Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
See Tad Is
Caricato da
mmathoorahDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
See Tad Is
Caricato da
mmathoorahCopyright:
Formati disponibili
4 ANALYSIS 4.
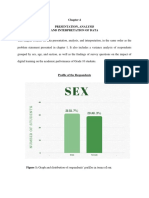
1 INTRODUCTION This chapter will analyze the data obtained from the survey and will test the different hypotheses developed. This is an important chapter as it is the basis for a researcher to analyze the data obtained, test various hypotheses in relation to the research objectives and draw conclusive inferences as a further step toward making feasible recommendations. 4.2 Gender A gender analysis has been carried out on the respondents. This is presented in the table below and illustrated using a bar chart Frequenc Percent y male 53 54.6 female 41 42.3 Total 94 96.9 System 3 3.1 97 100.0
6 0
5 0
4 0
3 0
2 0
Count
1 0
0 Mig is sn m a l e fm ea l e
gne edr
4.3 Age The age group of the respondents are given below : Age Frequenc y less than 31 20 20 to 35 40 35 to 50 16 above 50 7 Total 94 Percent 32.0 41.2 16.5 7.2 96.9
It is noted that 32 % are less than 20 years , 41 percent are between 20 to 35 while 24 % are above 35 years old .This information is shown below :
50
40
30
20
10
Count
0 Missing less than 20 20 to 35 35 to 50 above 50
Age
4.4 Education The level of education is an important factor in the use of internet . In this respect a cross tabulation has been carried out to identify the level of education of the respondents . This is shown below :
primary level up to SC up to HSC university
less 20 to 35 35 to 50 above 50 TOTAL than 20 4 6 10 19 11 1 31 9 18 9 40 4 5 1 16 6 1 7 32 40 12 94
From the above table , it is noted 10 respondents have received primary education and 10 respondents are university graduates . 32 and 40 respondents have read up to School certificate and Higher School certificate . The distribution of the level of education of the respondents are given below :
50
40
30
20
10
Count
0 Missing primary level up to sc up to hsc university
Education
4.5 Occupation Occupation is also a determining factor in the use of internet . In order to obtain a better understanding of the profile of the respondents , a cross tabulation has been carried out between employment and education . This is shown in the table below: Employed Employed Student unemploy self
primary level up to sc up to hsc universit y
public sector 4 13 15 2 34
Private sector 1 9 16 7 33 1 3 4
ed employed 3 2 3 8 2 7 3 3 15 10 32 40 12 94
Most of the respondents are either employees of the public sector ( N=34 ) or employees of the private sector ( N=33) 4 respondents are students , 8 are unemployed and 15 have their own businesses. The distribution of the level of education of the respondents are given below
40
30
20
10
Count
0 Missing Employed Private sec Student unemployed sel employed Employed piublic sec
occupation
4.6 Frequency of usage Respondents were required to state the frequency of using internet banking . rthis is shown in the table below
Frequency Percent
rare often regularly Total
10 40 44 94
10.6 42.6 46.8 100.0
10 respondents rarely used this service , 40 respondents. often use the service and 44 respondents use the service on a regular basis This information a has been illustrated in a bar chart below
50
40
30
20
10
Count
0 rare often regularly
How often you use the service
Type of services The type of services used by the respondents are given below Services Inter bank fund transfer Payment to other Number of respondents 46 23
personal account Payment to other local bank Verifying my account details Order checks book Stop lost/stolen check apply for credit limit change standing order transaction Saving/current/fixed deposit account foreign account debit/credit card
13 74 12 4 5 45 67 17 24
From the above table , it is noted that three services are widely used by respondents : Verifying my account details Saving/current/fixed deposit account standing order transaction The services which are rarely used are (a) Stop lost/stolen check (b) apply for credit limit change (c) Payment to other local bank N=4 N=5 N=13 N=74 N=67 N=45
4.6 INTERNET BANKING 4.6.1 Ease of Use
Ease of use is a factor that determine the frequency and intensity in the use of internet banking .in this respect respondents were required to give their views on a set of 8 statements . The result from the analysis is given in the table below : S.D 2 1 2 1 D 26 34 26 21 12 1 10 16 20 N 2 0 2 19 3 0 2 A 64 56 64 53 79 74 62 3 0 S.A 0 3 MEAN 3.2766 3.3617 3.3191 3.7128 3.5106 3.6596 3.2340 S.D 1.0308 .9600 .8578 .6819 .8519 .8367 1.1209
I find internet banking to be flexible to interact with I can use internet banking without anyone around to show me I can access various services simultaneously I find it easy to learn to use Internet Banking I require further training in using the internet Internet banking makes it easier for me to do my banking Generally I find online banking easy to use
In order to interpret the above data , the following scale has been used Mean :between 1 and 2 Mean : between 2 and 3 Mean : between 3 and 4 Mean between 4 and 5 very low low moderate to high very high
It is found out that mean scores fall in the range of 3.2340 to 3.7128. This demonstrate that ease of use is not a factor that inhibit the use of internet banking . The highest mean score relates to learning while the lowest factor relate to the ease of using internet banking The information above has been further analyzed through hypothesis testing . The aims is to identify the critical factor that determine the use of and accessibility to internet banking in term of (a) (b) (c) (d) Gender Age group Level of Education Occupation
The result from the tests are discussed below: The first test seek to determine as to whether gender is a factor that determine the ease of use or accessibility to internet banking H0 : Gender is a factor that determine the ease of using internet banking H1 : Gender is I not a factor that determine the ease of using internet banking The test result is given below : Ranks gender male female Total N 53 41 94 Mean Rank 44.43 51.46
Test Statistics EASET Chi1.565 Square df 1 Asymp. .211 Sig. a Kruskal Wallis Test b Grouping Variable: gender
A Kruskal Wallis Test has been carried out to determine whether gender is a factor that influence the ease of use or accessibility to internet banking At the statistical significance level of p=.05. , the test give evidence for accepting the null hypothesis ( p= . .211) . As such there is not sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis i.e Gender is a factor that determine the ease of using internet banking Age The second test seek to determine as to whether age is a factor that determine the ease of use or accessibility to internet banking H0 : Age is a factor that determine the ease of using internet banking
H1 : Age is not a factor that determine the ease of using internet banking The test result is given below Ranks Age EASET less than 20 20 to 35 35 to 50 above 50 Total Test Statistics EASET Chi5.723 Square df 3 Asymp. .126 Sig. a Kruskal Wallis Test b Grouping Variable: Age A Kruskal Wallis Test has been carried out to determine whether age is a factor that influence the ease of use or accessibility to internet banking At the statistical significance level of p=.05. , the test give evidence for accepting the null hypothesis ( p= . .126) . As such there is not sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis i.e Age is a factor that determine the ease of using internet banking Education The third test seeks to determine as to whether age is a factor that determine the ease of use or accessibility to internet banking H0 : Education is a factor that determine the ease of using internet banking H1 : Education is not a factor that determine the ease of using internet banking The test result is given below N 31 40 16 7 94 Mean Rank 45.69 45.94 60.66 34.36
Ranks Education primary level up to sc up to hsc universit y Total
N 10 32 40 12 94
Mean Rank 61.75 44.50 43.79 56.00
Test Statistics EASET Chi5.120 Square df 3 Asymp. .163 Sig. a Kruskal Wallis Test b Grouping Variable: Education A Kruskal Wallis Test has been carried out to determine whether education is a factor that influence the ease of use or accessibility to internet banking At the statistical significance level of p=.05. , the test give evidence for accepting the null hypothesis ( p= . .163) . As such there is not sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis i.e Education e is a factor that determine the ease of using internet banking Occupation The fourth test seeks to determine as to whether occupation is a factor that determine the ease of use or accessibility to internet banking H0 : Occupation H1 : Occupation is a factor that determine the ease of using internet banking is not a factor that determine the ease of using internet banking
The test result is given below : Ranks occupatio n
Mean Rank
Employe d piublic sector Employe d Private sector Student unemplo yed sel employed Total
34 33 4 8 15 94
45.96 52.94 32.25 54.81 39.20
Test Statistics EASET Chi4.725 Square df 4 Asymp. .317 Sig. a Kruskal Wallis Test b Grouping Variable: occupation
A Kruskal Wallis Test has been carried out to determine whether occupation is a factor that influence the ease of use or accessibility to internet banking At the statistical significance level of p=.05. , the test give evidence for accepting the null hypothesis ( p= . .163) . As such there is not sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis i.e Occupation is a factor that determine the ease of using internet banking
Summary of findings : The above results shoe that the age , gender , occupations ans education are factors that determine the ease that respondents use of internet banking
AWARENESS OF THE SERVICE This section deals with the level at which respondents are informed on the use of internet banking .
