Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Document 1
Caricato da
Kashiflonly MasoodboyDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Document 1
Caricato da
Kashiflonly MasoodboyCopyright:
Formati disponibili
M.M. 6.1 GENERAL MECHANICAL MAINTENANCE L T P 3 0 8 1.
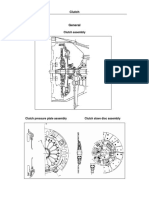
Lubrication (30%) a) Lubrication Principles: Friction, wear, necessity of Lubrication, types of Lubrication dry Lubrication, boundary Lubrication, hydrodynamic Lubrication, Sliding bearings, rolling element bearings, squeeze fillers, materials for bearings, Functions of lubricant. b) Lubricants: Sources, composition, additions, types of lubricants and their grades, standards tests for physical and chemical properties of lubricants, selecting the lubricant under various conditions. c) Lubricant application System: Sight feed, wick, forced, splash, gravity, points of lubrication, frequency, type and precaution for lubrication of machine tools, electric motors, power transmission. 2. Elements of Mechanical Maintenance: General features & types of bearings, clutches, brakes and couplings, Belt, chain and gear drives. Different types used in power transmission. Care and maintenance of the above elements, Trouble Shooting causes and remedies. (20%) 3. Piping and Hydraulic Systems: (20%) a) Cutting, bending, joining, sealing and testing of pipes and tubes, Pipe joints flexible soldered, screwed, flanged, identification of colour codes and markings b) Hydraulic circuits, circuit components, valves for controlling liquids, valve for hydraulic circuits. Changing the hydraulic fluids, Diagnosis, location and rectification of faults. The example of logical fault diagnosis, removal, servicing and refitting of fluid couplings. 4. Material Handling Equipment: (30%) a) Interplant transportation facilities and handling equipment, types of material handling equipment, Hoisting equipment, General characteristics for surface and overhead transporting facilities, Application of materials handling equipment. b) Hoisting appliances Chains and ropes, pulleys, sprockets and rope drums, Hooks forged, solid triangular, hinged triangular, Crane grabs for unit and piece loads, Electric lifting magnets, Arresting gear shock brakes, controlled brakes e.g. band, cone and disc brakes, Centrifugal brakes, Elevators cage elevators, stackers. List of Practicals 1. Use of lubricating oil equipment like oil gun, grease gun etc. 2. Maintaining correct level of oil. 3. Removing old lubricant, clearing and replenishing the machines with fresh lubricant. 4. Study of Pressure lubricating system. 5. Study of gearbox. 6. Sledding of hydraulic breaks system. 7. Clutch installation after removing the cracks. 8. Study of valves in hydraulic system. 9. Familiarization with grading of lubricating oil. 10. Joining a flexible pipe and checking its leakage in any hydraulic system.
M.M. 6.5
RESTORATION OF PARTS & MAINTENANCE MANAGEMENT
L T P 4 0 4 1. Maintenance: Concept of preventive and breakdown maintenance general maintenance procedure stepwise. Common maintenance tools, applications, devices, handling facilities and measuring instruments. (5%) 2. Fits and Tolerances: Common fits and tolerances as per IS: 919-1963, commonly used fits for various applications. Design tolerances on key width, shaft & housing keyway and diameter, different systems of spline fitting. (10%) 3. Maintenance Stages: Inspection, small repairs, medium repairs and complete overhaul. Details of work in each stage for maintenance of different metal cutting, metal working and material handling equipments. (10%) 4. Restoration of Machine parts: General restoration of parts likes0 bed ways and saddle ways of lathe, Guide ways of a plain milling machine. Clamping plates and wedges, worn out keyways and Splines, restoration of machine parts by welding, moralization and chromium plating. (15%) 5. Major overhaul of machine tool: Schedule of complete overhaul of a lathe machine giving the work distribution, planning and repair estimate. Common breakdowns in lathe, their causes and remedies, repairing the tailstock, threejaw chuck, machine spindle and Gearbox. (15%) Alignment testing of the repaired lathe. 6. Maintenance Personal management: Maintenance trades training, Maintenance supervisory training, Evaluation of maintenance jobs, Incentive payment to maintenance workers (10%) 7. Planning and Scheduling Maintenance Work: Work authorization and control Standard times for maintenance work, Work measurement (10%) 8. Maintenance stores and control: Maintenance stores control, Maintenance stores rooms, Inventory (5%) 9. Critical path method /PERT: Introduction to CPM/PERT, Sequence of Events Application of CPM/PERT in overhauling of a lathe (15%) 10. Maintenance Manuals and Reports : Need for a maintenance manual, Contents of manual, Maintenance manual topics, Manual writing or reporting (5%) LIST OF EXPERIMENTS: 1. Reconditioning of bed-ways of a lathe. 2. Reconditioning of knee way, table ways, column way of a milling machine. 3. Dismantling, repairing and assembling of a tailstock 4. Dismantling, repairing and assembling of a gearbox of a lathe. 5. Disassembling, repairing and assembling of apron of lathe. 6. Testing of a repaired lathe. 7. Dismantling, repairing and assembling of a drilling machine. 8. Dismantling, repairing and assembling of shapers.
