Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
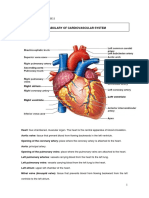
Principal Veins and Arteries
Caricato da
rodz_verDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Principal Veins and Arteries
Caricato da
rodz_verCopyright:
Formati disponibili
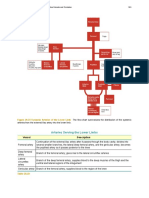
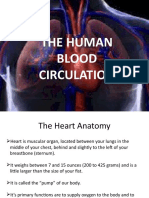
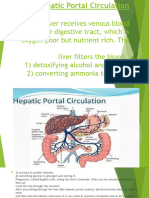
principal veins and arteries Arteries distribute oxygenated blood throughout the body, while veins carry deoxygenated
blood to the heart. Pulmonary arteries and veins function differently.
previous next
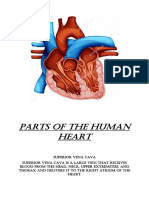
internal iliac artery Branch of the common iliac artery flowing to the pelvis, the genital organs and the inner thigh. superior vena cava Vein carrying deoxygenated blood from the upper body (above the diaphragm) back to the right atrium. great saphenous vein
Superficial vein collecting blood from the inner leg and thigh and receiving blood from certain veins of the foot; it is the longest vein in the body. abdominal aorta Fourth segment of the aorta circulating to all the organs and to the walls of the abdomen; it branches into the common iliac arteries.
urinary system femoral vein Vein collecting blood from the deep structures of the thighs and receives blood from the great saphenous vein, among others. superior mesenteric artery Branch of the abdominal aorta that supplies blood to the ascending colon and half of the transverse colon.
urinary system renal artery Branch of the abdominal aorta circulating blood to the kidney.
urinary system renal vein Large vein collecting blood from the kidney; it flows into the inferior vena cava.
urinary system pulmonary artery Artery carrying blood that is poor in oxygen and rich in carbon dioxide to the lungs; it is the only artery that transports oxygen-poor blood.
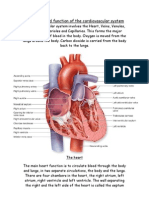
lungs basilic vein Large superficial vein of the inner surface of the arm; it connects to the humeral vein in the armpit to form the axillary vein. cephalic vein Superficial vein of the outer arm emptying into the axillary vein; it also receives blood from the superficial veins of the shoulder. arch of aorta Second segment of the aorta, which branches into the arteries flowing to the head and upper limbs; with the ascending aorta, it forms the arch of the aorta.
heart axillary vein Deep vein running through the hollow of the armpit and ending at the subclavian vein; it receives the flow of the shoulder and thorax veins, among others. subclavian vein
Vein collecting blood from the arm and part of the neck and face; it passes beneath the clavicle and receives the flow of the external jugular vein, among others. external jugular vein Vein carrying blood from the cranial walls, deep regions of the face and outer walls of the neck to the subclavian vein. internal jugular vein Vein collecting blood from the encephalon and from one portion of the face and neck; it is the largest vein in the neck. arch of foot artery Continuation of the dorsalis pedis artery; it divides into the arteries of the metatarsus. dorsalis pedis artery Artery flowing to the ankle and the back of the foot. anterior tibial artery Artery running along the front of the leg and supplying blood to the extensor muscles; it extends through the dorsal artery of the foot. femoral artery Main artery of the lower limb; it is a continuation of the external iliac artery and runs along the femur. common iliac artery Branch of the abdominal aorta that circulates blood to the pelvis and the lower limbs; it divides into the internal and external iliac arteries. superior mesenteric vein Vein collecting blood from a section of the intestine (small intestine, right colon); it is one of the veins that flows into the portal vein. inferior vena cava Vein carrying blood deoxygenated in the lower portion of the body (below the diaphragm) to the right atrium; it is the largest vein in the organism.
urinary system pulmonary vein Vein that returns blood to the heart after it has been oxygenated in the lungs; unlike other veins, the pulmonary veins carry oxygen-rich blood.