The responses are tabulated below: I have enough information about Internet Banking I'm aware of the benefits& risks in Internet Banking I have enough information about how to use Internet banking I have received information on internet banking from various means and sources S.D 1 34 0 0 D 18 21 16 5 7 3 N 3 A 69 39 69 78 2 8 S.A 3 MEAN 3.5851 2.4681 3.6064 3.9468 S.D .8726 1.3496 .7927 .5749
The mean score on three statements are in the range of 3.5851 and 3.9468. This shows that respondents have a high amount of information on the use of internet banking . However , a poor score( M=2.4681) has been achieved on the statement dealing with information on risk . As such , respondents feel that they are not well informed on the risk of using internet banking As with the previous analysis , the relationship between information and the following factors (i.e gender , age , occupation and education have been further explored . These are discussed below: Gender The aim of this test is to determine as to whether male and female respondents share a common view on the above four statements As such , the first test is as follows: H0 : Gender is a factor that determine the awareness of using internet banking H1 : Gender is I not a factor that determine the awareness The test result is given below Ranks gender of using internet banking
Mean Rank
male female Total
53 41 94
45.63 49.91
Test Statistics Chi-Square df Asymp. Sig. a Kruskal Wallis Test b Grouping Variable: gender AWET .589 1 .443
A Kruskal Wallis Test has been carried out to determine whether gender is a factor that influence the extent that respondents are informed on the use internet banking At the statistical significance level of p=.05. , the test give evidence for accepting the null hypothesis ( p= ) . As such there is not sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis . as such , gender is a factor that influence the extent that respondents are informed on the use internet banking Age The aim of this test is to determine as to whether there is a relationship between age and the extent that respondents have a high information H0 : Age is a factor that determine the of awareness ing internet banking H1 : Age is not a factor that determine of using awareness internet banking The test result is given below Ranks Age AWET less than 20 20 to 35 35 to 50 above 50 Total Test Statistics AWET Chi4.668 Square N 31 40 16 7 94 Mean Rank 50.32 48.44 35.31 57.50
df 3 Asymp. .198 Sig. a Kruskal Wallis Test b Grouping Variable: Age A Kruskal Wallis Test has been carried out to determine whether age is a factor that influence the extent that respondents are informed on the use internet banking At the statistical significance level of p=.05. , the test give evidence for accepting the null hypothesis ( p= ) . As such there is not sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis . As such , age is a factor that influence the extent that respondents are informed on the use internet banking Education In the previous analysis , it was found out that respondents are not too much aware of the risk of using internet banking . As such , this test aim at determining as to whether there is a relationship between age and the extent that respondents have a high information H0 : Education is a factor that determine awareness using internet banking H1 : Education is not a factor that determine of awareness using internet banking The test result is given below
Ranks Education primary level up to sc up to hsc universit y Total
N 10 32 40 12 94
Mean Rank 44.90 43.58 50.69 49.50
Test Statistics AWET Chi1.409 Square df 3 Asymp. .703 Sig.
a Kruskal Wallis Test b Grouping Variable: Education A Kruskal Wallis Test has been carried out to determine whether education is a factor that influence the extent that respondents are informed on the use internet banking At the statistical significance level of p=.05. , the test give evidence for accepting the null hypothesis ( p=.703 ) . As such there is not sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis . As such , education is a factor that influence the extent that respondents are informed on the use internet banking Occupation The statistics shows that most of respondents are employed in both the private and public sector . Mauritius is a country which rank among the top country in Africa whose population have a high level of literacy rate on the usage of internet . As such , the third test seeks to determine as to whether occupation is a determining factor with respect to the extent and level of awareness on the use of internet banking H0 : Occupation is a factor that determine awareness of using internet banking
H1 : Occupation is not a factor that determine awareness of using internet banking The result of the test is shown below Ranks occupation Employed public sector Employed Private sector Student unemployed sell employed Total Test Statistics AWET Chi2.527 Square df 4 Asymp. .640 Sig. a Kruskal Wallis Test b Grouping Variable: occupation N 34 33 4 8 15 94 Mean Rank 45.24 50.12 50.63 57.06 40.93
A Kruskal Wallis Test has been carried out to determine whether occupation is a factor that influence the extent that respondents are informed on the use internet banking At the statistical significance level of p=.05. , the test give evidence for accepting the null hypothesis ( p=..640 ) . As such there is not enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis . As such , occupation is a factor that influence the extent that respondents are informed on the use internet banking
Summary of findings The overall inference that can be drawn is that there is a multidimensional factors that determine the general awareness on the use of internet banking .Security is an area that has been given a low rating by the respondents
Security With increasing online services, banks face challenges in identifying and addressing consumer concerns about: transacting online; identifying areas of exposure or vulnerability due to insufficient disclosures; building and sustaining the confidence of customers; persuading customers to accept the impact of secure access technologies; and the carrying the cost of secure access technologies It is along these lines that respondents were required to give their views on a set of 4 statements , the result from the surveys are given below :
I trust in the ability of the bank to protect my confidentiality Use of digital signatures, encryption & authorization mechanisms provide a more secured Online Banking I know there is some risk to use 19 internet banking I trust in the technology the bank is using for internet
S.D 17
D 34 18
N 1 11
A 37 53
S.A 5 12
MEAN 2.7766
S.D 1.2881
3.6277 .9388
33 14
4 13
38 56 11
3.6277 2.6489
.9388 1.2067
