Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Glycolysis Pathway Generates ATP and Pyruvic Acid from Glucose
Caricato da
May TNDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Glycolysis Pathway Generates ATP and Pyruvic Acid from Glucose
Caricato da
May TNCopyright:
Formati disponibili
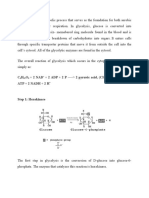
Step 1 The enzyme hexokinase phosphorylates (adds a phosphate group to) glucose in the cell's cytoplasm.
In the process, a phosphate group from ATP is transferred to glucose producing glucose 6-phosphate. Glucose (C6 H12 O6 ) + hexokinase + ATP ADP + Glucose 6-phosphate (C6 H11 O6 P1 ) Step 2 The enzyme phosphoglucoisomerase converts glucose 6-phosphate into its isomer fructose 6-phosphate. Isomers have the same molecular formula, but the atoms of each molecule are arranged differently. Glucose 6-phosphate (C6 H11 O6 P1 ) + Phosphoglucoisomerase Fructose 6-phosphate (C6 H11 O6 P1 ) Step 3 The enzyme phosphofructokinase uses another ATP molecule to transfer a phosphate group to fructose 6phosphate to form fructose 1, 6-diphosphate. Fructose 6-phosphate (C6 H11 O6 P1 ) + phosphofructokinase + ATP ADP + Fructose 1, 6-diphosphate (C6 H10 O6 P2 ) Step 4 The enzyme aldolase splits fructose 1, 6-diphosphate into two sugars that are isomers of each other. These two sugars are dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde phosphate. Fructose 1, 6-diphosphate (C6 H10 O6 P2 ) + aldolase Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (C3 H5 O3 P1 ) + Glyceraldehyde phosphate (C3 H5 O3 P1 ) Step 5 The enzyme phosphotriose isomerase rapidly inter-converts the molecules dihydroxyacetone phosphate and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate is removed as soon as it is formed to be used in the next step of glycolysis. Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (C3 H5 O3 P1 ) Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (C3 H5 O3 P1 ) Net result for steps 4 and 5: Fructose 1, 6-diphosphate (C6H10O6P2) 2 molecules of Glyceraldehyde phosphate (C3H5O3P1) Step 6 The enzyme glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase serves two functions in this step. First the enzyme transfers a hydrogen (H- ) from glyceraldehyde phosphate to the oxidizing agent nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) to form NADH. Next glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase adds a phosphate (P) from the cytosol to the oxidized glyceraldehyde phosphate to form 1, 3-diphoshoglyceric acid. This occurs for both molecules of glyceraldehyde phosphate produced in step 5. A. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase + 2 H- + 2 NAD+ 2 NADH + 2 H+ B. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase + 2 P + 2 glyceraldehyde phosphate (C3 H5 O3 P1 ) 2 molecules of 1,3-diphoshoglyceric acid (C3 H4 O4 P2 ) Step 7
The enzyme phosphoglycerokinase transfers a P from 1,3-diphoshoglyceric acid to a molecule of ADP to form ATP. This happens for each molecule of 1,3-diphoshoglyceric acid. The process yields two 3phosphoglyceric acid molecules and two ATP molecules. 2 molecules of 1,3-diphoshoglyceric acid (C3 H4 O4 P2 ) + phosphoglycerokinase + 2 ADP 2 molecules of 3phosphoglyceric acid (C3 H5 O4 P1 ) + 2 ATP Step 8 The enzyme phosphoglyceromutase relocates the P from 3-phosphoglyceric acid from the third carbon to the second carbon to form 2-phosphoglyceric acid. 2 molecules of 3-Phosphoglyceric acid (C3 H5 O4 P1 ) + phosphoglyceromutase 2 molecules of 2Phosphoglyceric acid (C3 H5 O4 P1 ) Step 9 The enzyme enolase removes a molecule of water from 2-phosphoglyceric acid to form phosphoenolpyruvic acid (PEP). This happens for each molecule of 2-phosphoglyceric acid. 2 molecules of 2-Phosphoglyceric acid (C3 H5 O4 P1 ) + enolase 2 molecules of phosphoenolpyruvic acid (PEP) (C3 H3 O3 P1 ) Step 10 The enzyme pyruvate kinase transfers a P from PEP to ADP to form pyruvic acid and ATP. This happens for each molecule of PEP. This reaction yields 2 molecules of pyruvic acid and 2 ATP molecules. 2 molecules of PEP (C3 H3 O3 P1 ) + pyruvate kinase + 2 ADP 2 molecules of pyruvic acid (C3 H4 O3 ) + 2 ATP
