Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
AP Biology Cells Test
Caricato da
chrwelch3Descrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
AP Biology Cells Test
Caricato da
chrwelch3Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Name: ______________________ Block: _______________
AP Biology Cells Test 09
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The creation of the cell theory as we commonly know it today is attributed to what scientists? a. Schleiden and Schwann b. Hooke and Leeuwenhoek c. Remak and Virchow d. Gorter and Grendel e. Davson and Danielli 2. When biologists wish to study the internal ultrastructure of cells, they most likely would use a. a light microscope. b. a scanning electron microscope. c. a transmission electronic microscope. d. A and C only e. A, B, and C 3. In the fractionation of homogenized cells using centrifugation, the primary factor that determines whether a specific cellular component ends up in the supernatant or the pellet is a. the relative solubility of the component. b. the size and weight of the component. c. the percentage of carbohydrates in the component. d. the number of enzymes in the fraction. e. the presence or absence of lipids in the component. 4. Which of the following comparisons between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is incorrect? a. The lack of organelles in prokaryotes means that they are structurally less complex than eukaryotes. b. The lack of internal membranes means that prokaryotes cannot compartmentalize function to the same extent as eukaryotes. c. All membrane function in prokaryotes is accomplished in the plasma membrane, while in eukaryotes, these functions are more distributed among the organelles. d. The specialization of function in organelles suggests that eukaryotes will contain a wider variety of phospholipids than prokaryotes. e. The lack of organelles in prokaryotes means that the basic cellular functions are different in prokaryotes than in eukaryotes. 5. Under which of the following conditions would you expect to find a cell with a predominance of free ribosomes? a. a cell that is secreting proteins b. a cell that is producing cytoplasmic enzymes c. a cell that is constructing its cell wall or extracellular matrix d. a cell that is digesting food particles e. a cell that is enlarging its vacuole 6. Which type of organelle is primarily involved in the synthesis of oils, phospholipids, and steroids? a. ribosome b. lysosome c. smooth endoplasmic reticulum d. mitochondrion e. contractile vacuole
7. Of the following, which is probably the most common route for membrane flow in the endomembrane system? a. Golgi lysosome ER plasma membrane b. tonoplast plasma membrane nuclear envelope smooth ER c. nuclear envelope lysosome Golgi plasma membrane d. rough ER vesicles Golgi plasma membrane e. ER chloroplasts mitochondrion cell membrane Refer to the following five terms to answer the following questions. Choose the most appropriate term for each phrase. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all. A. B. C. D. E. lysosome vacuole mitochondrion Golgi apparatus peroxisome
8. produces and modifies polysaccharides that will be secreted a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E 9. contains hydrolytic enzymes a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E 10. helps to recycle the cell's organic material a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E 11. one of the main energy transformers of cells a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E 12. contains enzymes that transfer hydrogen from various substrates to oxygen, producing H2 O2 a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E
13. a versatile plant compartment that may hold reserves of organic compounds or inorganic ions a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E 14. Grana, thylakoids, and stroma are all components found in a. vacuoles. b. chloroplasts. c. mitochondria. d. lysosomes. e. nuclei. 15. A biologist ground up some plant leaf cells and then centrifuged the mixture to fractionate the organelles. Organelles in one of the heavier fractions could produce ATP in the light, while organelles in the lighter fraction could produce ATP in the dark. The heavier and lighter fractions are most likely to contain, respectively, a. mitochondria and chloroplasts. b. chloroplasts and peroxisomes. c. peroxisomes and chloroplasts. d. chloroplasts and mitochondria. e. mitochondria and peroxisomes. 16. Which of the following contain the 9 + 2 arrangement of microtubules? a. cilia b. centrioles c. flagella d. A and C only e. A, B, and C 17. Which of the following statements about the cytoskeleton is incorrect? a. The dynamic aspect of cytoskeletal function is made possible by the assembly and disassembly of a few simple types of proteins into large aggregates. b. Microfilaments are structurally rigid and resist compression, while microtubules resist tension (stretching). c. Movement of cilia and flagella is the result of motor proteins causing microtubules to move relative to each other. d. Chemicals that block the assembly of the cytoskeleton would prevent many different processes in cells. e. Transport vesicles among the membranes of the endomembrane system depend on the function of the cytoskeleton.