banking From the above information , respondents have given a high rating to (a) Use of digital signatures, encryption & authorization mechanisms provide a more secured Online Banking ( M=3.6277) (b)I know there is some risk to use internet banking(M=3.6277) On the other hand , there is still some apprehension on the bank ability to create a high level of trust among its customers , This is reflected on the low score achieved on 2 factors as set out below : (a) I trust in the ability of the bank to protect my confidentiality ( M=2.7766) (b) I trust in the technology the bank is using for internet banking(M=2.6489) In line with the previous analysis , hypothesis testing have been carried out using the following factors : (a) Gender (b) Age (c) Education (d) Profession with a view to determine respondents views on the security of using internet banking
The result is summarized below : Factor Gender Age Education Profession p .953 .086 .654 .756 S/NS NS NS NS NS
On the basis of the result obtained, it can be safely inferred that the respondents perception on the security aspects of using internet banking are closely related to the following factors
(a) Gender (b) Age (c ) Education and (d) Profession Perceived Benefits Respondents were required to state the degree that they have benefited from that internet banking on a set of 4 statements: The statistics are given below :
Internet banking enables me to carry out my banking tasks more quickly Online banking gives me more financial control I find internet banking useful Accounts paid & funds are transferred without queues
S.D 1 10 0 2
D 16 20 34 26
N 0 2 0 2
A 74 62 59 64
S.A 3 0 1
MEAN
3.6596
S.D
.8367
3.2340 3.2872 3.3617
1.1209 .9796 .9600
From the above table , it is noted that the mean scores are in the range of 3.2340 to 3.6596. This indicate that more respondents find the use of internet banking to be beneficial
In line with the previous analysis , hypothesis testing have been carried out using the following factors : (e) Gender (f) Age (g) Education (h) Profession with a view to determine they influenced respondents views on the benefits of using internet banking
The result is summarized below : Factor P value S/NS
Gender Age Education Profession
,310 .598 .086 .654
Not Significant Not Significant Not Significant Not Significant
On the basis of the above figures it can be safely concluded that gender , age , education and occupation are determinants factors with respect to perceived benefits of using internet banking Convenience Respondents were asked to opine on the convenience of internet banking . The result from the analysis is given below : S.D A wide range of services are offered It is a convenient way of doing transaction There is a lot of time saving
1
D 21 12 22
N 19 3 2
A 53 79 70
S.A 0 0 0
MEAN
3.3191 3.7128 3.5106
S.D
.8578 .6819 .8519
0 0
From the above , respondents have given a high rating to all statements and the means are in the range of 3.7128 to 3.3191.
The factor convenience of doing business has received the highest rating (M=3.7128) and the factor relating to the variety of services has received the lowest rating (M=3.3191)
Overall , customers find internet banking to be convenient In line with the previous analysis , hypothesis testing have been carried out using the following factors : (i) Gender (j) Age (k) Education (l) Profession with a view to determine they influenced respondents views on the benefits of using internet banking
The result is summarized below : Factor Gender Age Education Profession P value .250 .076 .423 .201 S/NS Not significant Not significant Not significant Not significant
On the basis of the above figures it can be safely concluded that gender , age , education and occupation are determinants factors with respect to convenience of using internet banking
CUSTOMER SATISFACTION
In addition to the above analysis , this part of the analysis will consider the perception of respondents on their bank on a set of 5 dimensions : (a) Empathy ( b) Assurance
(a) Empathy Empathy is about giving customers individual attention and employees dealing with customers in a caring fashion. In this respect , respondents views were sought on this aspect on a set of 3 statements . The table below provides mean difference between expected level of satisfaction and the derived level of satisfaction on the various aspects of empathy and the p-value. Expectation (Mean) 3.5106 Perception (Mean ) 3.6596 Mean Difference 0.149 P value .209 S/NS NS
The bank understand the
need of their customers The bank responses to my queries are personalized The bank shows genuine concern and sympathy to my problem Overall score
3.2340 3.8085 3.5177
3.2872 3.1277 3.3582
0.0532 -0.6808 -0.1595
.722 .000 .029
NS S S
S-significant ( p value <= 0.05); NS- Not significant (p value >0.005) Table It is found from table that the overall mean difference value is negative ( Mean Difference: -0.1595) , thus indicating that respondents do not perceived the their bank to be empathic to their individual need . ,i.e the expected level of satisfaction is significantly ( p=..029) more than the derived level of satisfaction of the respondents However , Positive differences are noted for the banks understanding of the need of their customers and are responsive to their customers personal queries. However, it is found out that banks do not show genuine concern and sympathy to their customers problem.
The number of customers for each individual bank has been grouped using the mean differences between expectation and perception for each bank. This is shown in the table below : Between -2 Between and -1 -1 and 0 Bank A Bank B Bank C Bank D Bank E Others TOTAL % 1 4 1 0 1 0 7 0.07 10 11 5 2 3 5 36 0.38 0 8 5 1 6 4 2 26 0.28 Between 0 and 1 3 2 1 5 5 1 17 0.18 Between 1 and 2 4 1 0 2 0 1 8 0.09
From the above table it is noted that 45 % of the respondents are dissatisfied , 28% are indifferent while 27 % are satisfied on the empathy dimension .
The above data has been further analysed and the percentage of customers for each bank falling in the different categories is shown below :
Between -2 Between and -1 -1 and 0 Bank A Bank B Bank C Bank D Bank E Others Total % 0.04 0.17 0.13 0.00 0.08 0.00 0.07 0.38 0.48 0.63 0.13 0.23 0.56 0.38
0 0.31 0.22 0.13 0.40 0.31 0.22 0.28
Between 0 and 1 0.12 0.09 0.13 0.33 0.38 0.11 0.18
Between 1 and 2 0.15 0.04 0.00 0.13 0.00 0.11 0.09
From the above , it is noted that (a) Bank B has the highest percentages of the most dissatisfied customers (b) Both bank B and other bank has the highest percentage of dissatisfied customers (c) Bank D has the highest percentage of indifferent customers (d) Bank E has the highest percentage of satisfied customers (e) Bank A has the highest percentage of the most satisfied customers
On the basis of the above , a weighted mean score has been worked to determine the overall performance of the bank . The weight is taken to be the number of customers falling within a range . The median of a range has been taken to compute the overall mean score . This methodology will be also be used for other dimensions in this study .