Summary In summary, a single glucose molecule in glycolysis produces a total of 2 molecules of pyruvic acid, 2 molecules of ATP, 2 molecules of NADH and 2 molecules of water. Although 2 ATP molecules are used in steps 1-3, 2 ATP molecules are generated in step 7 and 2 more in step 10. This gives a total of 4 ATP molecules produced. If you subtract the 2 ATP molecules used in steps 1-3 from the 4 generated at the end of step 10, you end up with a net total of 2 ATP molecules produced. For a detailed view of the 10 steps, see: Details of the 10 Steps of Glycolysis.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- 10 Steps of GlycolysisDocumento3 pagine10 Steps of GlycolysisHayley WelshNessuna valutazione finora
- Non-Glycolytic Pathways of Metabolism of GlucoseDa EverandNon-Glycolytic Pathways of Metabolism of GlucoseValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (1)
- AbbyDocumento2 pagineAbbyCatherineEstevaPolinarNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycolysis: The 10-Step Process that Converts Glucose to Pyruvic AcidDocumento3 pagineGlycolysis: The 10-Step Process that Converts Glucose to Pyruvic AcidNiel DejarmeNessuna valutazione finora
- The 10 Step Process of GlycolysisDocumento3 pagineThe 10 Step Process of GlycolysisSerena BautistaNessuna valutazione finora
- CARB GLYCOLYSIS PATHWAYDocumento29 pagineCARB GLYCOLYSIS PATHWAYFatish BanguraNessuna valutazione finora
- Step 1: Phosphorylation of GlucoseDocumento3 pagineStep 1: Phosphorylation of Glucoseryuzaki92Nessuna valutazione finora
- Definitions: Oxidation and Reduction in Terms of Electron TransferDocumento7 pagineDefinitions: Oxidation and Reduction in Terms of Electron TransferSeepana DayakarNessuna valutazione finora
- Respiration-Glycolysis and Krebs CycleDocumento17 pagineRespiration-Glycolysis and Krebs CycleTwinkle MounamiNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycolysis Wps OfficeDocumento24 pagineGlycolysis Wps Officekristel ann matela100% (1)
- Steps of glycolysis: 10-step processDocumento3 pagineSteps of glycolysis: 10-step processIm jungkook JUSTIN SEAGULL A.K.A jungshookNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycolysis: Asma Afreen AiouDocumento14 pagineGlycolysis: Asma Afreen Aiousajjad khanNessuna valutazione finora
- GlycolysisDocumento9 pagineGlycolysisIshita SinghNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Steps Glycolysis ExplainedDocumento8 pagine10 Steps Glycolysis Explaineddani2703Nessuna valutazione finora
- GlycolysisDocumento12 pagineGlycolysisenrico andrionNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycolysis: Step 1: HexokinaseDocumento6 pagineGlycolysis: Step 1: HexokinaseAirra RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- 10 Steps GlycoDocumento7 pagine10 Steps GlycoRhianne Grace CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- GlycolysisDocumento24 pagineGlycolysisJhon Excell SanoNessuna valutazione finora
- GlycolysisDocumento36 pagineGlycolysisAbdimalik AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Biological Oxidation. JP: Caloric Value of FoodDocumento13 pagineBiological Oxidation. JP: Caloric Value of Foodsagar sagu100% (1)
- Daw MetabolismDocumento27 pagineDaw MetabolismAla OmerNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 5 - Aerobic Cellular RespirationDocumento5 pagineGroup 5 - Aerobic Cellular Respirationditucalan.ha2003Nessuna valutazione finora