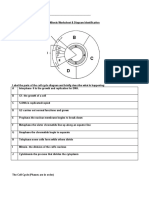
For the following questions, match the labeled component of the cell membrane in the figure below with its description.
18. fiber of the extracellular matrix a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E 19. ___ is a glycolipid, and ___ is a peripheral protein a. A; D b. B; D c. E; D d. B; E e. A; E 20. According to the fluid mosaic model of cell membranes, which of the following is a true statement about membrane phospholipids? a. They can move laterally along the plane of the membrane. b. They frequently flip-flop from one side of the membrane to the other. c. They occur in an uninterrupted bilayer, with membrane proteins restricted to the surface of the membrane. d. They are free to depart from the membrane and dissolve in the surrounding solution. e. They have hydrophilic tails in the interior of the membrane. 21. The surface of an integral membrane protein would be best described as a. hydrophilic. b. hydrophobic. c. amphipathic. d. completely covered with phospholipids. e. exposed on only one surface of the membrane. 22. What is one of the functions of cholesterol in animal cell membranes? a. facilitates transport of ions b. stores energy c. maintains membrane fluidity d. speeds diffusion e. phosphorylates ADP
23. What membrane-surface molecules are thought to be most important as cells recognize each other? a. phospholipids b. integral proteins c. peripheral proteins d. cholesterol e. glycoproteins 24. Which of the following statements is correct about diffusion? a. It is very rapid over long distances. b. It requires an expenditure of energy by the cell. c. It is a passive process in which molecules move from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. d. It is an active process in which molecules move from a region of lower concentration to one of higher concentration. e. It requires integral proteins in the cell membrane. 25. Water passes quickly through cell membranes because a. the bilayer is hydrophilic. b. it moves through hydrophobic channels. c. water movement is tied to ATP hydrolysis. d. it is a small, polar, charged molecule. e. it moves through aquaporins in the membrane. Use the diagram of the U-tube in the figure below to answer the following questions. The solutions in the two arms of this U-tube are separated by a membrane that is permeable to water and glucose but not to sucrose. Side A is half filled with a solution of 2 M sucrose and 1 M glucose. Side B is half filled with 1 M sucrose and 2 M glucose. Initially, the liquid levels on both sides are equal.
26. Initially, in terms of tonicity, the solution in side A with respect to that in side B is a. hypotonic. b. plasmolyzed. c. isotonic. d. saturated. e. hypertonic. 27. After the system reaches equilibrium, what changes are observed? a. The molarity of sucrose and glucose are equal on both sides. b. The molarity of glucose is higher in side A than in side B. c. The water level is higher in side A than in side B. d. The water level is unchanged. e. The water level is higher in side B than in side A.
28. A patient has had a serious accident and lost a lot of blood. In an attempt to replenish body fluids, distilled water, equal to the volume of blood lost, is transferred directly into one of his veins. What will be the most probable result of this transfusion? a. It will have no unfavorable effect as long as the water is free of viruses and bacteria. b. The patient's red blood cells will shrivel up because the blood fluid is hypotonic compared to the cells. c. The patient's red blood cells will swell because the blood fluid is hypotonic compared to the cells. d. The patient's red blood cells will shrivel up because the blood fluid is hypertonic compared to the cells. e. The patient's red blood cells will burst because the blood fluid is hypertonic compared to the cells. 29. You are working on a team that is designing a new drug. In order for this drug to work, it must enter the cytoplasm of specific target cells. Which of the following would not be a factor that determines whether the molecule enters the cell? a. size of the drug molecule b. polarity of the drug molecule c. charge on the drug molecule d. similarity of the drug molecule to other molecules transported by the target cells e. lipid composition of the target cells' plasma membrane 30. What is the voltage across a membrane called? a. water potential b. chemical gradient c. membrane potential d. osmotic potential e. electrochemical gradient 31. Which of the following characterizes the sodium-potassium pump? a. Sodium ions are pumped out of a cell against their gradient. b. Potassium ions are pumped into a cell against their gradient. c. The pump protein undergoes a conformational change. d. Only A and B are correct. e. A, B, and C are all correct. 32. What mechanisms do plants use to load sucrose produced by photosynthesis into specialized cells in the veins of leaves? a. an electrogenic pump b. a proton pump c. a contransport protein d. A and C only e. A, B, and C 33. White blood cells engulf bacteria through what process? a. exocytosis b. phagocytosis c. pinocytosis d. osmosis e. receptor-mediated exocytosis 34. All of the following membrane activities require energy from ATP hydrolysis except a. facilitated diffusion. b. active transport. c. Na+ ions moving out of the cell. d. proton pumps. e. translocation of potassium into a cell.
