Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Patho - Salivary Glands
Caricato da
09172216507Descrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Patho - Salivary Glands
Caricato da
09172216507Copyright:
Formati disponibili
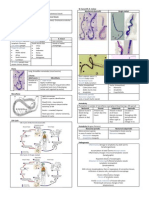
SALIVARY GLANDS Major: Ducts: Parotid 14 gm Submaxillary 7-8gm Sublingual 3gm Stensens (parotid) Whartins (submaxillary) Bartholins (sublingual)
al) OXYPHILIC ADENOMA Oncocytoma Benign; composed exclusively of oncocytic cells Due to radiation exposure Gross: brownish/yellowish consistency secondary to oxyphilic cells Cells clusters/sheets; cytoplasm deeply eosinophilic; chromatin component: compact Encapsulated; benign-looking WHARTINS TUMOR Cystadenoma lymphomatosum papilleferum (papilliferum?) M>F 70% bilateral Lobulated mass, may be fixed to the overlying skin and simulate malignancy Overlying skin: erythematous Papillary projections Biphasic tumor Oncocytic cells with lymphoid elements in stroma forming germinal centers Columnar cells with deeply eosinophilic cytoplasm Lymphocytes BASAL CELL ADENOMA Adult, F Tumors are encapsulated, sometimes cystic Picket fence appearance of cells; basaloid MUCOEPIDERMOID CARCINOMA Most common malignant salivary gland tumor in kids 4 cells: mucin-producing, squamous, intermediate, clear - Low-, intermediate-, high-grade Based on squamoid cells 98% survival for low-grade 56% survival for high-grade Grading: intracystic, neural invasion, necrosis, >4 mitoses/10hpf, anaplasia ACINIC CELL CARCINOMA Most common tumor in patients M>F Encapsulated round mass Solid, friable, grayish white Sheets of acinar cells FNAB not very sensitive; cells look benign; better to do excision ADENOID CYSTIC CARCINOMA Slowly growing, highly malignant Most common malignant tumor in minor salivary glands Growth patterns: cribriform, tubular, solid Excision Cells look very bland
Exocrine glands with ductal and acinar portion Parotid: serous Submaxillary: mixed (predominantly serous) Sublingual: mixed (predominantly mucinous) SIALOLITHIASIS Calculi More common in submaxillary gland - Crystalline compound carbonate apatite Consequences: obstruction and inflammation SIALADENITIS Acute: viruses (paramyxovirus, ) Acute suppurative o S. aureus, Strep sp., gram negative bacteria o PMNs Predisposing factors: dehydration, malnutrition, immunosuppression, sialolithiasis BENIGN MIXED TUMOR A.k.a. pleomorphic adenoma Most common neoplasm F>M 10x more common in parotid tail Well-circumscribed, solid on cut section, slippery Has a capsule; hemorrhagic area secondary to enlargement (pressure necrosis) Not painful; movable - Biphasic tumor: stromal elements, epithelial elements, chondromyxoid background bluish; hyaluronic acid component Can become malignant mixed tumor o 5-10% of BMT o Carcinoma expleomorphic adenoma o Long-standing tumor with sudden pain and facial paralysis Recurrence most likely is malignant SSx due to nerve compression/invasion of the nerve
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- DelormeDocumento6 pagineDelorme09172216507Nessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- 2010 Philippine Cancer Facts EstimatesDocumento70 pagine2010 Philippine Cancer Facts Estimates09172216507Nessuna valutazione finora
- A Prospective Randomised Trial To Compa... Chlorhexidine 2% For Skin DisinfectionDocumento8 pagineA Prospective Randomised Trial To Compa... Chlorhexidine 2% For Skin Disinfection09172216507Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Japanese Gastric Cancer Treatment 2014Documento19 pagineJapanese Gastric Cancer Treatment 201409172216507Nessuna valutazione finora