- Glycolysis: January 22, 2003Documento11 pagineGlycolysis: January 22, 2003Santhosh.S.UNessuna valutazione finora
- Steps of Glycolysis BiochemDocumento2 pagineSteps of Glycolysis BiochemShiro KagomeNessuna valutazione finora
- Stages of Cellular Respiration Notes #3 - Glycolysis, Krebs CycleDocumento20 pagineStages of Cellular Respiration Notes #3 - Glycolysis, Krebs CycleJillian Reyes SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycolysis PowerpointDocumento25 pagineGlycolysis PowerpointSam Christian DucoNessuna valutazione finora
- THE TEN REACTIONS OF GLYCOLYSIS - AND THE FATES OF PYRUVATEdocxDocumento6 pagineTHE TEN REACTIONS OF GLYCOLYSIS - AND THE FATES OF PYRUVATEdocxRubylyn VillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- 2 - Carbohydrate MetabolismDocumento30 pagine2 - Carbohydrate MetabolismcayyoanisNessuna valutazione finora
- GlycolysisDocumento49 pagineGlycolysisRochelle Antig100% (1)
- GlycolysisDocumento1 paginaGlycolysisNico BortolinNessuna valutazione finora
- Metabolism Overview: Catabolism and Anabolism ProcessesDocumento15 pagineMetabolism Overview: Catabolism and Anabolism ProcessesJohn Oliver AsiaNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycolysis Step of Carbohydrate MetabolismDocumento6 pagineGlycolysis Step of Carbohydrate MetabolismYeremia Adi WijayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Assignment - 20231106 - 003633 - 0000Documento17 pagineBiology Assignment - 20231106 - 003633 - 0000vikashjejusar1Nessuna valutazione finora
- BCH GlycolysisDocumento14 pagineBCH GlycolysisscholasticaNessuna valutazione finora
- RESPIRATIONDocumento2 pagineRESPIRATIONLizzie FernandoNessuna valutazione finora
- BCH 201 MBBS IV Glycolysis 21Documento14 pagineBCH 201 MBBS IV Glycolysis 21jacobsNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 2-Cellular RespirationDocumento14 pagineModule 2-Cellular RespirationMegan LoNessuna valutazione finora
- Metabolism of CarbohydrateDocumento29 pagineMetabolism of CarbohydrateAkanksha MishraNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycolysis: Derived From Greek Words: Glykys Sweet, Lysis SplittingDocumento41 pagineGlycolysis: Derived From Greek Words: Glykys Sweet, Lysis SplittingAvinashNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Respiration: General Biology I Jose Amado Ds. TorredaDocumento22 pagineCellular Respiration: General Biology I Jose Amado Ds. TorredaDyames TVNessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular Respiration: Glycolysis Generates ATPDocumento37 pagineCellular Respiration: Glycolysis Generates ATPPrince Kyle R. DolosoNessuna valutazione finora
- Fig. 8-CO, P. 171Documento33 pagineFig. 8-CO, P. 171Jonas JanssensNessuna valutazione finora
- 3 - GlycolysisDocumento5 pagine3 - GlycolysisCarlo carloNessuna valutazione finora
- 2Q Week 4 Lesson 1 GlycolysisDocumento34 pagine2Q Week 4 Lesson 1 GlycolysisKC DinglasNessuna valutazione finora
- Silz Recap 2 SolutionsDocumento5 pagineSilz Recap 2 SolutionschibuyeNessuna valutazione finora
- Pentose Phosphate Pathway ExplainedDocumento22 paginePentose Phosphate Pathway Explainedjitendermcse9816Nessuna valutazione finora
- Carbohydrate Metabolism: A Closer Look at GlycolysisDocumento37 pagineCarbohydrate Metabolism: A Closer Look at GlycolysisAdade Solomon Yao-SayNessuna valutazione finora
- PST 31215 Biochemistry IIDocumento54 paginePST 31215 Biochemistry IIkasun HerathNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycolysis GluconeogenesisDocumento66 pagineGlycolysis GluconeogenesisRahmad AllulNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycolysis: Net Production of Two Molecules of ATPDocumento8 pagineGlycolysis: Net Production of Two Molecules of ATPkarmakarrupsha48Nessuna valutazione finora