Mean Difference -2 to -1
Median Scare -1.5
Interpretation Most
-1 to 0 0 0 to 1 1 to 2
-.5 0 .5 1.5
dissatisfied Dissatisfied Indifferent Satisfied Most Dissatisfied
The data has been ranked and this is shown in the table below :
Bank A Bank B Bank C Bank D Bank E Others
Average Mean Score Ranking 0.2 -1.8 -0.7 0.9 -0.1 -0.1
2 nd 6 th 5th 1 st 3 rd 3 rd
On the criterion of fulfillment , Bank D has achieved the highest rank and Bank B has achieved the lowest rank The above findings have been confirmed by conducting a hypothesis testing : H0 : There is no difference on customers level of satisfaction on the empathy dimension between banks H1 : There is a difference on customers level of satisfaction on the empathy dimension between banks The result of the findings are given below : Ranks Bank Bank A N 26 49.71 Mean Rank
Bank B Bank C Bank D Bank E Others Total Test Statistics
23 8 15 13 9 94
32.85 40.13 65.43 54.08 45.72
Chi-Square df Asymp. Sig. a Kruskal Wallis Test b Grouping Variable: Choose your main bank
empathy 15.315 5 .009
A Kruskal Wallis Test to find out as to whether customers find their bank to be empathetic to their needs . At the statistical significance level of p=.05. , the test give evidence for rejecting the null hypothesis ( p=.009 )) . As such there is sufficient evidence to reject the null hypothesis i.e There is a difference on customers level of satisfaction on the empathy dimension between banks Responsiveness Although service organizations may imagine the Internet as a remote service, with opportunities to maintain a standardized approach in service delivery, customers do not regard the Internet as a remote service. They expect a lot of straightforward, honest and timely communication, strong interactivity, good interfacing with backstage activities and adequate support. In other word , they want their banks to be responsive .Responsiveness is about prompt service to customers, willingness to help customers and readiness to respond to customers' requests The table provides mean difference between expected level of satisfaction and the derived level of satisfaction on the various aspects of responsiveness , together with the p-value. The aspects considered are level of care , information to customers ,on line help and solving both technical and non technical problem
The bank takes care of the
Expectation (Mean) 3.8085
Perception (Mean ) 3.1277
Mean P Difference value -0.6808 .000
S/NS S
online problems promptly When a problem occurs the bank provide appropriate information to customers Information is given on what to do if the transaction is not processed In case of a problem, the site offers live help with a person The bank's website contains a section to help/guide me for common problems Bank helps quickly in technical & non-technical issues Overall
3.2766
3.4681
0.1915 .166
3.4149
2.6809
-0.734 .000
3.8617 3.2447
3.5000 2.5106
-0.3617 .000 -0.7341 .000
S S
3.3191 3.4876
3.7128 3.1667
0.3937 .004 -0.3209 .004
S S
S-significant ( p value <= 0.05); NS- Not significant (p value >0.005)
Overall , the difference between the expected and perceived level are significant at the 5% significance level It is found from the table that 5 out of the 6 mean difference values are negative indicating that the perceived level of satisfaction is less than the desired level of satisfaction: (a) Caring about online problem (b) Giving information for self help ( c) on line help (d) Content of website (e) Solving technical and non technical problem Mean Difference (-0.6808) Mean Difference (-0.734) Mean Difference (-0.3617) Mean Difference (-0.7341) Mean Difference (-0.7341)
On the other hand , customers are satisfied with respect to that bank giving an appropriate information to the customers when there is a problem
Overall , It is concluded that the respondents expectation are significantly more than their perception on the responsiveness dimension The number of customers falling in each range for each individual bank is shown in the table below : Between -2 Between and -1 -1 and 0 Bank A Bank B Bank C Bank D Bank E Others TOTAL % 1 1 0 0 1 0 7 0.07 18 17 5 8 7 5 36 0.38 0 6 2 2 1 2 1 26 0.28 Between 0 and 1 1 3 1 6 3 3 17 0.18 Between 1 and 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 8
On the basis of the above , it is noted that 45 respondents are dissatisfied with their bank , 28 % are indifferent and 18 % are satisfied The above data has been further analysed and the percentage of customers for each bank falling in the different categories are shown below :
Between -2 Between and -1 -1 and 0 Bank A Bank B Bank C Bank D Bank E Others Total % 0.04 0.04 0.00 0.00 0.08 0.00 0.07 0.69 0.74 0.63 0.53 0.54 0.56 0.38
0 0.23 0.09 0.25 0.07 0.15 0.11 0.28
Between 0 and 1 0.04 0.13 0.13 0.40 0.23 0.33 0.18
Between 1 and 2 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
From the above , it is noted that (f) (g) (h) (i) Bank E has the highest percentages of the most dissatisfied customers Both bank A and bank B have the highest percentage of dissatisfied customers Bank C has the highest percentage of indifferent customers Bank D has the highest percentage of satisfied customers
On the basis of the above , a weighted mean score has been worked to determine the overall performance of the bank . The data has been ranked and this is shown in the table below :
Bank A Bank B Bank C Bank D Bank E Others
Average Mean Score Ranking -2 -1.7 -0.4 -0.2 -0.7 -0.2
6 nd 5th 3th 1 st 4th 1 st
On the criterion of responsiveness , other bank and Bank D have achieved the highest ranking and Bank A has achieved the lowest rank The above finding is confirmed through the following test H0 : There is no difference on customers level dissatisfaction on the responsiveness dimension between banks H1 : There is a difference on customers level of dissatisfaction on the responsiveness dimension between banks
The findings are given below :
Ranks Choose your main bank Bank A Bank B Bank C Bank D Bank E Others Total Test Statistics
N 26 23 8 15 13 9 94
Mean Rank 45.67 35.43 52.50 54.37 55.88 55.61
Responsiveness Chi-Square df Asymp. Sig. a Kruskal Wallis Test b Grouping Variable: 7.986 5 .157
A Kruskal Wallis Test to find out as to whether customers opinion on the responsiveness dimension differs beteeen bank . At the statistical significance level of p=.05. , the test does not give evidence for rejecting the null hypothesis ( p=.009 )) . i.e There is no difference on customers level of dissatisfaction on the responsiveness dimension between banks Fulfillment Privacy concerns and the protection of users from the risk of fraud and financial loss have a strong impact on attitude toward use of online financial services (Montoya-Weiss et al., 2003). Depth of information content and availability has been found to be an important factor as it enables users to control the content. Customer perceptions of online shopping are also largely affected by issues such as the graphic style of the web site, including color, layout, print size and type, number of photographs and graphics, and animation (Hoffman and Novak, 1996; Hoque and Lohse, 1999). On this basis , respondents were required to opine on a set of 7 statements . The result is given below :
It allows transactions to be conducted quickly Pages load promptly Getting on the site is swift This site is always accessible for business This site initiates and operates immediately This site never crashes After entering my transaction information, the page neither locks nor freezes Overall
Expectation (Mean) 3.6170 3.9362 3.4681 2.8617 2.4468 3.1809 3.7340
Perception (Mean ) 3.4149 3.5213 3.2766 3.7340 3.0106 1.4468 2.7128
Mean Difference
P value .106
S/NS NS S NS NS S S S
-0.2021 -0.4149 .003 -0.1915 .142 .373 0.8723 .009 0.5638 -1.7341 .000 .000 -1.0212 -0.4119 000
3.3207
2.9088
S-significant ( p value <= 0.05); NS- Not significant (p value >0.005) It is found out that the result is significantly different on 4 statements i.e loading of pages, the responsiveness of the site , the reliability of the site and the usability of the site It is found from the table that 5 out of the 7 mean difference values are negative indicating that the perceived level of satisfaction is less than the desired level of satisfaction: These are : (a) It allows transactions to be conducted quickly (b) Pages load promptly Getting on the site is swift (d) This site never crashes (e) The page neither locks nor freezes M.D =-0.2021 M.D=-0.4149 M.D=-0.1915 M.D=-1.7341 M.D=-1.0212