lungs brachial artery Artery flowing along the humerus and supplying the flexor muscles of the arm; it divides into the radial and ulnar arteries at the bend in the elbow. axillary artery Artery crossing the hollow of the armpit and extending through the brachial artery; it also circulates through the thoracic wall and the shoulder. subclavian artery Main artery of the upper limb passing through the clavicle and extending through the axillary artery; it also flows to the lower section of the neck. common carotid artery Branch of the aorta flowing to the head and upper portion of the neck; it is divided into internal and external carotid arteries. principal veins and arteries -> principales venas y arterias El Diccionario Visual, a new valuable resource to learn Spanish. Includes 17 all-around themes to explore, including the human body, sciences and food.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Systemic CirculationDocumento5 pagineSystemic Circulationboitumelo5525Nessuna valutazione finora
- Parts of The Heart and Its Functions: Superior Vena CavaDocumento3 pagineParts of The Heart and Its Functions: Superior Vena CavaJoanna Carla Marmonejo Estorninos-WalkerNessuna valutazione finora
- Systemic Circulatory SystemDocumento4 pagineSystemic Circulatory SystemTinaRahmawatiKadabraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 14.1 - Cardiovascular System - Blood VesselsDocumento56 pagineChapter 14.1 - Cardiovascular System - Blood VesselsMichael PeraltaNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Vessels and CirculationDocumento45 pagineBlood Vessels and CirculationLloyd RebusiNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocumento2 pagineThe Cardiovascular SystembluewindNessuna valutazione finora
- Fungsi Dari CardiovascularDocumento2 pagineFungsi Dari CardiovascularNurhayatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal CirculationDocumento6 pagineFetal Circulationkc-orense-1005Nessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Vessels Study GuideDocumento2 pagineBlood Vessels Study GuideAce J. Gonzales100% (2)
- Systamic Circulation, Pulmonary CirculationDocumento2 pagineSystamic Circulation, Pulmonary CirculationAsher Eby VargeeseNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento2 pagineAnatomy and PhysiologyClint-Marie LaxaNessuna valutazione finora
- Branches of ArotaDocumento4 pagineBranches of ArotaAsher Eby VargeeseNessuna valutazione finora
- VASCULAR SYSTEM and BLOODDocumento70 pagineVASCULAR SYSTEM and BLOODDennyTemplonuevoNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomia y Fisiologuia General Libro-951-1000Documento50 pagineAnatomia y Fisiologuia General Libro-951-1000Felipe Aguirre CórdovaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Systemic CirculationDocumento1 paginaThe Systemic CirculationGrayson JamesNessuna valutazione finora
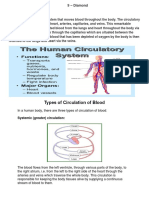
- Types of Circulation of BloodDocumento5 pagineTypes of Circulation of BloodZerria Ashley PatocNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Circulation of BloodDocumento4 pagineTypes of Circulation of BloodZerria Ashley PatocNessuna valutazione finora
- Ron Seraph Anjello Javier - Q1 Sci. 9 FA No.1Documento4 pagineRon Seraph Anjello Javier - Q1 Sci. 9 FA No.1Mute GuerreroNessuna valutazione finora
- Circular Pathway of Human Body.Documento21 pagineCircular Pathway of Human Body.Salman KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Pulmonary Circulation Is The Portion of The: Cardiovascular System Deoxygenated Blood Lungs Systemic CirculationDocumento1 paginaPulmonary Circulation Is The Portion of The: Cardiovascular System Deoxygenated Blood Lungs Systemic CirculationRose Ann AlerNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation 1Documento11 paginePresentation 1frenee aradanasNessuna valutazione finora
- Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm With Stanford A DissectionDocumento5 pagineThoracic Aortic Aneurysm With Stanford A Dissectionallyx_mNessuna valutazione finora
- Functions of HeartDocumento2 pagineFunctions of HeartBarnes WernerNessuna valutazione finora
