Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Pathophysiology Copd-Chf
Caricato da
Zaira BataloDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Pathophysiology Copd-Chf
Caricato da
Zaira BataloCopyright:
Formati disponibili
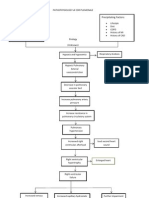
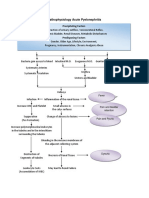
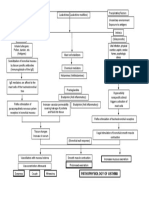
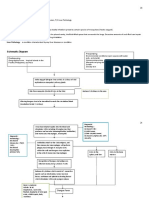
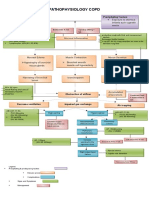
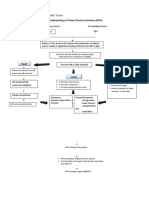
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Predisposing Factors: Family history of Asthma Age: 61
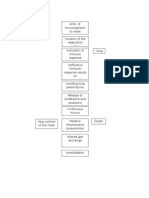
Entry of noxious particles or gases to the lungs
Precipitating factors: ALCOHOL: consume 1 bottle/1 L DIET: increase salt, fat LIFESTYLE: sedentary , smokes 1 pack/day
Induced production of neutrophils, macrophages, lymphocytes
Loss of elastin
Abnormal inflammation of the lung
Blockage or narrowing of the airways
Scar tissue formation Chronic Bronchitis
Damage to the alveolar walls
Alveolar hypoxia
Thickened airways Constant Irritation Produced excess smooth muscles and connective tissues
Decrease exchange of air in the surface area
Hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction Pulmonary hypertension Increased pulmonary vascular resistance
Excess secretion of mucus
Increase right ventricular workload
Fibrosis Thickening of vessel wall Increase pressure in the chest Narrowing of airway lumen Right ventricular hypertophy
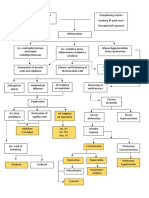
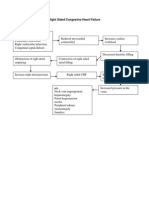
Right sided heart failure
Edema
Difficulty exhalation
Airflow limitation
Low oxygen supply
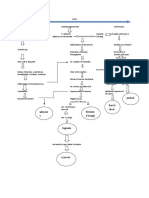
Inability to receive full pulmonary blood
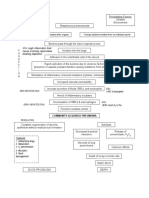
Atrial dilation, remodelling, sympathetic activation
Increase cell death to the heart
Increase pulmonary pressure Fluid movement from interstitium to alveoli
Backward flow of blood from systemic circulation
LEFT Manifestations Shortness of breath Use of accessory muscles when breathing Productive cough Rales Pale extremities fatigue
Decrease ventricular contraction
Inability to receive full systemic blood Increase amount of blood in left ventricle Decrease capacity to receive blood from left atrium Blood goes back to left atrium Increase left atrial workload Atrial dilation, remodeling, sympathetic activation Increase right ventricular workload Increase preload Right ventricular dilation, remodeling, sympathetic activation
RIGHT Manifestations Bipedal edema Distended Jugular neck veins @ 45 degree position Headache
Decrease renal perfusion Systemic congestion Increase sodium retention
Decrease capacity to receive blood from right atrium Blood goes back to right atrium
Increased osmotic pressure
Increased water reabsorption
Increase right atrial workload Increase left atrial pressure
Fluid overload
Edema
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failuretinayko100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Predisposing Factors Precipitating/Aggravating FactorsDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Predisposing Factors Precipitating/Aggravating Factorsguillermojerry100% (2)
- COPD PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DiagramDocumento2 pagineCOPD PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Diagramcris_198893% (15)
- Pathophysiology of GooDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of GooTania Noviza100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Heart FailureDocumento4 paginePathophysiology of Heart FailureTiger Knee100% (2)
- (Cor Pulmonale) PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocumento2 pagine(Cor Pulmonale) PATHOPHYSIOLOGYmilayango67% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DisorderDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DisorderBlessyl Mae EstenzoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating FactorsDocumento2 paginePathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating Factorsgodwinkent888Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)Documento32 pagineChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)matrixtrinityNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology PneumoniaDocumento2 paginePathophysiology PneumoniaSheila Mae Escalante67% (3)
- COPD PathoDocumento1 paginaCOPD PathoLeah May AnchetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Patho of COPD and CorP NewDocumento5 paginePatho of COPD and CorP NewInchan Montesines100% (1)
- Copd PathoDocumento1 paginaCopd PathoRey AngeloNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Bronchial AsthmaDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of Bronchial AsthmaFirenze Fil100% (21)
- COPD PathophysiologyDocumento1 paginaCOPD Pathophysiologyaj ajNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of COPDDocumento42 paginePathophysiology of COPDRegineCuasSulib100% (3)
- Copd Pathophysiology DiagramDocumento2 pagineCopd Pathophysiology DiagramVHyneh Basher100% (1)
- Community Acquired Pneumonia PathophysiologyDocumento3 pagineCommunity Acquired Pneumonia Pathophysiologyjordan aguilar67% (3)