However , positive difference have been noted ( i.e customers are satisfied ) on the accessibility of the site ( M.D= 0.8723 ) and responsiveness of the site (M.D =0.5638) Overall . the customers are dissatisfied on this dimension of the service . The mean difference is -0.4119
The mean differences for each bank is shown in the table below : Between -2 Between and -1 -1 and 0 Bank A Bank B Bank C Bank D Bank E Others Total % 3 3 0 0 0 0 6 0.06 20 18 5 11 9 7 70 0.74 0 2 0 2 0 3 0 7 0.07 Between 0 and 1 1 2 1 4 1 2 11 0.12 Between 1 and 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
From the above table it is noted that 80 % of the respondents are dissatisfied , 7 % are indifferent while 12 % are satisfied with the internet services provided by banks . The above data has been further analysed and the percentage of customers for each bank falling in the different categories is shown below :
Between -2 Between and -1 -1 and 0 Bank A Bank B Bank C Bank D Bank E Others Total % From the above , it is noted that 12 13 0 0 0 0 6 77 78 63 73 69 78 74
0 8 0 25 0 23 0 7
Between 0 and 1 4 9 13 27 8 22 12
Between 1 and 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
(j) Bank B has the highest percentages of the most dissatisfied customers (k) Both bank B and other bank has the highest percentage of dissatisfied customers
(l) Bank C has the highest percentage of indifferent customers (m)Bank D has the highest percentage of satisfied customers On the basis of the above , a weighted mean score has been worked to determine the overall performance of the bank . The data has been ranked and this is shown in the table below :
Bank A Bank B Bank C Bank D Bank E Others
Average Mean Score -2.8 -2.5 -0.4 -0.7 -0.8 -0.5
Ranking 6 th 5 th Ist 3rd 4 th 2 nd
On the criterion of fulfiment , Bank C has achieved the highest rank and Bank A has achieved the lowest rank The above findings have been confirmed by conducting a hypothesis testing : H0 : There is no difference on customers level of satisfaction on the fulfillment dimension between banks H1 : There is a difference on customers level of satisfaction on the fulfillment dimension between banks
The result is shown below Ranks Choose your main bank Bank A Bank B Bank C Bank D Bank E Others Total N 26 23 8 15 13 9 94 Mean Rank 35.27 42.46 61.25 57.77 58.73 50.17
Test Statistics Fulfillment Chi-Square 12.654 df 5 Asymp. Sig. .027 a Kruskal Wallis Test b Grouping Variable: Choose your main bank A Kruskal Wallis Test to find out as to whether customers opinion on the responsiveness dimension differs between bank . At the statistical significance level of p=.05. , the test give evidence for rejecting the null hypothesis ( p=.02)) . i.e There is a difference on customers level of satisfaction on the fulfillment dimension between banks
Assurance
Expectation Perception Mean P S/NS (Mean) (Mean ) Difference value When I access my account 3.0532 4.5000 1.4468 .000 S I feel secure. Bank X's web site instills confidence Bank X is very accurate in 3.2766 3.1170 -0.1596 .416 NS their responses to my queries/requests Bank x keep accurate 3.6596 3.2340 -0.4256 .004 S records of my account transactions 3.3298 3.6170 0.2872 .002 S Overall Score It is found from the table that all the mean difference values are positive for the confidence dimension (M.D =1.4468) and they are negative for the accuracy dimension ( M.D =-0.1596) and ( M.D =0.4256) Overall , customers appear to be satisfied on this dimension ( M.D =
0.2872)
The mean differences for each bank has bean grouped in 5 categories and is shown in the table below : Between -2 Between and -1 -1 and 0 Bank A Bank B Bank C Bank D Bank E Others Total % 2 6 4 0 5 3 6 0 2 5 4 3 2 2 Between 0 and 1 10 8 3 6 6 1 Between 1 and 2 6 6 1 1 2 0
From the above table it is noted that 80 % of the respondents are dissatisfied , 7 % are indifferent while 12 % are satisfied with the internet services provided by banks . The above data has been further analysed and the percentage of customers for each bank falling in the different categories is shown below : Between -2 Between and -1 -1 and 0 Bank A Bank B Bank C Bank D Bank E Others Total % 0.08 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.02 0.23 0.17 0.00 0.33 0.23 0.67 0.26 0 0.08 0.22 0.50 0.20 0.15 0.22 0.19 Between 0 and 1 0.38 0.35 0.38 0.40 0.46 0.11 0.36 Between 1 and 2 0.23 0.26 0.13 0.07 0.15 0.00 0.17
From the above , it is noted that (n) (o) (p) (q) (r) Bank A has the highest percentages of the most dissatisfied customers other bank has the highest percentage of dissatisfied customers Bank C has the highest percentage of indifferent customers Bank E has the highest percentage of satisfied customers Both Bank A and bank B have the most satisfied customer
On the basis of the above , a weighted mean score has been worked to determine the overall performance of the bank . The data has been ranked and it is shown in the table below :
Bank A Bank B Bank C Bank D
Average Mean Score 1.6 2.2 0.6 0.4
Ranking 2 nd 1 st 4 th 5 th 3rd 6 th
Bank E Others
0.9 -0.5
On the criterion of fulfiment , Bank A has achieved the highest rank and other banks has achieved the lowest rank The above findings have been confirmed by conducting a hypothesis testing : H0 : There is no difference on customers level of satisfaction on the assurance dimension between banks H1 : There is a difference on customers level of satisfaction on the assurance dimension between banks Choose your main bank Bank A Bank B Bank C Bank D Bank E Others Total N 26 23 8 15 13 9 94 Mean Rank 50.38 55.15 48.31 43.80 49.65 21.94
Chi-Square df Asymp. Sig.
AST 10.544 5 .061
A Kruskal Wallis Test to find out as to whether customers opinion on the responsiveness dimension differs beteeen bank . At the statistical significance level of p=.05. , the test give evidence for accepting the null hypothesis ( p=..061) . i.e There is no significant difference on customers level of satisfaction on the assurance dimension between banks
Reliability Reliability is judged by the ability of the service provider to deliver the services as promised, dependability in handling customers' service problems, performing services right the first time, providing services at the promised time and Keeping customers informed of any changes . Un this respect ,respondents were required to give their views on a set of 5 statements . The result is shown below:
The links on the websites are problem free, accurate and the pages download quickly The bank's website is running all the time/ always accessible Information content and text on the website are easy to understand Service is delivered
Expectation (Mean) 3.5957
Perception Mean (Mean ) Difference 3.3191 -0.2766
P S/NS value .092 NS
3.2766 3.9362 3.8404
3.3191 0.0425 3.3191 3.3191 -0.6171 -0.5213
.619 NS .000 S .000 S
exactly as promised The bank always provides the service at the promised time Overall
3.8298 3.6957
3.3191 3.3191
.000 S -0.5107 -.3766 .003 S
It is found from table that the overall mean difference value is negative ( Mean Difference: -.3766 ) , thus indicating that respondents do not perceived the their bank service to be reliable Positive differences is noted on the accessibility to the website (M.D=0.0425) However, it is found out customers are dissatisfied with respect of the following (a) Downloading (b) Information content Meeting promises (d) Timeliness M.D= -0.2766 M.D=-0.6171 M.D=-0.5213 M.D=-.3766
In addition, the result is significant at the 5 % significance level on the statements dealing with information content ,meeting promises and the timeliness of the service . In view that the mean difference are negative , this indicate a high level of dissatisfaction . The mean differences for each bank has bean grouped in 5 categories and is shown in the table below : Between -2 Between and -1 -1 and 0 Bank A Bank B Bank C Bank D Bank E Others Total % 7 8 3 3 3 1 25 9 3 1 3 4 4 24 0 2 2 0 2 2 2 10 Between 0 and 1 4 9 4 7 4 2 30 Between 1 and 2 4 1 0 0 0 0 5
From the above table , it is noted that 49 respondents are dissatisfied , 10 respondents are indifferent and 35 respondents are satisfied .