- CNCQ Basic Reading Chapter 7Documento10 pagineCNCQ Basic Reading Chapter 7Thiện NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora
- I. Anatomy and Pathophysiology: Cardiovascular System Heart Blood VesselDocumento5 pagineI. Anatomy and Pathophysiology: Cardiovascular System Heart Blood VesselDibb Fabiania Delos ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- 170 Anatomy Circulatory SystemDocumento12 pagine170 Anatomy Circulatory SystemJeah Mae SantosNessuna valutazione finora
- Handouts Science and Health VI The HeartDocumento3 pagineHandouts Science and Health VI The HeartjairaestrellaNessuna valutazione finora
- The MyocardiumDocumento8 pagineThe MyocardiumKyrene San Pedro RosalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiovascular and Respiratory SystemDocumento3 pagineCardiovascular and Respiratory SystemGodsend OparaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vocabulary of Cardiovascular System: Ingles Medico Ii - Clase 2Documento7 pagineVocabulary of Cardiovascular System: Ingles Medico Ii - Clase 2Agustín Bravo Arreyes100% (2)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento5 pagineAnatomy and PhysiologyNikka Aubrey Tegui-inNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy of A Human HeartDocumento3 pagineAnatomy of A Human HeartKina KinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Vascular or Circulatory System RemhilDocumento9 pagineVascular or Circulatory System Remhilremhil malicdemNessuna valutazione finora
- Fetal CirculationDocumento2 pagineFetal CirculationLeslie Cristine Abad0% (1)
- General.: Blood CirculationDocumento3 pagineGeneral.: Blood CirculationJessica MichaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Vessels and CirculationDocumento7 pagineBlood Vessels and CirculationAngelAkariNessuna valutazione finora
- Circulatory SystemDocumento111 pagineCirculatory SystemYounas Bhatti100% (1)
- Complete The Table. Structure Function: Superior Vena CavaDocumento2 pagineComplete The Table. Structure Function: Superior Vena CavaMudassara HussainNessuna valutazione finora
- P.E. 3 First AID: Submitted By: Jolifa Kairan Gary Section: Bachelor of Science and Criminology 2ADocumento29 pagineP.E. 3 First AID: Submitted By: Jolifa Kairan Gary Section: Bachelor of Science and Criminology 2AAlea Jane AranjuezNessuna valutazione finora
- BIO 302L Laboratory Report - Circulatory System - Group 5Documento9 pagineBIO 302L Laboratory Report - Circulatory System - Group 5Jv Dela CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- The Circulatory SystemDocumento10 pagineThe Circulatory Systemİlyas KumNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 1 The Organs of The Cardiovascular SystemDocumento37 pagineLesson 1 The Organs of The Cardiovascular SystemCarla BuzetaNessuna valutazione finora
- Circulatory System in HumansDocumento4 pagineCirculatory System in Humanspetra.t.ayalNessuna valutazione finora
- Mammalian CirculationDocumento1 paginaMammalian CirculationSathis VenkitasamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiovascular Sys Part 1Documento10 pagineCardiovascular Sys Part 1LawrenceNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To The Cardiovascular System EsparciaDocumento5 pagineIntroduction To The Cardiovascular System EsparciaJohnferson S. BornalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Lecture Notes Unit 7 Circulatory System - The Blood Vessels-1Documento10 pagineAnatomy Lecture Notes Unit 7 Circulatory System - The Blood Vessels-1hungerfighterNessuna valutazione finora
- HeartDocumento3 pagineHeartTasha CallangNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDocumento5 pagineAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartMuri CajucomNessuna valutazione finora
- Group 10Documento7 pagineGroup 10Victor OmoloNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood CirculationDocumento8 pagineBlood CirculationnorafidaishakNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As ADocumento6 pagineCardiovascular System: Up Your Cardiovascular System. Yourheart Works As AMalaquias VallejosNessuna valutazione finora
- AP BuildaHeart 2016Documento14 pagineAP BuildaHeart 2016Jorge MarroneNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocumento5 pagineAnatomy and PhysiologyCherry Oña AntoninoNessuna valutazione finora