35. In the yeast signal transduction pathway, after both types of mating cells have released the mating factors and the factors have bound to specific receptors on the correct cells, a. binding induces changes in the cells that lead to cell fusion. b. the cells then produce the a factor and the factor. c. one cell nucleus binds the mating factors and produces a new nucleus in the opposite cell. d. the cell membranes fall apart, releasing the mating factors that lead to new yeast cells. e. a growth factor is secreted that stimulates mitosis in both cells. 36. Paracrine signaling a. involves secreting cells acting on nearby target cells by discharging a local regulator into the extracellular fluid. b. requires nerve cells to release a neurotransmitter into the synapse. c. occurs only in paracrine yeast cells. d. has been found in plants but not animals. e. involves mating factors attaching to target cells and causing production of new paracrine cells. 37. From the perspective of the cell receiving the message, the three stages of cell signaling are a. the paracrine, local, and synaptic stages. b. signal reception, signal transduction, and cellular response. c. signal reception, nucleus disintegration, and new cell generation. d. the alpha, beta, and gamma stages. e. signal reception, cellular response, and cell division. 38. The signal transduction pathway in animal cells that use epinephrine a. activates the breakdown of glycogen in liver and skeletal muscle cells. b. is a classic example of synaptic signaling. c. operates independently of hormone receptors on target cells. d. A and B only e. A, B, and C 39. A small molecule that specifically binds to another molecule, usually a larger one a. is called a signal transducer. b. is called a ligand. c. is called a polymer. d. seldom is involved in hormonal signaling. e. usually terminates a signal reception. 40. Which of the following is (are) true of ligand-gated ion channels? a. They are important in the nervous system. b. They lead to changes in sodium and calcium concentrations in cells. c. They open or close in response to a chemical signal. d. Only A and B are true. e. A, B, and C are true. 41. Up to 60% of all medicines used today exert their effects by influencing what structures in the cell membrane? a. tyrosine-kinases receptors b. ligand-gated ion channel receptors c. growth factors d. G proteins e. cholesterol
42. Which of the following are chemical messengers that pass through the plasma membrane of cells and have receptor molecules in the cytoplasm? a. insulin b. nitric oxide c. testosterone d. B and C only e. A, B, and C 43. In general, a signal transmitted via phosphorylation of a series of proteins a. brings a conformational change to each protein. b. requires binding of a hormone to a cytosol receptor. c. cannot occur in yeasts because they lack protein phosphatases. d. requires phosphorylase activity. e. allows target cells to change their shape and therefore their activity. 44. Which of the following is/are considered second messengers? a. cAMP b. GTP c. calcium ions d. A and C e. A, B and C 45. The general name for an enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to a protein is a. phosphorylase. b. phosphatase. c. protein kinase. d. ATPase. e. protease. 46. Which of the following is not true of cell communication systems? a. Cell signaling was an early event in the evolution of life. b. Communicating cells may be far apart or close together. c. Most signal receptors are bound to the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope. d. Protein phosphorylation is a major mechanism of signal transduction. e. In response to a signal, the cell may alter activities by changes in cytosol activity or in transcription of RNA. 47. An inactive G protein is bound to, a. a G-protein coupled receptor b. GTP c. An integral membrane protein d. GDP e. a tyrosine-kinase receptor 48. G protein-coupled receptors are __ proteins, while G proteins are __ proteins a. integral; peripheral b. peripheral; integral c. integral; cytoplasmic d. peripheral; cytoplasmic e. cytoplasmic; integral 49. A fully activated receptor tyrosine kinase, a. is an unphosphorylated dimer b. has bound a ligand c. is a phosphorylated dimer d. is a phosphorylated monomer e. is an unphosphorylated monomer
