Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Midterm Review
Caricato da
snscott112Descrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Midterm Review
Caricato da
snscott112Copyright:
Formati disponibili
Question Excess tissue fluid. All reticular lymphoid organs are composed of reticular connective tissue except?
Large isolated clusters of lymphoid follicles, structurally similar to tonsils, that are located in the wall of the distal portion of small intestine Lymph nodes, spleen and tonsils. These types of cells differentiate in the thymus. Cells that recognize antigens and produce plasma cells. The lighter-staining center of a lymphoid follicles. Receives lymph drainage from the digestive organs.
Answer Edema Thymus Peyer's Patches
Lymphoid Organs T Cells B Cells Germinal Centers Cisterna Chyli
Internal portion of a lymph gland where cells are arranged Medulla in a cordlike fashion. Lymph exits the convex side of the lymph node through a number of these vessels. Lymph exits the convex side of the lymph node through a number of these vessels. Small organs associated with lymphatic vessels are termed: The distal portion of the small intestine contains clumps of lymph follicles called: The thymus is most active during: The lymphatic capillaries are: Lymph leaves a lymph node via: By secreting hormones, the thymus causes what cells to become immunocompetent? When the lymphatics are blocked due to tumors, the result is: What is a bubo? The lymph tissues found within the walls of the small intestine are called: Particularly large clusters of lymph nodes occur in all of the following locations except the: Digestive tract-associated lymphatic tissue includes all of Afferent Lymphatic Vessels Efferent Lymphatic Vessels Lymph nodes Peyer's patches Childhood More permeable than blood capillaries Efferent lymphatic vessels Lymphocytes Severe localized edema distal to the blockage An infected lymph node Peyer's patches Lower extremities Islets of Langerhans
the following except: Functions of the lymphatic system include: The tonsils located at the base of the tongue are the: Which of the following is not a normal component of lymph? A sentinel node is: Select the correct statement about lymph transport. Transport of excess tissue fluid to the blood vascular system Lingual tonsils Red blood cells The first node to receive lymph from an area suspected to be cancerous Lymph transport depends on the movement of adjacent tissues, such as skeletal muscles B cells produce plasma cells, which secrete antibodies in to the blood Lymphoid tissue is predominately reticular connective tissue
Select the correct statement about lymphocytes. Select the correct statement about lymphoid tissue.
A ring of lymphoid tissue that appears as a swelling of the Tonsil mucosa in the oral cavity is called a(n): Blood enters which of these vessels during ventricular systole? The tricuspid valve is closed: The second heart sound is heard during which phase of the cardiac cycle? Stenosis of the mitral valve may initially cause a pressure increase in the: If we were able to artificially alter the membrane permeability of pacemaker cells so that sodium influx is more rapid: Which of the following are involved directly in pulmonary circulation? Histologically, the _________ is squamous epithelium supported by a sparse connective tissue layer. A thrombus (blood clot) in the first branch of the arch of the aorta would affect the flow of blood to the: Cerebral blood flow is regulated by: A patient with essential hypertension might have pressures of 200/120 mm Hg. This hypertensive state could result in all of the following changes except: Aorta and pulmonary arteries When the ventricle is in systole Isovolumetric relaxation Pulmonary circulation Slow calcium channels in the pacemaker tissue would be cycling at a greater rate Right ventricle, pulmonary artery, and left atrium Tunica intima (interna) Right side of the head and neck and right upper arm Intrinsic autoregulatory mechanisms Decreased size of the heart muscle
This wave indicates depolarization of the atria just before P Wave
atrial contraction. A double walled fibrous sac that encloses the heart. The largest lymphatic vessels are called Lymph collecting or pooling from the lower extremities would first pool in the _____before moving up. Pericardium Ducts Cisterna Chili
The ____- are the simplest lymphoid organs and are found Tonsils at the entrance of the pharynx The appendix, tonsils, and Peyers patches collectively are MALT called _____. Highly specialized lymph capillaries called _____ are present in the villi of the intestinal mucosa. The thoracic duct of the lymphatic system empties into the _____. Lacteals Subclavian Vein
Lymph nodes have more_____ lymphatic vessels than ____ Afferent, Efferent lymphatic vessels. Tonsils have blind-ended structure called______. Crypts
Lymphatic _____ are formed from the union of the largest Trunks collecting vessels. Stores Blood Platelets Protein containing fluid within the lymphatic vessels. Receives lymph from most of the body. Speen Lymph Thoracic Duct
Isolated clusters of lymph follicles found in the wall of the Peyer's Patches small intestine. Small organs intimately associated with lymphatic vessels. lymph nodes First line of defense Second line of defense Third line of defense Nonspecific defense system Specific defense system Area where B cells become immunocompetent. Area where T cells become immunocompetent. Area where activated immunocompetent B and t cells recirculate. Area seeded by immunocompetent B and T cells. Skin and mucous membranes Inflammatory response Immune response Inflammatory response and skin and mucous membranes Immune response bone marrow thymus blood and lymph lymph nodes, spleen and other lymph