- Parts of The Human HeartDocumento4 pagineParts of The Human HeartKearly Joy VictorioNessuna valutazione finora
- Structure and Function of The Cardiovascular SystemDocumento5 pagineStructure and Function of The Cardiovascular SystemRachelHatcher123Nessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 4 Circulatory SystemDocumento157 pagineUnit 4 Circulatory SystemChandan ShahNessuna valutazione finora
- CIRCULATORYDocumento3 pagineCIRCULATORYSumbul ShoaibNessuna valutazione finora
- The Circulatory System (Heart)Documento3 pagineThe Circulatory System (Heart)NinaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Lab 2Documento44 pagineAnatomy Lab 2محمد جوابرهNessuna valutazione finora
- Aortic AneurysmDocumento61 pagineAortic AneurysmShaastieNessuna valutazione finora
- C. Common Cardinal VeinsDocumento6 pagineC. Common Cardinal VeinsTofik MohammedNessuna valutazione finora
- Heart Size MediastinalDocumento11 pagineHeart Size MediastinalSherry FeliciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiac MRI Made Easy 2008Documento164 pagineCardiac MRI Made Easy 2008Benjamin Gonzalez100% (1)
- COVERAM BP Decrease, Central Aortic and SynergyDocumento34 pagineCOVERAM BP Decrease, Central Aortic and Synergyputridewi22100% (1)
- MBBS 1 Year Questions - Anatomy II Ver1Documento25 pagineMBBS 1 Year Questions - Anatomy II Ver1sentilbalan@gmail.comNessuna valutazione finora
- Cardiovascular SystemDocumento101 pagineCardiovascular SystemBanessa Mae GarcianoNessuna valutazione finora
- MCQS, Emryology of The HeartDocumento22 pagineMCQS, Emryology of The HeartERIAS TENYWANessuna valutazione finora
- Tertiary SyphilisDocumento19 pagineTertiary SyphilisLakshya J BasumataryNessuna valutazione finora
- Q and A PolygraphyDocumento10 pagineQ and A PolygraphyQayes Al-Quqa67% (3)
- CPT PCM NHSNDocumento307 pagineCPT PCM NHSNYrvon RafaNessuna valutazione finora
- Venous System Arterial System: A. Artery A.A. Arteries L. Left R. Right v. Vein V.V. VeinsDocumento2 pagineVenous System Arterial System: A. Artery A.A. Arteries L. Left R. Right v. Vein V.V. VeinsJann ericka Jao100% (2)
- Classification of Congenital Heart DiseasesDocumento16 pagineClassification of Congenital Heart DiseasesdoctorriyasNessuna valutazione finora
- Pennington County Courant, March 22, 2012Documento14 paginePennington County Courant, March 22, 2012surfnewmediaNessuna valutazione finora
- Transport SystemDocumento2 pagineTransport Systemgnana87Nessuna valutazione finora
- Admixture Lesions in Congenital Cyanotic Heart Disease: Hemodynamic RoundsDocumento8 pagineAdmixture Lesions in Congenital Cyanotic Heart Disease: Hemodynamic RoundsTejeshwar ReddyNessuna valutazione finora
- POTS - Veterinary Anatomy SpecimensDocumento92 paginePOTS - Veterinary Anatomy Specimenssimonsaint100% (1)
- Cow's HeartDocumento10 pagineCow's HeartAllyzha AguilarNessuna valutazione finora
- Surface MarkingsDocumento123 pagineSurface Markingsdrmsupriya091159Nessuna valutazione finora
- ABSTRACT TEVAR - Achmad Ismail S Putra NewDocumento3 pagineABSTRACT TEVAR - Achmad Ismail S Putra NewPutra AchmadNessuna valutazione finora
- Penetrating Abdominal TraumaDocumento67 paginePenetrating Abdominal TraumarizkaNessuna valutazione finora
- Dr. Yash Kumar AchantaniDocumento65 pagineDr. Yash Kumar AchantaniJenniffer FNessuna valutazione finora
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocumento23 pagineThe Cardiovascular Systemrobhel740% (2)
- Icd 10 Ioce Code ListsDocumento154 pagineIcd 10 Ioce Code ListsGeorge SitanayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Interventional Cardiology ImagingDocumento255 pagineInterventional Cardiology ImagingArtur TarsaNessuna valutazione finora
- Anatomy Midterm Study GuideDocumento53 pagineAnatomy Midterm Study Guidelovelyc95Nessuna valutazione finora
- Antenatal and Intrapartum CareDocumento22 pagineAntenatal and Intrapartum Caresanjay vigneshNessuna valutazione finora
- Truncus ArteriosusDocumento9 pagineTruncus ArteriosusAkang KurniawanNessuna valutazione finora
- Biology Part 2 McqsDocumento55 pagineBiology Part 2 McqsJaved Ahmed ChandioNessuna valutazione finora