MM-602
I.C. Engines
L T P 3 2 1. Air cycles: Thermodynamic cycles, concept of reversibility of cycle, thermal efficiency and air standard efficiencies, Carnot cycle efficiency and its applications. Otto, Diesel and dual combustion cycles calculation of air standard efficiencies. Effect of compression ration. (25%) 2. Principles of I.C. Engines: Identification, location, functions and material of main parts, concept of terms like bore, stroke, dead centers, crank-throw, piston, displacement, mean piston speed, compression ratio and clearance volume. Working of two stroke and four stroke petrol and diesel engines- single cylinder and multi cylinder engines, valve timing diagrams, classifications and application of I.C. Engines. Introduction to Rotary Wankle engine. (25%) 3. Fuel System: Carburetion: Concept of carburetion, requirements of air fuel mixtures at various load conditions, simple carburetor and its limitations, modifications required in a simple carburetors to overcome the limitations (choke, idling devices, compensating jet, air bleed, solex carburetor, accelerating pump, principle and methods of fuel injection in diesel engines, control of fuel supply and types of nozzles. Working of a fuel injection pump. Fuel filters and mechanical fuel lift pump. (15%) 4. Ignition Systems: Importance of Ignition timing and ignition advance, battery ignition and Magneto ignition, Transistorized ignition. (10%) 5. Cooling of I.C. Engines: Necessity of cooling, cooling systems, functions of thermostat, anti-freezing mixtures. (10%) 6. I.C. Engine Testing: Calculation of I.H.P., B.H.P. and efficiencies Morse test, Mechanical, thermal, overall and relative efficiencies, heat balance charts. (15%) LIST OF PRACTICALS (I.C. ENGINES) 1. Study of various parts of I.C. Engines by mean of old condemned parts. 2. Draw the valve-timing diagram of a Diesel engine-single cylinder. 3. Study the working of a Solex carburetor by dismantling oil and locate various circuits. 4. Study the working of a carburetor used in scooter/motor cycle by dismantling it. 5. Study a Micro type fuel injection pump by dismantling it. 6. Study a Micro type fuel injector by dismantling it. 7. Study a Mechanical fuel lift pump by dismantling it. 8. Study a distributor of a 4-Cylinder petrol engine. 9. Locate and draw the cooling circuit of a multi cylinder engine and study the construction of the radiator. 10. Locate and draw the lubricating circuit of a single cylinder diesel engine. 11. To find out the I.H.P. by Morse Test. 12. To find out B.H.P. and specific fuel consumption of a given engine and draw graph of B.H.P. V/s fuel consumption specific fuel consumption and Mechanical efficiency. 13. Study the construction and working of reciprocating of compressor.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Ac MotorsDocumento76 pagineAc MotorsamarnathavulaNessuna valutazione finora
- NsksuppreccatlDocumento107 pagineNsksuppreccatlNaveen KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- 11312D 001 R004 Vertical Turbine Pump Motors PDFDocumento75 pagine11312D 001 R004 Vertical Turbine Pump Motors PDFJosé RamírezNessuna valutazione finora
- Diseño Pasajuntas 1Documento37 pagineDiseño Pasajuntas 1dorbarel100% (2)