50. Receptor tyrosine kinases that function even in the absence of signaling molecules can lead to, a. a decrease in enzymatic activity b. a decrease in transcription c. unregulated cell division d. increased neurotransmitter release e. decreased glycogen breakdown 51. Which of the following statements is not true? a. Mitosis produces new nuclei with exactly the same chromosomal endowment as the parent nucleus. b. Mitosis may occur without cytokinesis. c. Mitosis and cytokinesis are required for asexual reproduction. d. All cells come from a preexisting cell. e. The mitotic spindles in prokaryotic cells are composed of microtubules. The questions below refer to the following terms. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all. A. B. C. D. E. telophase anaphase prometaphase metaphase prophase
52. Two centrosomes are arranged at opposite poles of the cell. a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E 53. This is the longest of the mitotic stages. a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E 54. If cells in the process of dividing are subjected to colchicine, a drug that interferes with the functioning of the spindle apparatus, at which stage will mitosis be arrested? a. anaphase b. prophase c. telophase d. metaphase e. interphase 55. A cell containing 92 chromatids at metaphase of mitosis would, at its completion, produce two nuclei containing how many chromosomes? a. 12 b. 16 c. 23 d. 46 e. 92
56. Microtubules of the spindle originate from ___ and attach to ___ bound to chromatids. a. metaphase plates; centromeres b. centrosomes; kinetochores c. centromeres; kinetochores d. kinetochores; centrosomes e. centrosomes; centromeres 57. Cytokinesis usually, but not always, follows mitosis. If a cell completed mitosis but not cytokinesis, the result would be a cell with a. a single large nucleus. b. high concentrations of actin and myosin. c. two abnormally small nuclei. d. two nuclei. e. two nuclei but with half the amount of DNA. 58. How do the daughter cells at the end of mitosis and cytokinesis compare with their parent cell when it was in G1 of the cell cycle? a. The daughter cells have half the amount of cytoplasm and half the amount of DNA. b. The daughter cells have half the number of chromosomes and half the amount of DNA. c. The daughter cells have the same number of chromosomes and half the amount of DNA. d. The daughter cells have the same number of chromosomes and the same amount of DNA. e. The daughter cells have the same number of chromosomes and twice the amount of DNA. 59. Which of the following is true concerning cancer cells? a. They do not exhibit density-dependent inhibition when growing in culture. b. When they stop dividing, they do so at random points in the cell cycle. c. They are not subject to cell cycle controls. d. B and C only e. A, B, and C 60. A particular cyclin called cyclin E forms a complex with a cyclin-dependent kinase called Cdk 2. This complex is important for the progression of the cell from G1 into the S phase of the cell cycle. Which of the following statements is correct? a. The amount of cyclin E is greatest during the S phase. b. The amount of Cdk 2 is greater during G1 compared to the S phase. c. The amount of cyclin E is highest during G1 . d. The amount of Cdk 2 is greatest during G1 . e. The activity of the cyclin E/Cdk 2 complex is highest during G2 . Matching Match the following root words with their definitions a. loosen d. sheet/layer b. a little pipe e. green c. nucleus 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. chloro karyo lamin lyso tubul 10
ID: A
AP Biology Cells Test 09 Answer Section
MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. 44. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: A C B E B C D D A A C E B B D D B A B A C C E C E C C C E C E E B A A A B A B E D D A D PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: 1
Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept
