Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Guthrie Test Is One of Screening Test For Amino Acid Especially To Detect
Caricato da
AyioKunDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Guthrie Test Is One of Screening Test For Amino Acid Especially To Detect
Caricato da
AyioKunCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Mohd Hairi Bin A.Hamid Bsc.
. Medical Laboratory Technology (Hons) UniversitI Teknologi Mara, Malaysia (July 2009) Whole Blood Amino Acid Screening Test: Guthrie Test
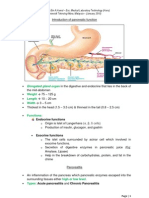
Introduction Guthrie test is one of screening test for amino acid especially to detect phenylketonuria (PKU) disease. It is also the semi-quantitative assay that used to detect the elevated level of phenylalanine (PA) in the blood. At Malaysia, the test is not mandatorily used (not common in our population). But at overseas, it is mandatorily used for newborn baby in the days (day 6 or 7) because most of their people have this disease when they become adult. Therefore, since birth; early prevention is required to reduce the phenylketonuria diseases patients. Purposes It is used to screen for phenylketonuria (PKU) disease and detect the elevated level of phenylalanine (PA) in the blood. Procedures A small amount of blood (from a heel puncture/ capillary puncture) is placed to a piece of filter paper. Then a small disc is punched out and placed on the agar gel containing -2thienylalanine and Bacillus subtilis When concentrations of PA increase, growth inhibition is overcome and zone of inhibition can be observed. The amount of growth is determined by measuring the diameter of colony present. Compare the diameter of each sample disk's colony with the colonies of reference disks. Some lab, use a fluorometric method for detection of phenylalanine (amount of fluorescent depend on the PA amount. Usually, an overnight incubation is enough to determine the abnormal level of phenylalanine in the blood.
Patient preparations The patient was recommended to fast 6-8 hours The patient should be avoided to use of drugs known to cause interference (certain antibiotic)
Mohd Hairi Bin A.Hamid Bsc. Medical Laboratory Technology (Hons) UniversitI Teknologi Mara, Malaysia (July 2009)
Patient should be > 24 hours old and have adequate protein intake for 48 hours prior to test Sample preparations Before sample is collected, make sure that patient was already ingested the protein given adequately. It is because inadequate protein ingestion can cause false negative result. Venipuncture: Wipe out the first drop of blood (it may contained tissue fluid). After sample is collected, make sure the laboratory slip present of date and time, the date and time of birth, and the time of first milk feeding. If the test is delayed, store the specimens 30C and 4C for 10 days and 60 days respectively. Ages that usually tested Commonly performed for newborn baby (0 2 weeks) Children Adult Occasionally performed this test... Disorders that determined by Guthrie test Phenylketonuria (more common) o This disease refers to phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH) deficiency. This enzyme used to convert phenylalanine (a/a) to the tyrosine (a/a). o When PAH deficient, phenylalanine is accumulates and is converted into phenylpyruvic acid, which is detected in the urine o Increase level of PA causing mental retardation, seizures and eczema. Congenital Hypothyroidism o It is due to thyroxine (growth hormone) deficiency. o Without this hormone, normal growth cannot occur. Growth hormone supplement is required. Cystic Fibrosis o Inherited condition that affects the lungs and digestive system. Medium chain acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase (MCAD) Deficiency o Is a condition in which fat metabolism is impaired. o Modification of the diet can reduce symptoms. Sickle Cell Disease o Affects the shape of RBC & reduces the ability of Hb to carry O2 around the body
Mohd Hairi Bin A.Hamid Bsc. Medical Laboratory Technology (Hons) UniversitI Teknologi Mara, Malaysia (July 2009)
References range Normal blood phenylalanine level: 1 mg/dL @ < 120 mol/L (SI Units) Abnormal blood phenylalanine level: 30 - 80 mg/dL @ 120 mol/L (SI Units) When high level of phenylalanine is detected (means positive Guthrie test), therefore, further confirmatory test should be performed. Interpretation High level of PA showed that releasing of PAH is decrease, there high level of PA cant converted to Thyroxine (growth hormone); as a result, PKU will obtained. Normal level of PA showed that releasing of PAH is adequate to convert PA to PAH; therefore absent phenylketonuria disease.
