor NatanyoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomi EyelidDocumento9 pagineAnatomi EyelidFelyana GunawanNessuna valutazione finora
- EDentistryy Textbook of Trigeminal NeuralgiaDocumento257 pagineEDentistryy Textbook of Trigeminal NeuralgiaLily BlossomNessuna valutazione finora
- Atlas of Human Anatomy - Including Student Consult Interactive Ancillaries and GuidesDocumento11 pagineAtlas of Human Anatomy - Including Student Consult Interactive Ancillaries and GuidesAndrijana StevancevicNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of The Rat The Nervous SystemDocumento61 pagineAnatomy of The Rat The Nervous SystemBelleopsisNessuna valutazione finora
- Nerves of The OrbitDocumento6 pagineNerves of The OrbitAshifa SahiraNessuna valutazione finora
- The Trigeminal and Facial NervesDocumento7 pagineThe Trigeminal and Facial NervesJose CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- Applied Anatomy - Trigeminal NerveDocumento8 pagineApplied Anatomy - Trigeminal NervefrabziNessuna valutazione finora
- InfraTemporal FossaDocumento34 pagineInfraTemporal FossaAhmed JawdetNessuna valutazione finora
- Quick Review PDFDocumento154 pagineQuick Review PDFDr PenCaster100% (1)