6.1 6.1 6.2 6.3 | Concept 6.4 6.4 6.4 6.4 6.4 6.4 6.5 6.4 6.5 6.5 6.5 6.6 6.6 7.1 7.1 7.1 7.1 7.1 7.1 7.2 7.2 7.3 7.3 7.3 7.3 7.4 7.4 7.4 7.5 7.4 11.1 11.1 11.1 11.1 11.2 11.2 11.2 11.2 11.3 11.3
ID: A 45. 46. 47. 48. 49. 50. 51. 52. 53. 54. 55. 56. 57. 58. 59. 60. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: C C D A C C E C D D D B D D E C PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 TOP: Concept 11.3 TOP: Concept 11.3
TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP: TOP:
Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept Concept
12.2 12.2 12.2 12.2 12.2 12.2 12.2 12.1 | Concept 12.2 12.3 12.3
MATCHING 61. 62. 63. 64. 65. ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: ANS: E C D A B PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: PTS: 1 1 1 1 1
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Cell Cycle WorksheetDocumento2 pagineThe Cell Cycle WorksheetLaarni Faye Sarmiento100% (1)
- Unit 1 TestDocumento5 pagineUnit 1 Testapi-485795043Nessuna valutazione finora
- 7.07mitosis QuizDocumento2 pagine7.07mitosis QuizAysha Mohideen50% (2)
- Cell Division Practice TestDocumento19 pagineCell Division Practice TestCorry SepviaNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis WorksheetDocumento2 pagineMitosis Worksheetkatherine corvera100% (2)
- Cell Division Objective QuestionsDocumento10 pagineCell Division Objective QuestionsSUREINTHARAAN A/L NATHAN Moe100% (1)
- Cell Unit TestDocumento2 pagineCell Unit Testapi-385753111Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cell To BiosphereDocumento38 pagineCell To BiospherezaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Processes Blank ReviewDocumento4 pagineCell Processes Blank ReviewDr-Qussai ZuriegatNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycolysis and Fermentation Worksheet ReviewDocumento3 pagineGlycolysis and Fermentation Worksheet ReviewMastentram WidjajaNessuna valutazione finora
- The-Cell-Cycle-Worksheet With AnswersDocumento3 pagineThe-Cell-Cycle-Worksheet With AnswersHiezel Dapat100% (1)
- Chapter 10 Science Cells TestDocumento5 pagineChapter 10 Science Cells TestShimaa SamirNessuna valutazione finora
- High School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Cell & Molecular BiologyDa EverandHigh School Biology: Questions & Explanations for Cell & Molecular BiologyNessuna valutazione finora
- 07 Test BankDocumento46 pagine07 Test Banke1153353Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Membrane and Cell Transport WebquestDocumento6 pagineCell Membrane and Cell Transport WebquestTracy NewKirkNessuna valutazione finora
- Action Potential NotesDocumento2 pagineAction Potential NotesJohn OsborneNessuna valutazione finora
- AP BIOLOGY MID TERM PRETEST REVIEWDocumento30 pagineAP BIOLOGY MID TERM PRETEST REVIEWKrisnavimala Krishnan0% (1)
- Passive and Active Transport Internet AssignmentDocumento4 paginePassive and Active Transport Internet AssignmentShalu PundirNessuna valutazione finora
- Circulation POGILDocumento4 pagineCirculation POGILDave KNessuna valutazione finora
- Mitosis Worksheet - CompletedDocumento4 pagineMitosis Worksheet - CompletedAbelNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Test PracticeDocumento7 pagineCell Test Practiceapi-240396878Nessuna valutazione finora
- Final Bioa 2015Documento10 pagineFinal Bioa 2015api-237801056100% (1)
- Cellular Reproduction and GeneticsDocumento47 pagineCellular Reproduction and GeneticsJean Marie Macadaeg OrdinarioNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Chapter 4 Test ReviewDocumento7 pagineBiology Chapter 4 Test ReviewCK. GohNessuna valutazione finora
- Meiosis-Webquest Answer KeyDocumento4 pagineMeiosis-Webquest Answer KeyAshwin Raghuraman0% (1)
- Question Bank Midterm 1Documento48 pagineQuestion Bank Midterm 1joselin MontenegroNessuna valutazione finora
- IB BIOLOGY SL TOPIC 3 Nucleic Acids & Proteins and Chemical Elements & WaterDocumento13 pagineIB BIOLOGY SL TOPIC 3 Nucleic Acids & Proteins and Chemical Elements & WaterweeNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Bio Chapter 13 Meiosis, Mel Bio 17, Mel Bio 16Documento32 pagineAP Bio Chapter 13 Meiosis, Mel Bio 17, Mel Bio 16EUNAH LimNessuna valutazione finora