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Treatment of Fistula in AnoDocumento30 pagineTreatment of Fistula in Ano09172216507Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Iraq-Journal Drain PediaDocumento5 pagineIraq-Journal Drain Pedia09172216507Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- Learn The Brachial Plexus in Five Minutes or LessDocumento21 pagineLearn The Brachial Plexus in Five Minutes or LesskavithaNessuna valutazione finora
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Medical Gross Anatomy-MusclesDocumento66 pagineMedical Gross Anatomy-Muscles09172216507Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- Tracheal MassesDocumento6 pagineTracheal Masses09172216507Nessuna valutazione finora
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- Board Exam PrimerDocumento9 pagineBoard Exam PrimerEngr Jibril Naval Labiao67% (3)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Aha Acls Algorithms 2010Documento13 pagineAha Acls Algorithms 2010Imania AssagafNessuna valutazione finora
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- COPD AsthmaDocumento16 pagineCOPD Asthma09172216507Nessuna valutazione finora
- Burn OintmentDocumento8 pagineBurn Ointment09172216507Nessuna valutazione finora
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- Determinants of The Nutritional Status of Mothers and Children in EthiopiaDocumento36 pagineDeterminants of The Nutritional Status of Mothers and Children in EthiopiaJoe FeghaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Educ NutritionDocumento4 pagineEduc Nutrition09172216507Nessuna valutazione finora
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- Learn The Brachial Plexus in Five Minutes or LessDocumento21 pagineLearn The Brachial Plexus in Five Minutes or LesskavithaNessuna valutazione finora
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- Abdomen ArteriesDocumento18 pagineAbdomen Arteries09172216507Nessuna valutazione finora
- r4f Pastest MnemonicsDocumento23 paginer4f Pastest MnemonicsplayuhzNessuna valutazione finora
- Cap Guidelines :) Please ReadDocumento101 pagineCap Guidelines :) Please ReadkaznielsNessuna valutazione finora
- Learn The Brachial Plexus in Five Minutes or LessDocumento21 pagineLearn The Brachial Plexus in Five Minutes or LesskavithaNessuna valutazione finora
- Topics 4 TH Bi PCMDocumento1 paginaTopics 4 TH Bi PCM09172216507Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- CBS ModulesDocumento1 paginaCBS Modules09172216507Nessuna valutazione finora
- Print - Normal Newborn - History and Physical Exam OutlineDocumento3 paginePrint - Normal Newborn - History and Physical Exam Outline09172216507Nessuna valutazione finora
- Med Mnemonic SDocumento149 pagineMed Mnemonic S09172216507Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Lymphatic FilariasisDocumento3 pagineLymphatic Filariasis09172216507Nessuna valutazione finora
- GastroschisisDocumento1 paginaGastroschisis09172216507Nessuna valutazione finora
- Installation 1. Install Advanced System Care Pro 2. Disconnect From The Internet 3. Enter Key: DFF7A-8204E-69ADE-0D5AA 4. DoneDocumento1 paginaInstallation 1. Install Advanced System Care Pro 2. Disconnect From The Internet 3. Enter Key: DFF7A-8204E-69ADE-0D5AA 4. Done09172216507Nessuna valutazione finora
- Installation 1. Install Advanced System Care Pro 2. Disconnect From The Internet 3. Enter Key: DFF7A-8204E-69ADE-0D5AA 4. DoneDocumento1 paginaInstallation 1. Install Advanced System Care Pro 2. Disconnect From The Internet 3. Enter Key: DFF7A-8204E-69ADE-0D5AA 4. Done09172216507Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (120)
- Etiology of The Psychopathic Serial KillerDocumento10 pagineEtiology of The Psychopathic Serial KillercomplinotionNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi GinjalDocumento33 pagineAnatomi Dan Fisiologi GinjalRizha Zhetira100% (1)