- Reconditioning of Bearing Surfaces and Shaft Ends (4153) : PivotDocumento15 pagineReconditioning of Bearing Surfaces and Shaft Ends (4153) : PivotTASHKEEL100% (1)
- Factor de Velocidad PetrocanadaDocumento2 pagineFactor de Velocidad PetrocanadasdfasdfNessuna valutazione finora
- Makerbot Replicator 2 Aluminum Z-Axis Stage Upgrade: InstructablesDocumento10 pagineMakerbot Replicator 2 Aluminum Z-Axis Stage Upgrade: InstructablesViktar SamuelNessuna valutazione finora
- NBC Training Report - Ball Bearing DivisionDocumento51 pagineNBC Training Report - Ball Bearing DivisionBrandon Johnson100% (6)
- Failure of Cooling Fan Shaft BearingsDocumento7 pagineFailure of Cooling Fan Shaft BearingsGuru Raja Ragavendran NagarajanNessuna valutazione finora
- PDF EnglishDocumento36 paginePDF EnglishSanti CheewabantherngNessuna valutazione finora
- CEP SamalkotDocumento96 pagineCEP SamalkotkukugargNessuna valutazione finora
- Ajax Preventative Maintenance ManualDocumento7 pagineAjax Preventative Maintenance ManualJavier PalaciosNessuna valutazione finora
- Dme Model 2Documento6 pagineDme Model 2YashwanthI-StyleKuttiNessuna valutazione finora
- Manual de Reparacion Motor Jac 4da1 Parte 4Documento100 pagineManual de Reparacion Motor Jac 4da1 Parte 4Anonymous iBenl3mNNessuna valutazione finora
- 2019 - Mumbai MMDDocumento93 pagine2019 - Mumbai MMDandy marinerNessuna valutazione finora
- High Efficiency Pumps PsDocumento2 pagineHigh Efficiency Pumps PsBehnamNessuna valutazione finora
- GEAR PUMP CATALOG - Transfer Pump Bunker To Settling - Hal 3Documento5 pagineGEAR PUMP CATALOG - Transfer Pump Bunker To Settling - Hal 3Izal Slanker's ObengblimbingkoncirengNessuna valutazione finora
- Blanket Wash Up DeviceDocumento12 pagineBlanket Wash Up DeviceSonia NaickerNessuna valutazione finora
- Ingersoll Rand Compressor Manual SS3L3Documento36 pagineIngersoll Rand Compressor Manual SS3L3Castoriadis100% (2)
- Sweeraj ProfileDocumento2 pagineSweeraj ProfileSwapnil NarkhedeNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanical Puller Catalog - EUDocumento20 pagineMechanical Puller Catalog - EUSergiSerranoNessuna valutazione finora
- PVV 540 PumpDocumento14 paginePVV 540 PumpMONANessuna valutazione finora
- Mahle MackVolvo1 PDFDocumento82 pagineMahle MackVolvo1 PDFAlexis SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- Sesv8010 Antifriction BearingsDocumento160 pagineSesv8010 Antifriction BearingsFrancisco Abarca G.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Maintenance Manual Intervals For ForkliftDocumento15 pagineMaintenance Manual Intervals For ForkliftMoataz SamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Brochure Browning MountedDocumento3 pagineBrochure Browning MountedPdroGsus Abregú TerronesNessuna valutazione finora
- Installation Ring Gear Installation ManualDocumento31 pagineInstallation Ring Gear Installation Manualscott100% (1)
- GN - 1.04 - Bearing Guidance Notes-SCIDocumento7 pagineGN - 1.04 - Bearing Guidance Notes-SCIraaaaajjjjjNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.0 2.0 The Importance of Maintenance 3.0 Maintenance Activites 4.0 Types of MaintenanceDocumento11 pagine1.0 2.0 The Importance of Maintenance 3.0 Maintenance Activites 4.0 Types of MaintenanceIstiQamahh MuhamadNessuna valutazione finora