Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Mataia New Era Europe
Caricato da
Mataia WatkinsDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Mataia New Era Europe
Caricato da
Mataia WatkinsCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Mataia Watkins
New Era Review
12.5.11
Blackmon
4th
Europe Germanic kingdoms invaders that organized successor states in place of Roman empires. Although did not establish a tightly centralized monarchy, they were successful. Influence of Christianity As some missionaries from Rome traveled out many tribes began to convert to Christianity. First kingdom that did was the Franks. Rise of the Franks Clovis Franks Although survived only for a short time, the Franks profoundly influenced the political, social, and cultural development of western Europe. Created a firm alliance with the western Christian church and helped Roman Christianity maintain its cultural and religious primacy in western Europe Clovis - Under Clovis, the Franks became the preeminent military and political power in western Europe. Organized campaigns to eliminate enemies. Transformed empire into most powerful and dynamic state of western Europe. St. Benedict and monasteries St. Benedict of Nursia strengthened the early monastic movement by providing it with disicipline and a sense of purpose. In 529, St. Benedict prepared a set of regulations known as Benedicts Rule for the monastic community that he had founded at Monte Casino, near Rome. Carolingian Empire -Royal clan established by Charlemagne, who expanded the Carolingian Empire into Spain, Bavaria, and Northern Italy. Charlemagne - 800s AD - built the first real empire in Europe since Rome. Became known as Charlemagne, Charles the Great. Would be called the Holy Roman Empire (north Italy, Germany, Belgium, and France) and brought back centralized government and Rome prestige. Charlemagne promoted art and education with the main focus on religion. Counts & Missi Domenici - "Envoys of the lord ruler," the noble and church emissaries sent out by Charlemagne. Feudalism - a set of legal and military customs in medieval Europe that flourished between the 9th and 15th centuries, which, broadly defined, was a system for ordering society around relationships derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labor. In order: kings, lords (lords, knights), vassals (lesser lords, lesser knights), and peasants (serfs). Lord- Vassal relationship - Once the commendation ceremony was complete, the lord and vassal were now in a feudal relationship with agreed-upon mutual obligations to one another. The vassal's principal obligation to the lord was to "aid", or military service. Using whatever equipment the vassal could obtain by virtue of the revenues from the fief, the vassal was responsible to answer to calls to military service on behalf of the lord. This security of military help was the primary reason the lord entered into the feudal relationship. In addition, the vassal could have other obligations to his lord, such as attendance at his court, whether manorial, baronial, both termed court baron, or at the king's court itself. Fief - A grant of land from a lord to a vassal. Manorialism - an essential element of feudal society, medieva las the organizing principle of rural economy that originated in the villa system of the Late Roman Empire, was widely practiced in western and parts of central Europe, and was slowly replaced by the advent of a money-based market economy and new forms of agrarian contract.
Three-field system Common way that farmers in Middle Ages rotated crops so that there was always one empty field Holy Roman Empire - Central and western European kingdom created at the Treaty of Verdun in in 843 and lasting until 1806. Vikings-Muslims-Magyars Magyars - Hungarian invaders who raided towns in Germany, Italy, and France in the ninth and tenth centuries. Muslims - During this time Muslim Turks were gaining control of the Holy Lands and threatening Byzantium. Vikings - the Norse explorers, warriors, merchants, and pirates who raided, traded, explored and settled in wide areas of Europe, Asia and the North Atlantic islands from the late 8th to the mid-11th century William the Conqueror - In 1066 Norman William the Conqueror invaded England (king died without heir)and defeated the Saxon king at the Battle of Hastings. Battle of Hastings 1066 - Battle where William the Conqueror defeated the Saxon king. Because William had French royal blood