- Cellular RespirationDocumento40 pagineCellular RespirationmsmimeeyNessuna valutazione finora
- DENGA-EY, Three-Carbon Stage of GlycolysisDocumento3 pagineDENGA-EY, Three-Carbon Stage of GlycolysisMelrhean GraceNessuna valutazione finora
- Lec Notes Carbohydrate Metabolism Glycolysis Kreb Cycle ETCDocumento12 pagineLec Notes Carbohydrate Metabolism Glycolysis Kreb Cycle ETCJonah Micah MangacoNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycolysis:: By: Lee, Yulin & Blessie EstrellesDocumento21 pagineGlycolysis:: By: Lee, Yulin & Blessie EstrellesJulienne Sanchez-SalazarNessuna valutazione finora
- Metabolism of carbohydrates via glycolysis pathwayDocumento18 pagineMetabolism of carbohydrates via glycolysis pathwayhiNessuna valutazione finora
- Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis: CC7 - Unit 2.3Documento20 pagineGlycolysis and Gluconeogenesis: CC7 - Unit 2.3Vaishali PathakNessuna valutazione finora
- Slides GlicóliseDocumento10 pagineSlides GlicóliseTãhsìn Ãhsäñ SãrkãrNessuna valutazione finora
- Naveen.K.L Natural ScienceDocumento15 pagineNaveen.K.L Natural Sciencekripa v k nairNessuna valutazione finora
- 16.2.1 GLYCOLYSIS: Cellular RespirationDocumento32 pagine16.2.1 GLYCOLYSIS: Cellular Respirationeryna sofeaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cancer Staging For Oral CancerDocumento8 pagineCancer Staging For Oral CancerMay TNNessuna valutazione finora
- WHO Oral Health Surveys Basic Methods 5th Edition 2013Documento137 pagineWHO Oral Health Surveys Basic Methods 5th Edition 2013Yhesid Ramírez100% (1)
- Oral Health QuestionnaireDocumento1 paginaOral Health QuestionnaireMay TNNessuna valutazione finora
- CamScanner Docs Scanned QuicklyDocumento3 pagineCamScanner Docs Scanned QuicklyMay TNNessuna valutazione finora
- Confirmation Form: Pillar Regional Conference (NCR)Documento1 paginaConfirmation Form: Pillar Regional Conference (NCR)Llano Multi-Purpose CooperativeNessuna valutazione finora
- ADL MATRIX STRATEGY FOR BPCL'S GROWTHDocumento17 pagineADL MATRIX STRATEGY FOR BPCL'S GROWTHSachin Nagar100% (1)
- 2002 AriDocumento53 pagine2002 AriMbarouk Shaame MbaroukNessuna valutazione finora
- ASIA INTERNATIONAL FURNITURE MATERIALS CONTRACTDocumento2 pagineASIA INTERNATIONAL FURNITURE MATERIALS CONTRACTSALOME URUCHI AGUILARNessuna valutazione finora
- Plenaristas León 2022xDocumento6 paginePlenaristas León 2022xGloria MontielNessuna valutazione finora
- CommunicationDocumento5 pagineCommunicationRyan TomeldenNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 s2.0 S1747938X21000142 MainDocumento33 pagine1 s2.0 S1747938X21000142 MainAzmil XinanNessuna valutazione finora
- Stage TwoDocumento34 pagineStage TwoThar LattNessuna valutazione finora
- Siart, Et. Al (2018) Digital GeoarchaeologyDocumento272 pagineSiart, Et. Al (2018) Digital GeoarchaeologyPepe100% (2)
- GCSE H3 02g4 02 3D TrigonometryDocumento2 pagineGCSE H3 02g4 02 3D TrigonometryAndrei StanescuNessuna valutazione finora
- Popular Mechanics 2010-06Documento171 paginePopular Mechanics 2010-06BookshebooksNessuna valutazione finora
- UN Habitat UPCL Myanmar TranslationDocumento254 pagineUN Habitat UPCL Myanmar TranslationzayyarNessuna valutazione finora
- CorentineDocumento559 pagineCorentinejames b willardNessuna valutazione finora
- EMI: English As A Medium of Instruction: A New Methodology To Teach English As A Foreign LanguageDocumento18 pagineEMI: English As A Medium of Instruction: A New Methodology To Teach English As A Foreign Languagepaola suarezNessuna valutazione finora
- Brake System PDFDocumento9 pagineBrake System PDFdiego diaz100% (1)
- Timothy Prehn CV 021209Documento4 pagineTimothy Prehn CV 021209Jason GomezNessuna valutazione finora