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocumento3 paginePathophysiology of PneumoniaKylie Golindang100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of MI, COPD and BPHDocumento10 paginePathophysiology of MI, COPD and BPHSarah Lim100% (1)
- (Patho) PTB COPDDocumento1 pagina(Patho) PTB COPDKyle HannahNessuna valutazione finora
- Patho PneumoniaDocumento2 paginePatho Pneumoniaailyne_galicia100% (2)
- COPD PTDocumento49 pagineCOPD PTSathish RathnamNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryDocumento4 paginePathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryJane Arian Berzabal0% (1)
- Hypertension PathophysiologyDocumento1 paginaHypertension PathophysiologyZaida Eunice EstabayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology Community Aquired Pneumonia and AnemiaDocumento3 paginePathophysiology Community Aquired Pneumonia and Anemiapa3kmedina100% (2)
- B. Diagram: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors EtiologyDocumento3 pagineB. Diagram: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating Factors EtiologyKenneth Torres100% (1)
- PathophysiologyDocumento4 paginePathophysiologyCee SanchezNessuna valutazione finora
- COPD PathoDocumento1 paginaCOPD PathoGlenn_Ancheta_2074100% (1)
- Patho AsthmaDocumento1 paginaPatho AsthmaAyel JimenezNessuna valutazione finora
- Copd PathoDocumento2 pagineCopd PathoAlvin RamirezNessuna valutazione finora
- Bronchial Asthma PathophysiologyDocumento1 paginaBronchial Asthma PathophysiologyElisa Kerr100% (2)
- Pathophysiology Acute Respiratory FailureDocumento2 paginePathophysiology Acute Respiratory FailureKimberly Regacho88% (8)
- COPD PathophysiologyDocumento1 paginaCOPD PathophysiologyJustin Ahorro-Dionisio33% (3)
- Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorsDocumento6 pagineNon-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorsNeil Andro Marcelo100% (1)
- Pathophysiology EmphysemaDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology Emphysemanursing concept mapsNessuna valutazione finora
- Pneumonia PathophysiologyDocumento1 paginaPneumonia PathophysiologyDee Sarajan100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of AsthmaDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of AsthmaAhyz100% (3)
- Pathophysiology Dengue 2Documento4 paginePathophysiology Dengue 2KatherineNessuna valutazione finora
- Dyspnea PresentationDocumento37 pagineDyspnea PresentationamgoperaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocumento2 paginePathophysiology of PneumoniaGeevine Cansino91% (11)
- Final Lung Cancer Concept MapDocumento3 pagineFinal Lung Cancer Concept MapKaycee TolingNessuna valutazione finora
- COPD PathophysioDocumento1 paginaCOPD Pathophysionanette flores dela cruzNessuna valutazione finora
- EMPHYSEMADocumento3 pagineEMPHYSEMATryx N' Krix TrimorNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept Map AsthmaDocumento4 pagineConcept Map AsthmaAstrid Moreno De LeonNessuna valutazione finora
- Copd PathDocumento2 pagineCopd Pathnursing concept maps100% (2)
- PP - Community-Acquired PneumoniaDocumento1 paginaPP - Community-Acquired Pneumonialpetallo100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of HyperthyroidismDocumento4 paginePathophysiology of HyperthyroidismKitty YuffieNessuna valutazione finora
- Copd Cad Pathophysiology (Revised)Documento3 pagineCopd Cad Pathophysiology (Revised)Israel Soria EsperoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocumento1 paginaPathophysiology of Pneumoniaoxidalaj97% (31)
- Right Sided Congestive Heart FailureDocumento1 paginaRight Sided Congestive Heart FailureEzraManzanoNessuna valutazione finora
- Pathophysiology of Patent Ductus Arteroisus (PDA)Documento2 paginePathophysiology of Patent Ductus Arteroisus (PDA)Rodel Yacas100% (1)
- KC PathoDocumento7 pagineKC PathoLomie GumayagayNessuna valutazione finora
- Pneumonia With DehydrationDocumento2 paginePneumonia With DehydrationSam ParkNessuna valutazione finora
- Copd Pulmonary Edema: DR Sunil Arora Professor Deptt of PathologyDocumento52 pagineCopd Pulmonary Edema: DR Sunil Arora Professor Deptt of PathologyMunesh SherawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease .: Swathi Swaroopa. BDocumento29 pagineChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease .: Swathi Swaroopa. BKavya sriNessuna valutazione finora
- Sesak Napas Arimbi (PBL)Documento50 pagineSesak Napas Arimbi (PBL)Endik SiswantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical Physiology of Respiration: Dr. M Qathar RF TDocumento76 pagineClinical Physiology of Respiration: Dr. M Qathar RF TTiwi Lestari TiwiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lower Respiratory DiseasesDocumento137 pagineLower Respiratory DiseasesVictor StevenNessuna valutazione finora
- Shock PresentationDocumento21 pagineShock Presentationapi-283170120Nessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento5 pagineDrug StudyZaira BataloNessuna valutazione finora
- Icu Journal MiDocumento2 pagineIcu Journal MiZaira BataloNessuna valutazione finora
- BudesonideDocumento7 pagineBudesonideZaira BataloNessuna valutazione finora
- AminophyllineDocumento9 pagineAminophyllineZaira BataloNessuna valutazione finora