there would be much confusion over land rights during the next 400 years. Bayeux Tapestry - an embroidered clothnot an actual tapestrynearly 70 meters (230 ft) long, which depicts the events leading up to the Norman conquest of England concerning William, Duke of Normandy and Harold, Earl of Wessex, later King of England, and culminating in the Battle of Hastings. Magna Carta 1215 - an English charter, originally issued in the year 1215 and reissued later in the 13th century in modified versions, which included the most direct challenges to the monarch's authority to date. The charter first passed into law in 1225. The 1297 version, with the long title (originally in Latin) The Great Charter of the Liberties of England, and of the Liberties of the Forest, still remains on the statutebooks of England and Wales. Three Estates - Term for the social classes of the spiritual estate (clergy), the military estate (feudal nobles), and the estate of peasants and serfs. Lay Investiture Controversy - Lay investiture was the appointment of bishops, abbots, and other church officials by feudal lords and vassals. No one questioned a king or noble's right to grant a bishop or abbot a fief and have him become a vassal, but the church did object to kings and nobles naming bishops or abbots. This lead to the controversy over weather the Pope or King controlled the empire. Vernacular literature - The language of the people; Martin Luther translated the Bible from the Latin of the Catholic church into the vernacular German. Black Death (plague) 1340s AD - one of the most devastating pandemics in human history, peaking in Europe between 1348 and 1350. Of several competing theories, the dominant explanation for the Black Death is the plague theory, which attributes the outbreak to the bacterium Yersinia pestis. Thought to have started in China, it traveled along the Silk Road and reached the Crimea by 1346. From there, probably carried by Oriental rat fleas living on the black rats that were regular passengers on merchant ships, it spread throughout the Mediterranean and Europe. Hundred Years War - Conflict between France and England (1337-1453) over control of lands in France. Guilds - Socially significant groups of craftspeople who regulated the production, sale, and quality of manufactured goods.
Hanseatic League middle class - the members of the upper class of the free imperial cities Hamburg, Bremen and Lbeck since the middle of the 17th century after the end of the Hanseatic league. A trading alliance in northern Europe in existence between the 13th and 17th centuries. Venice -dominated Mediterranean trade - middleman to Arab spice trade Renaissance- rebirth of classical thought - a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. - Enabled by wealth of Italian city-states and Church - Transmission of technology, science, math to West through Arabs in Spain and Crusades
Crusades First Crusade 1096 AD only success est. 4 Crusader states - a military expedition by Western Christianity to regain the Holy Lands taken in the Muslim conquest of the Levant, ultimately resulting in the recapture of Jerusalem. Fourth Crusade- sack of Constantinople - was originally intended to conquer Muslimcontrolled Jerusalem by means of an invasion through Egypt. Instead, in April 1204, the Crusaders of Western Europe invaded and conquered the Christian (Eastern Orthodox) city of Constantinople, capital of the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire). This is seen as one of the final acts in the Great Schism between the Eastern Orthodox Church and Roman Catholic Church - Little impact on Muslim world - Opened up Europe to new foods, spices, technologies
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Chapter 9 - Emerging Europe and The Byzantine EmpireDocumento30 pagineChapter 9 - Emerging Europe and The Byzantine EmpireJonathan Daniel KeckNessuna valutazione finora
- Middle Ages - 1 PDFDocumento5 pagineMiddle Ages - 1 PDFOjas GuptaNessuna valutazione finora
- Who Were The Franks? Ancient History 5th Grade | Children's HistoryDa EverandWho Were The Franks? Ancient History 5th Grade | Children's HistoryNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 GeografiaDocumento14 pagineUnit 1 GeografiaRocío MadolellNessuna valutazione finora
