Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Anatomy and Physio
Caricato da
Sunshine JaranillaDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Anatomy and Physio
Caricato da
Sunshine JaranillaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
VIII.
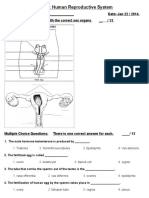
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY The Female Reproductive System Sexual included characteristics organs are divided into two types. sexual Primarycharacteristics are directly related to reproductive and thesex (genitalia). Secondary characteristics areattributes other than the sex organs that generally distinguish onesex from the other but are not essential to reproduction.
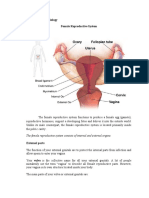
The Female Sexual Anatomy and Physiology The Female External Reproductive Organs Mons pubis/ veneris mountain of Venus, a pad of fattytissues that lies over the symphysis pubis covered by skinand at puberty covered by pubic hair that serves as acushion or protection to the symphysis pubis Labia Majora large lips, longitudinal fold from pereniumto pubis symphysis Labia Minora AKA Nymphae, soft and thin longitudinalfold created between labia majora Clitoris key, pea shaped erectile tissue composedof sensitive nerve endings; sight of sexual arousal infemales Fourchet tapers posteriorly of the labia majora. Sitefor episotomy
- Sensitive to manipulation, torn duringpregnancy Vestibule almond shaped area that contains the hymen,vaginal orifice and batholenes gland Urinary Meatus small opening of urethra/ openingfor urination Skenes Gland aka Paraurethral Gland, 2 smallmucus secreting glands for lubrication Hymen membranous tissue that covers the vaginalorifice Vaginal Orifice external opening of the vagina Bartholenes Gland paravaginal gland, secretesalkaline substance, neutralizes acidity of the vaginaDoderleins Bacillus responsible for vaginal acidityParumculae Mystiformes healing of a hymen Perenium muscular structure in between lower vaginaand anus Vagina female organ for sexual intercourse,passageway of menstruation, inches 8 10 cm longcontaining rugae Rugae permits considerable stretching without tearingduring delivery Uterus
hollow muscular organ, varies in size, weightand shape, organ of menstruation Size : 1 x 2 x 3 Shape : pear shaped, pregnant ovoid Weight : Uterine involution Non pregnant: 50-60 g Pregnant: 4th s t a g e 2nd w e e k 1000 g o f L a b o r : 1 0 0 0 g of Delivery: 500 g after
3rd w e e k s a f t e r d e l i v e r y : 3 0 0 g 5 6 Weeks after delivery: 50 60 g Parts of the Uterus Fundus upper cylindrical layer Corpus/ Body upper triangular layer Cervix lower cylindrical layer Isthmus lower uterine segment during pregnancy Muscular Composition: 3 main Muscles making possible expansion in all direction Endometrium muscle layer for menses Myometrium Power of labor Smooth muscles is considered to be Living Ligature (muscles of delivery, capable of closing) of the body Largest portion of the uterus Peremetrium Protects the entire uterus
Ovaries 2 female sex glandalmond shapeFxn: Ovulation,production of 2 hormones( estrogen andprogesterone)
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- ForeverDocumento1 paginaForeverSunshine JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- ForeverDocumento1 paginaForeverSunshine JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug Study On Emergency DrugsDocumento15 pagineDrug Study On Emergency DrugsCla96% (25)
- That's The Way I Loved YouDocumento1 paginaThat's The Way I Loved YouSunshine JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- A Place in This World LyricsDocumento1 paginaA Place in This World LyricsSunshine JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Collide Song LyricsDocumento1 paginaCollide Song LyricsSunshine JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hate That I Love YouDocumento2 pagineHate That I Love YouSunshine JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Collide Song LyricsDocumento1 paginaCollide Song LyricsSunshine JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Im SorryDocumento1 paginaIm SorrySunshine JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hegel and Idealism....Documento15 pagineHegel and Idealism....Sunshine JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Collide Song LyricsDocumento1 paginaCollide Song LyricsSunshine JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tergecef Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineTergecef Drug StudySunshine JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- 12 51Documento1 pagina12 51Sunshine JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- BioethicsDocumento17 pagineBioethicsSunshine JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- ForeverDocumento1 paginaForeverSunshine JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineDrug StudySunshine Jaranilla0% (1)