Affected Factors/ Limitations Premature infants may have false-positive result due to delayed development of liver (phenylalanine hydroxylase ). Infants tested before 24 hours of age, may have false negative result due to they have not ingested enough milk containing phenylalanine. False negative result can be obtained when vomiting was occurred (feeding problem); it is because the infant may not have tolerated enough milk containing phenylalanine. Antibiotic, aspirin and salicyclate (drugs) may influence the screening result. Molecular methods to diagnose PKU 1) High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) HPLC is a form of liquid chromatography functioned to separate compounds that are dissolved in solution. Compounds are separated by injecting a plug of the sample mixture onto the column. The different components in the mixture pass through the column at different rates due to differences in their partitioning behaviour between the mobile liquid phase and the stationary phase. HPLC is the method of choice to confirm a positive screening test. It is also used to monitor therapy. It is functioned to determine the quantity of acid amino present in the sample.
Mohd Hairi Bin A.Hamid Bsc. Medical Laboratory Technology (Hons) UniversitI Teknologi Mara, Malaysia (July 2009)
It is more popular to used due to: o More sensitive, o More accurate quantitative determination. o Suitable to separate non-volatile sample It is suitable to separate and identify the:
o
Proteins, amino acids, nucleic acids, hydrocarbons, carbohydrates, pharmaceuticals, pesticides, pigments, antibiotics, steroids, and another inorganic substance.
If identification is uncertain, GC-MS method was used.
2) Ion-exchange chromatography (IEC) The separation is based on the competition of different ionic compounds of the sample for the active sites on the ion-exchange resin (column packing) It can be used for any kind of charged molecule including large proteins, small nucleotides and amino acids. Cation exchange chromatography Anion exchange chromatography
Positively charged amino acid attracted to a negatively charged solid (stationary phase)
Negatively charged amino acid attracted to a positively charged solid (stationary phase)
Mohd Hairi Bin A.Hamid Bsc. Medical Laboratory Technology (Hons) UniversitI Teknologi Mara, Malaysia (July 2009)
3) Gas liquid chromatography (GLC) In GLC, the mobile phase is a gas (helium) and the stationary phase is a high boiling point liquid absorbed onto a solid.
4) Gas chromatography mass spectroscopy (GC-MS) GC-MS is a method that combined the characteristics of gas-liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry to identify different substances within a test sample. Gas-liquid chromatography separates the components of a mixture, and mass spectroscopy characterizes each of the components individually. Function: To determine the unknown amino acid or metabolites if necessary (eg: diagnosis of equivocal data by other methods). It is also not commonly used due to quantitation methods are generally sufficient for diagnosis. Applications of GC-MS include: o Drug detection, fire investigation, environmental analysis, explosives investigation o To detect substances in luggage or on human beings (Airport security) Treatments Do screening test during newborn of the baby (can identify and treat early) Avoid eating high protein foods especially high phenylalanine (Eg: meat, fish, eggs, cheese, milk) Eat more cereals, starches, fruits, and vegetables Check the phenylalanine level in your blood frequently (consistent normal level can be maintained) Therapies: Gene therapy and injectable form of PAH.
Mohd Hairi Bin A.Hamid Bsc. Medical Laboratory Technology (Hons) UniversitI Teknologi Mara, Malaysia (July 2009)