- The Renaissance: A Captivating Guide to a Remarkable Period in European History, Including Stories of People Such as Galileo Galilei, Michelangelo, Copernicus, Shakespeare, and Leonardo da VinciDa EverandThe Renaissance: A Captivating Guide to a Remarkable Period in European History, Including Stories of People Such as Galileo Galilei, Michelangelo, Copernicus, Shakespeare, and Leonardo da VinciNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9 - Emerging Europe and The Byzantine EmpireDocumento31 pagineChapter 9 - Emerging Europe and The Byzantine EmpireJonathan Daniel KeckNessuna valutazione finora
- MYP3 GH U1 NotesDocumento7 pagineMYP3 GH U1 NotestufygiuohiNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 Orders NotesDocumento5 pagine3 Orders Notesrwaliur78Nessuna valutazione finora
- Upload.c Uhse002 11n4Documento20 pagineUpload.c Uhse002 11n4eglotzNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 9 Emerging Europe ByzantineDocumento21 pagineCH 9 Emerging Europe Byzantineapi-268644570Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mx6 Socs ReviewerDocumento19 pagineMx6 Socs ReviewerJuliana PeninoyNessuna valutazione finora
- SS Worksheet 2 Medieval CivilizationDocumento8 pagineSS Worksheet 2 Medieval CivilizationPenny BesidNessuna valutazione finora
- Sources: Lecture Notes Iv England Under The Norman RuleDocumento6 pagineSources: Lecture Notes Iv England Under The Norman RuleJohn SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Second Year English L.M.D. Classes: Initiation To Civilization (ICL)Documento14 pagineSecond Year English L.M.D. Classes: Initiation To Civilization (ICL)Yana RbNessuna valutazione finora
- Middle Ages PacketDocumento13 pagineMiddle Ages PacketJess Mtz100% (4)
- Western Civilization - A Short Survey Europe in The Middle Ages The Early Middle AgesDocumento5 pagineWestern Civilization - A Short Survey Europe in The Middle Ages The Early Middle AgesUsoph Two PiecesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 6Documento5 pagineChapter 6Brahma Dutta DwivediNessuna valutazione finora
- Medieval Europe PPDocumento28 pagineMedieval Europe PPbtcherryNessuna valutazione finora
- GH2 Final (Part 1)Documento12 pagineGH2 Final (Part 1)karol_stuyNessuna valutazione finora
- Absolutism Review SheetDocumento6 pagineAbsolutism Review SheetPB and JalapenosNessuna valutazione finora
- 第六章 中世纪 识记要点 全Documento4 pagine第六章 中世纪 识记要点 全svb128128128Nessuna valutazione finora
- Early Modern Era: Birth of The Nation StateDocumento23 pagineEarly Modern Era: Birth of The Nation StateCloduald Bitong MaraanNessuna valutazione finora
- European HistoryDocumento8 pagineEuropean HistoryNaeem BaigNessuna valutazione finora
- Development of Feudalism in Western EuropeDocumento11 pagineDevelopment of Feudalism in Western Europenick445544100% (3)
- The Development of Feudalism in Medieval Europe TextDocumento12 pagineThe Development of Feudalism in Medieval Europe Textapi-233464494Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9 - Christian Societies Emerge in Europe, 600-1200Documento18 pagineChapter 9 - Christian Societies Emerge in Europe, 600-1200Jonathan Daniel KeckNessuna valutazione finora
- European Middle Ages 500 - 1500: A.K.A The Dark AgesDocumento45 pagineEuropean Middle Ages 500 - 1500: A.K.A The Dark AgesNikita SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- MasummaryDocumento6 pagineMasummaryapi-273873744Nessuna valutazione finora
- Europe Notes PDF-1Documento9 pagineEurope Notes PDF-1Abe Carelle B. GonzalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Historical Moments FinalDocumento10 pagineHistorical Moments FinalLucila Delgaudio (Lady Lemonade)Nessuna valutazione finora
- Global Outline Foundations of Christian Society in Western EuropeDocumento5 pagineGlobal Outline Foundations of Christian Society in Western EuropeSkyler KesslerNessuna valutazione finora
- Medieval ArchitectureDocumento4 pagineMedieval ArchitectureKia BaluyutNessuna valutazione finora
- Western Europe After The Fall of RomeDocumento48 pagineWestern Europe After The Fall of Romeaaazad22Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Importance of Charlemagne's Reforms For The Formation of Medieval EuropeDocumento3 pagineThe Importance of Charlemagne's Reforms For The Formation of Medieval EuropeNaNaixNessuna valutazione finora
- Thecrusadeschart CompleteDocumento3 pagineThecrusadeschart Completeapi-314784496Nessuna valutazione finora
- History Unit 4Documento7 pagineHistory Unit 4Hamza HajiNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary Unit 5Documento9 pagineSummary Unit 5yo yoNessuna valutazione finora
