Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
NCP For Pre-Op Incision Case
Caricato da
FAt TyDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
NCP For Pre-Op Incision Case
Caricato da
FAt TyCopyright:
Formati disponibili
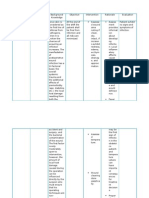
2.1 NCP Patients Name: Judy Marie Muring Attending Physician: Dr.
Theodore Abrenilla Room No: 219 Age: 28 years old
Chief Complaints: feeling of discomfort due to enlarged mass at right parieto-occipital area Nursing Care Plan (Pre- Operative) Needs/ Problem/ Cues Physiologic Deficit Sleep Objective Cues: -expression less face -frequent yawning -hours 3-4 hours Subjective Cues: Kuwang usahay ako tulog tungod Nursing Diagnosis Disturbed Sleep Inadequate sleep enlarged 4.5x14.0cm) occipitoSignificance Objectives of Care Nursing Actions to sleep/ Rationale
Disruption in After 8 hours Measures the individuals r/t pattern sleep may chronic. of holistic establish patient rest pattern: 1. large rest intake as bedtime nursing care, optimal
1. Inadequate Pattern:
usual diurnal the and to: a.
of will be able instruct 1. This helps who fluid otherwise may before need to void during night. 179) 2. daytime physical activities indicated, instruct and increase 2. Activity reduces stress and promotes as sleep. the 179) (NCP, but Gulanick, pg. the (NCP, establish patient to avoid patient
mass (12.1x wakefulness
be optimal pattern
on the right temporary or sleep/ parietal area Such of which causes disruption when in position lying both supine subjective distress apparent impairment in functional abilities.
evidenced by 4-6 hours of
Gulanick, pg.
sleep is only discomfort
may result in sleep
patient to avoid
aning bukol sa ako ulo, as verbalized by patient. the
Factors can include
that affect
strenuous activity bedtime 3. recommend 3. Many sleep quiet an environment people before
sleep patterns temporary changes in routines such as emotional problems specifically depression or anxiety. (NCP, Gulanick, pg. 177)
conducive sleep/ rest
to better in cool, dark, (NCP, Gulanick, pg. 179) environment.
4.
suggest 4.
These
engaging in a activities relaxing activity provide before bedtime relaxation and (calm reading relaxation technique) music, distraction prepare mind sleep. 179) 5. nursing (bedtime position) comfortable provide 5. These aids aids promote rest. care, (NCP, Gulanick, pg. 179) to in care. to the and for (NCP,
enjoyable book, body
Gulanick, pg.
6. teach about 6. This allows possible causes patient of sleeping participate difficulties and their
optimal ways to (NCP, treat them Gulanick, pg. 180) 7. instruct on 7. nonsleep enhancement techniques pharmacological sleep enhancement techniques can be lifetime. (NCP, Gulanick, pg. 180) used a throughout Non pharmacologic
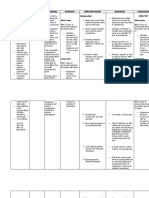
Psychologic Overload Disturbed
Body image is the attitude b. deal with
2. Change in Body Image: a person has or social involvement Objective Cues: change social involvement r/t feelings in about actual perceived function of the issues r/t or image
accept Measures of determine
to
or self- concept coping abilities body to accept/ deal issues of selfconcept r/t body image: 1. frequently visit 1. Provides and opportunities for listening to and
negative structure
-presence of about cystic lesion body at occipitoparietal area (12.1x 4.5x14.0cm) -change head structure Subjective Cues: Mauwaw sad usahay uban ang by patient. ko sa kay bukol, the in right
her all or parts of his/ her body. As important part of ones self- concept, body image disturbance can have a profound impact how individuals view overall selves. that individual places on body part or function may be important in determining The an importance their on an
acknowledge
the individual as concerns someone who is questions. worthwhile (NCP,
Gulanick, pg. 100) 2. encourage 2. To enhance of potential situations. (NCP, Gulanick, pg. 101) 3. alert staff to 3. monitor facial Because own they need to convey not the verbalization of handling anticipated conflicts
dako na kayo as verbalized
expressions and acceptance other nonverbal and behaviors revulsion when clients appearance is
the degree of disturbance than actual alteration in the structure or function. (NCP, Gulanick. Pg. 21) 4. at/ affected part the
affected. (NCP, Gulanick, pg. 101) encourage 4. To begin to touch changes body body (NCP, Gulanick, pg. 101) 5. help patient 5. to select and use minimize clothing/ makeup body changes and (NCP, Gulanick, pg. 101) 6. help the 6. Asking to body issues patient identify patient ways of coping remember that have been other useful past in the image enhance appearance. To into image. patient to look incorporate