References 1. Mary Hotaling (1998), Saunders Manual of Clinical Laboratory Science (1st Edition): Amino Acids and Proteins,, W.B Saunders Company. 2. Guthrie test (2009), Wikimedia Foundation, Inc; retrieved on 26th August 2009 from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Guthrie_test 3. What is the Guthrie test and why is it done? (2009), retrieved on 26th August 2009 from http://www.midwivesonline.com/parents/parents1//96 4. Phenylketonuria (2009) , retrieved on 26th August 2009 from http://www.answers.com/topic/pku 5. Chances' Choices Scene I: Michelle is saved by the starving bacteria (2007), Foundation for Blood Research, retrieved on 26th August 2009 from http://www.fbr.org/publications/cc/chances-choices.html 6. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectroscopy Background (1998), retrieved on 26th August 2009 from http://www.gmu.edu/departments/SRIF/tutorial/gcd/gc-ms2.htm 7. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (2009), retrieved on 26th August 2009 from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gas_chromatography-mass_spectrometry 8. Jim Clark (2007), High performance liquid chromatography, retrieved on 26th August 2009 from http://www.chemguide.co.uk/analysis/chromatography/highperformanceliquid.htm l 9. Jim Clark (2007), Gas-Liquid Chromatography, retrieved on 26th August 2009 from http://www.chemguide.co.uk/analysis/gasliquidchromatography.html 10. Principles of Ion Exchange Chromatography, Tosoh Bioscience LLC: The Chemistry of Innovation, Montgomeryville, PA retrieved on 26th August 2009 from http://www.separations.us.tosohbioscience.com/Products/Principle
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Handbook of Current and Novel Protocols for the Treatment of InfertilityDa EverandHandbook of Current and Novel Protocols for the Treatment of InfertilityMichael H. DahanNessuna valutazione finora
- Ethical Issues in Clinical Trials: Dr. Devesh D. GosaviDocumento86 pagineEthical Issues in Clinical Trials: Dr. Devesh D. Gosavidevesh gosaviNessuna valutazione finora
- Otc Advisor PainDocumento24 pagineOtc Advisor Painfarzad100% (2)
- Chapter 3 & 4 - Rights, Obligations, Duties and ResponsibiliDocumento26 pagineChapter 3 & 4 - Rights, Obligations, Duties and ResponsibiliChalie Mequanent100% (1)
- Case Study Analysis (1,2,3,4) ENDOCRINOLOGYDocumento3 pagineCase Study Analysis (1,2,3,4) ENDOCRINOLOGYDayledaniel Sorveto100% (1)
- نماذج اسئلة الهيئة السعودية للتخصصات الصحية للاخصائيين والاطباء بالمختبراتDocumento68 pagineنماذج اسئلة الهيئة السعودية للتخصصات الصحية للاخصائيين والاطباء بالمختبراتAhmed GaberNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit 1 PPT FinalDocumento9 pagineUnit 1 PPT FinalRochelle Anne Abad Banda100% (1)
- Ethics in Healthcare Case ScenariosDocumento1 paginaEthics in Healthcare Case ScenariosA CNessuna valutazione finora
- PSG 252 Lecture 4 Peptic Ulcer and Gastro ProtectionDocumento7 paginePSG 252 Lecture 4 Peptic Ulcer and Gastro ProtectionMichael TobilobaNessuna valutazione finora
- Orphan DrugsDocumento14 pagineOrphan DrugsLeah BralowNessuna valutazione finora
- AETCOM QuestionairDocumento3 pagineAETCOM Questionairlatest techs&tips100% (1)
- IFCC TF Ethics in Lab MedicineDocumento16 pagineIFCC TF Ethics in Lab MedicineDr.Deepanshu SinghalNessuna valutazione finora
- Early Clinical Exposure (Ece)Documento30 pagineEarly Clinical Exposure (Ece)sandeepNessuna valutazione finora
- 02 Family Oriented Medical RecordDocumento4 pagine02 Family Oriented Medical RecordFernandez-De Ala NicaNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Investigations HospitalDocumento14 pagineLaboratory Investigations HospitalgegeNessuna valutazione finora
- BiochemistryDocumento135 pagineBiochemistryPradip HamalNessuna valutazione finora
- CC Lab 6 TransesDocumento6 pagineCC Lab 6 TransesCiara PamonagNessuna valutazione finora
- Pharmaa Topnotch ReviewDocumento14 paginePharmaa Topnotch ReviewArianne Joy C. TamarayNessuna valutazione finora
- Thesis 2Documento70 pagineThesis 2Angeline Alpure MoralesNessuna valutazione finora