- UNIT 3 The Fragmentation of The Ancient WorldDocumento14 pagineUNIT 3 The Fragmentation of The Ancient WorldLuciano PacoNessuna valutazione finora
- Half Yealry WHG Examination NotesDocumento19 pagineHalf Yealry WHG Examination NotesThomas OrahaNessuna valutazione finora
- Controlling Information, and Beliefs/attitudes: Scandinavia Became Overpopulated, and Farming Did Not Support PopulationDocumento5 pagineControlling Information, and Beliefs/attitudes: Scandinavia Became Overpopulated, and Farming Did Not Support Populationnchung12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Crusades Revision NotesDocumento31 pagineCrusades Revision Notesgamebox3008Nessuna valutazione finora
- Historical Context: The Growth of Feudalism in The Middle AgesDocumento2 pagineHistorical Context: The Growth of Feudalism in The Middle AgesLorenzo CaramagnaNessuna valutazione finora
- ME Literature - Historical Background - Final PDFDocumento2 pagineME Literature - Historical Background - Final PDFPetra ĆurićNessuna valutazione finora
- European History: Middle Ages (500Ad-1000Ad) The Early Middle Ages (500 Ad - 1000 Ad)Documento12 pagineEuropean History: Middle Ages (500Ad-1000Ad) The Early Middle Ages (500 Ad - 1000 Ad)MarcusKlahnTokoeJr.Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Holy Roman Empire and The Church in The Middle AgesDocumento42 pagineThe Holy Roman Empire and The Church in The Middle Agesellyn cabellonNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1Documento8 pagineUnit 1Aran TzaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Fall of Orthodox EnglandDocumento101 pagineThe Fall of Orthodox EnglandAggelos-Olesya Kanakis100% (1)
- What Was Happening To Byzantium and Western Europe Around 1200Documento4 pagineWhat Was Happening To Byzantium and Western Europe Around 1200Chang Ho LeeNessuna valutazione finora
- History Lesson Note For Grade 9Documento7 pagineHistory Lesson Note For Grade 9Kalkidan KebedeNessuna valutazione finora
- The Middle Ages: 1.1 Political DevelopmentsDocumento26 pagineThe Middle Ages: 1.1 Political DevelopmentsJaime RuNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1Documento32 pagineLesson 1John DarwinNessuna valutazione finora
- Germanic TribesDocumento6 pagineGermanic TribesHassan ShehadiNessuna valutazione finora
- Medieval Europe: c.500 - 1500Documento54 pagineMedieval Europe: c.500 - 1500belen albinoNessuna valutazione finora
- World History VocabDocumento5 pagineWorld History VocabMarisa RhodesNessuna valutazione finora
- Research PaperDocumento11 pagineResearch PapermariabernadettesabarNessuna valutazione finora
- Middle Ages: The Holy Roman EmpireDocumento7 pagineMiddle Ages: The Holy Roman Empireratheesh1981Nessuna valutazione finora
- Early Middle AgesDocumento23 pagineEarly Middle AgesKata ÓnodiNessuna valutazione finora
- H&ss #3 #1 - Organization of Medieval Society and Feudalism in LatamDocumento10 pagineH&ss #3 #1 - Organization of Medieval Society and Feudalism in LatamGaloNessuna valutazione finora
- Barrier Solution: SituationDocumento2 pagineBarrier Solution: SituationIrish DionisioNessuna valutazione finora
- Taller InglesDocumento11 pagineTaller InglesMartín GonzálezNessuna valutazione finora
- CG Road EscortsDocumento3 pagineCG Road EscortsNeha SharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- International Law Detailed Notes For Css 2018Documento95 pagineInternational Law Detailed Notes For Css 2018Tooba Hassan Zaidi100% (1)
- The Giver Quiz 7-8Documento2 pagineThe Giver Quiz 7-8roxanaietiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Nobel Peace Prize 2018Documento4 pagineThe Nobel Peace Prize 2018khkhNessuna valutazione finora
- The Holy Rosary 2Documento14 pagineThe Holy Rosary 2Carmilita Mi AmoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Report On "Buying Behaviour: of Gold With Regards ToDocumento77 pagineProject Report On "Buying Behaviour: of Gold With Regards ToAbhishek MittalNessuna valutazione finora
- Linking Social Science Theories/Models To EducationDocumento2 pagineLinking Social Science Theories/Models To EducationAlexa GandioncoNessuna valutazione finora
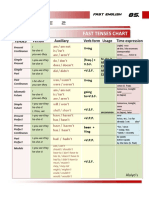
- Table 2: Fast Tenses ChartDocumento5 pagineTable 2: Fast Tenses ChartAngel Julian HernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- Small Hydro Power Plants ALSTOMDocumento20 pagineSmall Hydro Power Plants ALSTOMuzairmughalNessuna valutazione finora
- ICargo Mobility QantasDocumento4 pagineICargo Mobility QantasViswateja KrottapalliNessuna valutazione finora