and how they were managed may help the patient adjust to the current issue. (NANDA,
Doenges, pg. 23) 7. help the 7. Patient may changes that patient identify receive actual changes are not present or real, or they place unrealistic value or on a body structure function. (NANDA, Doenges, pg. 22) an
Knowledge Psychologic Deficit 3. Inadequate Deficient deficit is a lack cognitive of c. identify
known information about condition Objective Cues: -does answer directly questions been asked -ask questions twice Subjective Cues: Gipasagdan raman sad ni namo nagtu-o na dili kay mi ni
Knowledge: Inadequate information about the know
information or psychomotor skills
interferences to
Measures
to
learning identify to learning: with 1. determine 1. May not be emotionally or mentally capable time. (NANDA, Doenges, pg. 320) 2. provide 2. Encourages continuation of efforts. (NANDA, Doenges, pg. 321) 3. written guidelines provide 3. Reinforces info/ learning for process. Doenges, pg. 323) 4. patient knows begin 4. Limits information the sense of being already overwhelmed. and (NANDA, this patients ability physically, to learn
and specific interferences to actions them
the required for deal recovery, maintenance, or health promotion. Information should made available when the patient wants and needs it, the pace the patient determines, and using the teaching strategy most effective. (NCP, Gulanick, pg. 116) the patient seems be
condition r/t health unfamiliarity not with information the resources
positive reinforcement
patient to refer (NANDA, to as necessary
mutubo, as verbalized by the patient.
move to what Doenges, pg. the patient does 322)
not
know,
progressing from simple to complex 5. patient provide 5. Promotes of over active role for sense in control situation. (NANDA, Doenges, pg. 322) 6. provide 6. May assist with further information learning resources (magazines, newspaper, clippings) 7. objectives clearly learners terms learning process
about additional learning/ promote learning own (NANDA, Doenges, pg. 322) state 7. To meet learners in needs. (NANDA, Doenges, pg. 321) at pace.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Nursing Care Plan PreoperativeDocumento5 pagineNursing Care Plan Preoperativekuro hanabusaNessuna valutazione finora
- Operating Room WriteDocumento2 pagineOperating Room WritemodiNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Intra FinalDocumento7 pagineNCP Intra FinalRoxanne Ganayo ClaverNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Modified Radical MastectomyDocumento5 pagineNCP Modified Radical MastectomyIvan Jules P. PALMARESNessuna valutazione finora
- AppendectomyDocumento4 pagineAppendectomyKyre LandinginNessuna valutazione finora
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study TramadolDocumento3 pagineCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study TramadolhahahahaaaaaaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Disturbed Sleep PatternDocumento3 pagineDisturbed Sleep PatternLorette Diane C. Roque100% (2)
- NCP Impaired SkinDocumento2 pagineNCP Impaired Skinarjay2306_obcq100% (1)
- NCP (BPH)Documento8 pagineNCP (BPH)NataCo50% (2)
- Impaired Physical Mobility...Documento3 pagineImpaired Physical Mobility...Christy BerryNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Breast CADocumento3 pagineNCP Breast CAHannah Lacambra100% (1)
- Risk For InfectionDocumento5 pagineRisk For InfectionRochelle Corneta JoreNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: Tetanus DateDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan Format Name: - Medical Diagnosis: Tetanus DateSheryl Ann Barit PedinesNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP 2 LRDR For PrintDocumento2 pagineNCP 2 LRDR For PrintGeorge PandaNessuna valutazione finora
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento4 pagineCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjomsportg0% (1)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implemantation Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 pagineAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implemantation Rationale EvaluationChloie Marie Rosalejos100% (1)
- Total Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Pre-OperativeDocumento2 pagineTotal Abdominal Hysterectomy Bilateral Salpingo Oophorectomy (Tahbso) Nursing Responsibilities Rationale Pre-OperativeMiar QuestNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 pagineAssessment Explanation of The Problem Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationRodolfo Bong SemaneroNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Pain NCPDocumento2 pagineAcute Pain NCPCaren AntonioNessuna valutazione finora