The above data has been further analyzed and the percentage of customers for each bank falling in the different categories is shown below : Between -2 Between and -1 -1 and 0 Bank A Bank B Bank C Bank D Bank E Others Total 0.27 0.35 0.38 0.20 0.23 0.11 0.27 0.35 0.13 0.13 0.20 0.31 0.44 0.26 0 0.08 0.09 0.00 0.13 0.15 0.22 0.11 Between 0 and 1 0.15 0.39 0.50 0.47 0.31 0.22 0.32 Between 1 and 2 0.15 0.04 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.05
From the above , it is noted that (s) Bank B and Bank C has the highest percentages of the most dissatisfied customers (t) Bank A and other bank have the highest percentage of dissatisfied customers (c ) other bank has the highest percentage of indifferent customers (u) Bank C has the highest percentage of satisfied customers (v) Bank A have the most satisfied customer On the basis of the above , a weighted mean score has been worked to determine the overall performance of the bank . The data has been ranked and this is shown in the table below :
Bank A Bank B Bank C Bank D Bank E Others
Average Mean Score Ranking -1.4 -1.5 -0.6 -0.5 -0.9 -0.5
5th 6 th 3rd 1 st 4th 1 st
Although the weighted mean score is negative for all banks , Bank D and :other banks are giving a relatively better service than the other banks The above findings have been confirmed by conducting a hypothesis testing : H0 : There is no difference on customers level of satisfaction on the reliability dimension between banks H1 : There is a difference on customers level of satisfaction on the reliability dimension between banks
Bank Bank A Bank B Bank C Bank D Bank E Others Total
N 26 23 8 15 13 9 94 Reliability 1.623 5 .898
Mean Rank 45.52 46.28 42.44 54.33 50.42 45.22
Chi-Square df Asymp. Sig.
A Kruskal Wallis Test to find out as to whether customers opinion on the responsiveness dimension differs between bank . At the statistical significance level of p=.05. , the test give evidence for accepting the null hypothesis ( p=.898) . i.e There is a no difference on customers level of satisfaction on the reliability dimension between banks Summary of findings : The above analysis has shown that customer satisfaction is a multi dimension issue and it is dependent on various factors such as (a) age (b) education (c) gender and
(d) occupation The analysis also shows that there is a difference on the quality of the internet banking services provided by banks in Mauritius . The next chapter will make some recommendations to address those issues.
5.0 Recommendations 5.1 Introduction In this chapter, appropriate recommendations have been made to deal with the identified apprehension raised by respondents s on the use of internet banking . 5.2 Security The analysis has shown that respondents are not well aware on the inherent risk of using internet banking . Banks should inform their customers on state of the art technology they are using to address this issue and these should be regularly communicated to their customers 5.3 Empathy Respondents are of the view that bank do not show genuine concern and sympathy to their problem From the analysis , it is found out that Bank B and :other banks have received a poor rating on the empathy dimension. In order to overcome these weaknesses , it is important for these banks to :to hire people who like people. to challenge them to develop better method, to give them the authority to solve problem , to provide adequate training and to recognize and reward them for their performance 5.4 Assurance Most respondents have stated that banks do not takes care of the online problems promptly, information is not given on what to do if the transaction is not processed. Moreover , , the site does not offers on line help and the website does contain a section to help/guide users for common problems. These problems occur mainly with Bank A , B and E . In this respect , these bank should reengineer their website to contain those features 5.5 Accessibility Many respondents have shown concern on to the accessibility to web site . These problems are more common at B and the other banks. In this respect , these banks should address these problems using state of the art technology . In addition , these bank could resort to a benchmarking exercise with the other banks , 5.6 Accuracy
Accuracy is also an area which causes some dissatisfaction among the respondents . A priori , banks should investigate into the factors that are causing customers to loose confidence in their bank . In addition , these banks should improve their mechanism to handle customer complaints , From the analysis , these problems occur mainly at A and the other bank 5.7 Reliability From the previous analysis , Bank A , Bank B and the other banks have been given a low rating on the reliability dimension .This can arise from the technology being used by the bank as well as inadequate management commitment to service quality and the perception of infeasibility that is not all customer expectations can be met In this respect , it is recommended that banks should give a high priority to this issue 5.8 Risk The study has also shown that respondents are still uncertain on the following issues : risk of using internet banking and confidentiality of information . In this respect , it is recommend that all the banks should intensify these aspect in the promotion of their services and should regularly communicate to their customers on the bank initiative to address those factors
6 CONCLUSION 6.1 Introduction Overall, the findings has shown that people have still some apprehension on the use of internet banking . Moreover , there is some difference on the quality of internet banking services among banks .In this respect , appropriate recommendations have been made in this study . 6.2 Area for further study In view that there are wide difference in the internet banking services among banks , further research could be done on the use of benchmarking to improve the quality of services in the area of internet banking
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Sample AnalysisDocumento23 pagineSample AnalysisGopaul UshaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Three Research Methodology 3.1Documento27 pagineChapter Three Research Methodology 3.1Joseph JboyNessuna valutazione finora
- Impact in Learning IT Among HIV Orphanage Children in Malaysia Oct 2019Documento9 pagineImpact in Learning IT Among HIV Orphanage Children in Malaysia Oct 2019Iezma MadzinNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Four Data Analysis and Presentation of FindingsDocumento21 pagineChapter Four Data Analysis and Presentation of FindingsRephah KitaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Chi Square TestDocumento7 pagineChi Square TestShruti S KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Information: Chapter - Iv Analysis and Interpretation of DataDocumento37 pagineData Information: Chapter - Iv Analysis and Interpretation of DataShankar ChinnusamyNessuna valutazione finora
- Analysis & Interpretation of DataDocumento42 pagineAnalysis & Interpretation of DataSaili SarmalkarNessuna valutazione finora