- Ijarah Tuto QnsDocumento3 pagineIjarah Tuto QnsSULEIMANNessuna valutazione finora
- ReinsuranceDocumento142 pagineReinsuranceabhishek pathakNessuna valutazione finora
- Wine Express Motion To DismissDocumento19 pagineWine Express Motion To DismissRuss LatinoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sample of Notarial WillDocumento3 pagineSample of Notarial WillJF Dan100% (1)
- RBI ResearchDocumento8 pagineRBI ResearchShubhani MittalNessuna valutazione finora
- ChinduDocumento1 paginaChinduraghavbiduru167% (3)
- Jewish Reception of Greek Bible Versions (N. de Lange - J. G. Krivoruchko) PDFDocumento348 pagineJewish Reception of Greek Bible Versions (N. de Lange - J. G. Krivoruchko) PDFFray Duván OfmNessuna valutazione finora
- Pierre Bonnard: La Revue BlancheDocumento2 paginePierre Bonnard: La Revue BlancheHdjsNessuna valutazione finora
- SIP REPORT Bindu PDFDocumento61 pagineSIP REPORT Bindu PDFRahul HissariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grameenphone Integrates Key Technology: Group 1 Software Enhances Flexible Invoice Generation SystemDocumento2 pagineGrameenphone Integrates Key Technology: Group 1 Software Enhances Flexible Invoice Generation SystemRashedul Islam RanaNessuna valutazione finora
- HRM in NestleDocumento21 pagineHRM in NestleKrishna Jakhetiya100% (1)
- Actividad N°11 Ingles 4° Ii Bim.Documento4 pagineActividad N°11 Ingles 4° Ii Bim.jamesNessuna valutazione finora
- Final Advert For The Blue Economy PostsDocumento5 pagineFinal Advert For The Blue Economy PostsKhan SefNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 1Documento3 pagineAssignment 1Bahle DlaminiNessuna valutazione finora
- A Wolf by The Ears - Mattie LennonDocumento19 pagineA Wolf by The Ears - Mattie LennonMirNessuna valutazione finora
- California Department of Housing and Community Development vs. City of Huntington BeachDocumento11 pagineCalifornia Department of Housing and Community Development vs. City of Huntington BeachThe Press-Enterprise / pressenterprise.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Southwest CaseDocumento13 pagineSouthwest CaseBhuvnesh PrakashNessuna valutazione finora
- Aradau Security Materiality SDDocumento22 pagineAradau Security Materiality SDTalleres NómadaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Hotel on Place Vendôme: Life, Death, and Betrayal at the Hotel Ritz in ParisDa EverandThe Hotel on Place Vendôme: Life, Death, and Betrayal at the Hotel Ritz in ParisValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (49)
- The Rape of Nanking: The History and Legacy of the Notorious Massacre during the Second Sino-Japanese WarDa EverandThe Rape of Nanking: The History and Legacy of the Notorious Massacre during the Second Sino-Japanese WarValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (63)
- Hunting Eichmann: How a Band of Survivors and a Young Spy Agency Chased Down the World's Most Notorious NaziDa EverandHunting Eichmann: How a Band of Survivors and a Young Spy Agency Chased Down the World's Most Notorious NaziValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (157)
- We Crossed a Bridge and It Trembled: Voices from SyriaDa EverandWe Crossed a Bridge and It Trembled: Voices from SyriaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (30)
- Dunkirk: The History Behind the Major Motion PictureDa EverandDunkirk: The History Behind the Major Motion PictureValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (19)
- Bind, Torture, Kill: The Inside Story of BTK, the Serial Killer Next DoorDa EverandBind, Torture, Kill: The Inside Story of BTK, the Serial Killer Next DoorValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (77)
- Reagan at Reykjavik: Forty-Eight Hours That Ended the Cold WarDa EverandReagan at Reykjavik: Forty-Eight Hours That Ended the Cold WarValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (4)
- Rebel in the Ranks: Martin Luther, the Reformation, and the Conflicts That Continue to Shape Our WorldDa EverandRebel in the Ranks: Martin Luther, the Reformation, and the Conflicts That Continue to Shape Our WorldValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (4)
- Digital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyDa EverandDigital Gold: Bitcoin and the Inside Story of the Misfits and Millionaires Trying to Reinvent MoneyValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (51)