- Doxofylline: D 400 MG TabletsDocumento33 pagineDoxofylline: D 400 MG TabletsBibek Singh Mahat100% (2)
- Nature of TechnopreneurshipDocumento4 pagineNature of Technopreneurshiprichard nuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento2 pagineAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationRomeo Avecilla CabralNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan: Sweating Temperature Rigors Nausea Vomiting Diarrhoea Lethargy MalaiseDocumento1 paginaNursing Care Plan: Sweating Temperature Rigors Nausea Vomiting Diarrhoea Lethargy Malaise06eltianNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP MCMC Post OperativeDocumento3 pagineNCP MCMC Post OperativeKristiyanong KabataanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lung Cancer (Nursing Care)Documento5 pagineLung Cancer (Nursing Care)heiyuNessuna valutazione finora
- ImmobilityDocumento1 paginaImmobilitymicopoliNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP For Post Op Wound and FractureDocumento6 pagineNCP For Post Op Wound and FractureAlyssa Marie0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan - 2Documento2 pagineNursing Care Plan - 2Micah Jonah Elicaño100% (1)
- Discharge Plan Methods InstructionsDocumento5 pagineDischarge Plan Methods InstructionsKirk CabasaNessuna valutazione finora
- AppendectomyDocumento2 pagineAppendectomyJoshua Triumfante De Vera IIINessuna valutazione finora
- Drugs Mechanism of Action Nursing Responsibilities OMXDocumento5 pagineDrugs Mechanism of Action Nursing Responsibilities OMXEmmanuelRodriguezNessuna valutazione finora
- Rani Ti Dine Tramadol Ketorolac in Paracetamol Drug StudyDocumento10 pagineRani Ti Dine Tramadol Ketorolac in Paracetamol Drug StudyIv'z TandocNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care PlanDocumento3 pagineNursing Care PlanInah Arcellana100% (2)
- NCP For Risk For Acute PainDocumento3 pagineNCP For Risk For Acute PainAngelgodess Athena-envyNessuna valutazione finora
- Discharge Planning EnglishDocumento11 pagineDischarge Planning Englishrahmat hidayatNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP (Or) ThyroidectomyDocumento3 pagineNCP (Or) ThyroidectomyChiz CorreNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP Proper - Obstructive JaundiceDocumento8 pagineNCP Proper - Obstructive JaundiceWyen Cabatbat100% (2)
- NCPDocumento3 pagineNCPNika LoNessuna valutazione finora
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocumento7 pagineImpaired Physical MobilityVianah Eve EscobidoNessuna valutazione finora
- J.Paquit NCP ECCEDocumento7 pagineJ.Paquit NCP ECCEJon Gab Paquit100% (1)
- Drug Study, NCP, and Discharge Plan For AppendectomyDocumento12 pagineDrug Study, NCP, and Discharge Plan For AppendectomyApril80% (5)
- Acute Pain OsteosarcomaDocumento8 pagineAcute Pain OsteosarcomaMaryjoy Gabriellee De La Cruz100% (1)
- Drug Study - CaDocumento3 pagineDrug Study - Casaint_ronald8Nessuna valutazione finora
- Case Study StabDocumento7 pagineCase Study StabMari Jasmeen Estrada Noveda100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan (Compartment Sydnrome)Documento6 pagineNursing Care Plan (Compartment Sydnrome)Zyiv BalogalNessuna valutazione finora
- Health Teaching PlanDocumento7 pagineHealth Teaching PlanJack Bangcoyo100% (1)
- NCP Acute Pain OB Ward PDFDocumento2 pagineNCP Acute Pain OB Ward PDFambiit25Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ncp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasDocumento4 pagineNcp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasFran LanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeDocumento2 pagineNursing Care Plan: Risk For Disuse SyndromeRozsy FakhrurNessuna valutazione finora
- Acute Pain and Impaired Skin Integrity PostopDocumento9 pagineAcute Pain and Impaired Skin Integrity PostopKach Kurrs0% (1)
- VI. Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocumento3 pagineVI. Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationJenny AjocNessuna valutazione finora
- Risk For InfectionDocumento1 paginaRisk For InfectionAcmihs Dequilla100% (8)
- NCP FinalDocumento7 pagineNCP FinalRuss RussNessuna valutazione finora
- NCP ImmobilityDocumento2 pagineNCP Immobilityxxxcamzxxx67% (6)
- Nurs460 ProposalDocumento2 pagineNurs460 ProposalmhavranekNessuna valutazione finora
- Using Occupation To Facilitate Self-Awareness in People Who Have Acquired Brain Injury: A Pilot StudyDocumento12 pagineUsing Occupation To Facilitate Self-Awareness in People Who Have Acquired Brain Injury: A Pilot StudyDanonino12Nessuna valutazione finora