- Nursing Management: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocumento2 pagineNursing Management: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationSunshine JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Tests and ResultsDocumento13 pagineLab Tests and ResultsSunshine JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Homo HabilisDocumento27 pagineHomo HabilisSunshine JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- BioethicsDocumento17 pagineBioethicsSunshine JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tergecef Drug StudyDocumento2 pagineTergecef Drug StudySunshine JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Gastroenteritis With Moderate Dehydration, Congenital IchthyosisDocumento36 pagineAcute Gastroenteritis With Moderate Dehydration, Congenital IchthyosisSunshine JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Teaching ChildrenDocumento7 pagineTeaching ChildrenSunshine JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- I Killed Him Because I Love HimDocumento2 pagineI Killed Him Because I Love HimSunshine JaranillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- Science DLL q2w3Documento5 pagineScience DLL q2w3ANGELBERT PEDNGA0% (1)
- (K4) Male Reproductive SystemDocumento73 pagine(K4) Male Reproductive SystemJane Andrea Christiano DjianzonieNessuna valutazione finora
- The Ultimate Male Orgasm PDFDocumento4 pagineThe Ultimate Male Orgasm PDFDavid Hosam50% (2)
- Sexual Reproduction in Humans: Chapter - I Reproduction SystemsDocumento18 pagineSexual Reproduction in Humans: Chapter - I Reproduction Systemsrajendra110778Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 ReproductionDocumento12 pagineChapter 4 ReproductionPraveena MoganNessuna valutazione finora
- Q2 - First Summative TestDocumento3 pagineQ2 - First Summative TestMilagros ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- Actually Get Your Girl Off With These Revealing Truths About The Female OrgasmDocumento9 pagineActually Get Your Girl Off With These Revealing Truths About The Female OrgasmSalty VixenNessuna valutazione finora
- Primary Sex CharacteristicsDocumento3 paginePrimary Sex CharacteristicsJolina VelascoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mouse sperm longer than elephant's. Nose swells during sex like penisDocumento1 paginaMouse sperm longer than elephant's. Nose swells during sex like penisChad OsorioNessuna valutazione finora
- 3Documento26 pagine3Dion Devilin YouNessuna valutazione finora
- Uts Sexual Self - ClassDocumento8 pagineUts Sexual Self - ClassMark Joseph Maggay0% (1)
- School of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing DepartmentDocumento2 pagineSchool of Health and Allied Health Sciences Nursing DepartmentRosemarie R. ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- MENSTRUAL CYCLEI-Investigatory-project-of-biologyDocumento22 pagineMENSTRUAL CYCLEI-Investigatory-project-of-biologyAkshayNessuna valutazione finora
- Male Reproductive SystemsDocumento8 pagineMale Reproductive SystemsHayley WelshNessuna valutazione finora
- So What Is A Vulva Anyway Final BookletDocumento17 pagineSo What Is A Vulva Anyway Final BookletAdrianaVeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Period Power by Maisie HillDocumento11 paginePeriod Power by Maisie HillsimasNessuna valutazione finora
- Kuis 1 Active Learning Anatomi Genitalia FemininaDocumento3 pagineKuis 1 Active Learning Anatomi Genitalia FemininaeugeniaNessuna valutazione finora
- Tips For A Healthy Vagina.: Every Person Is Different. Learn What Is Normal For YouDocumento2 pagineTips For A Healthy Vagina.: Every Person Is Different. Learn What Is Normal For Youjason manalotoNessuna valutazione finora
- Worksheet. Menstrual Cycle.Documento5 pagineWorksheet. Menstrual Cycle.Rigel Del CastilloNessuna valutazione finora
- Sexual Response CycleDocumento7 pagineSexual Response CycleHana-Lou TaquiquiNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson Plan 2020-2021Documento7 pagineLesson Plan 2020-2021MELIE BAGARESNessuna valutazione finora
- Clear Water That Comes Out During Sex - Google SearchDocumento1 paginaClear Water That Comes Out During Sex - Google SearchMiranda UrbanoNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 The Reproductive SystemDocumento122 pagine2 The Reproductive SystemBryan Lloyd Ballestar RayatNessuna valutazione finora
- Reproduction System Terminology QuizDocumento6 pagineReproduction System Terminology QuizIrams KitchenNessuna valutazione finora
- Quiz 9 Human Reproduction Pregnancy Menstruation GraphsDocumento4 pagineQuiz 9 Human Reproduction Pregnancy Menstruation GraphsCamille FrancoNessuna valutazione finora
- Bagian-Bagian Nama PhantomDocumento9 pagineBagian-Bagian Nama PhantomAlviNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology OvaryDocumento6 pagineAnatomy and Physiology OvaryFretchell Aripal MontesNessuna valutazione finora
- HistologyDocumento6 pagineHistologyarezoo bahramiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 36-1 Reproductive SystemsDocumento25 pagineChapter 36-1 Reproductive Systemsnancie8Nessuna valutazione finora
- Floor to Windows Sex PositionsDocumento7 pagineFloor to Windows Sex PositionsRizqi AmaluddinNessuna valutazione finora