- Desperate Sons: Samuel Adams, Patrick Henry, John Hancock, and the Secret Bands of Radicals Who Led the Colonies to WarDa EverandDesperate Sons: Samuel Adams, Patrick Henry, John Hancock, and the Secret Bands of Radicals Who Led the Colonies to WarValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (7)
- The Great Fire: One American's Mission to Rescue Victims of the 20th Century's First GenocideDa EverandThe Great Fire: One American's Mission to Rescue Victims of the 20th Century's First GenocideNessuna valutazione finora
- Hubris: The Tragedy of War in the Twentieth CenturyDa EverandHubris: The Tragedy of War in the Twentieth CenturyValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (23)
- The Lost Peace: Leadership in a Time of Horror and Hope, 1945–1953Da EverandThe Lost Peace: Leadership in a Time of Horror and Hope, 1945–1953Nessuna valutazione finora
- Knowing What We Know: The Transmission of Knowledge: From Ancient Wisdom to Modern MagicDa EverandKnowing What We Know: The Transmission of Knowledge: From Ancient Wisdom to Modern MagicValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (25)
- The Future of Capitalism: Facing the New AnxietiesDa EverandThe Future of Capitalism: Facing the New AnxietiesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (17)
- Making Gay History: The Half-Century Fight for Lesbian and Gay Equal RightsDa EverandMaking Gay History: The Half-Century Fight for Lesbian and Gay Equal RightsNessuna valutazione finora
- The Quiet Man: The Indispensable Presidency of George H.W. BushDa EverandThe Quiet Man: The Indispensable Presidency of George H.W. BushValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Principles for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailDa EverandPrinciples for Dealing with the Changing World Order: Why Nations Succeed or FailValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (237)
- Witness to Hope: The Biography of Pope John Paul IIDa EverandWitness to Hope: The Biography of Pope John Paul IIValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (58)
- The Ship of Dreams: The Sinking of the Titanic and the End of the Edwardian EraDa EverandThe Ship of Dreams: The Sinking of the Titanic and the End of the Edwardian EraValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (38)
- Never Surrender: Winston Churchill and Britain's Decision to Fight Nazi Germany in the Fateful Summer of 1940Da EverandNever Surrender: Winston Churchill and Britain's Decision to Fight Nazi Germany in the Fateful Summer of 1940Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (45)
- The Faithful Executioner: Life and Death, Honor and Shame in the Turbulent Sixteenth CenturyDa EverandThe Faithful Executioner: Life and Death, Honor and Shame in the Turbulent Sixteenth CenturyValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (77)
- The OSS and CIA: The History of America’s Intelligence Community during World War II and the Establishment of the Central Intelligence AgencyDa EverandThe OSS and CIA: The History of America’s Intelligence Community during World War II and the Establishment of the Central Intelligence AgencyValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (27)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterDa EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (410)
- They All Love Jack: Busting the RipperDa EverandThey All Love Jack: Busting the RipperValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (30)
- The Master of Disguise: My Secret Life in the CIADa EverandThe Master of Disguise: My Secret Life in the CIANessuna valutazione finora
- 1963: The Year of the Revolution: How Youth Changed the World with Music, Fashion, and ArtDa Everand1963: The Year of the Revolution: How Youth Changed the World with Music, Fashion, and ArtValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5)
- Project MK-Ultra: The History of the CIA’s Controversial Human Experimentation ProgramDa EverandProject MK-Ultra: The History of the CIA’s Controversial Human Experimentation ProgramValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (13)
- Daughters of the Flower Fragrant Garden: Two Sisters Separated by China’s Civil WarDa EverandDaughters of the Flower Fragrant Garden: Two Sisters Separated by China’s Civil WarValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (14)
- Citizen Soldiers: The U S Army from the Normandy Beaches to the Bulge to the Surrender of GermanyDa EverandCitizen Soldiers: The U S Army from the Normandy Beaches to the Bulge to the Surrender of GermanyValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (32)