- Stress ReflectionDocumento2 pagineStress ReflectionariixannaaNessuna valutazione finora
- Fear Reduction, Relaxation, AND BiofeedbackDocumento14 pagineFear Reduction, Relaxation, AND BiofeedbackriyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Behavioral Activation Group Therapy: Therapist ManualDocumento37 pagineBehavioral Activation Group Therapy: Therapist ManualcaballeroNessuna valutazione finora
- Psycho EducationDocumento65 paginePsycho EducationLaura GuiseNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer (Keyboard)Documento1 paginaComputer (Keyboard)Ryza Carmela PagalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Absence REST UserDocumentationDocumento9 pagineAbsence REST UserDocumentationYonny Isidro RendonNessuna valutazione finora
- 1152-1619622711350-Unit 04 - Database Design and Development - Reworded - 2021Documento16 pagine1152-1619622711350-Unit 04 - Database Design and Development - Reworded - 2021kaushal abeysekera17% (6)
- Tempos Var HaydnDocumento9 pagineTempos Var HaydnElision06Nessuna valutazione finora
- Portofolio Bahasa Inggris SyaliaDocumento22 paginePortofolio Bahasa Inggris SyaliaSyalia Ratri AndiniNessuna valutazione finora
- SAS Hash Objects FinalDocumento91 pagineSAS Hash Objects FinalRamakant Sharma100% (1)
- Online Instructions For Chapter 2: Divide-And-Conquer: Algorithms Analysis and Design (CO3031)Documento16 pagineOnline Instructions For Chapter 2: Divide-And-Conquer: Algorithms Analysis and Design (CO3031)Trần Quốc KhangNessuna valutazione finora
- Hollywood - Lewis CapaldiDocumento3 pagineHollywood - Lewis CapaldiBuy ExpressNessuna valutazione finora
- (123doc) Bai Tap Bo Tro Family and Friends 4 Special Edition 2Documento12 pagine(123doc) Bai Tap Bo Tro Family and Friends 4 Special Edition 2Bao ChauNessuna valutazione finora
- DeontologiaDocumento151 pagineDeontologiaMarcos BriceñoNessuna valutazione finora
- African Proverbial Sayings - A Paremilogical Reading of Achebe's Arrow of GodDocumento13 pagineAfrican Proverbial Sayings - A Paremilogical Reading of Achebe's Arrow of GodChiara Zwicky Sarkozy100% (1)
- PAMTCIDocumento2 paginePAMTCIDarwin Nacion ManquiquisNessuna valutazione finora
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocumento2 pagineDetailed Lesson PlanJohnmel TrillesNessuna valutazione finora
- Different Types of SQL JoinsDocumento12 pagineDifferent Types of SQL JoinsKarla Hernández AburtoNessuna valutazione finora
- Reading and Writing Skills PRE TESTDocumento16 pagineReading and Writing Skills PRE TESTRJay SebandalNessuna valutazione finora
- MTC8 0602 Q2 FPFDocumento28 pagineMTC8 0602 Q2 FPFJohn Philip ReyesNessuna valutazione finora
- B1 Video Extra Worksheets and Teachers NotesDocumento6 pagineB1 Video Extra Worksheets and Teachers NotesdanamezeiNessuna valutazione finora
- DP 2 2 Practice Achmad SusmonoDocumento4 pagineDP 2 2 Practice Achmad SusmonoACHMAD SUSMONONessuna valutazione finora
- Emma Jane AustenDocumento4 pagineEmma Jane Austen4vrwqrtrd2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Compliance Score: 41.3% 121 of 293 Rules Passed 0 of 293 Rules Partially PassedDocumento54 pagineCompliance Score: 41.3% 121 of 293 Rules Passed 0 of 293 Rules Partially PassedRobert PatkoNessuna valutazione finora
- Loss-In-weight Feeder - Intecont TersusDocumento220 pagineLoss-In-weight Feeder - Intecont TersusneelakanteswarbNessuna valutazione finora
- Rebirth of FreedomDocumento9 pagineRebirth of FreedomJoanna Louisa Gabawan0% (1)
- Philippians 3 1 14Documento6 paginePhilippians 3 1 14Benjamin Thomas ClarkNessuna valutazione finora
- 04 Uic - Plane Geometry - 2017 KeyDocumento5 pagine04 Uic - Plane Geometry - 2017 KeyJazyl PeralesNessuna valutazione finora
- The Spanish Creation of The Philippines: The Birth of A NationDocumento30 pagineThe Spanish Creation of The Philippines: The Birth of A NationTricia May Cagaoan100% (1)
- Alt Shortcuts ListDocumento3 pagineAlt Shortcuts ListRAJUNessuna valutazione finora
- Oneirocritica - Dream Analysis in The 2nd Century ADDocumento3 pagineOneirocritica - Dream Analysis in The 2nd Century ADPetro VourisNessuna valutazione finora
- Present ContinuousDocumento6 paginePresent ContinuousProfr Héctor BelloNessuna valutazione finora
- Adrien Bledstein, Tamar and The Coat of Many ColorsDocumento19 pagineAdrien Bledstein, Tamar and The Coat of Many ColorsJonathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Intelligent Control: Lecturer: VU VAN PHONGDocumento22 pagineIntelligent Control: Lecturer: VU VAN PHONGNam NguyễnNessuna valutazione finora