- INPUT-effectiveness of Virtual LaboratoryDocumento21 pagineINPUT-effectiveness of Virtual Laboratorynena marie evalaroza100% (1)
- Statistics 1510 Survey Data AnalysisDocumento6 pagineStatistics 1510 Survey Data AnalysisGeorge W. Minder IVNessuna valutazione finora
- Pratik PresentationDocumento26 paginePratik PresentationPratik Malla ThakuriNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation, Analysis, and Interpretation of Data: 1. Respondent's ProfileDocumento5 paginePresentation, Analysis, and Interpretation of Data: 1. Respondent's ProfilefgfgfNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment 3 FBADocumento14 pagineAssignment 3 FBAMin MinNessuna valutazione finora
- BBA 4009 Competitive AnalysisDocumento20 pagineBBA 4009 Competitive AnalysisVentusNessuna valutazione finora
- Comparative AnalysisDocumento9 pagineComparative Analysissamantha.tura4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Educational Statistics: Final ExaminationDocumento6 pagineEducational Statistics: Final ExaminationBonjovi HajanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nur 028 Sas 11 20Documento5 pagineNur 028 Sas 11 20Noven CalambroNessuna valutazione finora
- Written Work 13 - Chi-Square ApplicationsDocumento8 pagineWritten Work 13 - Chi-Square ApplicationsDanrey PasiliaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Bstat CheckDocumento9 pagineBstat Checkritam chakrabortyNessuna valutazione finora
- Assignment SPSSDocumento13 pagineAssignment SPSSNiluka Nil nuwanNessuna valutazione finora
- BMA331 JP MorganDocumento7 pagineBMA331 JP Morganmanyaki SlicesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Four and Five FiDocumento17 pagineChapter Four and Five FimcpridemariraNessuna valutazione finora
- MuzammalDocumento4 pagineMuzammalUzair RazzaqNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - 4 Data Analysis and InterpretationDocumento36 pagineChapter - 4 Data Analysis and InterpretationNagireddy KalluriNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 MethodologyDocumento9 pagineChapter 3 Methodologywauie densingNessuna valutazione finora
- Business ResearchDocumento35 pagineBusiness ResearchAbdul AzimNessuna valutazione finora
- Chi-Square of Independence Araza, Gulferic, LucabanDocumento39 pagineChi-Square of Independence Araza, Gulferic, LucabanVenusNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4Documento9 pagineChapter 4Loraine PlatillaNessuna valutazione finora
- Results, Data Analysis and DiscussionsDocumento14 pagineResults, Data Analysis and Discussionsuniversal printerNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter - 4 Analysis and InterpretationDocumento81 pagineChapter - 4 Analysis and InterpretationS.SeethalakshmiNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4Documento19 pagineChapter 4chandrujayaraman1205Nessuna valutazione finora
- Final Research Project Report On: Master of Business AdministrationDocumento10 pagineFinal Research Project Report On: Master of Business AdministrationGopalaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 3 AngelineDocumento5 pagineChapter 3 AngelineAngelo CompahinayNessuna valutazione finora
- Revised - Chapter 4 - 07 14 2022Documento7 pagineRevised - Chapter 4 - 07 14 2022niveraknollNessuna valutazione finora
- Data Analysis and InterpretationDocumento18 pagineData Analysis and InterpretationDivya RajaveluNessuna valutazione finora
- BBA 4009 Competitive Analysis (Assignment)Documento16 pagineBBA 4009 Competitive Analysis (Assignment)VentusNessuna valutazione finora
- MTH410 S14 Lecture 01 May 12 - Mo-WedDocumento153 pagineMTH410 S14 Lecture 01 May 12 - Mo-WedzaidNessuna valutazione finora
- CHAPTERFOURTEDYDocumento7 pagineCHAPTERFOURTEDYJohn Cedric PerezNessuna valutazione finora
- Summary of Findings, Recommendations and ConclusionsDocumento14 pagineSummary of Findings, Recommendations and ConclusionsChandrakala v VenkateshNessuna valutazione finora
- Foudation of Business Analytics - Tiktok in VietnamDocumento15 pagineFoudation of Business Analytics - Tiktok in VietnamNguyễn Đào Minh UyênNessuna valutazione finora
- Bus 173 Project.1912526630Documento10 pagineBus 173 Project.1912526630ninadrahman268Nessuna valutazione finora
- Business Statistics AssignmentDocumento16 pagineBusiness Statistics Assignmentew1vcyqaNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4 ProfileDocumento9 pagineChapter 4 ProfileRon Magno100% (1)
- Seatwork 12 Analysis of Variance ANOVA Simple Linear RegressionDocumento17 pagineSeatwork 12 Analysis of Variance ANOVA Simple Linear RegressionDanrey PasiliaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Servicequalityof Canara BankDocumento49 pagineServicequalityof Canara BankRichard Lawrence50% (4)
- Institute of Management Studies and Research: KLE Society'sDocumento22 pagineInstitute of Management Studies and Research: KLE Society'sRutuja HukkeriNessuna valutazione finora
- QUESTIONAIREDocumento18 pagineQUESTIONAIREGracia LuhongNessuna valutazione finora
- SHS Immersion Q4 Week-1Documento7 pagineSHS Immersion Q4 Week-1Jullianne Rhoema HerederoNessuna valutazione finora
- Results and Findings, Summary, Conclusion, and RecommendationsDocumento12 pagineResults and Findings, Summary, Conclusion, and RecommendationsFAUSTINO HANNAH JAYENessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Four Data Presentation, Analysis and Interpretation 4.0Documento7 pagineChapter Four Data Presentation, Analysis and Interpretation 4.0DesilynQuibuyenVillanuevaNessuna valutazione finora
- BBA4009 Au Lee YauDocumento18 pagineBBA4009 Au Lee YauChristopher AuNessuna valutazione finora
- A Correlational Study On Working Environment and Job Satisfaction of The Call Center AgentsDocumento19 pagineA Correlational Study On Working Environment and Job Satisfaction of The Call Center AgentsSophia BiacoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mid-Term of Scientific WritingDocumento44 pagineMid-Term of Scientific WritingNguyễn UyênNessuna valutazione finora
- Students Opinion On Online LearningDocumento9 pagineStudents Opinion On Online Learning17ust030Nessuna valutazione finora
- MCQDocumento5 pagineMCQBahauddin BalochNessuna valutazione finora
- Social Studies Project School Based Assessment (S.B.A) (Year 2017)Documento20 pagineSocial Studies Project School Based Assessment (S.B.A) (Year 2017)Keron ThomasNessuna valutazione finora
- Answer BookDocumento10 pagineAnswer BookAshish AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- STAT 125 HK Business Statistics Midterm ExamDocumento65 pagineSTAT 125 HK Business Statistics Midterm Examandrebaldwin100% (1)
- SB T222WSB 7 Statistic ReportDocumento13 pagineSB T222WSB 7 Statistic ReportHoang Khanh Linh NguyenNessuna valutazione finora
- Work N FamilyDocumento1 paginaWork N FamilymmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- Add Notes - Lean and 7 WastesDocumento7 pagineAdd Notes - Lean and 7 WastesNguyễn Phương AnhNessuna valutazione finora