- Polygraphy ReviewDocumento129 paginePolygraphy ReviewKAPITAN TUMBANessuna valutazione finora
- Abdominal TraumaDocumento8 pagineAbdominal Traumahatem alsrour100% (2)
- EmgDocumento6 pagineEmgDhabia AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Cells: Cells: The Building Blocks of LifeDocumento8 pagineCells: Cells: The Building Blocks of Lifems_m_tan100% (8)
- AP Biology Unit 2 - Cell Structure and FunctionDocumento12 pagineAP Biology Unit 2 - Cell Structure and FunctionSam SankarNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Chapter TestDocumento4 paginePractice Chapter Testhossam mohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 11.4 MeiosisDocumento9 pagineCH 11.4 MeiosisKelsey Koehler0% (1)
- 5.7 Cell TransportDocumento6 pagine5.7 Cell TransportMonica B. BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- CH8 DNA Structure and Replication 2021Documento4 pagineCH8 DNA Structure and Replication 2021EmileMcBrokeNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Structure and Function TestDocumento3 pagineCell Structure and Function TestStefanie PonsonNessuna valutazione finora
- 2008 Biology: InsightDocumento23 pagine2008 Biology: InsightXavier GavinNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Transport Test ReviewDocumento3 pagineCell Transport Test ReviewJohn Kevin NocheNessuna valutazione finora
- Dna and Rna Structure Worksheet - EddyDocumento3 pagineDna and Rna Structure Worksheet - Eddyapi-429499161Nessuna valutazione finora
- AP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 23Documento12 pagineAP Biology Reading Guide Chapter 23shkjsdhfskjd60% (5)
- Chapter 16 Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocumento8 pagineChapter 16 Molecular Basis of InheritanceMahesh T MadhavanNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.3 Section Quiz: Dna ReplicationDocumento1 pagina8.3 Section Quiz: Dna Replicationsev :3Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Test: Cell ReproductionDocumento3 pagineChapter Test: Cell Reproductionapi-25965241Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Organelles Assessment Ch 6 and 8Documento3 pagineCell Organelles Assessment Ch 6 and 8cshining330% (1)
- Worksheet - Enzymes - ReviewDocumento3 pagineWorksheet - Enzymes - Reviewapi-270403367100% (1)
- USABODocumento2 pagineUSABOkcinvinciblemanNessuna valutazione finora
- QUIZ 01 (Answer Key)Documento1 paginaQUIZ 01 (Answer Key)Tego Shei Harumi100% (1)
- Cell Division Practice Test 15Documento4 pagineCell Division Practice Test 15MING ZHUNessuna valutazione finora
- 2.1 Molecules To Metabolism: Molecular Biology Is The Chemistry of Living OrganismsDocumento25 pagine2.1 Molecules To Metabolism: Molecular Biology Is The Chemistry of Living OrganismsAbdul HalimNessuna valutazione finora
- Intro To Energy WorksheetDocumento2 pagineIntro To Energy WorksheetMelecia SeniorNessuna valutazione finora
- Genetics: Sex Determination in HumansDocumento4 pagineGenetics: Sex Determination in HumansAlyn Mondrano AlonzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Test NotesDocumento4 pagineCell Test Notesapi-237427942Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Organelle MatchingDocumento3 pagineCell Organelle MatchingElla LaretaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocumento41 pagineCell Structure and FunctionAhkyluzLaniazNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 1 The Science of Biology Test ADocumento7 pagineChapter 1 The Science of Biology Test ATUTORKIMNessuna valutazione finora
- Cell Biology Questions and AnswersDocumento14 pagineCell Biology Questions and Answersapi-19916399Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter One Study GuideDocumento2 pagineChapter One Study GuideLaurie Gardner100% (1)
- FIS1014 - Cell Biology: Quest International University Perak (Qiup)Documento12 pagineFIS1014 - Cell Biology: Quest International University Perak (Qiup)Hematharshini SaravenakumarNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQs and True-FalseDocumento10 pagineMCQs and True-Falsehussain AltaherNessuna valutazione finora
- AP Biology Cell Structure Test ReviewDocumento8 pagineAP Biology Cell Structure Test Reviewkwilliams1994Nessuna valutazione finora