- The Regulation of Privacy and Data Protection in The Use of Electronic Health InformationDocumento227 pagineThe Regulation of Privacy and Data Protection in The Use of Electronic Health Informationrodrigur8036Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chemical Pathology II HIV AIDSDocumento33 pagineChemical Pathology II HIV AIDSSimeon AdebisiNessuna valutazione finora
- Quality Assurance IN Histopathology: QC Should Consider The Whole ProcessDocumento38 pagineQuality Assurance IN Histopathology: QC Should Consider The Whole Processalrasheed2020Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ethical Guidelines For Medical Research ICMRDocumento120 pagineEthical Guidelines For Medical Research ICMRHARIS KKNessuna valutazione finora
- Autoimmunity and Autoimmune DisordersDocumento46 pagineAutoimmunity and Autoimmune DisordersJennifer EvansNessuna valutazione finora
- Imuune Thrombocytopenia (Itp)Documento34 pagineImuune Thrombocytopenia (Itp)Roshandiep GillNessuna valutazione finora
- 15-17 - 7-PDF - Community Medicine With Recent Advances - 3 PDFDocumento3 pagine15-17 - 7-PDF - Community Medicine With Recent Advances - 3 PDFdwimahesaputraNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To HematologyDocumento61 pagineIntroduction To HematologyThis is PonyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ÿßÿ ŸäŸîŸÑŸá ŸÖŸáŸÖŸá Study DesignDocumento3 pagineŸßÿ ŸäŸîŸÑŸá ŸÖŸáŸÖŸá Study DesignaliNessuna valutazione finora
- Learning ObjectivesDocumento3 pagineLearning ObjectivesYosep BeNessuna valutazione finora
- Fisrt Commented ProposalDocumento35 pagineFisrt Commented ProposalahmedabdikerimNessuna valutazione finora
- CISP UG Compilation 2019 PDFDocumento189 pagineCISP UG Compilation 2019 PDFskdon05Nessuna valutazione finora
- Oncology Questions by DR - OkashaDocumento31 pagineOncology Questions by DR - Okashamohammed okashaNessuna valutazione finora
- Routine and Acute Clinical ChemistryDocumento2 pagineRoutine and Acute Clinical ChemistryMohamed MounirNessuna valutazione finora
- PrinsDocumento44 paginePrinsPalagiri MadhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Glucose c111 RocheDocumento3 pagineGlucose c111 RocheHarditya FirdhausNessuna valutazione finora
- Toxicology Coverage Midterm Exam PDFDocumento17 pagineToxicology Coverage Midterm Exam PDFNestor BargioNessuna valutazione finora
- HPLC ThesisDocumento21 pagineHPLC ThesisDolly SurelaNessuna valutazione finora
- Manchester Anaemia GuideDocumento13 pagineManchester Anaemia Guidemubzy14Nessuna valutazione finora
- 2 Public Health For Primary Health CareDocumento32 pagine2 Public Health For Primary Health CarehervwNessuna valutazione finora
- Laboratory Tests For EndocrinologyDocumento6 pagineLaboratory Tests For EndocrinologyAnastasia100% (1)
- Prelim 1st Topic HEALTH CARE SYSTEMDocumento5 paginePrelim 1st Topic HEALTH CARE SYSTEMRochelle Anne Abad Banda100% (1)
- N.sepsis 2Documento129 pagineN.sepsis 2cooldude_secbad1712100% (1)
- Lecture 1 BiophysicsDocumento22 pagineLecture 1 Biophysicsmaxwell amponsahNessuna valutazione finora
- Evidence Based Medicine Beginners HandbookDocumento40 pagineEvidence Based Medicine Beginners HandbookcmegmhiNessuna valutazione finora
- ADR Final1Documento10 pagineADR Final1Rubina BisankheNessuna valutazione finora
- Tumour Markers PPT by DR VijayDocumento31 pagineTumour Markers PPT by DR Vijaydr vijay60% (5)
- Concept of PreventionDocumento48 pagineConcept of Preventionmahmoud100% (1)
- Biochemical MethodsDocumento119 pagineBiochemical MethodsElias Libay100% (1)
- Poct - QCDocumento43 paginePoct - QCKinjalka GhoshNessuna valutazione finora
- From The Capillaries Into The Capsule ThroughDocumento3 pagineFrom The Capillaries Into The Capsule ThroughRashid DayaoNessuna valutazione finora
- Internal DiseaseDocumento55 pagineInternal Diseaseshilpa sekhar278Nessuna valutazione finora
- Git 2Documento18 pagineGit 2Mateen ShukriNessuna valutazione finora
- The Accuracy of Substituted Judgments in Patients With Terminal DiagnosesDocumento9 pagineThe Accuracy of Substituted Judgments in Patients With Terminal DiagnosesgremnisayNessuna valutazione finora