- IPA Assignment Analyzes New Public AdministrationDocumento8 pagineIPA Assignment Analyzes New Public AdministrationKumaran ViswanathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Effect of Social Media On The Academic PerformanceDocumento55 pagineEffect of Social Media On The Academic PerformanceFJ Asufra100% (2)
- An Introduction To Community DevelopmentDocumento21 pagineAn Introduction To Community DevelopmentThuyAnh NgnNessuna valutazione finora
- 31 Legacy of Ancient Greece (Contributions)Documento10 pagine31 Legacy of Ancient Greece (Contributions)LyreNessuna valutazione finora
- Non-Destructive Examination & Standard CF Acceptance For - Forgsd - Pipe Work Stub PiecesDocumento2 pagineNon-Destructive Examination & Standard CF Acceptance For - Forgsd - Pipe Work Stub PiecesveeramalaiNessuna valutazione finora
- CalculationDocumento24 pagineCalculationhablet1100% (1)
- 6.1.3 Final Exam - Exam (Exam)Documento8 pagine6.1.3 Final Exam - Exam (Exam)parker3poseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Best Mesl StudoDocumento15 pagineBest Mesl StudoJoenielNessuna valutazione finora
- Laser Module 5Documento25 pagineLaser Module 5Luis Enrique B GNessuna valutazione finora
- Action Plan On GadDocumento1 paginaAction Plan On GadCherish Devora ArtatesNessuna valutazione finora
- DLP Din8Documento2 pagineDLP Din8KOUDJIL MohamedNessuna valutazione finora
- Studying Supply and Demand of Software Maintenance and Evolution ServicesDocumento6 pagineStudying Supply and Demand of Software Maintenance and Evolution ServicesJorge Arturo Moreno VeasNessuna valutazione finora
- Company Profile HighlightsDocumento7 pagineCompany Profile HighlightsRaynald HendartoNessuna valutazione finora
- Tithi PRAVESHADocumento38 pagineTithi PRAVESHAdbbircs100% (1)
- Coating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsDa EverandCoating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeDa EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (14)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionDa EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (3)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsDa EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (146)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableDa EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (22)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilDa EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (9)
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksDa EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingDa EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (10)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolDa EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolNessuna valutazione finora
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsDa EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (3)
- Introduction to Strategies for Organic SynthesisDa EverandIntroduction to Strategies for Organic SynthesisNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (90)
- Napoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryDa EverandNapoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (25)
- Guidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementDa EverandGuidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementValutazione: 5 su 5 stelle5/5 (1)
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableDa EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableNessuna valutazione finora
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeDa EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- The History of Chemistry (Vol.1&2): Complete EditionDa EverandThe History of Chemistry (Vol.1&2): Complete EditionValutazione: 1 su 5 stelle1/5 (1)