tissues Area where antigen challenge and clonal selection are most likely to occur. The process whereby neutrophils and other white blood cells are attracted to the inflammatory site is called: Which of the following is not a function of the inflammatory response? Which of the following is characteristic of antibodies? B lymphocytes develop immunocopetence in the: Which of the following is not a type of T cell? Immunological memory lymph nodes, spleen and other lymph tissues Chemotaxis replaces injured tissue with connective tissue composed of heavy and light polypeptide chains Bone Marrow Antigenic response that recognizes and mounts an attack on antigens previously encountered ability to distinguish between closely related antigens ability to recognize proteins on own tissue cells as self and not attack them an inability of the immune system to recognize self, resulting in attack of self cells by the immune system
Specificity Recognition of self from non-self Autoimmune disease
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDa EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDa EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDa EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDa EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDa EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDa EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDa EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDa EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDa EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDa EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Da EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Valutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDa EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDa EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Da EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Valutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDa EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDa EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDa EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDa EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDa EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (45)
- Bodyblade Exercise Guide WallchartDocumento1 paginaBodyblade Exercise Guide WallchartDavid Leonardo Rodriguez SarmientoNessuna valutazione finora
- Muscle Stretching in Manual Therapy I - The Extremities (Team Nanban) (TPB)Documento177 pagineMuscle Stretching in Manual Therapy I - The Extremities (Team Nanban) (TPB)CNPOULIS100% (22)
- BDS Curriculum - Rguhs PDFDocumento177 pagineBDS Curriculum - Rguhs PDFDilesh PradhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuro 2 AnsDocumento14 pagineNeuro 2 AnsSantiago AldayNessuna valutazione finora
- Thera-Band Instruction Manual v5Documento22 pagineThera-Band Instruction Manual v5Voinea Ionut100% (3)
- Electrotherapy 1 Viva QuestionsDocumento9 pagineElectrotherapy 1 Viva QuestionsAmaan Shafique100% (2)
- Lecture 2 Hearing and Equilibrium PhysiologyDocumento52 pagineLecture 2 Hearing and Equilibrium PhysiologyHomeground entertainment100% (1)
- Action Potential Generation in Cardiac MuscleDocumento10 pagineAction Potential Generation in Cardiac MuscleAhmad HaNessuna valutazione finora
- Critical Hits - Teeth & Claws DamageDocumento3 pagineCritical Hits - Teeth & Claws DamageМихаил ПотаповNessuna valutazione finora
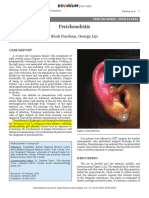
- Perichondritis: Shah Darshan, George LijiDocumento4 paginePerichondritis: Shah Darshan, George LijiThasia IsabelitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Meiky - Sport InjuryDocumento62 pagineDr. Meiky - Sport InjuryEndah Dwi AstutiNessuna valutazione finora
- Century Tuna 6-Week Workout Challenge Calendar: Week 1 Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Day 6 Day 7Documento6 pagineCentury Tuna 6-Week Workout Challenge Calendar: Week 1 Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Day 4 Day 5 Day 6 Day 7Magnolia Masangcay-DalireNessuna valutazione finora
- Week 11 Endocrinology Part 2 3Documento12 pagineWeek 11 Endocrinology Part 2 3Toff GoyenecheaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac Mechanics: With Thad WilsonDocumento26 pagineCardiac Mechanics: With Thad WilsonpasambalyrradjohndarNessuna valutazione finora
- Endocrine System and AdolescenceDocumento22 pagineEndocrine System and Adolescencenia tombriNessuna valutazione finora
- Cranial Nerves TableDocumento2 pagineCranial Nerves TableKim Ocampo RojasNessuna valutazione finora
- Head and Neck Anatomy 1Documento7 pagineHead and Neck Anatomy 1an leNessuna valutazione finora
- Day 1 - 2-Brain and Spine - Basic Spine Anatomy 4ADocumento5 pagineDay 1 - 2-Brain and Spine - Basic Spine Anatomy 4AAla'a Emerald AguamNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 5 The Integumentary SystemDocumento25 pagineChapter 5 The Integumentary Systemlolasparkle100% (2)
- How To Work The Arms Without Gym Equipment PDFDocumento2 pagineHow To Work The Arms Without Gym Equipment PDFKatie FarndenNessuna valutazione finora
- Bilateral Macrostomia: Interesting Case SeriesDocumento4 pagineBilateral Macrostomia: Interesting Case Seriesahmed bouzouidaNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of CT Brain Reporting PDFDocumento15 pagineSummary of CT Brain Reporting PDFMainak DeNessuna valutazione finora
- Samudrika LakshanamDocumento4 pagineSamudrika LakshanamGoutham RajNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 9: Joints and 10, Muscular SystemDocumento93 pagineChapter 9: Joints and 10, Muscular Systemgabbs_123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Lesson Plan On Tissues.Documento15 pagineAnatomy Lesson Plan On Tissues.Divya Chauhan100% (2)
- Computed Tomography of The Lung: Johny A. Verschakelen Walter de WeverDocumento229 pagineComputed Tomography of The Lung: Johny A. Verschakelen Walter de WeverPaulo VizcardoNessuna valutazione finora
- Orthopedic Implants CatalogDocumento112 pagineOrthopedic Implants CatalogMuhammad Shoaib JavedNessuna valutazione finora
- DPT SyllabusDocumento277 pagineDPT Syllabusshahidmahboob60100% (1)
- NCM 103 Case Analysis 1 (Ms. Perez)Documento7 pagineNCM 103 Case Analysis 1 (Ms. Perez)Josefina Isabel GullasNessuna valutazione finora