- Withholding and Withdrawing Life SupportDocumento3 pagineWithholding and Withdrawing Life SupportNURSETOPNOTCHERNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 Blood Banking and Serology PDFDocumento4 pagine8 Blood Banking and Serology PDFMariel AbatayoNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanisms of Drug Toxicity: Proceedings of the Third International Pharmacological MeetingDa EverandMechanisms of Drug Toxicity: Proceedings of the Third International Pharmacological MeetingH. RaškováNessuna valutazione finora
- Virulent & PathogenicityDocumento1 paginaVirulent & PathogenicityAyioKunNessuna valutazione finora
- Automation in Hematology LabDocumento8 pagineAutomation in Hematology LabAyioKunNessuna valutazione finora
- Chromatography (Priciple & Applications)Documento8 pagineChromatography (Priciple & Applications)AyioKunNessuna valutazione finora
- High Low Trace Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen Sulphur: ProteinDocumento11 pagineHigh Low Trace Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen Sulphur: ProteinAyioKunNessuna valutazione finora
- Liver Function TestDocumento7 pagineLiver Function TestAyioKun100% (1)
- Pancreatic Function TestDocumento9 paginePancreatic Function TestAyioKunNessuna valutazione finora
- HemoglobinDocumento5 pagineHemoglobinAyioKunNessuna valutazione finora
- Arthropod-Borne Viruses: An OverviewDocumento19 pagineArthropod-Borne Viruses: An OverviewSUTHANNessuna valutazione finora
- QualityDocumento19 pagineQualityRakesh SehrawatNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemiluminescent ImmunoassayDocumento4 pagineChemiluminescent ImmunoassayAyioKun100% (1)
- RespiratoryDocumento28 pagineRespiratorySUTHANNessuna valutazione finora
- Herpes VirusesDocumento71 pagineHerpes VirusesAyioKunNessuna valutazione finora
- Pa Tho GenesisDocumento32 paginePa Tho GenesisCarolina MazaroNessuna valutazione finora
- Agarose Gel ElectrophoresisDocumento5 pagineAgarose Gel ElectrophoresisAyioKun100% (3)
- HepatitisDocumento55 pagineHepatitisSUTHAN100% (1)
- Control of Viral Diseases: Derek WongDocumento43 pagineControl of Viral Diseases: Derek WongAyioKunNessuna valutazione finora
- TestsDocumento38 pagineTestsSUTHANNessuna valutazione finora
- RespiratoryDocumento28 pagineRespiratorySUTHANNessuna valutazione finora
- HivDocumento29 pagineHivSUTHAN100% (2)
- Herpesvirus Infections in Immunocompromised Patients: An OverviewDocumento29 pagineHerpesvirus Infections in Immunocompromised Patients: An OverviewAyioKunNessuna valutazione finora
- Herpes VirusesDocumento71 pagineHerpes VirusesAyioKunNessuna valutazione finora
- Pa Tho GenesisDocumento32 paginePa Tho GenesisCarolina MazaroNessuna valutazione finora
- Molecular VirologyDocumento11 pagineMolecular VirologySUTHANNessuna valutazione finora
- Arthropod-Borne Viruses: An OverviewDocumento19 pagineArthropod-Borne Viruses: An OverviewSUTHANNessuna valutazione finora
- Virus SummaryDocumento1 paginaVirus SummaryAyioKunNessuna valutazione finora
- HepatitisDocumento55 pagineHepatitisSUTHAN100% (1)
- EnterovirusesDocumento21 pagineEnterovirusesSUTHANNessuna valutazione finora
- DiarrhoeaDocumento16 pagineDiarrhoeaSUTHANNessuna valutazione finora
- CongenitalDocumento25 pagineCongenitalSUTHANNessuna valutazione finora
- Pgs 145-59, Neonatal Immunity by Constantin Bona (Humana Press) 2004 - $145.00Documento401 paginePgs 145-59, Neonatal Immunity by Constantin Bona (Humana Press) 2004 - $145.00Riki TobingNessuna valutazione finora
- An Effective Solution To Optimise Health Status and Nutrient Utilisation - GUSTOR AQUADocumento5 pagineAn Effective Solution To Optimise Health Status and Nutrient Utilisation - GUSTOR AQUAInternational Aquafeed magazineNessuna valutazione finora
- HEMA 2 - Midterm Topic 3 - Anemia of Bone Marrow DisorderDocumento10 pagineHEMA 2 - Midterm Topic 3 - Anemia of Bone Marrow DisorderLowenstein JenzenNessuna valutazione finora