- Antenatal Power PointDocumento135 pagineAntenatal Power PointBULARON, Gerry Mar ANessuna valutazione finora
- SR Elite, Aiims s60, MPL & LTC Neet Grand Test - 7 Paper (09!07!2022)Documento24 pagineSR Elite, Aiims s60, MPL & LTC Neet Grand Test - 7 Paper (09!07!2022)sobhan chinnuNessuna valutazione finora
- Revision Notes On Structural Organisation in Animals NEET 2023 - Free PDF DownloadDocumento26 pagineRevision Notes On Structural Organisation in Animals NEET 2023 - Free PDF Downloadi uploadNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology of Digestive SystemDocumento34 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of Digestive SystemIan IsidroNessuna valutazione finora
- Orange SurgeryDocumento3 pagineOrange SurgeryMichele Fantin100% (1)
- Lectures No 4 Introduction & Method of Tissue Preparation & Specimen Reception & FixationDocumento27 pagineLectures No 4 Introduction & Method of Tissue Preparation & Specimen Reception & FixationAbdallah AlasalNessuna valutazione finora
- Antibody Screening - Kupang - 2016Documento59 pagineAntibody Screening - Kupang - 2016yuni.kartika.ndoen92Nessuna valutazione finora
- The Digestive Organs Pathway To The Centre Rosina Sonnenschmidt.08154Documento15 pagineThe Digestive Organs Pathway To The Centre Rosina Sonnenschmidt.08154Sohail LatifNessuna valutazione finora
- 2018 - Mouse Cre-LoxP SystemDocumento13 pagine2018 - Mouse Cre-LoxP SystemLucas PaulaNessuna valutazione finora
- ChloroplastDocumento9 pagineChloroplastJuan Sebastian Rosero GuarinNessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular Immunology: Claire L. Harris, Richard B. Pouw, David Kavanagh, Ruyue Sun, Daniel RicklinDocumento31 pagineMolecular Immunology: Claire L. Harris, Richard B. Pouw, David Kavanagh, Ruyue Sun, Daniel Ricklinguugle gogleNessuna valutazione finora
- Pe 1 Module 3Documento25 paginePe 1 Module 3Dimple BolotaoloNessuna valutazione finora
- Automation in Blood Banking - DR ShreyaDocumento80 pagineAutomation in Blood Banking - DR ShreyaDr sakshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Inflammation. Etiology. Vascular Changes. Cellular Events in Inflammation. Acute Inflammation. Morphologic PatternsDocumento57 pagineInflammation. Etiology. Vascular Changes. Cellular Events in Inflammation. Acute Inflammation. Morphologic PatternsZauzaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cosmtic Diploma SyllabusDocumento11 pagineCosmtic Diploma SyllabusPrakash VerekarNessuna valutazione finora
- Optha Eyelids Orbit Lacrimal DR - Hernando L. Cruz JRDocumento11 pagineOptha Eyelids Orbit Lacrimal DR - Hernando L. Cruz JRJack Ortega PuruggananNessuna valutazione finora
- Hematology Lecture on Anemia Classification and DiagnosisDocumento22 pagineHematology Lecture on Anemia Classification and DiagnosisHaibat Sultan StationeryNessuna valutazione finora
- Q2 - First Summative TestDocumento3 pagineQ2 - First Summative TestMilagros ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- PGY 451 2009 Exam 1 With AnswersDocumento6 paginePGY 451 2009 Exam 1 With AnswersJackson FoxNessuna valutazione finora
- Childrens FBC Reference Ranges PDFDocumento1 paginaChildrens FBC Reference Ranges PDFCerianne BodionganNessuna valutazione finora
- 1.epulis Fissuratum: ClassificationDocumento3 pagine1.epulis Fissuratum: ClassificationArafat Masud NiloyNessuna valutazione finora
- Crossmatching, Types, Principle, Procedure and InterpretationDocumento5 pagineCrossmatching, Types, Principle, Procedure and InterpretationMerhan FoudaNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine SystemmmDocumento3 pagineEndocrine SystemmmTricia GorozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cognitive Psychology Connecting Mind Research and Everyday Experience 4th Edition Goldstein Test BankDocumento36 pagineCognitive Psychology Connecting Mind Research and Everyday Experience 4th Edition Goldstein Test Bankscrawlrootcapn0srm8100% (27)
- 18.19 the-role-of-the-supraglottic-area-in-voice-production-2161-119X.S1-001Documento7 pagine18.19 the-role-of-the-supraglottic-area-in-voice-production-2161-119X.S1-001Diana Carolina Cerón EstradaNessuna valutazione finora