- Infección y Reinfección SARS-Cov-2Documento6 pagineInfección y Reinfección SARS-Cov-2lugasalo4996Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 Drug MetabolismDocumento14 pagineChapter 4 Drug MetabolismNicole AguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Medical Microbiology Thesis TopicsDocumento5 pagineMedical Microbiology Thesis TopicsWriteMyPaperIn3HoursSingapore100% (2)
- Ocular Drug PDFDocumento4 pagineOcular Drug PDFPpa Gpat AmitNessuna valutazione finora
- Vet Obst Lecture 4 Congenital Fetal Defects (Teratology)Documento34 pagineVet Obst Lecture 4 Congenital Fetal Defects (Teratology)gnpobsNessuna valutazione finora
- Escherichia Coli, and Enteric: Enteric Indicator Organisms in FoodsDocumento7 pagineEscherichia Coli, and Enteric: Enteric Indicator Organisms in Foodssiddharth2907Nessuna valutazione finora
- Module 08: Genetics: Student ObjectivesDocumento9 pagineModule 08: Genetics: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNessuna valutazione finora
- Scope and Application of Genetic Engineering RS Maam HWDocumento29 pagineScope and Application of Genetic Engineering RS Maam HWRani SapkotaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathological and Physiological Age-Related ChangesDocumento39 paginePathological and Physiological Age-Related ChangesSajida Bibi NoonariNessuna valutazione finora
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Guia " Niveles Biológicos de Organización"Documento5 pagineGuia " Niveles Biológicos de Organización"Jasmín GálvezNessuna valutazione finora
- Midterm 1 2017 QuestionsDocumento11 pagineMidterm 1 2017 QuestionsDerrick ThompsonNessuna valutazione finora
- Congenital Hypo ThyroidDocumento3 pagineCongenital Hypo Thyroidabbhyasa5206Nessuna valutazione finora
- Physical CarcinogenesisDocumento3 paginePhysical CarcinogenesisamaraadhithiyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Application of The Bethesda Classification For Thyroid FNABDocumento12 pagineApplication of The Bethesda Classification For Thyroid FNABJudrelle Krizia MarianoNessuna valutazione finora
- Collins CSEC Biology Practice Multiple Choice QuestionsDocumento120 pagineCollins CSEC Biology Practice Multiple Choice QuestionsAlvesia Weatherhead100% (2)
- (Select Companies Highlighted) : Tallahassee Jacksonville PensacolaDocumento1 pagina(Select Companies Highlighted) : Tallahassee Jacksonville PensacolaCocoNessuna valutazione finora
- Hershey ChaseDocumento1 paginaHershey Chasemkohli64Nessuna valutazione finora
- Protective Effect of Allium Cepa L. (Onion) Against Potassium Bromate-Induced Hematological, Biochemical and Histopathological Alterations in RatsDocumento7 pagineProtective Effect of Allium Cepa L. (Onion) Against Potassium Bromate-Induced Hematological, Biochemical and Histopathological Alterations in RatsInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNessuna valutazione finora
- Khan Academy Notes - Biomolecules For MCATDocumento50 pagineKhan Academy Notes - Biomolecules For MCATJuanNessuna valutazione finora
- General ToxicologyDocumento57 pagineGeneral ToxicologyOhoodNessuna valutazione finora
- Layers of The Abdominal WallDocumento3 pagineLayers of The Abdominal WallRosemarie Cunanan GrifoniNessuna valutazione finora
- Instrument Introduction: Automatic Hematology Analyzer Seeing Beyond LimitDocumento2 pagineInstrument Introduction: Automatic Hematology Analyzer Seeing Beyond LimitCarla YcoNessuna valutazione finora
- Otita MedieDocumento5 pagineOtita MedieRoxana SurliuNessuna valutazione finora
- Biodiversity and Health The Cooperation ProjectsDocumento11 pagineBiodiversity and Health The Cooperation ProjectsTenri AshariNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurophroline LeafletDocumento8 pagineNeurophroline LeaflethermanchitraNessuna valutazione finora
- GE and DrugDocumento7 pagineGE and DrugryanfransNessuna valutazione finora
- Restriction EndonucleaseDocumento4 pagineRestriction EndonucleaseGaurav PandeyNessuna valutazione finora