- Journal ReadingDocumento20 pagineJournal ReadingTarsiah Ningsih IINessuna valutazione finora
- Module 3 Mendelian GeneticsDocumento14 pagineModule 3 Mendelian GeneticsRaiza AwatNessuna valutazione finora
- Gaucher Disease (Type I) : SymptomsDocumento6 pagineGaucher Disease (Type I) : SymptomsDewi YantiNessuna valutazione finora
- Strengths Weaknesses of The Modern GSDDocumento12 pagineStrengths Weaknesses of The Modern GSDapi-208346542100% (1)
- A CRISPR Way To Block PERVs - Engineering OrgansDocumento3 pagineA CRISPR Way To Block PERVs - Engineering OrgansFrancisco Baca DejoNessuna valutazione finora
- 2017 - Fut VirolDocumento10 pagine2017 - Fut VirolKashif HaleemNessuna valutazione finora
- (Methods in Molecular Biology 1060) Herman Waldmann (Auth.), Michael Steinitz (Eds.) - Human Monoclonal Antibodies - Methods and Protocols-Humana Press (2014)Documento367 pagine(Methods in Molecular Biology 1060) Herman Waldmann (Auth.), Michael Steinitz (Eds.) - Human Monoclonal Antibodies - Methods and Protocols-Humana Press (2014)KoaLa AyuNdhaNessuna valutazione finora
- Komplemen Dan SitokinDocumento38 pagineKomplemen Dan SitokinIful SaifullahNessuna valutazione finora
- SyllabusDocumento10 pagineSyllabusAnonymous KCtOAUZIyNessuna valutazione finora
- How I Treat Mixed-Phenotype Acute LeukemiaDocumento10 pagineHow I Treat Mixed-Phenotype Acute LeukemiawenyinriantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Sofia Mubarika 180522Documento42 pagineSofia Mubarika 180522Nanik AndianiNessuna valutazione finora
- Phloem Promoters in Transgenic Sweet Orange Are Differentially Triggered BY Candidatus Liberibacter AsiaticusDocumento9 paginePhloem Promoters in Transgenic Sweet Orange Are Differentially Triggered BY Candidatus Liberibacter Asiaticusrene123 GutierrezNessuna valutazione finora
- Understanding Alzheimers DiseaseDocumento494 pagineUnderstanding Alzheimers Diseasegezedka100% (3)
- Hemophilic Arthropathy 2007Documento11 pagineHemophilic Arthropathy 2007Yuga RahmadanaNessuna valutazione finora
- Leukemia Thesis PDFDocumento5 pagineLeukemia Thesis PDFjpwvbhiig100% (2)
- Gould39s Pathophysiology For The Health Professions 5th Edition PDF DownloadDocumento3 pagineGould39s Pathophysiology For The Health Professions 5th Edition PDF DownloadShawn0% (4)
- Pediatric Cholestasis: Epidemiology, Genetics, Diagnosis, and Current ManagementDocumento5 paginePediatric Cholestasis: Epidemiology, Genetics, Diagnosis, and Current ManagementAnnisa SusiloNessuna valutazione finora
- Genesis Group 1 Research PaperDocumento28 pagineGenesis Group 1 Research PaperKristel De VeraNessuna valutazione finora
- Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis e Etiology, Serum Autoantibodies, Anemia, Hematinic Deficiencies, and ManagementDocumento11 pagineRecurrent Aphthous Stomatitis e Etiology, Serum Autoantibodies, Anemia, Hematinic Deficiencies, and ManagementorizaNessuna valutazione finora
- ScleritisDocumento3 pagineScleritisPangala NitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Neural Regulation of RespirationDocumento19 pagineNeural Regulation of RespirationAbeer SallamNessuna valutazione finora
- Down Syndrome Research Paper ThesisDocumento4 pagineDown Syndrome Research Paper Thesisfvg4mn01100% (1)
- Genetic Testing Policyrevised 3117Documento5 pagineGenetic Testing Policyrevised 3117Clang ServerNessuna valutazione finora
- Tec No StudiesDocumento34 pagineTec No StudiesarthurhuntNessuna valutazione finora
- Types and The Functions of WHITE BLOOD CELLSDocumento3 pagineTypes and The Functions of WHITE BLOOD CELLSSakura UchihaNessuna valutazione finora
- 40 Days Prayer GuideDocumento27 pagine40 Days Prayer GuideSathya Poorani100% (7)
- Determination of Lethal Dose Ld50of Venom of Four Different Poisonous Snakes Found in PakistanDocumento4 pagineDetermination of Lethal Dose Ld50of Venom of Four Different Poisonous Snakes Found in PakistanSutirtho MukherjiNessuna valutazione finora