- PHD 3 SypnosisMathoorahDocumento15 paginePHD 3 SypnosisMathoorahmmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- PHD 3 SypnosisMathoorahDocumento15 paginePHD 3 SypnosisMathoorahmmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- Work N FamilyDocumento1 paginaWork N FamilymmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- Work N FamilyDocumento1 paginaWork N FamilymmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- Work N FamilyDocumento1 paginaWork N FamilymmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- PHD Bodha Proposal2Documento13 paginePHD Bodha Proposal2mmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- PHD Bodha Proposal2Documento13 paginePHD Bodha Proposal2mmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- Work N FamilyDocumento1 paginaWork N FamilymmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- Work N FamilyDocumento1 paginaWork N FamilymmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- Performance AppraisalDocumento29 paginePerformance Appraisalmmathoorah0% (1)
- PHD Bodha Proposal2Documento13 paginePHD Bodha Proposal2mmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- Work N FamilyDocumento1 paginaWork N FamilymmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- Program Based Budgeting 1Documento79 pagineProgram Based Budgeting 1mmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- PHD 3 SypnosisMathoorahDocumento15 paginePHD 3 SypnosisMathoorahmmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- PHD 3 SypnosisMathoorahDocumento15 paginePHD 3 SypnosisMathoorahmmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- Program Based Budgeting 1Documento79 pagineProgram Based Budgeting 1mmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- Program Based Budgeting 1Documento79 pagineProgram Based Budgeting 1mmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- Dcorporate Governance RatingsDocumento107 pagineDcorporate Governance RatingsmmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- Swot Analysis of Private Tuition in MauritiusDocumento16 pagineSwot Analysis of Private Tuition in Mauritiusmmathoorah100% (1)
- University of Technology of Mauritius: Aartee BeeharryDocumento29 pagineUniversity of Technology of Mauritius: Aartee BeeharrymmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- Program Based Budgeting 1Documento79 pagineProgram Based Budgeting 1mmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- Dcorporate Governance RatingsDocumento107 pagineDcorporate Governance RatingsmmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- University of Technology of Mauritius: Aartee BeeharryDocumento29 pagineUniversity of Technology of Mauritius: Aartee BeeharrymmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- SequencingDocumento36 pagineSequencingNarasi R Chari100% (1)
- QuestionnaireCSr KIRIVANIDocumento1 paginaQuestionnaireCSr KIRIVANImmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- QuestionnaireCSr KIRIVANIDocumento1 paginaQuestionnaireCSr KIRIVANImmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- Questionnaire ChitDocumento11 pagineQuestionnaire ChitmmathoorahNessuna valutazione finora
- Wu2018 JournalDocumento27 pagineWu2018 JournalSyafrie MuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- Making Instant Multimedia Linking Multimedia Objects:: Steps To Use Publish and SubscribeDocumento23 pagineMaking Instant Multimedia Linking Multimedia Objects:: Steps To Use Publish and SubscribeDhinesh PdnNessuna valutazione finora
- CMD and Port NumberDocumento15 pagineCMD and Port Numberyami adiNessuna valutazione finora
- MIDAS API Documentation v2.00Documento57 pagineMIDAS API Documentation v2.00MIDASNessuna valutazione finora
- The SAGE Handbook of New MediaDocumento333 pagineThe SAGE Handbook of New MediaLidia PituleaNessuna valutazione finora
- The Arabian NightsDocumento430 pagineThe Arabian NightsMontez WilliamsNessuna valutazione finora
- 8.2.8 Lab - Using Wireshark To Examine Ethernet FramesDocumento7 pagine8.2.8 Lab - Using Wireshark To Examine Ethernet Framesbui lamNessuna valutazione finora
- Amtrak Trackside WiFi RFP IntroductionDocumento11 pagineAmtrak Trackside WiFi RFP IntroductionEsme VosNessuna valutazione finora
- CV - Bhashitha PrasangaDocumento4 pagineCV - Bhashitha PrasangaAkshay KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Opnet TutorialDocumento8 pagineOpnet TutorialBee MUNessuna valutazione finora
- Session 2 - EBEIS Overview & General Workflow Process - Region 10Documento31 pagineSession 2 - EBEIS Overview & General Workflow Process - Region 10Ian Khay CastroNessuna valutazione finora
- RECON BRX 2017 Analyzing Mifare Classic CrackingDocumento21 pagineRECON BRX 2017 Analyzing Mifare Classic CrackingpaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Empowerment of Women: MethodsDocumento3 pagineEmpowerment of Women: MethodsmonicaNessuna valutazione finora
- CSC Quiz 2Documento4 pagineCSC Quiz 2Jaya MalathyNessuna valutazione finora
- SH CX 9.1.5dDocumento68 pagineSH CX 9.1.5dDent TewinNessuna valutazione finora
- ReflectionDocumento4 pagineReflectionHafizi ZsharpNessuna valutazione finora
- Google Keep Headers FREEBIE Product InfoDocumento6 pagineGoogle Keep Headers FREEBIE Product InfoEnrique AlejandroNessuna valutazione finora
- How To Upload and Display Image PHP HTML SQLDocumento4 pagineHow To Upload and Display Image PHP HTML SQLMaurice MutetiNessuna valutazione finora
- League Improvement ChecklistDocumento6 pagineLeague Improvement ChecklistCody KuchulisNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To HP Load Runner Getting Familiar With Load Runner 4046Documento28 pagineIntroduction To HP Load Runner Getting Familiar With Load Runner 4046DurgaCharan KanaparthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Detailed Project Report: "Government User Network" For Service Delivery at Village LevelDocumento164 pagineDetailed Project Report: "Government User Network" For Service Delivery at Village Levelsagar cherryNessuna valutazione finora
- Medford Garage Final Report 10.15.11Documento182 pagineMedford Garage Final Report 10.15.11Medford Public Schools and City of Medford, MANessuna valutazione finora
- Io T2Documento6 pagineIo T2Rupesh MaratheNessuna valutazione finora
- Advertainment or Adcreep - Game Players' Attitudes Toward Advertising and Product Placements in Computer GamesDocumento19 pagineAdvertainment or Adcreep - Game Players' Attitudes Toward Advertising and Product Placements in Computer GamesSerban SergiuNessuna valutazione finora
- Ebook - Electronics Tutorial PDFDocumento213 pagineEbook - Electronics Tutorial PDFHari Laxman M100% (1)
- Information Security Lms PDFDocumento6 pagineInformation Security Lms PDFSuraj DoshiNessuna valutazione finora
- Concept Map Rubric: Level 4 Level 3 Level 2 Level 1Documento1 paginaConcept Map Rubric: Level 4 Level 3 Level 2 Level 1nhold v100% (1)
- Cloud Computing: Bangladesh PerspectiveDocumento4 pagineCloud Computing: Bangladesh PerspectiveFaisal Pasha100% (1)
- HTTP Chunked Encoding - HttpWatchDocumento3 pagineHTTP Chunked Encoding - HttpWatchHector David ZenitNessuna valutazione finora
- EchoLife HG520s Home Gateway Quick StartDocumento14 pagineEchoLife HG520s Home Gateway Quick StartAdi CatanescuNessuna valutazione finora